HTTP response status code 408 Request Timeout is a client error that is returned by the server to indicate that a request is coming in too slowly from a client and it is unwilling to wait for it to be completed, thus terminating the connection.
Usage
When the 408 Request Timeout error message is received, it means that a client has initiated a request but for some reason, it has not been transmitted in full. This may occur because an internet connection is very slow, or has been dropped. The response will include the Connection header, specifying that it has been closed.
Upon receiving the Connection: close header, the client can attempt the request again.
Note
Search engines like Google will not index a URL with 408 Request Timeout response status, and consequently, URLs that have been indexed in the past but are now returning this HTTP status code will be removed from the search results.
Example
In the example, the client begins to send a 10K PDF file to the server, but the connection is suffering from intermittent connectivity issues and the server concludes that the transmission, in its entirety, is too slow. As such, it cancels the HTTP request and closes the connection. Sometime later, when the connection is more stable, the client attempts to retransmit the file and it is successful.
Initial request
PUT /docs HTTP/1.1
Host: www.example.ai
Content-Type: applications/pdf
Content-Length: 10000
Initial response
HTTP/1.1 408 Request Timeout
Connection: Close
Content-Type: text/html
Content-Length: 198
<html>
<head>
<title>Connection Close</title>
</head>
<body>
<p>The transmission was not received quickly enough. Check internet connectivity and please try again.</p>
</body>
</html>
Next request
PUT /docs HTTP/1.1
Host: www.example.ai
Content-Type: applications/pdf
Content-Length: 10000
<File transfer successful for PDF file>
Final response
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
Code references
.NET
HttpStatusCode.RequestTimeout
Rust
http::StatusCode::REQUEST_TIMEOUT
Rails
:request_timeout
Go
http.StatusRequestTimeout
Symfony
Response::HTTP_REQUEST_TIMEOUT
Python3.5+
http.HTTPStatus.REQUEST_TIMEOUT
Java
java.net.HttpURLConnection.HTTP_CLIENT_TIMEOUT
Apache HttpComponents Core
org.apache.hc.core5.http.HttpStatus.SC_REQUEST_TIMEOUT
Angular
@angular/common/http/HttpStatusCode.RequestTimeout
Takeaway
The 408 Request Timeout status code is a client error that the server sends when an HTTP request is taking too long to complete. Common reasons for this are slow or broken internet connections. If the connection is restored, the client can make the request again.
See also
- Connection
- 504 Gateway Timeout
- RFC 7231
Last updated: June 29, 2022
Умные люди придумали коды, по которым можно определить, что произошло с HTTP-запросом. Успешен ли он, произошло ли перенаправление. Или же все закончилось ошибкой. Как раз об ошибках и будем говорить в этой статье. Вкратце расскажу, какие они бывают и с чем связаны.
А еще тут будет парочка забавных (и не очень) пикч и анимаций на тему описанных ошибок. Хоть какое-то развлечение.
Ошибки со стороны клиента (4xx)
Для начала перечислим коды ошибок на стороне клиента. Вина за их появление ложится на плечи обоих участников соединения.
400 Bad Request
Такой ответ от браузера можно получить в том случае, если сервер не смог правильно отреагировать на запрос со стороны пользователя. Часто код 400 возникает при попытке клиента получить доступ к серверу без соблюдения правил оформления синтаксиса протокола передачи гипертекста (HTTP). Повторный запрос не стоит отправлять до тех пор, пока не будет исправлена ошибка (или несколько из них).
401 Unauthorized
Код 401 возникает при попытке клиента получить доступ к серверу, используя неправильные данные для авторизации. По сути, используется, когда пользователь вводит неправильный логин и пароль на ресурсе, где требуется эта информация для входа. Читайте: Как исправить ошибку 401
402 Payment Required
Эта ошибка сообщает клиенту о том, что для успешного выполнения запроса ему необходимо оплатить доступ к серверу. Изначально код 402 должен был стать неким стандартом для цифровой валюты и оплаты контента в сети. Но не срослось. До сих пор нет единого решения по поводу того, как должны выглядеть платежи в сети. Также нет и единого решения по поводу того, как стоит использовать 402.
Все еще считается, что код существует с расчетом на будущее. Сейчас почти не используется и поддерживается не всеми браузерами.
403 Forbidden
Почти то же, что и 401. Сервер снова не разрешает к нему подключиться, хотя с запросом все в порядке. Просто нет доступа. Причем повторная авторизация с другими логином и паролем никак не помогут. Все вопросы к владельцам сервера (но не всегда). Инструкция по устранению ошибки.
Творчество на тему знаменитой киносаги
404 Not Found
Легендарная ошибка, ставшая популярным мемом. 404 оповещает клиента о том, что его запрос ведет в никуда. Код возникает, когда пользователь пытается попасть на страницу, которой не существует. Например, когда случайно ошибается при вводе ссылки и вводит ее с опечаткой. Или же пытается получить доступ к странице, которой на сайте уже нет.
В отличие от других кодов, страницу с 404 частенько кастомизируют, создавая для нее уникальный дизайн. Мало того, что это выглядит симпатичнее, так еще и полезнее для посетителей. Можно прямо на странице с ошибкой разъяснить, что произошло и как дальше действовать.

И таких вариаций тысячи. Каждый пытается добавить в оформление что-то свое.
405 Method Not Allowed
405 сообщает клиенту о том, что метод, используемый при запросе, не разрешен. В качестве примера можно привести попытку со стороны клиента ввести данные в форму с помощью GET, когда она работает только с POST. Ну и в таком же духе.
406 Not Acceptable
Ошибка 406 сообщает о том, что страница передает контент, который не может быть распознан клиентом. Возможно, проблема в методе сжатия или в формате страницы. Иногда сюда же приплетают неправильные настройки кодировки.
Этот код редко используют на практике, так как его появления можно избежать, предоставив пользователю информацию на сайте в том виде, который его браузер способен принять. Посетитель сайта по итогу получит не то, что ожидал, но хотя бы не ошибку.
407 Proxy Authentication Required
Этот код тоже похож на 401. Только на этот раз логин и пароль нужны не для основного сервера, а для прокси, который находится между клиентом и сервером. Обычно в теле ошибки содержится информация о том, как можно правильно пройти авторизацию и получить доступ к ресурсу.
408 Request Timeout
408 говорит нам о том, что сервер пожелал разорвать соединение с клиентом, потому что оно никак не используется. Происходит это в том случае, если сервер буквально устал ждать, пока наладится соединение с ним. Поэтому такую ошибку часто можно лицезреть после очень долгой и безуспешной загрузки какого-нибудь сайта.
Многие серверы не отправляют никаких сообщений, а просто прерывают соединение по той же причине. На запрос уходит больше времени, чем на то полагается.

В Мистере Роботе частенько называли серии в честь ошибок HTTP (весь четвертый сезон в нумерации 4хх). В честь 408, например, назвали восьмую серию четвертого сезона
409 Conflict
Сообщение о конфликте возникает, когда запрос со стороны клиента не соответствует тому, чего ожидает сервер. В качестве примера приводят проблемы при проверки версий, когда пользователь пытается с помощью метода PUT загрузить на сервер новый файл, но там уже имеется более новая версия того же файла. Конфликта версий можно легко избежать, загрузив корректную версию.
410 Gone
Своего рода аналог 404. Разница лишь в том, что 410 намекает на перманентность отсутствия страницы. Так что этот код стоит использовать, когда на 100% уверен, что страница ушла в небытие (ну или с текущего адреса) навсегда. В любом другом случае есть универсальный 404.
411 Length Required
411 оповещает пользователя о том, что сервер не желает принимать запрос со стороны клиента, потому что в нем не определен заголовок Content-Length. Да, это первый код в подборке, который смогут понять только люди, сведущие в настройке серверов. По-простому уложить сущность HTML-заголовков в этот материал не получится.
412 Precondition Failed
Еще один код, сообщающий о том, что сервер отклонил запрос пользователя и не разрешает доступ к выбранному ресурсу. Проблемы возникают при неправильной настройке работы методов, отличающихся от GET и HEAD.
413 Payload Too Large/Request Entity Too Large
Код 413 говорит нам, что запрос, который посылает клиент на сервер, слишком большой. Поэтому сервер отказывается его обрабатывать и разрывает соединение. Обычно это происходит при попытке загрузить на ресурс какой-то файл, превышающий ограничение, выставленное в настройках сервера. Соответственно, решается проблема изменением настроек сервера.
414 URI Too Long
Чем-то этот код похож на предыдущий. Здесь тоже идет речь о превышение лимита. Только теперь это касается не запроса со стороны клиента, а длины URI. То есть ссылки. Выходит, что адрес, используемый клиентом, больше, чем тот, что может обработать сервер. Как-то так.
Такая ошибка иногда выскакивает при попытке взломать ресурс. Сайт так реагирует на слишком частые попытки воспользоваться потенциальными дырами в безопасности.
415 Unsupported Media Type
Ошибка 415 возникает, когда клиент пытается загрузить на сервер данные в неподходящем формате. В таком случае сервер просто отказывается принимать посылаемые файлы и разрывает соединение. Как и в случае с 413.
416 Range Not Satisfiable
Подобный ответ можно ожидать, если клиент запрашивает у сервера определенные данные, но эти данные на сервере не соответствуют запросу. То есть, грубо говоря, вы просите у сервера какой-то набор данных с заранее заданным размером, а в итоге оказывается, что размер этих данных меньше, чем объем, указанный в запросе. Серверу ничего не остается, кроме как послать вас, ведь он не обучен поведению в таких ситуациях.
417 Expectation Failed
Такая ошибка высвечивается, когда ожидания сервера не совпадают с данными в запросе клиента. Сведения об ожиданиях прописываются в заголовке Expect заранее. Так что можно ознакомиться с ними, чтобы выяснить, как решить названную проблему.
418 I’m a teapot
Код 418 можно увидеть, если сервер откажется варить кофе, потому что он чайник. Это первоапрельская шутка. Естественно, 418 не используется нигде всерьез и просто существует как дань памяти программистам-юмористам, придумавшим это в 1998 году.

У Google получился такой симпатичный чайник
421 Misdirected Request
Появляется когда запрос клиента переправляется на сервер, который не может дать на него адекватный ответ. Например, если запрос был отправлен на ресурс, который вообще не настроен обрабатывать запросы извне.
Чтобы исправить проблему, можно попробовать переподключиться к ресурсу заново или попробовать другое соединение.
422 Unprocessable Entity
Код 422 говорит, что сервер вроде бы принял запрос, понял его, все хорошо, но из-за семантических ошибок корректно обработать не смог. Значит, где-то в запросе затаилась логическая ошибка, мешающая корректному взаимодействию клиента и сервера. Надо ее найти и исправить.
423 Locked
Обычно на этот код напарываются, когда запрашиваемый ресурс оказывается под защитой. Используемые клиентом методы блокируются на уровне сервера. Это делается, чтобы обезопасить данные, хранящиеся на защищенной странице. Без логина и пароля выудить информацию с такого сервера не получится.
424 Failed Dependency
424 сообщает о том, что для выполнения запроса со стороны клиента успешно должна завершиться еще одна или несколько параллельных операций. Если какая-то из них «провалится», то «помрет» все соединение сразу, и обработать запрос до конца не получится. Аналогичное происходит, если некорректно был обработан один из предыдущих запросов.
425 Too Early
Появляется в ответ на запрос, который может быть моментально запущен заново. Сервер не рискует и не берется за его обработку, чтобы не подставиться под так называемую «атаку повторного воспроизведения».
426 Upgrade Required
Тут нам прямо сообщают, что сервер не желает с нами общаться, пока мы не перейдем на более современный протокол. Наткнуться на такую ошибку очень тяжело, но в случае появления, скорее всего, будет достаточно установить браузер посвежее.
428 Precondition Required
428 выскакивает, если пользователь отправляет запрос на сервер, но получает некорректные или неактуальные данные. Так ресурс оповещает о необходимости внести в запрос информацию о предварительных условиях обработки данных. Только так он сможет гарантировать получение клиентом нужной информации.
429 Too Many Requests
Здесь все просто. Ошибка появляется, когда клиент отправляет на сервер слишком много запросов в короткий промежуток времени. Очень похоже на поведение взломщиков. По этой причине запрос моментально блокируется.

431 Request Header Fields Too Large
Из названия понятно, что ошибка с кодом 431 появляется из-за того, что в запросе клиента используются слишком длинные заголовки (неважно, один или несколько из них). Исправляется это с помощью сокращения заголовков и повторной отправки запроса. В теле ошибки обычно отображается краткая информация о том, как пользователь может решить эту проблему самостоятельно.
444 No Response
Этот код вам вряд ли удастся увидеть. Он отображается в лог-файлах, чтобы подтвердить, что сервер никак не отреагировал на запрос пользователя и прервал соединение.
449 Retry With
Код используется в расширениях компании Microsoft. Он сигнализирует о том, что запрос от клиента не может быть принят сервером. Причиной становятся неверно указанные параметры. Сама 449 ошибка говорит о необходимости скорректировать запрос и повторить его снова, подготовив к работе с сервером.
450 Blocked by Windows Parental Controls
450 код увидят дети, попавшие под действие системы «Родительский контроль» компании Microsoft. По сути, ошибка говорит о том, что с компьютера попытались зайти на заблокированный ресурс. Избежать этой ошибки можно изменением параметров родительского контроля.
451 Unavailable For Legal Reasons
Этот код сообщает клиенту, что он не может попасть на запрашиваемый ресурс из юридических соображений. Скорее всего, доступ был заблокирован из-за каких-нибудь государственных санкций, нового законодательства или цензуры со стороны властей. В общем, все вопросы к государству и провайдеру связи.

Читайте также


Комьюнити теперь в Телеграм
Подпишитесь и будьте в курсе последних IT-новостей
Подписаться
Список ошибок на стороне сервера (5xx)
Теперь поговорим об ошибках, которые возникают где-то на сервере. Все они связаны с запросами, которые не удается обработать на том конце. Пользователь зачастую в их появлении не виноват.
500 Internal Server Error
Этот код возникает, когда сервер сталкивается с непредвиденными обстоятельствами. Такими, которые и сам не может пояснить. Как, собственно, и завершить запрос со стороны пользователя. По факту, эта ошибка говорит нам что-то вроде «Я не могу подобрать более подходящий код ошибки, поэтому лови 500 и делай с этим, что хочешь». Мы писали о нем чуть подробнее тут.
Дело не в тебе, дело во мне (С)
501 Not Implemented
501 говорит нам, что функциональность, необходимая для обработки запроса со стороны клиента, попросту не реализована на сервере. Он не сможет корректно обработать используемый метод.
Иногда в теле ошибки еще пишут что-то в духе «Приходите попозже, возможно, в будущем нужная функция появится».
502 Bad Getaway
Можно встретить в том случае, если запрашиваемый сервер выступает в роли шлюза или прокси. Возникает из-за несогласования протоколов между вышестоящим серверов и его шлюзом. Рассказываем о том, как ее исправить, в этой статье.
503 Service Unavailable
Появляется, когда сервер не может обработать запрос клиента по одной из двух технических причин:
- Слишком много пользователей в текущий момент пытаются отправить запросы, и у сервера не остается ресурсов, чтобы ответить кому-либо еще.
- На сервере ведутся технические работы, временно блокирующие его работу.
Обычно ошибка 503 носит временный характер, и для ее решения достаточно немного подождать.
504 Gateway Timeout
Ошибка похожа на 408. Здесь же прокси-сервер пытается выйти на контакт с вышестоящим сервером, но не успевает это сделать до истечения тайм-аута. Отсюда и ошибка.

505 HTTP Version Not Supported
Этот код похож на 426. Он тоже связан с неподходящей версией протокола HTTP. В этом случае нужно обеспечить и клиента, и сервер единой версией. Она, как правило, указывается в запросе со стороны пользователя.
506 Variant Also Negotiates
Обычно с такой ошибкой сталкиваются только в том случае, если сервер изначально настроен неправильно. То есть это не сиюминутная проблема, а что-то серьезное на уровне базовой конфигурации. Тут придется потрудиться разработчикам. Выявить проблему и разрешить ее.
507 Insufficient Storage
Код 507 встречается в тех ситуациях, когда серверу не хватает пространства в хранилище для обработки запроса со стороны клиента. Проблема решается освобождением места или расширением доступного пространства. Тогда сервер сможет без проблем обработать запрос пользователя.
508 Loop Detected
Таким кодом сервер отзовется в случае, если заметит бесконечный цикл в запросе клиента. Можно расценивать его как провал запроса и выполняемой операции в целом.
509 Bandwidth Limit Exceeded
Возникает, если сервер начинает потреблять больше трафика, чем ему позволено.
510 Not Extended
Появляется, если клиент посылает запрос на использование какого-либо расширения, отсутствующего на сервере. Чтобы исправить проблему, надо убрать декларирование неподдерживаемого расширения из запроса или добавить поддержку на сервер.
511 Network Authentication Required
511 код говорит о том, что перед тем как выйти в сеть, надо авторизоваться (ввести логин и пароль). Можно воспринимать это неким PPPoE подключением, когда от клиента требуются данные для авторизации.
Заключение
Закончили. Это все ошибки, которыми отзывается HTTP, если на стороне сервера или клиента что-то пошло не так. Наткнуться на большую их часть довольно тяжело. Особенно, если вы раньше только серфили в интернете, а не занимались разработкой сайтов. А тем, кто входит в эту стезю, полезно знать основные ошибки, так как, скорее всего, придется не раз их исправлять.
Encountering HTTP status code errors can be frustrating and stressful. This is especially true when you don’t know what the message means or what’s causing it. One of the errors you might be dealing with is HTTP 408 Request Timeout.
Fortunately, you can take a handful of steps to troubleshoot and resolve this issue. You’ll simply need a basic understanding of what could be causing the HTTP 408 error, then implement solutions to fix it.
In this post, we’ll explain the HTTP 408 status code and some common causes of the error. Then we’ll walk you through eight potential solutions for resolving it. Let’s jump in!
Check Out Our Video Guide to Fixing the HTTP 408 Error
What the HTTP 408 Status Code Is
HTTP status codes indicate the status of a client’s request. They can also redirect clients to different resources, depending on their requests.
The most common HTTP status code is 404, which indicates that the requested resource could not be found. Other common status codes include 200 (OK), 400 (Bad Request), and 500 (Internal Server Error).
Status codes are divided into five categories:
- Informational: The server is still processing the request.
- Successful: The request was completed successfully.
- Redirects: The client should be redirected to a different resource.
- Client Errors: There was an error with the request.
- Server Errors: There was an error with the server.
HTTP 408 falls into the category of client errors. The status code communicates that the server did not receive a timely response from the client and that the server timed out waiting for the request. This can happen if the client takes too long to send the request or the server is too busy to process it.
The HTTP 408 error is similar to the 504 Gateway Timeout status code. However, the former doesn’t come from a gateway or proxy server. Instead, it comes directly from the web server the client is connected to.
Encountering HTTP status code errors can be frustrating and stressful. 😰 This guide can help. 🛠Click to Tweet
Common Causes of the HTTP 408 Request Timeout Error
There are a handful of potential reasons behind the HTTP 408 request timeout error. These causes include:
- Network latency
- Clients timing out
- Servers being too busy to handle the request
The 408 Request Timeout error means the request you sent to the website server took longer than the server was prepared to wait. It can happen due to heavy traffic on the internet or a slow connection on your side.
The problem with this status code is that it can occur for both client-side and server-side-related reasons. In other words, although the 408 error is categorized as a client error, this doesn’t necessarily mean the issue stems from the browser or device. It’s possible that the server is misconfigured or isn’t handling requests correctly.
How To Fix the HTTP 408 Error (8 Solutions)
Now that we understand more about the HTTP 408 status code, let’s discuss how you can resolve it. Below are eight potential solutions you can use, separated into two categories: client-side and server-side.
Client-Side
Below are some client-side solutions you can use to resolve the HTTP 408 error!
1. Back Up Your Site
The first thing you should do before troubleshooting the HTTP 408 error is back up your website. Then, if anything goes wrong while trying to fix the issue, you will have a full, updated version of your files and database to restore.
There are several methods you can use to back up your site. One is the manual approach. This method involves using a Secure File Transfer Protocol (SFTP) client, such as FileZilla. After receiving your SFTP credentials from your host and connecting to the server, you can download your files from the root directory (public_html folder).
Next, you’ll need to download your database via phpMyAdmin. If you’re a Kinsta user, you can access this through MyKinsta > Sites > Info:

Then select Open phpMyAdmin to launch the database manager. Select your site’s database from the menu:

Next, click on Export at the top of the screen. Make sure to select SQL under Format, then click on Go. Your database file should begin downloading.
You can also use a backup plugin such as UpdraftPlus. After installing and activating the plugin, navigate to Settings > UpdraftPlus Backups in your WordPress dashboard, then click on Backup Now:

A third option is to back up your site through your web host. At Kinsta, you can view your existing backups by logging into MyKinsta and then navigating to the Backups tab:

You can create up to five manual backups, which are automatically stored for two weeks. We also offer DevKinsta, a free local WordPress development tool you can use for staging and backing up your site to a local environment.
You can do this by going to DevKinsta and selecting the Import from Kinsta option. You may need to verify your hosting credentials. Once you choose your site, DevKinsta handles the rest.
2. Check the URL
One of the reasons you may be seeing the HTTP 408 status code error is that you simply typed the wrong URL into the browser. Therefore, you should now double-check the URL to ensure you didn’t make any typos.
Pay close attention to the domain name, especially if there are slashes or hyphens. Try re-entering the URL and then reloading the page. If the timeout request error is still present, you can move on to the next solution.
3. Review Recent Database Changes
If you’ve made any recent changes to your database, they may be causing the HTTP 408 error. You’ll need to revert any changes you’ve made to fix the issue.
Recently installed extensions or updates to your database may have altered database records that are causing problems. To see if this is the case, we recommend opening your database (phpMyAdmin) and manually going through to check any tables or records that have been recently modified. If you find any, revert them to their original states.
4. Uninstall Extensions and Plugins
Adding extensions and plugins to your site can cause various incompatibility issues and errors, including the HTTP 408 status code. One of the easiest ways to see whether this is the case is to deactivate all of the plugins on your site.
If you have access to your WordPress dashboard, you can do this by navigating to Plugins from the admin area, selecting all of the installed plugins, then selecting Deactivate from the Bulk actions dropdown menu. Now click on Apply:

If you don’t have access to your dashboard, you can bulk deactivate your extensions by connecting to your site via SFTP, then renaming the plugins folder to something like “plugins_old”.
Revisit your site. You can assume a plugin was to blame if you no longer see the error message.
You’ll need to reactivate each plugin one by one, checking the site in between. Once you see the error message again, you’ll have to uninstall that extension and find a replacement (or contact the developer for more information).
5. Roll Back Recent Changes
If you’ve recently made any changes to your WordPress site, such as installing a new plugin or updating the WordPress software, you might be seeing the HTTP 408 error. New tools can sometimes lead to configuration problems. You can roll back recent changes by restoring your site to a previous version.
If you’re a Kinsta user, open your MyKinsta dashboard, then navigate to Sites and select your site. Next, click on Backups.
From the list of backups, find the version you want to restore, click on Restore to, then select Staging or Live:

Next, you can confirm the backup restoration and click on Restore backup. Once the backup is complete, you can check to see whether the error message is still displaying.
Server-Side
If none of the above solutions worked, the HTTP 408 error might be caused by a server-side issue. Let’s look at potential solutions you can use to resolve it.
6. Check Server Config Files
One of the ways you can determine the cause of the HTTP 408 error is to check your server configuration files via SFTP. The process for doing so will depend on your server software.
Chances are that your server is either running on Apache or Nginx. If you’re a Kinsta user, we use Nginx.
If you’re using Apache, you can look for the .htaccess file within your site’s root directory. When you locate the file, open it and look for the following lines:
- KeepAliveTimeout
- RequestReadTimeout
If you find these directives, you can comment them out by using the # symbol prefix before the line. Then you can save the file and reload the page in your browser.
If you’re a Kinsta user, you can check your .htaccess file by opening your MyKinsta dashboard and navigating to your website under Sites. Locate the SFTP/SSH section to get your credentials, then use them to connect to your site via an FTP client.
Next, navigate to the public_html folder, then locate and open the .htaccess file:

Look for either of the directives listed above. If you see any of these rules, comment them out and save your changes.
7. Review Application Logs
Your server-side logs can be invaluable for providing information about your applications, including what they did, the pages requested, the servers connected to, and more. If you’re a Kinsta user, you can check your error logs using the log viewer in MyKinsta.
If you’re not using a Kinsta hosting plan or your host doesn’t provide a logging tool, you can insert the following code into your wp-config.php file:
define( 'WP_DEBUG', true );
define( 'WP_DEBUG_LOG', true );
define( 'WP_DEBUG_DISPLAY', false );This will enable WordPress debugging mode.
From MyKinsta, navigate to Sites > Logs:

Here, you’ll find the Log viewer that displays your error logs. You can click on access.log from the dropdown menu. This is where you can find all the HTTP requests from your website. You can also look for any HTTP 408 requests using the search bar.
If you locate any errors, you can use the information to pinpoint which web page is causing the issue. This can help you narrow down the source of the problem.
8. Debug Apps or Scripts
At this point, if you’re still seeing the HTTP 408 error, it’s time to debug your site. There are a handful of options you can use for this process.
One is to use a plugin such as Query Monitor:

This free plugin debugs your website’s performance and development. It enables you to check database queries, scripts, timing, and more.
Another option is using an Application Performance Monitoring (APM) tool. This software helps you monitor and optimize the performance of your website or application.
Using an APM tool can help you debug your site by giving insight into its performance and the location of any bottlenecks. This information can help you identify and fix any issues causing your website to run slowly or have other performance problems.
You can use our Kinsta APM Tool. It’s a custom-designed performance monitoring tool for WordPress sites that helps you identify performance issues. It’s also free for all sites hosted with us.
You can access the Kinsta AMP via your MyKinsta dashboard by navigating to Sites > Kinsta APM:

Once you enable the APM, you can use a variety of tools and features. These include diagnosing performance issues and monitoring results.
It’s easier than you may think to fix this pesky issue. 😌 Here’s how to get started… ✅Click to Tweet
Summary
HTTP status codes can provide a wide range of information about client and server requests. However, some of these messages indicate problems, such as the HTTP 408 Request Timeout error.
As we discussed in this post, the source of the issue may be either client- or server-side. To troubleshoot and resolve the status code error, you should review and roll back recent changes, check your server configuration file and application logs, and debug your apps and scripts.
Do you want to switch to hosting that provides easy access to software for identifying, testing, and fixing issues on your site? Check out our Kinsta hosting plans to learn more about our APM and development tools!

Are you familiar with the frustration of encountering a 408 Request Timeout error while browsing a website?
This error occurs when your web browser fails to receive a timely response from the server, disrupting your browsing experience.
But don’t worry! This step-by-step guide will help you troubleshoot and fix the annoying HTTP 408 Request Timeout error.
Whether you’re unsure about the meaning of the error message or what’s causing it, we’ve got you covered. So let’s delve into the HTTP 408 status code, explore its common causes, and present you with potential solutions to get you back to smooth browsing.
- What Does the HTTP 408 Error Code Mean
- Exploring Common Causes of the HTTP 408 Request Timeout Error
- How to Resolve the HTTP 408 Error (8 Easy Solutions)
- Addressing the Issue on the Client Side
- Addressing the Issue on the Server-Side
- Tips to Avoid a 408 Request Timeout Error
What Does the HTTP 408 Error Code Mean
HTTP 408 status code is returned when a server timeout occurs due to a slow client request. It means the server terminated the connection, resulting in the client receiving the 408 Request Timeout message.
HTTP status codes communicate request status and can redirect clients to different resources. Common codes include:
- 200 (OK)
- 400 (Bad Request)
- 500 (Internal Server Error)
These status codes can be categorized into 5 groups:
| Error Codes | What They Mean |
| Informational | The server is still processing the request |
| Successful | The request has been successfully fulfilled |
| Redirects | The client should be redirected to a different resource |
| Client Errors | There was an error with the client’s request |
| Server Errors | There was an error with the server |
It is worth mentioning that the HTTP 408 error differs from the 504 Gateway Timeout status code, which is typically associated with the gateway or proxy servers. In contrast, the 408 error is directly generated by the web server with which the client is communicating.
WordPress Hosting Tailored for Developers & Agencies
Unlock your full potential as a developer or agency: Amplify productivity, deliver exceptional client experiences, and scale with ease.
Exploring Common Causes of the HTTP 408 Request Timeout Error
The occurrence of a 408 Request Timeout error can be attributed to various factors. Let’s delve into the 5 common triggers:
1. Server Overload
When a server becomes overwhelmed with numerous incoming requests, it may struggle to respond to all of them within the allocated time. Consequently, some requests may time out, resulting in the 408 error.
2. Network Issues
A weak or unreliable internet connection can also contribute to a 408 Request Timeout error.
3. Large File Downloads
Attempting to download large files, such as videos or images, can lead to a 408 Request Timeout error. If the server slowly transmits the file, the browser may assume the request has failed due to the extended waiting time.
4. Server Maintenance
During server maintenance or updates, the server may undergo temporary periods of unavailability. Accessing the server during these times can result in a 408 error as it cannot respond to the request.
5. Firewall or Security Settings
In some cases, strict firewall or security settings can interfere with the communication between your browser and the server. This can result in a request timeout if the server’s response is blocked or delayed.
6. Proxy Server Issues
If you are using a proxy server to connect to the internet, misconfigured settings or connection problems with the proxy server can cause a 408 error. The proxy server may fail to establish a timely connection with the destination server, resulting in a timeout.
If you’re experiencing some other issue, you might want to check out our guide on common WordPress issues.
How to Resolve the HTTP 408 Error (8 Easy Solutions)
Now that we have understood the HTTP 408 status code, let’s explore the solutions to resolve it. Below, we will discuss potential remedies from both the client-side and server-side perspectives.
Addressing the Issue on the Client Side
Client-side refers to the user’s side, where the web browser or application is making the request to the server. Client-side issues can include network problems, browser settings, or large file downloads that may cause the request to time out.
Here are a few solutions from the client side that can help resolve the HTTP 408 error:
1. Review Recent Database Modifications
Consider recent database changes as a potential cause of the HTTP 408 error. Revert any recent modifications to resolve the issue.
Pay attention to the installed extensions or updates that may have altered database records, leading to conflicts or errors. For example, check a specific table modified by a new plugin using a database management tool like phpMyAdmin.
Also, manually review recently modified tables or records for changes causing the HTTP 408 error. Revert problematic alterations to their original states.
2. Perform a Site Backup
You should prioritize website backup as a precaution for troubleshooting the HTTP 408 error. We recommend creating a comprehensive backup to secure your files and database.
There are various methods available to back up your website. Below are the two easy approaches for website backup:
Methods for website backup:
Method #1. Manual method using SFTP client like FileZilla:
- Obtain SFTP credentials from the hosting provider.
- Connect to the server and download files from the root directory (typically in the public_html folder).
Method #2. Cloudways users:
- Use the Cloudways platform to create backups conveniently and ensure data safety.
First, we’ll cover backup creation using the Cloudways platform, then explore the manual backup process.
How to Backup Your Application Using the Cloudways Platform
Here is a step-by-step guide on how to download the backup of your application from the Cloudways platform to your local computer:
- Step 1: Log in to the Cloudways platform and select the target server.
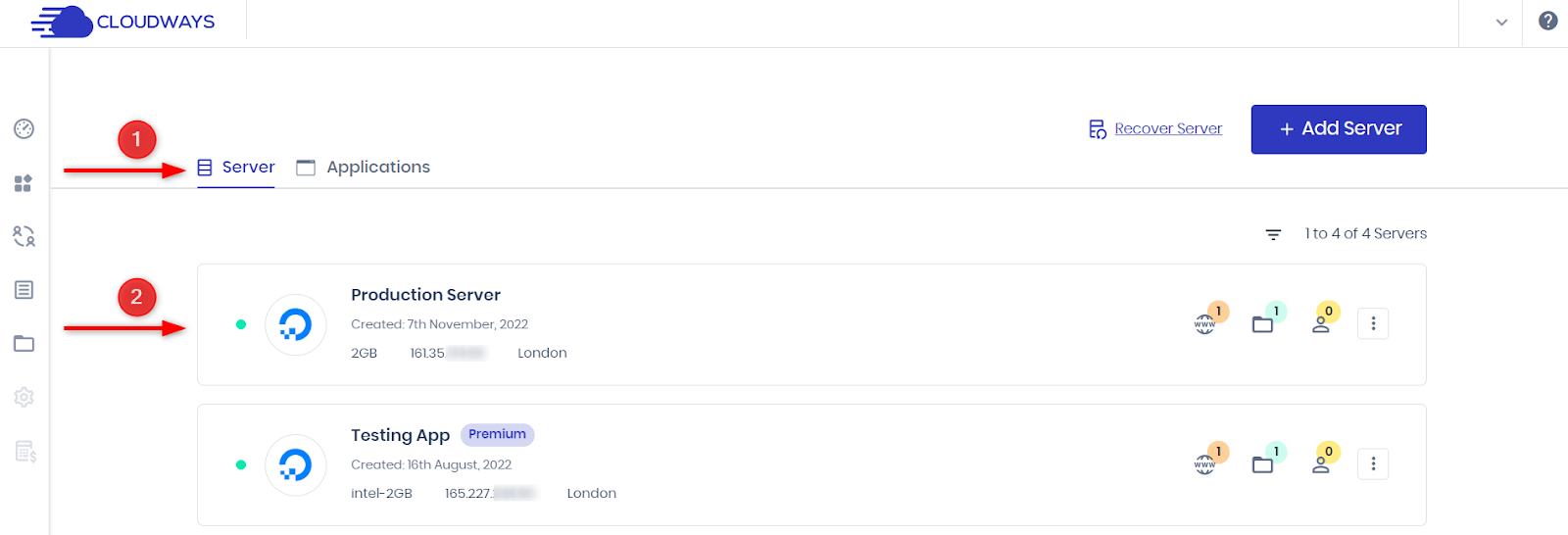
- Step 2: Go to Backups in the left menu and enable Local Backups.
Optional: Click Take Backup Now for an immediate backup.
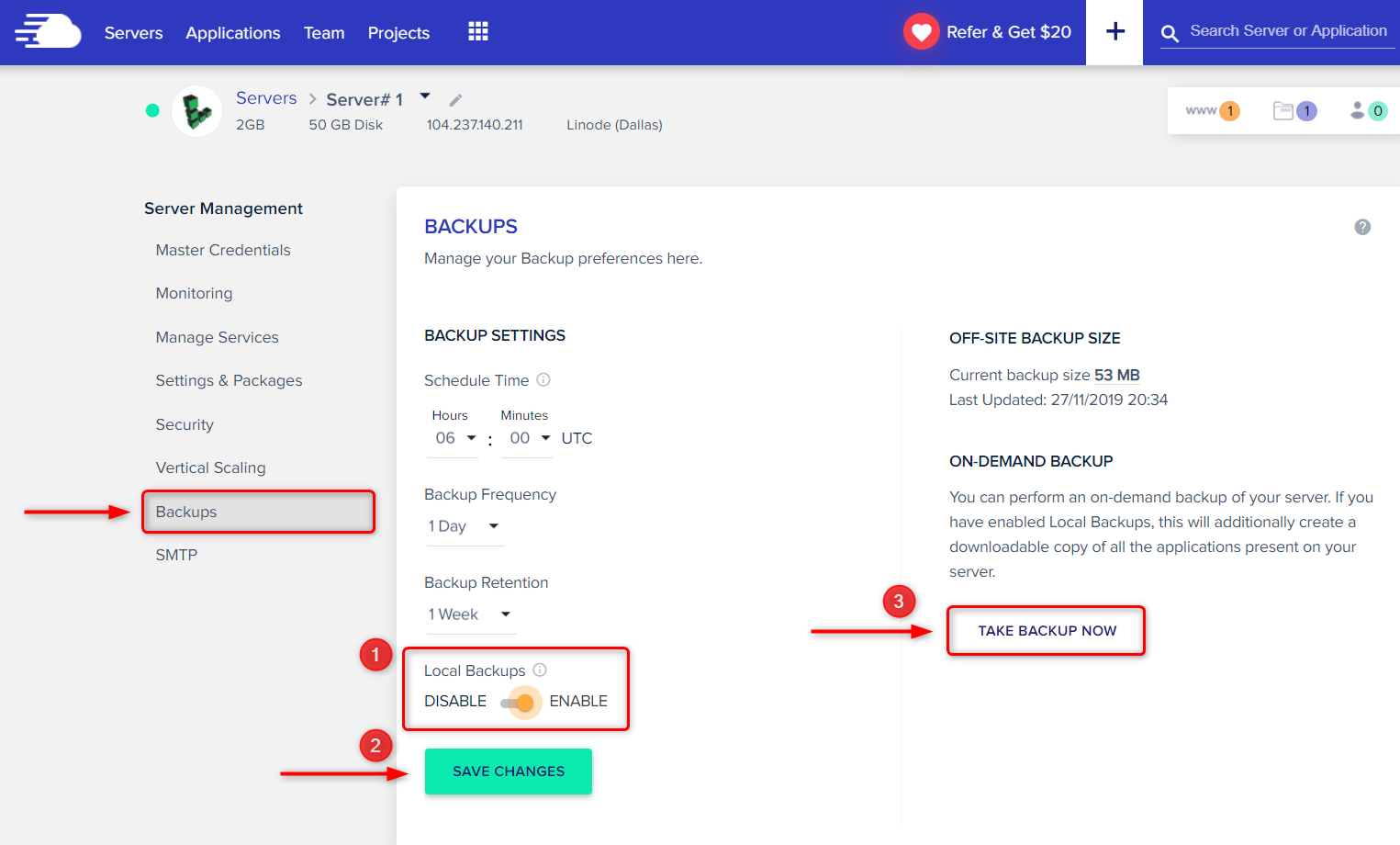
- Step 3: Connect to your server via SFTP (Secure File Transfer Protocol) using your Master Credentials to establish the remote server connection.
- Step 4: Navigate to /applications/<your_application_name>/local_backups.
Note: Only the most recent backup is available locally. Off-site backups follow the scheduled frequency and settings.
By following these steps, you will successfully backup your application using the Cloudways platform.
How to Manually Backup & Download WordPress Files Via an FTP Client
To backup your WordPress files using an FTP client, follow these steps:
- Navigate to your WordPress site’s root directory.
- Set up an FTP connection with the destination storage using FTP credentials, host IP address, and port number.
- Launch an FTP client like FileZilla.
- Enter the credentials and click on “Quickconnect” to initiate a connection with the server.
- Select all the files and folders you want to back up. These typically include the entire WordPress installation directory.
- Download the selected files and folders to your local host or storage location.
Note: Using the backup functionality provided by the Cloudways platform offers a simpler and user-friendly experience. It saves time and effort compared to manual FTP backups.
3. Verify the URL
Sometimes, the HTTP 408 error can occur if a URL requiring specific credentials is accidentally requested, resulting in a request timeout.
Possible cause: Mistyping the URL in the browser. We recommend doing the following measures:
- Check the URL for typos, including the domain name, slashes, and hyphens.
- Re-enter the URL and refresh the page if a typo is suspected.
If the request timeout error persists, proceed to the next troubleshooting step.
4. Revert Recent Updates
To roll back recent changes and resolve the HTTP 408 error on your WordPress site, consider restoring your site to a previous version if recent changes (e.g., new plugin installation or WordPress update) caused the error.
And if you’re a Cloudways user, you can take advantage of its point-in-time restore feature, which includes automated offsite server-level backups and on-demand application-level backups.
Note: Cloudways Autoscale users can refer to this specific guide for instructions.
Now let’s restore a point-in-time backup using Cloudways Flexible:
- Log in to the Cloudways Platform.
- Navigate to “Servers” and select the server with your desired application.

- Click on the application name under the “www” section.
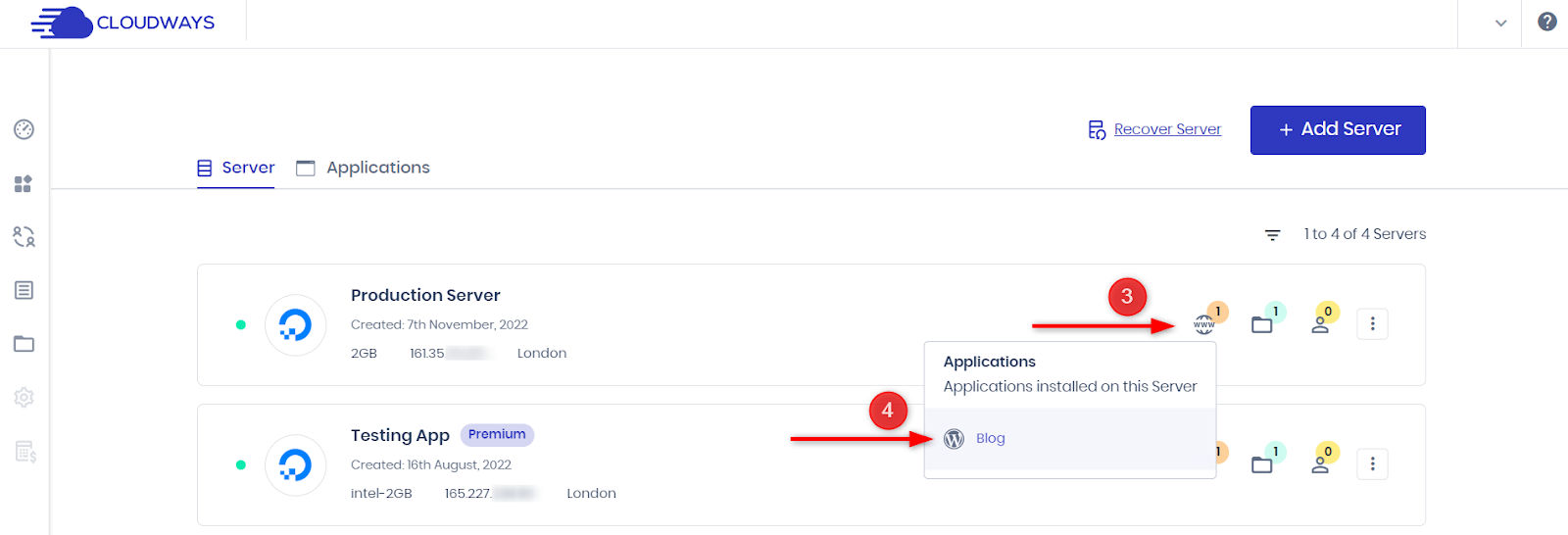
- Under “Application Management,” select “Backup and Restore.”
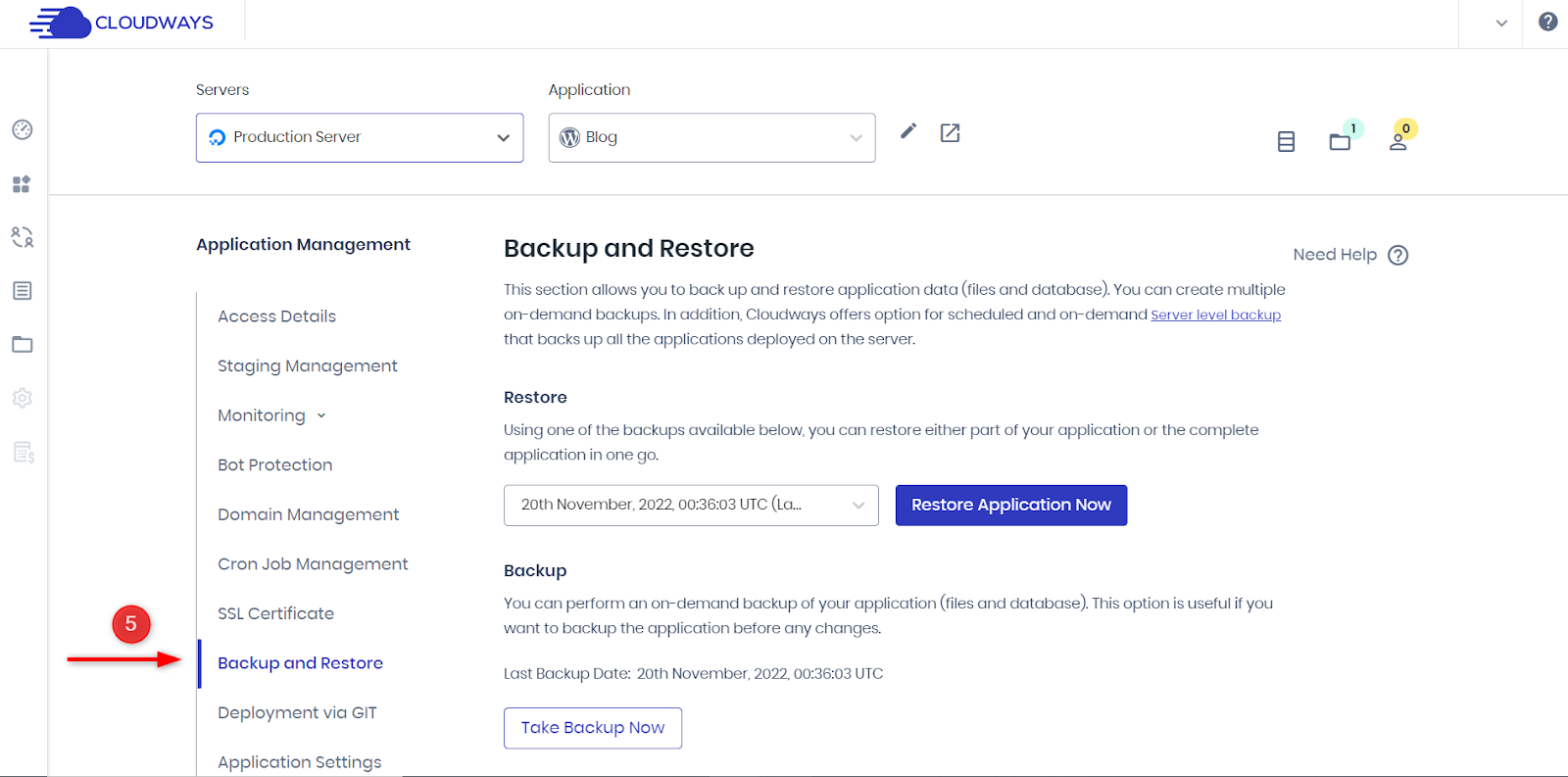
- Select the desired restore point from the dropdown.
- Click “Restore Application Now.”
Important considerations:
- Ensure sufficient disk space before restoring.
- Choose complete restore or specific file/database restore based on your needs.
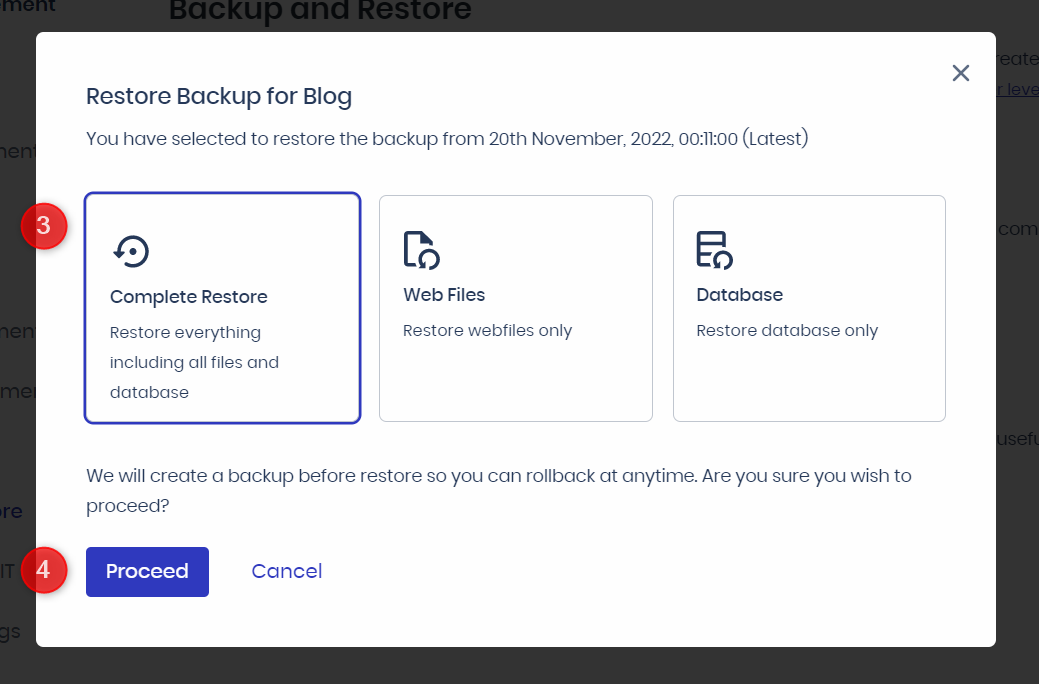
- Restore duration depends on application data size.
- You will receive a notification upon completion.
By following these steps, you can perform a point-in-time restore of your Cloudways application, helping you revert to a previous version and potentially resolving the HTTP 408 error.
5. Remove Extensions and Plugins
Adding extensions and plugins to your website can sometimes lead to compatibility issues and errors, including the HTTP 408 status code. To investigate if this is the cause, you can perform the following steps:
- Deactivate all plugins in the WordPress dashboard:
- Navigate to the Plugins section and select all installed plugins.
- From the Bulk Actions dropdown menu, choose “Deactivate” and click “Apply.”
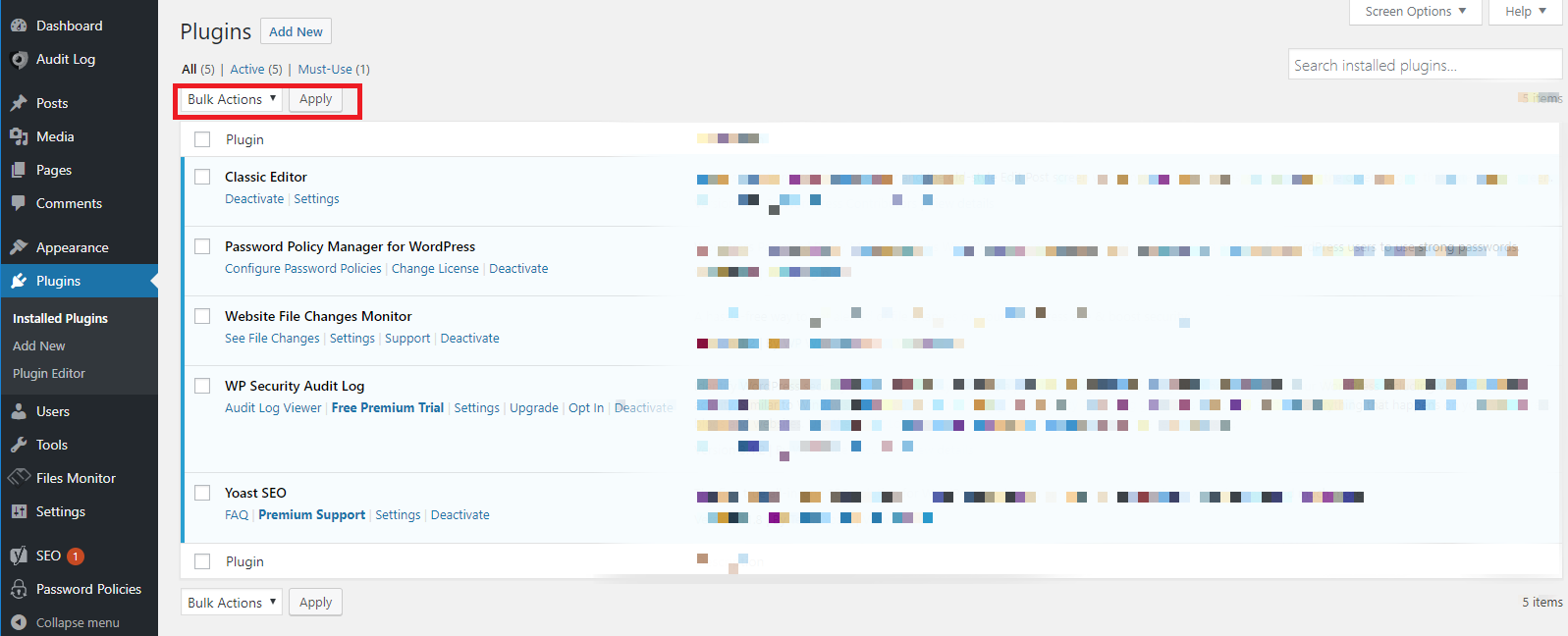
- Alternative deactivation method: In case you are unable to access the dashboard, you can connect to your site via SFTP and rename the plugins folder to something like “plugins_old”. This action will effectively deactivate all plugins.
- Check if the error is resolved after deactivation. Reactivate plugins one by one and observe if the error reoccurs. Identify the problematic plugin causing the error.
- Uninstall the problematic plugin and consider finding a suitable alternative or contacting the developer for further assistance.
By systematically deactivating and reactivating plugins, you can identify and resolve the plugin-related cause of the HTTP 408 error on your website.
Addressing the Issue on the Server-Side
Server-side refers to the server receiving and processing the client’s requests. Server-side issues can include server overload, maintenance, or misconfigurations that lead to the server being unable to respond within the allocated time, resulting in the 408 error.
The issue likely lies on the server side if the previous solutions did not resolve the HTTP 408 error. In such cases, it is necessary to explore alternative solutions to resolve the error.
6. Review Application Logs
You can troubleshoot the HTTP 408 error from a server-side perspective in two ways.
If you use WordPress, you can access logs by enabling the WordPress debugging mode in the wp-config.php file. Simply insert the following code:
define('WP_DEBUG', true);
define('WP_DEBUG_LOG', true);
define('WP_DEBUG_DISPLAY', false);
For Cloudways users, monitoring application logs through the Cloudways Platform offers a convenient option. Here’s how you can do it:
- Log in to the Cloudways Platform and select your desired application.
- Navigate to the “Monitoring” section and click on “Logs.”
- Click the “Access Logs” section to view recent log entries or the “Error Logs” to view recent Apache error logs.
By accessing and analyzing server-side logs, you can gather crucial information to diagnose and address the HTTP 408 error from a server-side perspective.
7. Troubleshoot Apps or Scripts
Debugging refers to the process of identifying and resolving bugs or errors in your code. If you are still encountering the HTTP 408 error on your website, it is necessary to debug your site. To simplify the bug monitoring process for your WordPress site, you can utilize WordPress debugging plugins.
Take Control of Your WordPress Projects with Cloudways
Enjoy robust features like easy scalability, one-click staging, advanced security, and blazing-fast performance.
1. Query Monitor
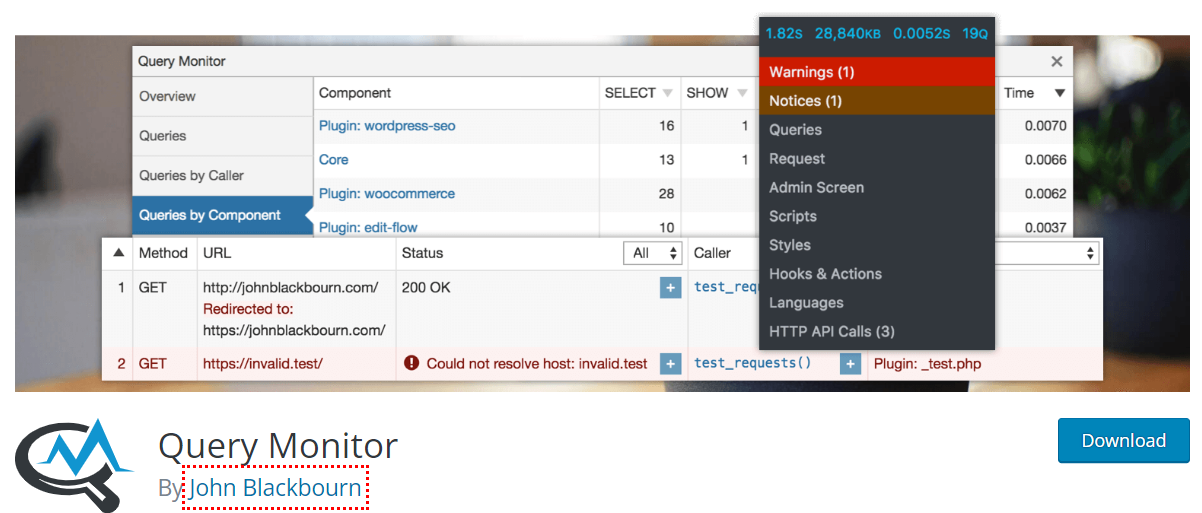
Query Monitor is a WordPress plugin that adds a developer tool panel to your WordPress dashboard. It offers database queries, PHP errors, HTTP API calls, hooks and actions, editor block disabling, and enqueued scripts and stylesheets.
With Query Monitor, you can gather extensive information for effective debugging.
2. New Relic

Another option for comprehensive debugging is New Relic, a premium tool. It provides monitoring of user experience, mapping the WordPress architecture, identifying broken permalinks, analyzing site performance, and proactively detecting anomalies.
New Relic helps you gather troubleshooting data and ensures an optimal experience for your visitors.
Troubleshooting via Application Performance Monitoring
Another option is utilizing an Application Performance Monitoring (APM) tool to help you monitor and optimize your site’s performance.
Here’s how you can use the New Relic APM feature on the Cloudways platform to monitor your application:
- Log in to your New Relic account.
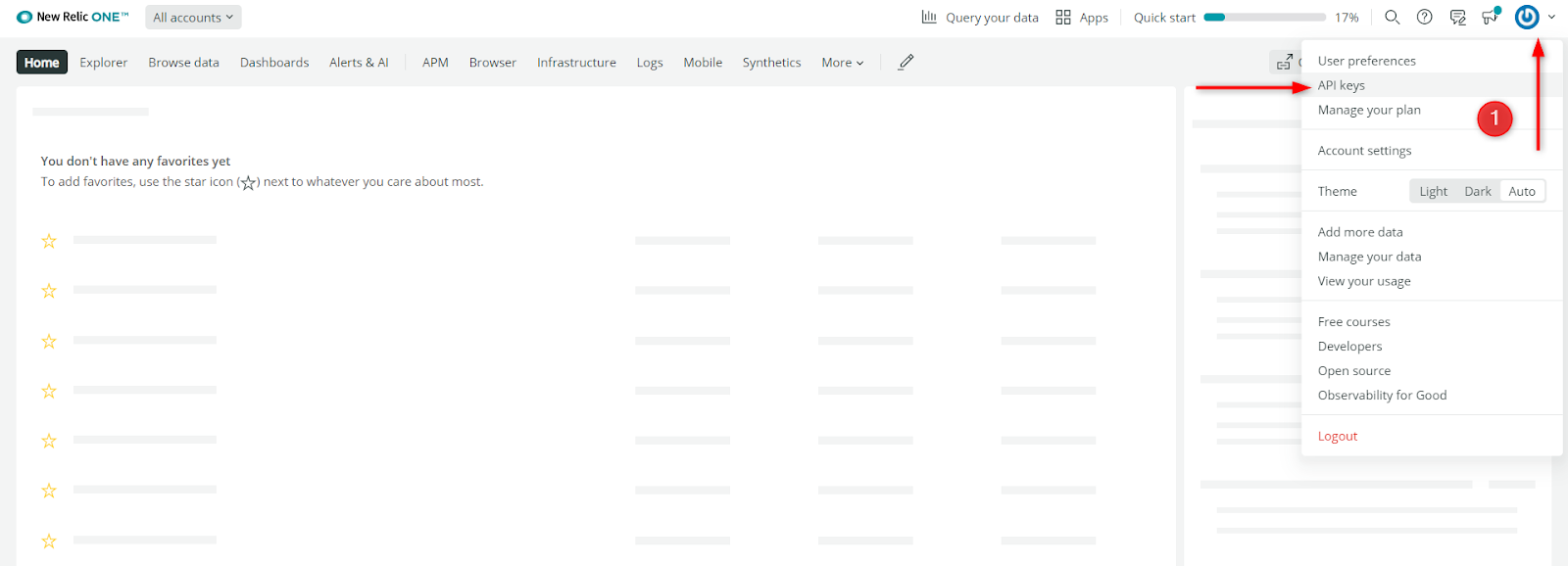
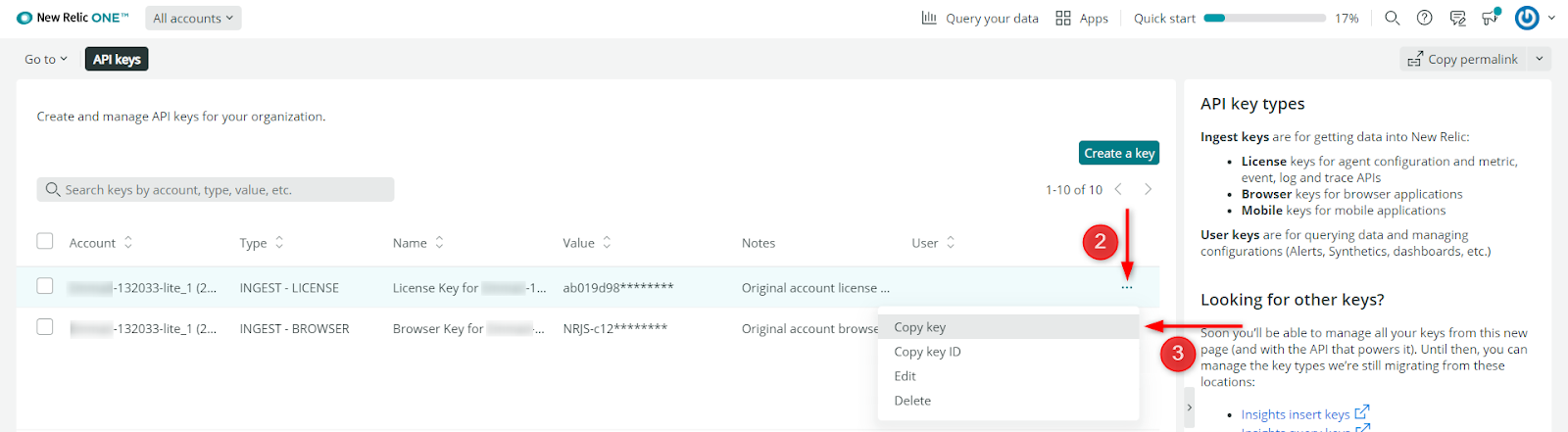
- Open the User Menu and select API Keys.
- Locate your license key labeled as “Original account license key.” Click on the ellipsis (…) to view more options.
- Copy your license key.
- Log in to the Cloudways Platform.
- Go to Servers and choose the desired server.

- Under Server Management, select Monitoring and switch to the New Relic tab.
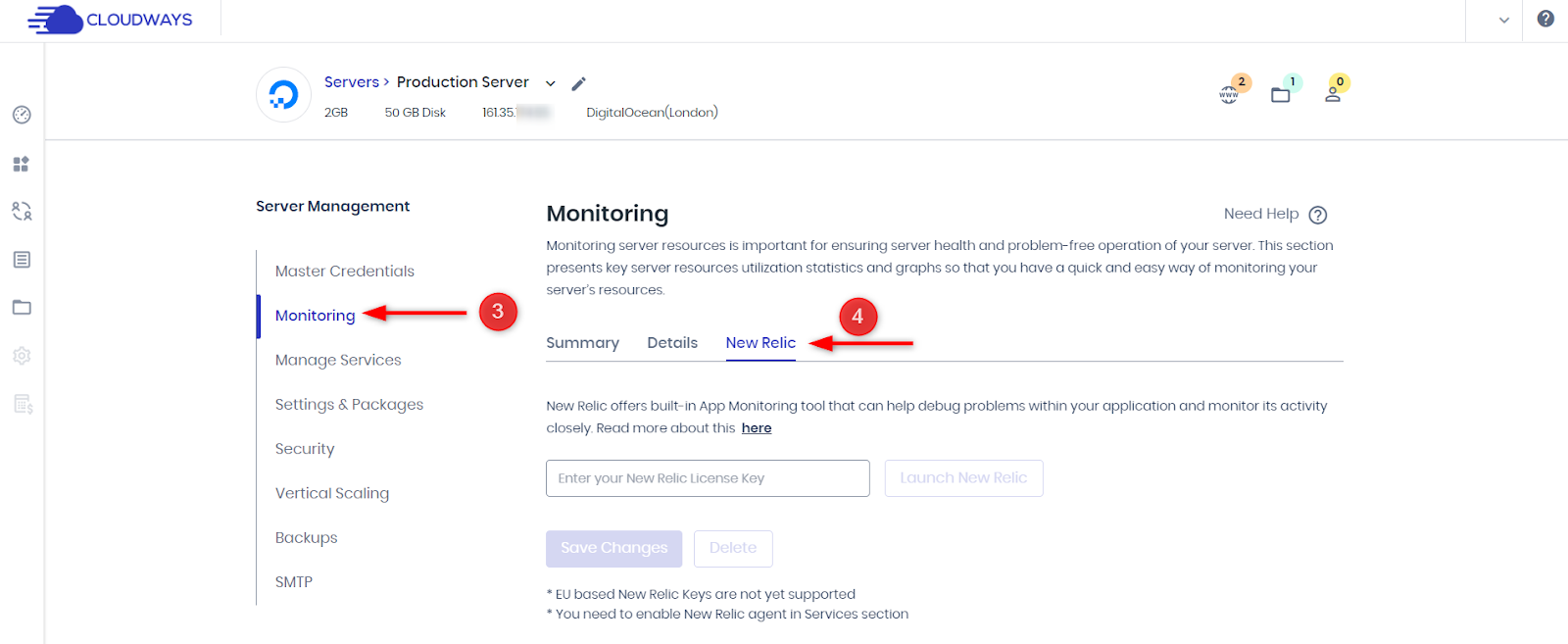
- Enter your New Relic License Key and save the changes.
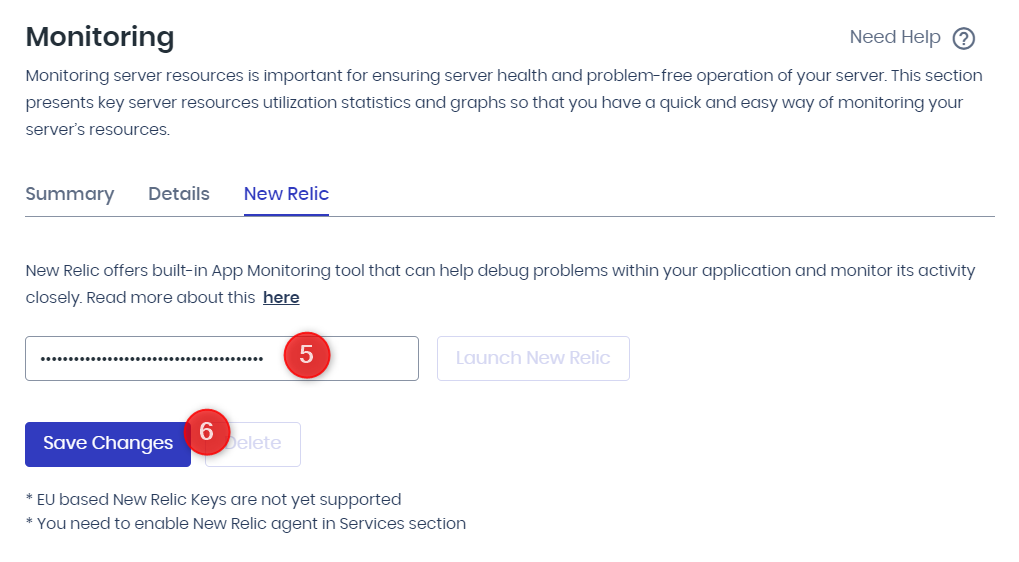
- Enable the New Relic service in Server Management > Manage Services.

- Start monitoring your applications through New Relic APM.
Using WordPress debugging plugins or premium tools like New Relic and employing an APM tool can simplify your WordPress site’s monitoring and troubleshooting process, enhancing its functionality.
8. Validate Server Configuration Files
If you are still experiencing the HTTP 408 error and want to identify its cause, you can check your server configuration files using SFTP. The specific steps may vary depending on whether your server is running on Apache or Nginx.
For Apache users:
- Locate the .htaccess file in your site’s root directory.
- Open the file and search for the lines containing “KeepAliveTimeout” and “RequestReadTimeout”.
- Comment out these lines by adding “#” at the beginning of each line.
- Save the file and then reload the page in your browser.
In the case of a WordPress site hosted on an Apache Web Server, follow these steps to access and edit the .htaccess file:
- Connect to your server using an FTP client like FileZilla.
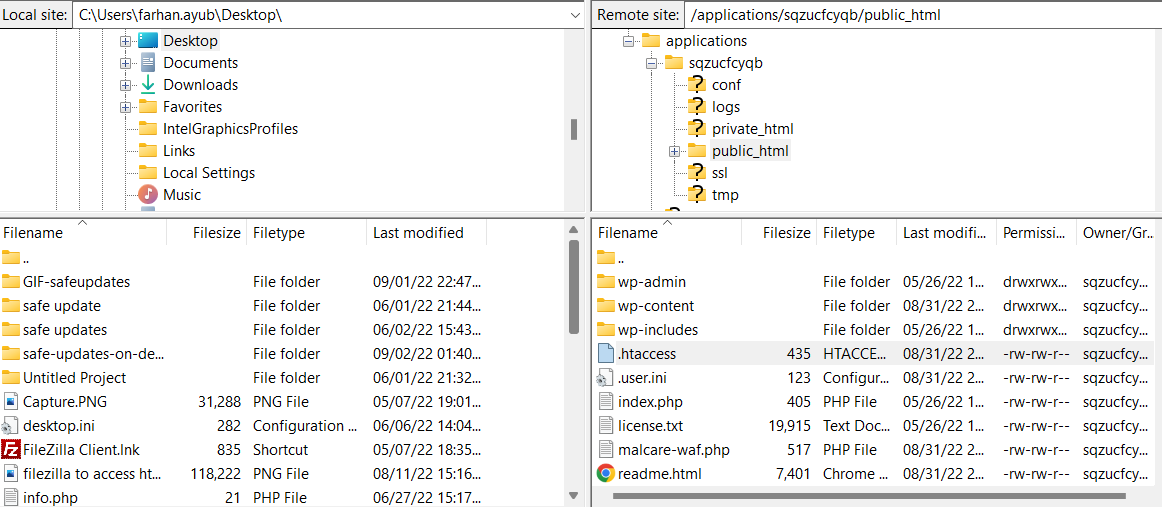
- Navigate to the root folder of your WordPress application (e.g., “/applications/sqzucfcyqb/public_html”).
- Locate the .htaccess file within the “public_html” folder.
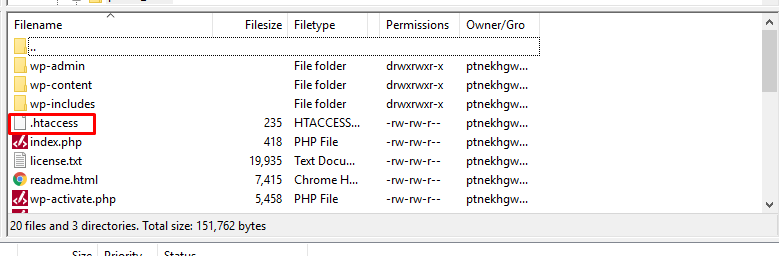
- Right-click on the file and select the “View/Edit” option to open it in a text editor.
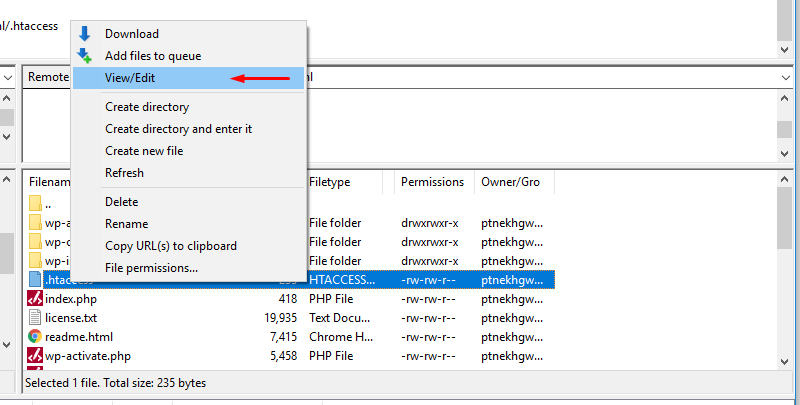
- Make the necessary changes to the file and save it.
Following these steps, you can fix the HTTP 408 Request Timeout error.
Unleash Your Agency’s Potential with Managed WordPress Hosting
Experience the freedom and efficiency your agency deserves: Streamline workflows, optimize resources, and exceed client expectations.
4 Tips to Avoid a 408 Request Timeout Error
Here are 5 effective measures to prevent a 408 Request Timeout error and improve your browsing experience:
1. Use a Reliable Internet Connection:
Ensure you have a stable Internet connection to minimize the chances of encountering a 408 error. Consider upgrading your plan or switching to a different Internet service provider if necessary.
2. Keep Your Browser and Operating System Up-To-Date:
Regularly update your browser and operating system to avoid compatibility issues and ensure a smooth and secure browsing experience.
3. Clear Your Browser Cache Regularly:
Periodically clear your browser cache to prevent website loading issues. This can be done by accessing your browser settings and clearing the cache manually or setting up automated cache clearing at regular intervals.
4. Avoid Downloading Large Files:
Downloading large files can strain the server and increase the likelihood of a 408 error. Consider using a download manager or splitting large files into smaller parts to avoid encountering this problem.
5. Disable or Adjust Firewall and Security Settings:
In some cases, overactive firewall or security settings can interfere with the communication between your browser and the server, resulting in a request timeout. Temporarily disabling or adjusting these settings can help troubleshoot the issue.
Summary
The 408 Request Timeout error occurs when the server terminates the connection due to a request taking too long to complete. And resolving this error involves taking several steps to identify and address the underlying causes. Here’s a summary of the key actions to take:
- Review recent changes: Roll back any recent website or server configuration modifications that may be causing the timeout error.
- Check server configuration and logs: Analyze your server configuration files and application logs to detect any misconfigurations or errors that could be causing the issue.
- Debug applications and scripts: Identify and address any coding errors or inefficiencies in your applications and scripts that could be causing the request timed out error.
By following these troubleshooting steps, you can increase your chances of resolving the 408 error and improving your overall browsing experience.
Remember to maintain a stable internet connection, keep your browser and operating system up to date, avoid downloading large files excessively, and regularly clear your browser cache to minimize the risk of encountering timeout errors.
Other 4XX Errors and How to Fix Them
- How to Fix WordPress 403 Forbidden Error
- How to Fix 405 Method Not Allowed in WordPress
- Fix the “413 Request Entity Too Large” Error in WordPress
- How to Fix 429 Too Many Requests Error in WordPress
- Fix the “413 Request Entity Too Large” Error in WordPress
FAQs
How do I fix a 408 request timeout step by step?
Follow the steps below to fix a 408 request timeout error:
- Safely back up your website.
- Verify the accuracy of the URL.
- Evaluate recent database modifications.
- Remove or disable extensions and plugins.
- Revert recent changes to your website.
- Review server configuration files.
- Examine application logs for insights.
- Debug applications or scripts as needed.
What causes a 408 error?
A 408 Request Timeout error typically occurs when the server terminates the connection because the requested operation exceeds the timeout period. It happens when the server waits for additional information from the client, which is not provided within the specified timeframe. Resultingly, the server sends a 408 Request Timeout message to the client, indicating a delayed request.
How does Error 408 affect the speed of your webpage?
Error 408, or the Request Timeout error, does not directly affect webpage speed. It is a communication issue between the client and the server. The impact on webpage speed is minimal.
Share your opinion in the comment section.
COMMENT NOW
Share This Article
Customer Review at 
“Beautifully optimized hosting for WordPress and Magento”
Arda Burak [Agency Owner]
Abdul Rehman
Abdul is a tech-savvy, coffee-fueled, and creatively driven marketer who loves keeping up with the latest software updates and tech gadgets. He’s also a skilled technical writer who can explain complex concepts simply for a broad audience. Abdul enjoys sharing his knowledge of the Cloud industry through user manuals, documentation, and blog posts.
Feb 8, 2018 11:00:50 AM |
408 Request Timeout: What It Is and How to Fix It
The 408 Request Timeout is an HTTP response status code indicating that the server did not receive a complete request from the client within the server’s allotted timeout period.
The 408 Request Timeout is an HTTP response status code indicating that the server did not receive a complete request from the client within the server’s allotted timeout period. The 408 Request Timeout error code appears similar to the 504 Gateway Timeout error we explored in a previous article, which indicates that that a server acting as a gateway or proxy timed out. However, the 408 Request Timeout error isn’t a message from a gateway or proxy server somewhere in the node chain, but is a direct message from the active server the client has connected to (like a the web server)
It can be difficult to find the cause of unexpected HTTP response codes and the 408 Request Timeout error code is no exception. With a potential pool of over 50 status codes used to represent the complex relationship between the client, a web application, a web server, and (possibly) multiple third-party web services, determining the cause of a particular status code can be challenging, even under the best of circumstances.
In this article we’ll explore the 408 Request Timeout in greater depth by looking at what might cause this message to appear, including a few tips you can use to diagnose and debug the appearance of this error within your own application. We’ll even look at a number of the most popular content management systems (CMSs) for potential problem areas that could cause your own website to be unexpectedly generating 408 Request Timeout errors. Let’s dive right in!
Server- or Client-Side?
All HTTP response status codes within the 4xx category are considered client error responses. Errors in the 4xx category contrast with those from the 5xx category, such as the aforementioned 504 Gateway Timeout we examined earlier, which are considered server error responses. That said, the appearance of a 4xx error doesn’t necessarily mean the issue is on the client side (the «client», in this case, is typically the web browser or device being used to access the application). Oftentimes, if you’re trying to diagnose an issue within your own application, you can immediately ignore most client-side code and components, such as HTML, cascading style sheets (CSS), client-side JavaScript, and so forth. This doesn’t apply solely to web sites, either. Smart phone applications often implement modern looking user interfaces that are actually powered by normal web applications behind the scenes.
On the other hand, the server could be the root cause of a 408 Request Timeout error. In some cases, the server may be misconfigured and may be handling requests improperly, which can result in 408 code responses and other troublesome traffic routing issues. We’ll explore some of these scenarios (and potential solutions) down below, but be aware that, even though the 408 Request Timeout is considered a client error response, it doesn’t necessarily mean we can rule out either the client nor the server as the culprit in this scenario. In these situations, the server is still the network object that is producing the 408 Request Timeout and returning it as the HTTP response code to the client, but it could be that the client is causing the issue in some way.
Start With a Thorough Application Backup
As usual, it is better to have played it safe at the start than to screw something up and come to regret it later on down the road. As such, it is critical that you perform a full backup of your application, database, and all other components of your website or application before attempting any fixes or changes to the system. Even better, if you have the capability, create a complete copy of the application and stick the copy on a secondary staging server that is either inactive, or publicly inaccessible. This will give you a clean testing ground on which to test all potential fixes needed to resolve the issue, without threatening the security or sanctity of your live application.
Diagnosing a 408 Request Timeout
A 408 Request Timeout response code indicates that the server did not receive a complete request from the client within a specific period of time tracked by the server (i.e. the timeout period). As specified in the RFC7235 HTTP/1.1 Semantics and Content standards document server should include the special Connection header with the close directive as part of its response (e.g. Connection: close), which informs the client that the connection should be closed. Put simply, a 408 code informs the client that the server has decided to close the connection rather than continue waiting for the transaction to complete. Upon receiving the Connection: close header the client can opt to repeat the original request using a new connection.
Most modern browsers implement HTTP preconnection mechanisms, which provides the user agent (i.e. browser) to speed up overall web surfing experiences by essentially predicting what resources — and therefore connections — the client may be using in the immediate future. The full scope of how browsers use these mechanisms is well beyond the scope of this article, but you can check out the W3C Resource Hints documentation for more details.
Troubleshooting on the Client-Side
Since the 408 Request Timeout is a client error response code, it’s best to start by troubleshooting any potential client-side issues that could be causing this error. Here are a handful of tips to try on the browser or device that is giving you problems.
Check the Requested URL
The most common cause of a 408 Request Timeout is simply inputting an incorrect URL. Many servers are tightly secured, so as to disallow unexpected requests to resources that a client/user agent should not have access to. It may be that the requested URL is slightly incorrect, which is causing the user agent to request an unintended resource, which may be routed through a proxy server that requires authentication. For example, a request to the URI https://airbrake.io/login might route requests through a separate proxy server used to handle user authentication. If the original request did not contain appropriate credentials, the result could be a 408 Request Timeout error response. It’s always a good idea to double-check the exact URL that is returning the 408 Request Timeout error to make sure it is intended resource.
Debugging Common Platforms
If you’re running common software packages on the server that is responding with the 408 Request Timeout, you may want to start by looking into the stability and functionality of those platforms first. The most common content management systems — like WordPress, Joomla!, and Drupal — are all typically well-tested out of the box, but once you start making modifications to the underlying extensions or PHP code (the language in which nearly all modern content management systems are written in), it’s all too easy to cause an unforeseen issue that results in a 408 Request Timeout.
There are a few tips below aimed at helping you troubleshoot some of these popular software platforms.
Rollback Recent Upgrades
If you recently updated the content management system itself just before the 408 Request Timeout appeared, you may want to consider rolling back to the previous version you had installed when things were working fine. Similarly, any extensions or modules that you may have recently upgraded can also cause server-side issues, so reverting to previous versions of those may also help. For assistance with this task, simply Google «downgrade [PLATFORM_NAME]» and follow along. In some cases, however, certain CMSs don’t really provide a version downgrade capability, which indicates that they consider the base application, along with each new version released, to be extremely stable and bug-free. This is typically the case for the more popular platforms, so don’t be afraid if you can’t find an easy way to revert the platform to an older version.
Uninstall New Extensions, Modules, or Plugins
Depending on the particular content management system your application is using, the exact name of these components will be different, but they serve the same purpose across every system: improving the capabilities and features of the platform beyond what it’s normally capable of out of the box. But be warned: such extensions can, more or less, take full control of the system and make virtually any changes, whether it be to the PHP code, HTML, CSS, JavaScript, or database. As such, it may be wise to uninstall any new extensions that may have been recently added. Again, Google the extension name for the official documentation and assistance with this process.
Check for Unexpected Database Changes
It’s worth noting that, even if you uninstall an extension through the CMS dashboard, this doesn’t guarantee that changes made by the extension have been fully reverted. This is particularly true for many WordPress extensions, which are given carte blanche within the application, including full access rights to the database. Unless the extension author explicitly codes such things in, there are scenarios where an extension may modify database records that don’t «belong» to the extension itself, but are instead created and managed by other extensions (or even the base CMS itself). In those scenarios, the extension may not know how to revert alterations to database records, so it will ignore such things during uninstallation. Diagnosing such problems can be tricky, but I’ve personally encountered such scenarios multiple times, so your best course of action, assuming you’re reasonably convinced an extension is the likely culprit for the 408 Request Timeout, is to open the database and manually look through tables and records that were likely modified by the extension.
Above all, don’t be afraid to Google your issue. Try searching for specific terms related to your issue, such as the name of your application’s CMS, along with the 408 Request Timeout. Chances are you’ll find someone who has experienced the same issue.
Troubleshooting on the Server-Side
If you aren’t running a CMS application — or even if you are, but you’re confident the 408 Request Timeout isn’t related to that — here are some additional tips to help you troubleshoot what might be causing the issue on the server-side of things.
Confirm Your Server Configuration
Your application is likely running on a server that is using one of the two most popular web server softwares, Apache or nginx. At the time of publication, both of these web servers make up 84% of the world’s web server software! Thus, one of the first steps you can take to determine what might be causing these 408 Request Timeout response codes is to check the configuration files for your web server software for unintentional redirect or request handling instructions.
To determine which web server your application is using you’ll want to look for a key file. If your web server is Apache then look for an .htaccess file within the root directory of your website file system. For example, if your application is on a shared host you’ll likely have a username associated with the hosting account. In such a case, the application root directory is typically found at the path of /home/<username>/public_html/, so the .htaccess file would be at /home/<username>/public_html/.htaccess.
If you located the .htaccess file then open it in a text editor and look for lines that use KeepAliveTimeout or RequestReadTimeout directives. KeepAliveTimeout is part of the core module, while RequestReadTimeout is from the reqtimeout module in Apache. Covering exactly how these directives work is well beyond the scope of this article, however, the basic concept is that these timeout directives inform the server to allow for incoming client requests to take only a certain amount of time before they are considered failed and closed via a 408 response.
For example, here we’re using the RequestReadTimeout directive to set header and body timeouts of 15 and 30 seconds:
RequestReadTimeout header=15 body=30
Look for any strange timeout directives in the .htaccess file that don’t seem to belong, then try temporarily commenting them out (using the # character prefix) and restarting your web server to see if this resolves the issue.
On the other hand, if your server is running on nginx, you’ll need to look for a completely different configuration file. By default this file is named nginx.conf and is located in one of a few common directories: /usr/local/nginx/conf, /etc/nginx, or /usr/local/etc/nginx. Once located, open nginx.conf in a text editor and look for client_body_timeout, client_header_timeout, or keepalive_timeout directives, which are all part of the http_core Nginx module. For example, here is a simple block directive (i.e. a named set of directives) that configures a virtual server for airbrake.io and sets the client header and body timeouts to 15 and 30 seconds, respectively:
server {
listen 80;
listen 443 ssl;
server_name airbrake.io;
client_header_timeout 15s;
client_body_timeout 30s;
keepalive_timeout 60s;
}
Have a look through your nginx.conf file for any abnormal _timeout directives and comment out any abnormalities before restarting the server to see if the issue was resolved.
Configuration options for each different type of web server can vary dramatically, so we’ll just list a few popular ones to give you some resources to look through, depending on what type of server your application is running on:
- Apache
- Nginx
- IIS
- Node.js
- Apache Tomcat
Look Through the Logs
Nearly every web application will keep some form of server-side logs. Application logs are typically the history of what the application did, such as which pages were requested, which servers it connected to, which database results it provides, and so forth. Server logs are related to the actual hardware that is running the application, and will often provide details about the health and status of all connected services, or even just the server itself. Google «logs [PLATFORM_NAME]» if you’re using a CMS, or «logs [PROGRAMMING_LANGUAGE]» and «logs [OPERATING_SYSTEM]» if you’re running a custom application, to get more information on finding the logs in question.
Debug Your Application Code or Scripts
If all else fails, it may be that a problem in some custom code within your application is causing the issue. Try to diagnose where the issue may be coming from through manually debugging your application, along with parsing through application and server logs. Ideally, make a copy of the entire application to a local development machine and perform a step-by-step debug process, which will allow you to recreate the exact scenario in which the 408 Request Timeout occurred and view the application code at the moment something goes wrong.
No matter the cause — and even if you managed to fix this particular error this time around — the appearance of an issue like the 408 Request Timeout within your own application is a good indication you may want to implement an error management tool, which will help you automatically detect errors and will alert you the instant they occur. Airbrake’s error monitoring software provides real-time error monitoring and automatic exception reporting for all your development projects. Airbrake’s state of the art web dashboard ensures you receive round-the-clock status updates on your application’s health and error rates. No matter what you’re working on, Airbrake easily integrates with all the most popular languages and frameworks. Plus, Airbrake makes it easy to customize exception parameters, while giving you complete control of the active error filter system, so you only gather the errors that matter most.
Check out Airbrake’s error monitoring software today and see for yourself why so many of the world’s best engineering teams use Airbrake to revolutionize their exception handling practices!
