Local folder or tarball paths
This section provides information on the following issues:
| Type of error: | Error message: |
|---|---|
| General startup issues | — Error messages in the Package Manager window — Package Manager missing or window doesn’t open — Problems after upgrading Unity to new version — Resetting your project’s package configuration |
| Package installation issues | — Package installation fails — Unable to add package from Git URL |
| Problems installing git dependencies | — No ‘git’ executable was found — git-lfs: command not found — Repository not found — Could not read Username: terminal prompts disabled — Can’t update Git version |
| Asset StoreA growing library of free and commercial assets created by Unity and members of the community. Offers a wide variety of assets, from textures, models and animations to whole project examples, tutorials and Editor extensions. More info See in Glossary packages (My Assets) |
— ‘Failed to parse Http response’ in My Assets context |
| Scoped registries | — Missing ‘My Registries’ in the Package Manager window |
| Issues when building packages | — Missing MonoBehaviour errors — Loading error for hostfxr.dll on Windows |
You can also run the Unity Package Manager Diagnostics tool if you are experiencing problems that might be network-related. For more information, see Diagnose network issues.
Error messages in the Package Manager window
The Package Manager displays error indicators in the Package Manager window when it encounters problems.
System-wide issues
-
Network connection issues
Error messages appear in the status bar when the Package Manager has detected an issue that isn’t related to a specific package. For example, if the Package Manager can’t access the package registry server, it displays this message in the status bar:

Network error message -
Error refreshing assets (or Error refreshing packages)
If your network can’t reach the package registry server, it’s probably because there is a connection problem with the network. When you or your system administrator diagnose and fix the network error, the status bar clears.
If your network connection is working, but you aren’t signed into your Unity account, the Package Manager doesn’t display any Asset Store packages. When you try to use the My Assets context, the Package Manager displays an error in the status bar:

Logged out of Unity account Click the Sign in button inside the list view to sign into your Unity account through the Unity Hub.
Package-specific issues
-
If a specific package has a problem when loading or installing (for example, when determining which package versions to load), the error icon (
 ) appears in the package list next to the compromised package (A). To find out what the problem is, open the compromised package’s details view to see the detailed error message (B):
) appears in the package list next to the compromised package (A). To find out what the problem is, open the compromised package’s details view to see the detailed error message (B):
Dependency error message
Package Manager missing or window doesn’t open
The Package Manager window might get moved offscreen or hidden by another window. When this happens, it looks like the Package Manager window failed to open. In this case, you can try to reset the window layout (Window > Layouts > Default) and reopen the Package Manager window again.
If the Package Manager window still doesn’t appear, check your Unity Console windowA Unity Editor window that shows errors, warnings and other messages generated by Unity, or your own scripts. More info
See in Glossary:
Failed to resolve packages: The file [<project-path>/Packages/manifest.json] is not valid JSON:
Unexpected token '}' at 44:1
}
This error message indicates that your manifest.json file is malformed. It also tells you the line number where the Package Manager failed to parse the file, so you can fix the JSON. There are a number of online validators that you can use to try to correct the problem. Once you save the corrected file, Unity reloads the Package Manager window.
If you upgraded from an early version of the Unity Editor, there may be other problems with your package manifestEach package has a manifest, which provides information about the package to the Package Manager. The manifest contains information such as the name of the package, its version, a description for users, dependencies on other packages (if any), and other details. More info
See in Glossary file:
-
As of 2019.3, your
manifest.jsonfile should not contain any references to the com.unity.package-manager-ui package. You can either reset your project’s package configuration or remove the following line from the manifest’s dependencies list:"com.unity.package-manager-ui": "2.1.1", -
Check to see if your project manifestEach Unity project has a project manifest, which acts as an entry point for the Package Manager. This file must be available in the
<project>/Packagesdirectory. The Package Manager uses it to configure many things, including a list of dependencies for that project, as well as any package repository to query for packages. More info
See in Glossary uses “exclude” as a package version. This is an obsolete value for the dependencies property. If you find any lines like these, remove the entire line. Package Manager only installs packages that are explicitly included as a dependency in your project, so once you remove that entry, Package Manager ignores the package and doesn’t install it.
If the Package Manager still fails to load, follow the procedure under Resetting your project’s package configuration.
Problems after upgrading Unity to new version
When you upgrade a project to a newer Unity version, the Package Manager automatically updates incompatible packages to newer compatible versions. However, if your package doesn’t compile, the Package Manager displays error messages in the Console.
To correct these messages, read the error messages and fix any problems you can. For example, a package might be missing a dependency on another package or version. In that case, you can try and install the package yourself.
You can also try the following sequence of solutions until you find something that works:
- Back up and then delete the
Packagesfolder under your project. - Back up and then delete the package sources in your project’s
Packagesfolder, leaving only themanifest.jsonfile. Then try to reload the project. - Create a new empty project. If the Package Manager window loads successfully, replace the
Library/PackageCache/com.unity.package-manager-ui@<version>folder in the failing project with the same folder from the newly created project. - As a last resort, you can reset your project to the default packageUnity automatically pre-installs a select number of default packages (for example, the Analytics Library, Unity Timeline, etc.) when you create a new project. This differs from a bundled package because you don’t need to install it and it differs from a built-in package because it extends Unity’s features rather than being able to enable or disable them.
See in Glossary configuration and add back packages one at a time until it works.
Resetting your project’s package configuration
If a project has too many package issues, you can reset your project back to the default package configuration for the Editor’s version of Unity. This operation resets all packages in your project. This might not fix the source of the problem, but it can help you figure out what the problem is.
Note: You can’t undo resetting your package configuration, so make sure you back up the manifest.json file first or make sure your project is under source control. You can also take extra precautions by cloning your project and testing out the operation on the clone before proceeding.
To return to the default package configuration, select Reset Packages to defaults from the Help menu.

Resetting a clone of your project
You can also test the return to the default packages before you perform the final change:
-
Clone your project by copy-pasting your project folder and renaming it so that it is easy to find (for example, if your project is called
MyProjectthen you could use something likeclone_MyProject). -
Load your newly cloned project.
-
From the Help menu, select Reset Packages to defaults.
Depending on the size of your project, this might take a few minutes.
-
Check that it successfully reset the packages. If so, you can perform the operation safely on the original project.
Package installation fails
If you are trying to install a new package from the registry and it is not working, it might be due to permission problems.
You must have full permissions on the cache folder:
- Windows:
C:UsersyournameAppDataLocalUnitycache - macOS:
~/Library/Unity/cache - Linux:
~/.config/unity3d/cache
It might be a problem with the network. Check your firewall and proxy settings.
Sometimes institutional environments, such as schools, government offices, or network-protected workplaces set up proxy servers to control traffic between the network and the Internet, and use their own server certificates which are not recognized by Unity or the Package Manager. Talk to your network administrator.
Unable to add package from Git URL
See Repository not found.
No ‘git’ executable was found
If you try to install a package from a git URL, a message similar to this appears:
Cannot perform upm operation: Unable to add package
[https://github.example.com/myuser/myrepository.git]:
No 'git' executable was found. Please install Git on your system and restart Unity [NotFound]
UnityEditor.EditorApplication:Internal_CallUpdateFunctions()
git-lfs: command not found
If you are trying to download a package that uses Git LFS (Large File Storage), you might see this error message:
Error when executing git command. git-lfs filter-process: command not found.
This indicates that Git LFS is probably not installed on your machine. To make sure, you could test it on the command line:
git lfs --version
If you see something like this, Git LFS is installed:
git-lfs/2.8.0 (GitHub; darwin amd64; go 1.12.7)
Otherwise, you can install it by following the Bitbucket GitHub instructions.
Repository not found
If you specify a location that does not exist, a message similar to this one appears in the Unity Console:
Cannot perform upm operation: Unable to add package [https://mycompany.github.com/gitproject/com.mycompany.mypackage.git]:
Error when executing git command. fatal: repository 'https://mycompany.github.com/gitproject/com.mycompany.mypackage.git/' not found
[NotFound]
UnityEditor.EditorApplication:Internal_CallUpdateFunctions() (at /Users/builduser/buildslave/unity/build/Editor/Mono/EditorApplication.cs:310)
Check your spelling. To make sure you are using the correct URL, go to the repository’s page and copy the URL from the Clone button:

Click the button to the right of the URL on GitHub (A) or GitLab (B) to copy the URL to your clipboard.
If the location of the repository is correct, there may be another problem with the URL:
- If you are targeting a specific revision, make sure your revision comes last. For example:
https://github.example.com/myuser/myrepository1.git#revision - If you are targeting a revision and the package is not at the root, make sure the
pathquery parameter precedes the revision anchor. For example:https://github.example.com/myuser/myrepository.git?path=/example/folder#v1.2.3
Could not read Username: terminal prompts disabled
If you are trying to install a package from a private repository that requires authentication, a message similar to this one appears in the Unity Console:
Cannot perform upm operation: Unable to add package [https://mycompany.github.com/gitproject/com.mycompany.mypackage.git]:
Error when executing git command. fatal: could not read Username for 'https://mycompany.github.com': terminal prompts disabled
[NotFound]
UnityEditor.EditorApplication:Internal_CallUpdateFunctions() (at /Users/builduser/buildslave/unity/build/Editor/Mono/EditorApplication.cs:310)
This message is likely due to the fact that Package Manager does not provide an interactive terminal or dialog where you can enter your username and password for HTTP, or your passphrase to unlock your SSH key:
-
With HTTP(S), every time you log onto BitBucket, GitHub or GitLab you need to enter your username and password in a terminal or a dialog box. However, the Package Manager does not provide an interactive terminal or dialog where you can enter your username and password for HTTP(S).
To bypass this, use one of the workarounds suggested in Solutions for HTTPS.
-
SSH uses a pair of public and private SSH keys. You can add your public SSH key to Bitbucket, GitHub or GitLab and then access repositories without having to enter a username and password.
However, if you have set up a passphrase to keep your SSH key safe, you still have to enter that passphrase in a terminal or a dialog box in order to authorize your key. In that case, you can use an SSH agent that can unlock your SSH key to authenticate with the Package Manager on your behalf.
Solutions for HTTPS
The Package Manager does not provide an interactive terminal or dialog where you can enter your HTTP(S) username and password. To bypass this, use one of these workarounds:
- Use a credential manager (Git Credential Manager for Windows or OSXKeyChain). Credential managers handle sending the password without having to use a terminal or a command prompt.
- Use git-credentials from a terminal or command prompt. Then launch the Hub from the same terminal so that Unity has access to the cached or stored credentials.
- Use SSH to authenticate instead. If you set up your SSH key without a passphrase, the Package Manager doesn’t have to decrypt it in order to authenticate with the Git server. If you decide to use a passphrase for added security, you can still get around the authentication problem by using the ssh-agent on either macOS or Windows.
Solutions for SSH
If you are using the SSH protocol to install a package by Git URL, you might get an authentication error from Git. This typically happens when you set up a private SSH key on your local machine that is protected by a passphrase.
The solution to this problem is to set up an SSH agent that can unlock your SSH key to authenticate with the Package Manager on your behalf. Follow the instructions in the section that corresponds to your operating system:
- Setting up OpenSSH for Windows
- Adding SSH keys to your SSH Agent for macOS
Setting up OpenSSH for Windows
The native Windows OpenSSH version of the ssh-agent works better than the version available by default with Git for Windows. This procedure explains how to set up the OpenSSH client and add your key to its ssh-agent. If you are using Git for Windows, you can also prioritize the native Windows OpenSSH over the Git for Windows SSH agent:
-
Make sure the OpenSSH Client is installed by searching for it in the Windows Settings Optional features window (Start > Settings, then search for “Optional features”). This applies to Windows 10+.
-
Check your
%PATH%environment variable to make sure the native Windows OpenSSH location appears (for example,C:WINDOWSSystem32OpenSSH).Note: If you are already using Git for Windows, make sure the native Windows OpenSSH location appears before the Git for Windows SSH location in your
%PATH%variable. This ensures that Windows uses the native Windows OpenSSH agent over the Git for Windows SSH agent. -
In a PowerShell terminal, start the
ssh-agentprocess and make sure it starts automatically:# Set the ssh-agent service to start automatically and manually start it now Get-Service ssh-agent | Set-Service -StartupType Automatic # Run the ssh-agent process to start the ssh-agent service ssh-agent -
Import your key into the ssh-agent by running
ssh-addon the command line and then following the instructions. By default, the agent adds the%USERPROFILE%.sshid_rsakey and prompts you for the password.# Import the key ssh-addTo use a different key, you can specify it as an argument:
# Set the ssh-agent service to start automatically and manually start it now ssh-add <your-secure-ssh-key-name>If you can’t remember the name of your key, you can ask the agent to list them:
ssh-add -l -
If you installed Git for Windows, reset the
%GIT-SSH%environment variable to make sure that Git always uses the native Windows OpenSSH version of the ssh-agent:[Environment]::SetEnvironmentVariable("GIT_SSH", "$((Get-Command ssh).Source)", [System.EnvironmentVariableTarget]::User)
Adding SSH keys to your SSH Agent for macOS
Use the ssh-add command to add your SSH keys to the ssh-agent running on your macOS system. The command parameter you use depends on your version of macOS:
-
Prior to macOS 12, use:
ssh-add -K ~/.ssh/<your-secure-ssh-key-name> -
Starting with macOS 12, use:
ssh-add --apple-use-keychain ~/.ssh/<your-secure-ssh-key-name>
After you run this command, the terminal asks for the password to unlock your SSH key and then adds it to the macOS keychain. However, once you restart your system, every key stored in the ssh-agent is reset.
To prevent re-entering your password after restarting your system, open the ~/.ssh/config file (or create one if you don’t find it), and add the following:
Host *
UseKeychain yes
AddKeysToAgent yes
IdentityFile ~/.ssh/<your-secure-ssh-key-name>
Restart your machine to apply these changes.
Can’t update Git version
If you are trying to update your Git dependencyThe Package Manager retrieves Git dependencies from a Git repository directly rather than from a package registry. Git dependencies use a Git URL reference instead of a version, and there’s no guarantee about the package quality, stability, validity, or even whether the version stated in its package.json file respects Semantic Versioning rules with regards to officially published releases of this package. More info
See in Glossary to a newer version from the repository, but it’s not working, it’s probably because your Git dependency is locked. If you want to update your Git dependency to a newer version from the repository, use the Add package from git URL button and enter a Git URL. For more information, see Locked Git dependencies.
‘Failed to parse Http response’ in My Assets context
If you see the following message in the Console window when trying to download an Asset Store package, there might be a problem with your Asset Store cache:
[PackageManager] Error Failed to parse response. UnityEditor.AsyncHTTPClientone(State, Int32)
To solve this problem, delete all downloaded assets from the Asset Store package directory and then try downloading the assets again.
Warning: If your project contains a lot of asset data, this might take a lot of time and bandwidth to re-download everything.
Missing ‘My Registries’ in the Package Manager window
Not all registry providers are compatible with Unity’s Package Manager. If the package registry server you added does not implement the /-/v1/search or /-/all endpoints, your scoped registry is not compatible with Unity’s Package Manager, and doesn’t appear in the My Registries context in the Package Manager window.
Missing MonoBehaviour errors
While building, if there are a lot of errors about Missing Behavior, the UnityLinker might be mistakenly stripping out a component that it thinks is unreferenced. It often does this because the stripping level is too aggressive. For example, if you have a prefabAn asset type that allows you to store a GameObject complete with components and properties. The prefab acts as a template from which you can create new object instances in the scene. More info
See in Glossary in an AssetBundle that references the SpriteShape component in the 2D SpriteShape package, the object might be missing and might generate compiler warnings.
To fix this, you can either lower the stripping level for the UnityLinker or declare the package’s assemblies inside the link.xml file in order to preserve them from being stripped:
<linker>
<assembly fullname="Unity.2D.SpriteShape.Runtime" preserve="all"/>
<assembly fullname="Unity.2D.Common.Runtime" preserve="all"/>
</linker>
For more information on stripping levels and the UnityLinker, see Managed code stripping.
Loading error for hostfxr.dll on Windows
If the Console reports that the hostfxr.dll library was found, but Unity failed to load it from C:<path_to_app>hostfxr.dll, you can fix this error on Windows 7 or Windows Server 2008 R2 by installing both KB2999226 and KB2533623 patches.
Local folder or tarball paths
Local folder or tarball paths
This section provides information on the following issues:
| Type of error: | Error message: |
|---|---|
| General startup issues | — Error messages in the Package Manager window — Package Manager missing or window doesn’t open — Problems after upgrading Unity to new version |
| Package installation issues | — Package installation fails — Unable to add package from Git URL — Insufficient drive space |
| Package signature issues | — Package version has no signature — Package version doesn’t have a valid signature |
| Problems installing git dependencies | — No ‘git’ executable was found — git-lfs: command not found — Repository not found — Could not read Username: terminal prompts disabled — Can’t update Git version |
| Asset StoreA growing library of free and commercial assets created by Unity and members of the community. Offers a wide variety of assets, from textures, models and animations to whole project examples, tutorials and Editor extensions. More info See in Glossary packages (My Assets) |
— ‘Failed to parse Http response’ in My Assets context |
| Scoped registries | — Missing ‘My Registries’ in the Package Manager window |
| Issues when building packages | — Missing MonoBehaviour errors |
You can also run the Unity Package Manager Diagnostics tool if you are experiencing problems that might be network-related. For more information, see Diagnose network issues.
Error messages in the Package Manager window
The Package Manager displays error indicators in the Package Manager window when it encounters problems.
System-wide issues
-
Network connection issues
Error messages appear in the status bar when the Package Manager has detected an issue that isn’t related to a specific package. For example, if the Package Manager can’t access the package registry server, it displays this message in the status bar:

Network error message -
Error refreshing assets (or Error refreshing packages)
If your network can’t reach the package registry server, it’s probably because there is a connection problem with the network. When you or your system administrator diagnose and fix the network error, the status bar clears.
If your network connection is working, but you aren’t signed into your Unity account, the Package Manager doesn’t display any Asset Store packages. When you try to use the My Assets context, the Package Manager displays an error in the status bar:

Logged out of Unity account Click the Sign in button inside the list view to sign into your Unity account through the Unity Hub.
Package-specific issues
-
If a specific package has a problem when loading or installing (for example, when determining which package versions to load), the error icon (
 ) appears in the package list next to the compromised package (A). To find out what the problem is, open the compromised package’s details view to see the detailed error message (B):
) appears in the package list next to the compromised package (A). To find out what the problem is, open the compromised package’s details view to see the detailed error message (B):
Dependency error message
Package Manager missing or window doesn’t open
The Package Manager window might get moved offscreen or hidden by another window. When this happens, it looks like the Package Manager window failed to open. In this case, you can try to reset the window layout (Window > Layouts > Default) and reopen the Package Manager window again.
If the Package Manager window still doesn’t appear, check your Unity Console windowA Unity Editor window that shows errors, warnings and other messages generated by Unity, or your own scripts. More info
See in Glossary:
Failed to resolve packages: The file [<project-path>/Packages/manifest.json] is not valid JSON:
Unexpected token '}' at 44:1
}
This error message indicates that your manifest.json file is malformed. It also tells you the line number where the Package Manager failed to parse the file, so you can fix the JSON. There are a number of online validators that you can use to try to correct the problem. Once you save the corrected file, Unity reloads the Package Manager window.
If you upgraded from an early version of the Unity Editor, there may be other problems with your package manifestEach package has a manifest, which provides information about the package to the Package Manager. The manifest contains information such as the name of the package, its version, a description for users, dependencies on other packages (if any), and other details. More info
See in Glossary file:
-
As of 2019.3, your
manifest.jsonfile should not contain any references to the com.unity.package-manager-ui package. Remove the following line from the manifest’s dependencies list:"com.unity.package-manager-ui": "2.1.1", -
Check to see if your project manifestEach Unity project has a project manifest, which acts as an entry point for the Package Manager. This file must be available in the
<project>/Packagesdirectory. The Package Manager uses it to configure many things, including a list of dependencies for that project, as well as any package repository to query for packages. More info
See in Glossary uses “exclude” as a package version. This is an obsolete value for the dependencies property. If you find any lines like these, remove the entire line. Package Manager only installs packages that are explicitly included as a dependency in your project, so once you remove that entry, Package Manager ignores the package and doesn’t install it.
Problems after upgrading Unity to new version
When you upgrade a project to a newer Unity version, the Package Manager automatically updates incompatible packages to newer compatible versions. However, if your package doesn’t compile, the Package Manager displays error messages in the Console.
To correct these messages, read the error messages and fix any problems you can. For example, a package might be missing a dependency on another package or version. In that case, you can try and install the package yourself.
You can also try the following sequence of solutions until you find something that works:
- Back up and then delete the
Packagesfolder under your project. - Back up and then delete the package sources in your project’s
Packagesfolder, leaving only themanifest.jsonfile. Then try to reload the project. - Create a new empty project. If the Package Manager window loads successfully, replace the
Library/PackageCache/com.unity.package-manager-ui@<version>folder in the failing project with the same folder from the newly created project.
Package installation fails
If you are trying to install a new package from the registry and it is not working, it might be due to permission problems.
You must have full permissions on the cache folder:
- Windows:
C:UsersyournameAppDataLocalUnitycache - macOS:
~/Library/Unity/cache - Linux:
~/.config/unity3d/cache
It might be a problem with the network. Check your firewall and proxy settings.
Sometimes institutional environments, such as schools, government offices, or network-protected workplaces set up proxy servers to control traffic between the network and the Internet, and use their own server certificates which are not recognized by Unity or the Package Manager. Talk to your network administrator.
Unable to add package from Git URL
See Repository not found.
Insufficient drive space
If your installation drive is out of space or low on space, consider changing the location of the package caches:
- To change the global cache, see Customize the global cache location.
- To change the Asset Store cache, see Customize the Asset Store cache location.
Package version has no signature
This message can appear when you fetch a Unity package from a scoped registry. Unity signs packages that it creates, except for older packages, which aren’t necessarily re-signed in later releases. If you copy an unsigned Unity package from a scoped registry to another registry, Package Manager can’t determine if the package content is safe and identical to the original package.
If you encounter this message, try these solutions:
- Use another version of the package.
- Fetch the Unity package from the Unity Registry.
- If you own the scoped registry, make sure you copy the newest version of the package from the Unity Registry.
Package version doesn’t have a valid signature
Packages have a signature to ensure that the content wasn’t changed before or during transit. An invalid signature typically occurs in the following situations:
- Someone published the package with modifications on their own registry.
- An error occurred while transferring the file to the end user.
In both cases, Package Manager considers the package to be potentially malicious.
When you encounter an invalid signature, you can try to install a different version of the package. You should also avoid using Unity packages from a registry other than the Unity Registry.
If you are sharing a Unity package that contains a fix, consider using a Git URL or embedding the package in your project.
No ‘git’ executable was found
If you try to install a package from a git URL, a message similar to this appears:
Cannot perform upm operation: Unable to add package
[https://github.example.com/myuser/myrepository.git]:
No 'git' executable was found. Please install Git on your system and restart Unity [NotFound]
UnityEditor.EditorApplication:Internal_CallUpdateFunctions()
git-lfs: command not found
If you are trying to download a package that uses Git LFS (Large File Storage), you might see this error message:
Error when executing git command. git-lfs filter-process: command not found.
This indicates that Git LFS is probably not installed on your machine. To make sure, you could test it on the command line:
git lfs --version
If you see something like this, Git LFS is installed:
git-lfs/2.8.0 (GitHub; darwin amd64; go 1.12.7)
Otherwise, you can install it by following the Bitbucket GitHub instructions.
Repository not found
If you specify a location that does not exist, a message similar to this one appears in the Unity Console:
Cannot perform upm operation: Unable to add package [https://mycompany.github.com/gitproject/com.mycompany.mypackage.git]:
Error when executing git command. fatal: repository 'https://mycompany.github.com/gitproject/com.mycompany.mypackage.git/' not found
[NotFound]
UnityEditor.EditorApplication:Internal_CallUpdateFunctions() (at /Users/builduser/buildslave/unity/build/Editor/Mono/EditorApplication.cs:310)
Check your spelling. To make sure you are using the correct URL, go to the repository’s page and copy the URL from the Clone button:

Click the button to the right of the URL on GitHub (A) or GitLab (B) to copy the URL to your clipboard.
If the location of the repository is correct, there may be another problem with the URL:
- If you are targeting a specific revision, make sure your revision comes last. For example:
https://github.example.com/myuser/myrepository1.git#revision - If you are targeting a revision and the package is not at the root, make sure the
pathquery parameter precedes the revision anchor. For example:https://github.example.com/myuser/myrepository.git?path=/example/folder#v1.2.3
Could not read Username: terminal prompts disabled
If you are trying to install a package from a private repository that requires authentication, a message similar to this one appears in the Unity Console:
Cannot perform upm operation: Unable to add package [https://mycompany.github.com/gitproject/com.mycompany.mypackage.git]:
Error when executing git command. fatal: could not read Username for 'https://mycompany.github.com': terminal prompts disabled
[NotFound]
UnityEditor.EditorApplication:Internal_CallUpdateFunctions() (at /Users/builduser/buildslave/unity/build/Editor/Mono/EditorApplication.cs:310)
This message is likely due to the fact that Package Manager does not provide an interactive terminal or dialog where you can enter your username and password for HTTP, or your passphrase to unlock your SSH key:
-
With HTTP(S), every time you log onto BitBucket, GitHub or GitLab you need to enter your username and password in a terminal or a dialog box. However, the Package Manager does not provide an interactive terminal or dialog where you can enter your username and password for HTTP(S).
To bypass this, use one of the workarounds suggested in Solutions for HTTPS.
-
SSH uses a pair of public and private SSH keys. You can add your public SSH key to Bitbucket, GitHub or GitLab and then access repositories without having to enter a username and password.
However, if you have set up a passphrase to keep your SSH key safe, you still have to enter that passphrase in a terminal or a dialog box in order to authorize your key. In that case, you can use an SSH agent that can unlock your SSH key to authenticate with the Package Manager on your behalf.
Solutions for HTTPS
The Package Manager does not provide an interactive terminal or dialog where you can enter your HTTP(S) username and password. To bypass this, use one of these workarounds:
- Use a credential manager (Git Credential Manager for Windows or OSXKeyChain). Credential managers handle sending the password without having to use a terminal or a command prompt.
- Use git-credentials from a terminal or command prompt, then launch the Hub from the same terminal so that Unity has access to the cached or stored credentials.
- Use SSH to authenticate instead. If you set up your SSH key without a passphrase, the Package Manager doesn’t have to decrypt it to authenticate with the Git server. If you decide to use a passphrase for added security, you can use the ssh-agent on either macOS or Windows to get around the authentication problem.
Solutions for SSH
If you use the SSH protocol to install a package by Git URL, you might get an authentication error from Git. This typically happens when you set up a private SSH key on your local machine that is protected by a passphrase.
The solution to this problem is to set up an SSH agent that can unlock your SSH key to authenticate with the Package Manager on your behalf. Follow the instructions in the section that corresponds to your operating system:
- Setting up OpenSSH for Windows
- Adding SSH keys to your SSH Agent for macOS
Setting up OpenSSH for Windows
The native Windows OpenSSH version of the ssh-agent works better than the version available by default with Git for Windows. This procedure explains how to set up the OpenSSH client and add your key to its ssh-agent. If you are using Git for Windows, you can also prioritize the native Windows OpenSSH over the Git for Windows SSH agent:
-
Make sure the OpenSSH Client is installed. To do this, search for it in the Windows Settings Optional features window (Start > Settings, then search for “Optional features”). This applies to Windows 10+.
-
Check your
%PATH%environment variable to make sure the native Windows OpenSSH location appears (for example,C:WINDOWSSystem32OpenSSH).Note: If you are already using Git for Windows, make sure the native Windows OpenSSH location appears before the Git for Windows SSH location in your
%PATH%variable. This ensures that Windows uses the native Windows OpenSSH agent over the Git for Windows SSH agent. -
In a PowerShell terminal, start the
ssh-agentprocess and make sure it starts automatically:# Set the ssh-agent service to start automatically and manually start it now Get-Service ssh-agent | Set-Service -StartupType Automatic # Run the ssh-agent process to start the ssh-agent service ssh-agent -
Import your key into the ssh-agent. To do this, run
ssh-addon the command line and then follow the instructions. By default, the agent adds the%USERPROFILE%.sshid_rsakey and prompts you for the password.# Import the key ssh-addTo use a different key, you can specify it as an argument:
# Set the ssh-agent service to start automatically and manually start it now ssh-add <your-secure-ssh-key-name>If you can’t remember the name of your key, you can ask the agent to list them:
ssh-add -l -
If you installed Git for Windows, reset the
%GIT-SSH%environment variable to make sure that Git always uses the native Windows OpenSSH version of the ssh-agent:[Environment]::SetEnvironmentVariable("GIT_SSH", "$((Get-Command ssh).Source)", [System.EnvironmentVariableTarget]::User)
Adding SSH keys to your SSH Agent for macOS
Use the ssh-add command to add your SSH keys to the ssh-agent running on your macOS system. The command parameter you use depends on your version of macOS:
-
Prior to macOS 12, use:
ssh-add -K ~/.ssh/<your-secure-ssh-key-name> -
Starting with macOS 12, use:
ssh-add --apple-use-keychain ~/.ssh/<your-secure-ssh-key-name>
After you run this command, the terminal asks for the password to unlock your SSH key and then adds it to the macOS keychain. However, once you restart your system, every key stored in the ssh-agent is reset.
To make sure you don’t need to re-enter your password after you restart your system, open the ~/.ssh/config file (or create one if you don’t find it), and add the following:
Host *
UseKeychain yes
AddKeysToAgent yes
IdentityFile ~/.ssh/<your-secure-ssh-key-name>
Restart your machine to apply these changes.
Can’t update Git version
If you are trying to update your Git dependencyThe Package Manager retrieves Git dependencies from a Git repository directly rather than from a package registry. Git dependencies use a Git URL reference instead of a version, and there’s no guarantee about the package quality, stability, validity, or even whether the version stated in its package.json file respects Semantic Versioning rules with regards to officially published releases of this package. More info
See in Glossary to a newer version from the repository, but it’s not working, it’s probably because your Git dependency is locked. If you want to update your Git dependency to a newer version from the repository, use the Add package from git URL button and enter a Git URL. For more information, see Locked Git dependencies.
‘Failed to parse Http response’ in My Assets context
If you see the following message in the Console window when you try to download an Asset Store package, there might be a problem with your Asset Store cache:
[PackageManager] Error Failed to parse response. UnityEditor.AsyncHTTPClientone(State, Int32)
To solve this problem, delete all downloaded assets from the Asset Store package directory and then try to download the assets again.
Warning: If your project contains a lot of asset data, it might take a lot of time and bandwidth to re-download everything.
Missing ‘My Registries’ in the Package Manager window
Not all registry providers are compatible with Unity’s Package Manager. If the package registry server you added does not implement the /-/v1/search or /-/all endpoints, your scoped registry is not compatible with Unity’s Package Manager, and doesn’t appear in the My Registries context in the Package Manager window.
Missing MonoBehaviour errors
While building, if there are a lot of errors about Missing Behavior, the UnityLinker might be mistakenly stripping out a component that it thinks is unreferenced. It often does this because the stripping level is too aggressive. For example, if you have a prefabAn asset type that allows you to store a GameObject complete with components and properties. The prefab acts as a template from which you can create new object instances in the scene. More info
See in Glossary in an AssetBundle that references the SpriteShape component in the 2D SpriteShape package, the object might be missing and might generate compiler warnings.
To fix this, you can either lower the stripping level for the UnityLinker or declare the package’s assemblies inside the link.xml file in order to preserve them from being stripped:
<linker>
<assembly fullname="Unity.2D.SpriteShape.Runtime" preserve="all"/>
<assembly fullname="Unity.2D.Common.Runtime" preserve="all"/>
</linker>
For more information on stripping levels and the UnityLinker, see Managed code stripping.
Local folder or tarball paths
Local folder or tarball paths
This section provides information on the following issues:
| Type of error: | Error message: |
|---|---|
| General startup issues | — Error messages in the Package Manager window — Package Manager missing or window doesn’t open — Problems after upgrading Unity to new version — Resetting your project’s package configuration |
| Package installation issues | — Package installation fails — Packages not recognized — Unable to add package from Git URL — Insufficient drive space |
| Package signature issues | — Package version has no signature — Package version doesn’t have a valid signature |
| Problems installing git dependencies | — No ‘git’ executable was found — git-lfs: command not found — Repository not found — Could not read Username: terminal prompts disabled — Can’t update Git version |
| Asset StoreA growing library of free and commercial assets created by Unity and members of the community. Offers a wide variety of assets, from textures, models and animations to whole project examples, tutorials and Editor extensions. More info See in Glossary packages (My Assets) |
— ‘Failed to parse Http response’ in My Assets context |
| Scoped registries | — Missing ‘My Registries’ in the Package Manager window |
| Issues when building packages | — Missing MonoBehaviour errors — Loading error for hostfxr.dll on Windows |
You can also run the Unity Package Manager Diagnostics tool if you are experiencing problems that might be network-related. For more information, see Diagnose network issues.
Error messages in the Package Manager window
The Package Manager displays error indicators in the Package Manager window when it encounters problems.
System-wide issues
-
Network connection issues
Error messages appear in the status bar when the Package Manager has detected an issue that isn’t related to a specific package. For example, if the Package Manager can’t access the package registry server, it displays this message in the status bar:

Network error message -
Error refreshing assets (or Error refreshing packages)
If your network can’t reach the package registry server, it’s probably because there is a connection problem with the network. When you or your system administrator diagnose and fix the network error, the status bar clears.
If your network connection is working, but you aren’t signed into your Unity account, the Package Manager doesn’t display any Asset Store packages. When you try to use the My Assets context, the Package Manager displays an error in the status bar:

Logged out of Unity account Click the Sign in button inside the list view to sign into your Unity account through the Unity Hub.
Package-specific issues
-
If a specific package has a problem when loading or installing (for example, when determining which package versions to load), the error icon (
 ) appears in the package list next to the compromised package (A). To find out what the problem is, open the compromised package’s details view to see the detailed error message (B):
) appears in the package list next to the compromised package (A). To find out what the problem is, open the compromised package’s details view to see the detailed error message (B):
Dependency error message
Package Manager missing or window doesn’t open
The Package Manager window might get moved offscreen or hidden by another window. When this happens, it looks like the Package Manager window failed to open. In this case, you can try to reset the window layout (Window > Layouts > Default) and reopen the Package Manager window again.
If the Package Manager window still doesn’t appear, check your Unity Console windowA Unity Editor window that shows errors, warnings and other messages generated by Unity, or your own scripts. More info
See in Glossary:
Failed to resolve packages: The file [<project-path>/Packages/manifest.json] is not valid JSON:
Unexpected token '}' at 44:1
}
This error message indicates that your manifest.json file is malformed. It also tells you the line number where the Package Manager failed to parse the file, so you can fix the JSON. There are a number of online validators that you can use to try to correct the problem. Once you save the corrected file, Unity reloads the Package Manager window.
If you upgraded from an early version of the Unity Editor, there may be other problems with your package manifestEach package has a manifest, which provides information about the package to the Package Manager. The manifest contains information such as the name of the package, its version, a description for users, dependencies on other packages (if any), and other details. More info
See in Glossary file:
-
As of 2019.3, your
manifest.jsonfile should not contain any references to the com.unity.package-manager-ui package. You can either reset your project’s package configuration or remove the following line from the manifest’s dependencies list:"com.unity.package-manager-ui": "2.1.1", -
Check to see if your project manifestEach Unity project has a project manifest, which acts as an entry point for the Package Manager. This file must be available in the
<project>/Packagesdirectory. The Package Manager uses it to configure many things, including a list of dependencies for that project, as well as any package repository to query for packages. More info
See in Glossary uses “exclude” as a package version. This is an obsolete value for the dependencies property. If you find any lines like these, remove the entire line. Package Manager only installs packages that are explicitly included as a dependency in your project, so once you remove that entry, Package Manager ignores the package and doesn’t install it.
If the Package Manager still fails to load, follow the procedures under Packages not recognized and Resetting your project’s package configuration.
Problems after upgrading Unity to new version
When you upgrade a project to a newer Unity version, the Package Manager automatically updates incompatible packages to newer compatible versions. However, if your package doesn’t compile, the Package Manager displays error messages in the Console.
To correct these messages, read the error messages and fix any problems you can. For example, a package might be missing a dependency on another package or version. In that case, you can try and install the package yourself.
You can also try the following sequence of solutions until you find something that works:
- Back up and then delete the
Packagesfolder under your project. - Back up and then delete the package sources in your project’s
Packagesfolder, leaving only themanifest.jsonfile. Then try to reload the project. - Create a new empty project. If the Package Manager window loads successfully, replace the
Library/PackageCache/com.unity.package-manager-ui@<version>folder in the failing project with the same folder from the newly created project. - As a last resort, you can reset your project to the default packageUnity automatically pre-installs a select number of default packages (for example, the Analytics Library, Unity Timeline, etc.) when you create a new project. This differs from a bundled package because you don’t need to install it and it differs from a built-in package because it extends Unity’s features rather than being able to enable or disable them.
See in Glossary configuration and add back packages one at a time until it works.
Resetting your project’s package configuration
If a project has too many package issues, you can reset your project back to the default package configuration for the Editor’s version of Unity. This operation resets all packages in your project. This might not fix the source of the problem, but it can help you figure out what the problem is.
Note: You can’t undo resetting your package configuration, so make sure you back up the manifest.json file first or make sure your project is under source control. You can also take extra precautions by cloning your project and testing out the operation on the clone before proceeding.
To return to the default package configuration, select Reset Packages to defaults from the Help menu.

Resetting a clone of your project
You can also test the return to the default packages before you perform the final change:
-
Clone your project by copy-pasting your project folder and renaming it so that it is easy to find (for example, if your project is called
MyProjectthen you could use something likeclone_MyProject). -
Load your newly cloned project.
-
From the Help menu, select Reset Packages to defaults.
Depending on the size of your project, this might take a few minutes.
-
Check that it successfully reset the packages. If so, you can perform the operation safely on the original project.
Package installation fails
If you are trying to install a new package from the registry and it is not working, it might be due to permission problems.
You must have full permissions on the cache folder:
- Windows:
C:UsersyournameAppDataLocalUnitycache - macOS:
~/Library/Unity/cache - Linux:
~/.config/unity3d/cache
It might be a problem with the network. Check your firewall and proxy settings.
Sometimes institutional environments, such as schools, government offices, or network-protected workplaces set up proxy servers to control traffic between the network and the Internet, and use their own server certificates which are not recognized by Unity or the Package Manager. Talk to your network administrator.
Packages not recognized
If you see a lot of compilation errors, this might indicate that Unity is not recognizing the packages in your existing project. In this case, you might be missing a .NET component.
For Windows:
- Download and install Visual Studio 2017 version 15.9.0 or higher with the .NET Core cross-platform development workload selected under Other Toolsets.
- Download and install the .NET SDK v2.2.101 component.
For MacOS:
-
Download and install the .NET SDK v2.2.101 component.
-
Install any recommended updates in Visual Studio
-
Use homebrew to brew and install mono:
brew update brew install mono # optional brew upgrade mono -
If necessary, delete the
Library/obj/tempfolder under your project and restart Unity. -
If you are still experiencing difficulties, try rebooting your computer as well.
Unable to add package from Git URL
See Repository not found.
Insufficient drive space
If your installation drive is out of space or low on space, consider changing the location of the package caches:
- To change the global cache, see Customize the global cache location.
- To change the Asset Store cache, see Customize the Asset Store cache location.
Package version has no signature
This message can appear when you fetch a Unity package from a scoped registry. Unity signs packages that it creates, except for older packages, which aren’t necessarily re-signed in later releases. If you copy an unsigned Unity package from a scoped registry to another registry, Package Manager can’t determine if the package content is safe and identical to the original package.
If you encounter this message, try these solutions:
- Use another version of the package.
- Fetch the Unity package from the Unity Registry.
- If you own the scoped registry, make sure you copy the newest version of the package from the Unity Registry.
Package version doesn’t have a valid signature
Packages have a signature to ensure that the content wasn’t changed before or during transit. An invalid signature typically occurs in the following situations:
- Someone published the package with modifications on their own registry.
- An error occurred while transferring the file to the end user.
In both cases, Package Manager considers the package to be potentially malicious.
When you encounter an invalid signature, you can try to install a different version of the package. You should also avoid using Unity packages from a registry other than the Unity Registry.
If you are sharing a Unity package that contains a fix, consider using a Git URL or embedding the package in your project.
No ‘git’ executable was found
If you try to install a package from a git URL, a message similar to this appears:
Cannot perform upm operation: Unable to add package
[https://github.example.com/myuser/myrepository.git]:
No 'git' executable was found. Please install Git on your system and restart Unity [NotFound]
UnityEditor.EditorApplication:Internal_CallUpdateFunctions()
git-lfs: command not found
If you are trying to download a package that uses Git LFS (Large File Storage), you might see this error message:
Error when executing git command. git-lfs filter-process: command not found.
This indicates that Git LFS is probably not installed on your machine. To make sure, you could test it on the command line:
git lfs --version
If you see something like this, Git LFS is installed:
git-lfs/2.8.0 (GitHub; darwin amd64; go 1.12.7)
Otherwise, you can install it by following the Bitbucket GitHub instructions.
Repository not found
If you specify a location that does not exist, a message similar to this one appears in the Unity Console:
Cannot perform upm operation: Unable to add package [https://mycompany.github.com/gitproject/com.mycompany.mypackage.git]:
Error when executing git command. fatal: repository 'https://mycompany.github.com/gitproject/com.mycompany.mypackage.git/' not found
[NotFound]
UnityEditor.EditorApplication:Internal_CallUpdateFunctions() (at /Users/builduser/buildslave/unity/build/Editor/Mono/EditorApplication.cs:310)
Check your spelling. To make sure you are using the correct URL, go to the repository’s page and copy the URL from the Clone button:

Click the button to the right of the URL on GitHub (A) or GitLab (B) to copy the URL to your clipboard.
If the location of the repository is correct, there may be another problem with the URL:
- If you are targeting a specific revision, make sure your revision comes last. For example:
https://github.example.com/myuser/myrepository1.git#revision - If you are targeting a revision and the package is not at the root, make sure the
pathquery parameter precedes the revision anchor. For example:https://github.example.com/myuser/myrepository.git?path=/example/folder#v1.2.3
Could not read Username: terminal prompts disabled
If you are trying to install a package from a private repository that requires authentication, a message similar to this one appears in the Unity Console:
Cannot perform upm operation: Unable to add package [https://mycompany.github.com/gitproject/com.mycompany.mypackage.git]:
Error when executing git command. fatal: could not read Username for 'https://mycompany.github.com': terminal prompts disabled
[NotFound]
UnityEditor.EditorApplication:Internal_CallUpdateFunctions() (at /Users/builduser/buildslave/unity/build/Editor/Mono/EditorApplication.cs:310)
This message is likely due to the fact that Package Manager does not provide an interactive terminal or dialog where you can enter your username and password for HTTP, or your passphrase to unlock your SSH key:
-
With HTTP(S), every time you log onto BitBucket, GitHub or GitLab you need to enter your username and password in a terminal or a dialog box. However, the Package Manager does not provide an interactive terminal or dialog where you can enter your username and password for HTTP(S).
To bypass this, use one of the workarounds suggested in Solutions for HTTPS.
-
SSH uses a pair of public and private SSH keys. You can add your public SSH key to Bitbucket, GitHub or GitLab and then access repositories without having to enter a username and password.
However, if you have set up a passphrase to keep your SSH key safe, you still have to enter that passphrase in a terminal or a dialog box in order to authorize your key. In that case, you can use an SSH agent that can unlock your SSH key to authenticate with the Package Manager on your behalf.
Solutions for HTTPS
The Package Manager does not provide an interactive terminal or dialog where you can enter your HTTP(S) username and password. To bypass this, use one of these workarounds:
- Use a credential manager (Git Credential Manager for Windows or OSXKeyChain). Credential managers handle sending the password without having to use a terminal or a command prompt.
- Use git-credentials from a terminal or command prompt, then launch the Hub from the same terminal so that Unity has access to the cached or stored credentials.
- Use SSH to authenticate instead. If you set up your SSH key without a passphrase, the Package Manager doesn’t have to decrypt it to authenticate with the Git server. If you decide to use a passphrase for added security, you can use the ssh-agent on either macOS or Windows to get around the authentication problem.
Solutions for SSH
If you use the SSH protocol to install a package by Git URL, you might get an authentication error from Git. This typically happens when you set up a private SSH key on your local machine that is protected by a passphrase.
The solution to this problem is to set up an SSH agent that can unlock your SSH key to authenticate with the Package Manager on your behalf. Follow the instructions in the section that corresponds to your operating system:
- Setting up OpenSSH for Windows
- Adding SSH keys to your SSH Agent for macOS
Setting up OpenSSH for Windows
The native Windows OpenSSH version of the ssh-agent works better than the version available by default with Git for Windows. This procedure explains how to set up the OpenSSH client and add your key to its ssh-agent. If you are using Git for Windows, you can also prioritize the native Windows OpenSSH over the Git for Windows SSH agent:
-
Make sure the OpenSSH Client is installed. To do this, search for it in the Windows Settings Optional features window (Start > Settings, then search for “Optional features”). This applies to Windows 10+.
-
Check your
%PATH%environment variable to make sure the native Windows OpenSSH location appears (for example,C:WINDOWSSystem32OpenSSH).Note: If you are already using Git for Windows, make sure the native Windows OpenSSH location appears before the Git for Windows SSH location in your
%PATH%variable. This ensures that Windows uses the native Windows OpenSSH agent over the Git for Windows SSH agent. -
In a PowerShell terminal, start the
ssh-agentprocess and make sure it starts automatically:# Set the ssh-agent service to start automatically and manually start it now Get-Service ssh-agent | Set-Service -StartupType Automatic # Run the ssh-agent process to start the ssh-agent service ssh-agent -
Import your key into the ssh-agent. To do this, run
ssh-addon the command line and then follow the instructions. By default, the agent adds the%USERPROFILE%.sshid_rsakey and prompts you for the password.# Import the key ssh-addTo use a different key, you can specify it as an argument:
# Set the ssh-agent service to start automatically and manually start it now ssh-add <your-secure-ssh-key-name>If you can’t remember the name of your key, you can ask the agent to list them:
ssh-add -l -
If you installed Git for Windows, reset the
%GIT-SSH%environment variable to make sure that Git always uses the native Windows OpenSSH version of the ssh-agent:[Environment]::SetEnvironmentVariable("GIT_SSH", "$((Get-Command ssh).Source)", [System.EnvironmentVariableTarget]::User)
Adding SSH keys to your SSH Agent for macOS
Use the ssh-add command to add your SSH keys to the ssh-agent running on your macOS system. The command parameter you use depends on your version of macOS:
-
Prior to macOS 12, use:
ssh-add -K ~/.ssh/<your-secure-ssh-key-name> -
Starting with macOS 12, use:
ssh-add --apple-use-keychain ~/.ssh/<your-secure-ssh-key-name>
After you run this command, the terminal asks for the password to unlock your SSH key and then adds it to the macOS keychain. However, once you restart your system, every key stored in the ssh-agent is reset.
To make sure you don’t need to re-enter your password after you restart your system, open the ~/.ssh/config file (or create one if you don’t find it), and add the following:
Host *
UseKeychain yes
AddKeysToAgent yes
IdentityFile ~/.ssh/<your-secure-ssh-key-name>
Restart your machine to apply these changes.
Can’t update Git version
If you are trying to update your Git dependencyThe Package Manager retrieves Git dependencies from a Git repository directly rather than from a package registry. Git dependencies use a Git URL reference instead of a version, and there’s no guarantee about the package quality, stability, validity, or even whether the version stated in its package.json file respects Semantic Versioning rules with regards to officially published releases of this package. More info
See in Glossary to a newer version from the repository, but it’s not working, it’s probably because your Git dependency is locked. If you want to update your Git dependency to a newer version from the repository, use the Add package from git URL button and enter a Git URL. For more information, see Locked Git dependencies.
‘Failed to parse Http response’ in My Assets context
If you see the following message in the Console window when you try to download an Asset Store package, there might be a problem with your Asset Store cache:
[PackageManager] Error Failed to parse response. UnityEditor.AsyncHTTPClientone(State, Int32)
To solve this problem, delete all downloaded assets from the Asset Store package directory and then try to download the assets again.
Warning: If your project contains a lot of asset data, it might take a lot of time and bandwidth to re-download everything.
Missing ‘My Registries’ in the Package Manager window
Not all registry providers are compatible with Unity’s Package Manager. If the package registry server you added does not implement the /-/v1/search or /-/all endpoints, your scoped registry is not compatible with Unity’s Package Manager, and doesn’t appear in the My Registries context in the Package Manager window.
Missing MonoBehaviour errors
While building, if there are a lot of errors about Missing Behavior, the UnityLinker might be mistakenly stripping out a component that it thinks is unreferenced. It often does this because the stripping level is too aggressive. For example, if you have a prefabAn asset type that allows you to store a GameObject complete with components and properties. The prefab acts as a template from which you can create new object instances in the scene. More info
See in Glossary in an AssetBundle that references the SpriteShape component in the 2D SpriteShape package, the object might be missing and might generate compiler warnings.
To fix this, you can either lower the stripping level for the UnityLinker or declare the package’s assemblies inside the link.xml file in order to preserve them from being stripped:
<linker>
<assembly fullname="Unity.2D.SpriteShape.Runtime" preserve="all"/>
<assembly fullname="Unity.2D.Common.Runtime" preserve="all"/>
</linker>
For more information on stripping levels and the UnityLinker, see Managed code stripping.
Loading error for hostfxr.dll on Windows
If the Console reports that the hostfxr.dll library was found, but Unity failed to load it from C:<path_to_app>hostfxr.dll, you can fix this error on Windows 7 or Windows Server 2008 R2 by installing both KB2999226 and KB2533623 patches.
Local folder or tarball paths
В этом разделе содержится информация по следующим вопросам:
| Тип ошибки | Сообщение об ошибке: |
|---|---|
| General startup issues | — Error messages in the Package Manager window — Package Manager missing or window doesn’t open — Problems after upgrading Unity to new version — Resetting your project’s package configuration |
| Package installation issues | — Package installation fails — Packages not recognized |
| Problems installing git dependencies | — No ‘git’ executable was found — git-lfs: command not found — Repository not found — Could not read Username: terminal prompts disabled — Can’t update Git version |
|
Asset StoreA growing library of free and commercial assets created by Unity and members of the community. Offers a wide variety of assets, from textures, models and animations to whole project examples, tutorials and Editor extensions. More info See in Словарь packages (My Assets) |
— ‘Failed to parse Http response’ in My Assets context |
| Scoped registries | — Missing ‘My Registries’ in the Package Manager window |
| Issues when building packages | — Missing MonoBehaviour errors — Loading error for hostfxr.dll on Windows |
Вы также можете запустить инструмент Diagnostics диспетчера пакетов Unity, если у вас возникли проблемы, которые могут быть связаны с сетью. Дополнительную информацию см. в разделе Проблемы с сетью.
Error messages in the Package Manager window
Диспетчер пакетов отображает индикаторы ошибок в окне диспетчера пакетов при возникновении проблем:
-
Общесистемные проблемы
Сообщения об ошибках, которые появляются в строке состояния, указывают на то, что диспетчер пакетов обнаружил проблему, не связанную с конкретным пакетом. Например, если диспетчер пакетов не может получить доступ к серверу реестра пакетов, он отображает это сообщение в строке состояния:

Сообщение об ошибке сети Если ваша сеть не может подключиться к серверу реестра пакетов, возможно, это связано с проблемой подключения к сети. Когда вы или ваш системный администратор исправляете сетевую ошибку, строка состояния очищается.
Если ваше сетевое соединение работает, но вы не вошли в свою учетную запись Unity, диспетчер пакетов не не отображать пакеты Asset Store. При попытке использовать контекст My Assets диспетчер пакетов отображает ошибку в строке состояния:

Вышел из учетной записи Unity Нажмите кнопку Sign in в списке, чтобы войти в свою учетную запись Unity через Центр Unity.
-
Проблемы, связанные с пакетом
Если при загрузке или установке определенного пакета возникает проблема (например, при определении версий пакета для загрузки), значок ошибки (
 ) отображается в списке пакетов рядом со скомпрометированным пакетом (A). Чтобы выяснить, в чем проблема, откройте представление сведений о скомпрометированном пакете и просмотрите подробное сообщение об ошибке (B):
) отображается в списке пакетов рядом со скомпрометированным пакетом (A). Чтобы выяснить, в чем проблема, откройте представление сведений о скомпрометированном пакете и просмотрите подробное сообщение об ошибке (B):
Сообщение об ошибке зависимости
Package Manager missing or window doesn’t open
Окно диспетчера пакетов может быть перемещено за пределы экрана или скрыто другим окном. Когда это происходит, похоже, что окно диспетчера пакетов не открылось. В этом случае вы можете попытаться сбросить макет окна (Window > Layouts > Default) и снова открыть окно диспетчера пакетов.
Если окно диспетчера пакетов по-прежнему не отображается, проверьте окно консоли Unityокно редактора Unity, в котором отображаются ошибки, предупреждения и другие сообщения, созданные Unity или вашими собственными сценариями. Подробнее
См. в Словарь:
Failed to resolve packages: The file [/Packages/manifest.json] is not valid JSON:
Unexpected token '}' at 44:1
}
Это сообщение об ошибке указывает на то, что ваш файл manifest.json имеет неверный формат. Он также сообщает вам номер строки, в которой диспетчеру пакетов не удалось проанализировать файл, чтобы вы могли исправить ошибку JSON. Существует ряд онлайн-валидаторов, которые вы можете использовать, чтобы попытаться решить проблему. Как только вы сохраните исправленный файл, Unity перезагрузит окно диспетчера пакетов.
Если вы выполнили обновление с ранней версии редактора Unity, могут возникнуть другие проблемы с вашим манифестом пакетаКаждый пакет имеет манифест, который предоставляет информацию о пакете диспетчеру пакетов. Манифест содержит такую информацию, как имя пакета, его версия, описание для пользователей, зависимости от других пакетов (если есть) и другие подробности. Дополнительная информация
См. в файле Словарь:
-
В версии 2019.3 ваш файл
manifest.jsonне должен содержать никаких ссылок на пакет com.unity.package-manager-ui. Вы можете либо сбросить конфигурацию пакета вашего проекта, либо удалить следующую строку из списка зависимостей манифеста:"com.unity.package-manager-ui": "2.1.1",
-
Проверьте, есть ли в вашем манифесте проектакаждый проект Unity манифест проекта , который действует как точка входа для диспетчера пакетов. Этот файл должен находиться в каталоге
/Packages. Диспетчер пакетов использует его для настройки многих вещей, включая список зависимостей для этого проекта, а также любой репозиторий пакетов для запроса пакетов. Дополнительная информация
См. Словарь функция «exclude» в качестве пакетной версии. Это устаревшее значение для зависимостей
См. в свойстве Словарь. Если вы найдете такие строки, удалите всю строку. Диспетчер пакетов устанавливает только те пакеты, которые явно включены в ваш проект как зависимость, поэтому после удаления этой записи диспетчер пакетов игнорирует пакет и не устанавливает его.
Если диспетчер пакетов по-прежнему не загружается, следуйте инструкциям в разделах Нераспознанные пакеты и Сброс конфигурации пакета вашего проекта.
Problems after upgrading Unity to new version
При обновлении проекта до более новой версии Unity диспетчер пакетов автоматически обновляет несовместимые пакеты до более новых совместимых версий. Однако, если ваш пакет не компилируется, диспетчер пакетов отображает сообщения об ошибках в консоли.
Чтобы исправить эти сообщения, прочтите сообщения об ошибках и устраните все возможные проблемы. Например, в пакете может отсутствовать зависимость от другого пакета или версии. В этом случае вы можете попробовать установить пакет самостоятельно.
Вы также можете попробовать следующую последовательность решений, пока не найдете то, что работает:
- Создайте резервную копию и удалите папку
Packagesв своем проекте. - Создайте резервную копию, а затем удалите исходные коды пакетов в папке
Packagesвашего проекта, оставив только файлmanifest.json. Затем попробуйте перезагрузить проект. - Создайте новый пустой проект. Если окно диспетчера пакетов загружается успешно, замените папку
Library/PackageCache/com.unity.package-manager-ui@в неудачном проекте на ту же папку из только что созданный проект. - В крайнем случае вы можете сбросить свой проект до пакета по умолчаниюUnity автоматически предварительно устанавливает выбранное количество пакетов по умолчанию (например, Analytics Library, Unity Timeline и т. д.) при создании нового проекта. Он отличается от встроенного пакета тем, что его не нужно устанавливать, и отличается от встроенного пакета тем, что расширяет возможности Unity, а не позволяет включать или отключить их.
Просмотрите в конфигурации Словарь и добавляйте обратно пакеты по одному, пока не заработает.
Resetting your project’s package configuration
Если в проекте слишком много проблем с пакетами, вы можете сбросить проект до конфигурации пакетов по умолчанию для редакторской версии Unity. Эта операция сбрасывает все пакеты в вашем проекте. Это может не устранить источник проблемы, но может помочь вам понять, в чем проблема.
Примечание. Вы не можете отменить сброс конфигурации пакета, поэтому сначала создайте резервную копию файла manifest.json или убедитесь, что ваш проект находится под управлением исходного кода. Вы также можете принять дополнительные меры предосторожности, клонировать свой проект и протестировать операцию на клоне, прежде чем продолжить.
Чтобы вернуться к конфигурации пакета по умолчанию, выберите Reset Packages to defaults в меню Help.
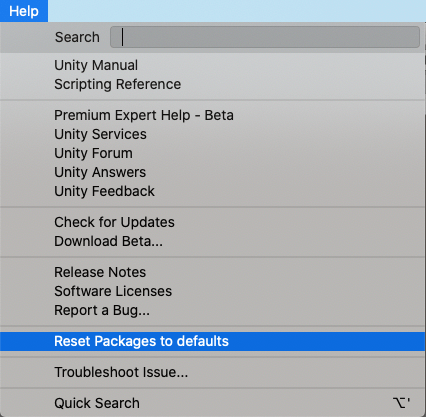
Resetting a clone of your project
Вы также можете протестировать возврат к пакетам по умолчанию, прежде чем вносить окончательные изменения:
-
Клонируйте свой проект, скопировав папку проекта и переименовав ее, чтобы ее было легко найти (например, если ваш проект называется
MyProject, вы можно использовать что-то вродеclone_MyProject). -
Загрузите новый клонированный проект.
-
В меню «Help» выберите Reset Packages to defaults.
В зависимости от размера вашего проекта это может занять несколько минут.
-
Убедитесь, что он успешно сбросил пакеты. Если это так, вы можете безопасно выполнить операцию в исходном проекте.
Package installation fails
Если вы пытаетесь установить новый пакет из реестра, и он не работает, это может быть связано с проблемами с правами доступа.
У вас должны быть полные права доступа к папке кеша:
- Windows:
C:UsersyournameAppDataLocalUnitycache - MacOS:
~/Users/Library/Unity/cache
Это может быть проблема с сетью. Проверьте настройки брандмауэра и прокси-сервера.
Иногда учреждения, такие как школы, государственные учреждения или защищенные сетью рабочие места, настраивают прокси-серверы для управления трафиком между сетью и Интернетом и используют собственные сертификаты сервера, которые не распознаются Unity или диспетчером пакетов. Поговорите со своим сетевым администратором.
Packages not recognized
Если вы видите много ошибок компиляции, это может означать, что Unity не распознает пакеты в вашем существующем проекте. В этом случае вам может не хватать компонента .NET.
Для Windows:
- Загрузите и установите Visual Studio 2017 версии 15.9.0 или выше с рабочей нагрузкой .NET Core cross-platform development workload, выбранной в разделе Other Toolsets.
- Загрузите и установите компонент .NET SDK v2.2.101.
Для MacOS:
-
Загрузите и установите компонент .NET SDK v2.2.101.
-
Установите все рекомендуемые обновления в Visual Studio
-
Используйте homebrew для приготовления и установки mono:
brew update
brew install mono # optional
brew upgrade mono
-
При необходимости удалите папку
Library/obj/tempв своем проекте и перезапустите Unity. -
Если вы по-прежнему испытываете трудности, попробуйте также перезагрузить компьютер.
No ‘git’ executable was found
Если вы попытаетесь установить пакет с URL-адреса git, появится сообщение, похожее на это:
Cannot perform upm operation: Unable to add package
[https://github.example.com/myuser/myrepository.git]:
No 'git' executable was found. Please install Git on your system and restart Unity [NotFound]
UnityEditor.EditorApplication:Internal_CallUpdateFunctions()
git-lfs: command not found
Если вы пытаетесь загрузить пакет, использующий Git LFS (большое файловое хранилище), вы можете увидеть следующее сообщение об ошибке:
Error when executing git command. git-lfs filter-process: command not found.
Это указывает на то, что Git LFS, вероятно, не установлен на вашем компьютере. Чтобы убедиться, вы можете проверить это в командной строке:
git lfs --version
Если вы видите что-то подобное, Git LFS установлен:
git-lfs/2.8.0 (GitHub; darwin amd64; go 1.12.7)
В противном случае вы можете установить его, выполнив Bitbucket GitHub.
Repository not found
Если указать несуществующее расположение, в Консоли Unity появится сообщение, похожее на это:
Cannot perform upm operation: Unable to add package [https://mycompany.github.com/gitproject/com.mycompany.mypackage.git]:
Error when executing git command. fatal: repository 'https://mycompany.github.com/gitproject/com.mycompany.mypackage.git/' not found
[NotFound]
UnityEditor.EditorApplication:Internal_CallUpdateFunctions() (at /Users/builduser/buildslave/unity/build/Editor/Mono/EditorApplication.cs:310)
Проверьте правописание. Чтобы убедиться, что вы используете правильный URL-адрес, перейдите на страницу репозитория и скопируйте URL-адрес из кнопки «Клонировать»:

Нажмите кнопку справа от URL-адреса на GitHub (A) или GitLab (B), чтобы скопировать URL-адрес в буфер обмена.
Если расположение репозитория верное, может быть другая проблема с URL-адресом:
- Если вы настраиваете таргетинг на конкретную версию, убедитесь, что ваша версия стоит последней. Например:
https://github.example.com/myuser/myrepository1.git#revision - Если вы нацелены на ревизию, а пакет не находится в корне, убедитесь, что параметр запроса
pathпредшествует привязке ревизии. Например:
https://github.example.com/myuser/myrepository.git?path=/example/folder#v1.2.3
Could not read Username: terminal prompts disabled
Если вы пытаетесь установить пакет из частного репозитория, для которого требуется аутентификация, в консоли Unity появится сообщение, похожее на это:
Cannot perform upm operation: Unable to add package [https://mycompany.github.com/gitproject/com.mycompany.mypackage.git]:
Error when executing git command. fatal: could not read Username for 'https://mycompany.github.com': terminal prompts disabled
[NotFound]
UnityEditor.EditorApplication:Internal_CallUpdateFunctions() (at /Users/builduser/buildslave/unity/build/Editor/Mono/EditorApplication.cs:310)
Это сообщение, вероятно, связано с тем, что диспетчер пакетов не предоставляет интерактивный терминал или диалоговое окно, где вы можете ввести свое имя пользователя и пароль для HTTP или парольную фразу для разблокировки ключа SSH:
-
При использовании HTTP(S) каждый раз, когда вы входите в BitBucket, GitHub или GitLab, вам необходимо вводить имя пользователя и пароль в терминале или диалоговом окне. Однако диспетчер пакетов не предоставляет интерактивный терминал или диалоговое окно, где вы можете ввести свое имя пользователя и пароль для HTTP(S).
Чтобы избежать этого, используйте один из обходных путей, предложенных в разделе Решения для HTTPS.
-
SSH использует пару открытых и закрытых ключей SSH. Вы можете добавить свой открытый SSH-ключ в Bitbucket, GitHub или GitLab, а затем получить доступ к репозиториям без ввода имени пользователя и пароля.
Однако, если вы установили парольную фразу для обеспечения безопасности своего ключа SSH, вам все равно придется ввести эту парольную фразу в терминал или диалоговое окно, чтобы авторизовать свой ключ. В этом случае вы можете использовать агент SSH, который может разблокировать ваш ключ SSH для аутентификации в диспетчере пакетов от вашего имени.
Решения для HTTPS
Диспетчер пакетов не предоставляет интерактивный терминал или диалоговое окно, где вы можете ввести свое имя пользователя и пароль HTTP(S). Чтобы обойти это, используйте один из следующих обходных путей:
- Используйте диспетчер учетных данных (Git Credential-Manager для Windows или OSXKeyChain). Менеджеры учетных данных обрабатывают отправку пароля без использования терминала или командной строки.
- Используйте git-credential-Storage из терминала или командная строка. Затем запустите Hub с того же терминала, чтобы у Unity был доступ к кэшированным или сохраненным учетным данным.
- Вместо этого используйте SSH для аутентификации. Если вы настроили свой SSH-ключ без парольной фразы, диспетчеру пакетов не нужно его расшифровывать для аутентификации на сервере Git. Если вы решите использовать парольную фразу для дополнительной безопасности, вы все равно можете обойти проблему аутентификации, используя ssh-agent в любой из macOS или Windows.
Решения для SSH
Если вы используете протокол SSH для установки пакета по URL-адресу Git, вы можете получить ошибку аутентификации от Git. Обычно это происходит, когда вы настраиваете закрытый ключ SSH на локальном компьютере, который защищен парольной фразой.
Решение этой проблемы заключается в настройке агента SSH, который может разблокировать ваш ключ SSH для аутентификации в диспетчере пакетов от вашего имени. Следуйте инструкциям в разделе, соответствующем вашей операционной системе:
- Настройка OpenSSH для Windows
- Добавление ключей SSH в агент SSH для macOS
Настройка OpenSSH для Windows
Собственная версия OpenSSH для Windows ssh-agent работает лучше, чем версия, доступная по умолчанию с Git для Windows. Эта процедура объясняет, как настроить клиент OpenSSH и добавить свой ключ в его ssh-агент. Если вы используете Git для Windows, вы также можете отдать приоритет собственному Windows OpenSSH над агентом Git для Windows SSH:
-
Убедитесь, что клиент OpenSSH установлен, выполнив поиск в окне настроек Windows Optional features (Start > Settings, затем найдите «Optional features»). Это относится к Windows 10+.
-
Проверьте переменную среды
%PATH%, чтобы убедиться, что отображается собственное расположение Windows OpenSSH (например,C:WINDOWSSystem32 OpenSSH).Примечание. Если вы уже используете Git для Windows, убедитесь, что собственное расположение Windows OpenSSH указано перед расположением Git для Windows SSH в вашем
%PATH%переменная. Это гарантирует, что Windows использует собственный агент Windows OpenSSH вместо агента Git для Windows SSH. -
В терминале PowerShell запустите процесс
ssh-agentи убедитесь, что он запускается автоматически:# Set the ssh-agent service to start automatically and manually start it now
Get-Service ssh-agent | Set-Service -StartupType Automatic
# Run the ssh-agent process to start the ssh-agent service
ssh-agent
-
Импортируйте свой ключ в ssh-agent, запустив
ssh-addв командной строке и следуя инструкциям. По умолчанию агент добавляет ключ%USERPROFILE%.sshid_rsaи запрашивает пароль.# Import the key
ssh-add
Чтобы использовать другой ключ, вы можете указать его в качестве аргумента:
# Set the ssh-agent service to start automatically and manually start it now
ssh-add
Если вы не можете вспомнить название своего ключа, вы можете попросить агента перечислить их:
ssh-add -l -
Если вы установили Git для Windows, сбросьте переменную среды
%GIT-SSH%, чтобы убедиться, что Git всегда использует собственную версию ssh-agent для Windows OpenSSH:[Environment]::SetEnvironmentVariable("GIT_SSH", "$((Get-Command ssh).Source)", [System.EnvironmentVariableTarget]::User)
Добавление ключей SSH в агент SSH для macOS
Используйте следующую команду, чтобы добавить ключи SSH в ssh-agent, работающий на вашей macOS. система:
ssh-add -K ~/.ssh/
После выполнения этой команды терминал запрашивает пароль для разблокировки ключа SSH, а затем добавляет его в цепочку ключей macOS. Однако после перезагрузки системы все ключи, хранящиеся в ssh-agent, сбрасываются.
Чтобы предотвратить повторный ввод пароля после перезагрузки системы, откройте файл ~/.ssh/config (или создайте его, если вы его не найдете) и добавьте следующее:
Host *
UseKeychain yes
AddKeysToAgent yes
IdentityFile ~/.ssh/
Перезагрузите компьютер, чтобы применить эти изменения.
Can’t update Git version
Если вы пытаетесь обновить свою зависимость Git, диспетчер пакетов получает зависимости Git непосредственно из репозитория Git, а не из реестр пакетов. Зависимости Git используют ссылку URL-адреса Git вместо версии, и нет никаких гарантий относительно качества, стабильности, достоверности пакета или даже того, соответствует ли версия, указанная в его файле package.json. Правила семантического управления версиями в отношении официально опубликованных выпусков этого пакета. Дополнительная информация
Посмотрите в Словарь более новую версию из репозитория, но она не работает, вероятно, это связано с тем, что ваша зависимость от Git заблокирована. Если вы хотите обновить свою зависимость Git до более новой версии из репозитория, используйте кнопку Добавить пакет из URL-адреса git и введите URL-адрес Git. Дополнительные сведения см. в разделе Заблокированные зависимости Git.
‘Failed to parse Http response’ in My Assets context
Если вы видите следующее сообщение в окне консоли при попытке загрузить пакет Asset Store, возможно, возникла проблема с кешем Asset Store:
[PackageManager] Error Failed to parse response. UnityEditor.AsyncHTTPClientone(State, Int32)
Чтобы решить эту проблему, удалите все загруженные ресурсы из каталога пакетов Asset Store, а затем повторите попытку загрузки ресурсов.
Предупреждение. Если ваш проект содержит много данных об объектах, повторная загрузка может занять много времени и трафика.
Missing ‘My Registries’ in the Package Manager window
Не все поставщики реестра совместимы с диспетчером пакетов Unity. Если добавленный вами сервер реестра пакетов не реализует конечные точки /-/v1/search или /-/all, ваш реестр с заданной областью не совместим с диспетчером пакетов Unity и не отображается в контексте My Registries в окне диспетчера пакетов.
Missing MonoBehaviour errors
Во время сборки, если возникает много ошибок, связанных с отсутствующим поведением, UnityLinker может по ошибке удалить компонент, который, по его мнению, не указан. Часто это происходит из-за слишком агрессивного уровня зачистки. Например, если у вас есть префабтип актива, который позволяет хранить GameObject вместе с компонентами и свойствами. Префаб действует как шаблон, из которого вы можете создавать новые экземпляры объектов на сцене. Подробнее
См. в Словарь в AssetBundle, который ссылается на компонент SpriteShape в пакете 2D SpriteShape. , объект может отсутствовать и вызывать предупреждения компилятора.
Чтобы исправить это, вы можете либо понизить уровень разделения для UnityLinker, либо объявить сборки пакета в файле link.xml, чтобы предотвратить их удаление:
<linker>
<assembly fullname="Unity.2D.SpriteShape.Runtime" preserve="all"/>
<assembly fullname="Unity.2D.Common.Runtime" preserve="all"/>
</linker>
Дополнительную информацию об уровнях удаления и UnityLinker см. в разделе Управляемое удаление кода.
Loading error for hostfxr.dll on Windows
Если консоль сообщает, что библиотека hostfxr.dll найдена, но Unity не удалось загрузить ее из C:\ hostfxr.dll, вы можете исправить эту ошибку в Windows 7 или Windows Server 2008 R2, установив обе KB2999226 и KB2533623 исправления.
In some Unity versions, whenever you create a project, Unity displays an Unity Package Manager Error dialog. However retrying can’t solve the problem. Today let’s see how to fix this error.
Solutions
Solution 1
Maybe an empty hosts file is the cause, which Unity have already fixed in later versions. But in the meantime, you should check the content of your hosts file. It would be located in:
On Windows:
C:WindowsSystem32driversetchosts
On macOS:
/etc/hosts
Make sure the localhost host name is defined like “127.0.0.1 localhost”.
Solution 2
Another solution is to set the UNITY_NOPROXY environment variable to localhost:
On Windows command prompt
setx UNITY_NOPROXY localhost,127.0.0.1
On Mac terminal
export UNITY_NOPROXY=localhost,127.0.0.1
Solution 3
Thirdly you can check if your anti-virus software is preventing the Unity Package Manager process to start. In this case, you can disable your anti-virus software for a few minutes to test if it works. If it did, configure your anti-virus to whitelist the NodeJS bundled with Unity (Under Unity installation folder, /Tools/nodejs/node.exe on Windows or /Tools/nodejs/bin/node on other platforms).
Solution 4
If all the above solutions can’t solve the Unity Package Manager Error, certainly you should install a new version of Unity, lol. See Download and install Unity by Unity Hub.
Post Views: 793
