Assuming you are in a QWidget from which you want to display an error message, you can simply use QMessageBox.critical(self, "Title", "Message"), replace self by another (main widget for example) if you are not is a QWidget class.
Edit: even if you are not in a QWidget (or don’t want to inherit from it), you can just use None as parent with for instance QMessageBox.critical(None, "Title", "Message").
Edit, here is an example of how to use it:
# -*-coding:utf-8 -*
from PyQt5.QtWidgets import QApplication, QMessageBox
import sys
# In this example, success is False by default, and
# - If you press Cancel, it will ends with False,
# - If you press Retry until i = 3, it will end with True
expectedVal = 3
def MyFunction(val: int) -> bool:
return val == expectedVal
app = QApplication(sys.argv)
i = 1
success = MyFunction(i)
while not success:
# Popup with several buttons, manage below depending on choice
choice = QMessageBox.critical(None,
"Error",
"i ({}) is not expected val ({})".format(i, expectedVal),
QMessageBox.Retry | QMessageBox.Cancel)
if choice == QMessageBox.Retry:
i += 1
print("Retry with i = {}".format(i))
success = MyFunction(i)
else:
print("Cancel")
break
if success:
# Standard popup with only OK button
QMessageBox.information(None, "Result", "Success is {}".format(success))
else:
# Standard popup with only OK button
QMessageBox.critical(None, "Result", "Success is {}".format(success))
@Meller008
Если я правильно понял вопрос, то например
if error:
QMessageBox.critical(self, "Ошибка ", "Выделите элемент который хотите изменить", QMessageBox.Ok)Ответ написан
более трёх лет назад
Комментировать
Комментировать
'''
О диалоге
Ошибка диалогового окна
Предупреждение Диалог
Вопрос: диалог
Сообщение Диалог
'''
import sys
from PyQt5.QtWidgets import *
from PyQt5.QtCore import *
from PyQt5.QtGui import *
class QMessageboxDemo(QWidget):
def __init__(self):
super(QMessageboxDemo,self).__init__()
self.initUI()
def initUI(self):
self.setWindowTitle("Cmessagebox Case")
self.resize(300,400)
layout = QVBoxLayout()
self.button1 = QPushButton(«Дисплей о диалоге»)
self.button1.clicked.connect(self.showdialog)
# Диалог отображения сообщения
self.button2 = QPushButton(«Дисплейное сообщение» Диалог ')
self.button2.clicked.connect(self.showdialog)
#предостережение
self.button3 = QPushButton(«Диалог предупреждения отображения»)
self.button3.clicked.connect(self.showdialog)
#
self.button4 = QPushButton(«Дисплей ошибки Диалог»)
self.button4.clicked.connect(self.showdialog)
# Диалог вопроса
self.button5 = QPushButton(«Дисплей вопрос диалог»)
self.button5.clicked.connect(self.showdialog)
layout.addWidget(self.button1)
layout.addWidget(self.button2)
layout.addWidget(self.button3)
layout.addWidget(self.button4)
layout.addWidget(self.button5)
self.setLayout(layout)
def showdialog(self):
text = self.sender().text()
if text == «Дисплей о диалоге»:
# Qmessagebox.about (self, 'title', 'content')
QMessageBox.about(self,'на',«Это вопрос о диалоге»)
elif text == «Дисплейное сообщение» Диалог ':
reply = QMessageBox.information(self,'Новости',«Это сообщение сообщение».,
QMessageBox.Yes | QMessageBox.No,QMessageBox.Yes)
print(reply)
elif text == «Диалог предупреждения отображения»:
QMessageBox.warning(self,'предостережение',«Это диалог предупреждения», QMessageBox.Yes | QMessageBox.No,QMessageBox.Yes)
elif text == «Дисплей ошибки Диалог»:
QMessageBox.critical(self, 'ошибка', «Это диалоговое окно ошибки», QMessageBox.Yes | QMessageBox.No, QMessageBox.Yes)
elif text == «Дисплей вопрос диалог»:
QMessageBox.critical(self, 'Подсказка', «Это оперативное диалоговое окно», QMessageBox.Yes | QMessageBox.No, QMessageBox.Yes)
if __name__ == '__main__':
app =QApplication(sys.argv)
main = QMessageboxDemo()
main.show()
app.exit(app.exec_())

In this article, we will discuss the Message Box Widget of the PyQT5 module. It is used to display the message boxes. PyQt5 is a library used to create GUI using the Qt GUI framework. Qt is originally written in C++ but can be used in Python. The latest version of PyQt5 can be installed using the command:
pip install PyQt5
What is a Message Box?
Message Boxes are usually used for declaring a small piece of information to the user. It gives users a pop-up box, that cannot be missed, to avoid important errors and information being missed by the users and in some cases, the user cannot continue without acknowledging the message box.
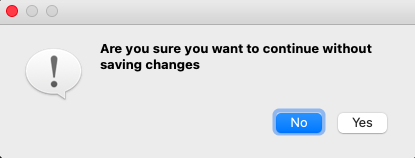
Based on the applications there are four types of message boxes. The following is the syntax for creating a message box. For any of the boxes, instantiation needs to be done.
Syntax:
msg_box_name = QMessageBox()
Now according to the requirement an appropriate message box is created.
Types of Message Box
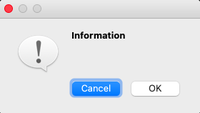
Information Message Box
This type of message box is used when related information needs to be passed to the user.
Syntax:
msg_box_name.setIcon(QMessageBox.Information)
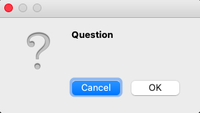
Question Message Box
This message box is used to get an answer from a user regarding some activity or action to be performed.
Syntax:
msg_box_name.setIcon(QMessageBox.Question)
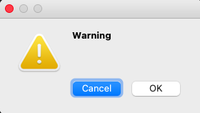
Warning Message Box
This triggers a warning regarding the action the user is about to perform.
Syntax:
msg_box_name.setIcon(QMessageBox.Warning)
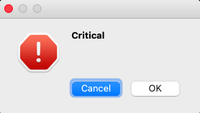
Critical Message Box
This is often used for getting the user’s opinion for a critical action.
Syntax:
msg_box_name.setIcon(QMessageBox.Critical)
Creating a simple Message Box using PyQt5
Now to create a program that produces a message box first import all the required modules, and create a widget with four buttons, on clicking any of these a message box will be generated.
Now for each button associate a message box that pops when the respective button is clicked. For this first, instantiate a message box and add a required icon. Now set appropriate attributes for the pop that will be generated. Also, add buttons to deal with standard mechanisms.
Given below is the complete implementation.
Program:
Python
import sys
from PyQt5.QtWidgets import *
def window():
app = QApplication(sys.argv)
w = QWidget()
b1 = QPushButton(w)
b1.setText("Information")
b1.move(45, 50)
b2 = QPushButton(w)
b2.setText("Warning")
b2.move(150, 50)
b3 = QPushButton(w)
b3.setText("Question")
b3.move(50, 150)
b4 = QPushButton(w)
b4.setText("Critical")
b4.move(150, 150)
b1.clicked.connect(show_info_messagebox)
b2.clicked.connect(show_warning_messagebox)
b3.clicked.connect(show_question_messagebox)
b4.clicked.connect(show_critical_messagebox)
w.setWindowTitle("PyQt MessageBox")
w.show()
sys.exit(app.exec_())
def show_info_messagebox():
msg = QMessageBox()
msg.setIcon(QMessageBox.Information)
msg.setText("Information ")
msg.setWindowTitle("Information MessageBox")
msg.setStandardButtons(QMessageBox.Ok | QMessageBox.Cancel)
retval = msg.exec_()
def show_warning_messagebox():
msg = QMessageBox()
msg.setIcon(QMessageBox.Warning)
msg.setText("Warning")
msg.setWindowTitle("Warning MessageBox")
msg.setStandardButtons(QMessageBox.Ok | QMessageBox.Cancel)
retval = msg.exec_()
def show_question_messagebox():
msg = QMessageBox()
msg.setIcon(QMessageBox.Question)
msg.setText("Question")
msg.setWindowTitle("Question MessageBox")
msg.setStandardButtons(QMessageBox.Ok | QMessageBox.Cancel)
retval = msg.exec_()
def show_critical_messagebox():
msg = QMessageBox()
msg.setIcon(QMessageBox.Critical)
msg.setText("Critical")
msg.setWindowTitle("Critical MessageBox")
msg.setStandardButtons(QMessageBox.Ok | QMessageBox.Cancel)
retval = msg.exec_()
if __name__ == '__main__':
window()
Output
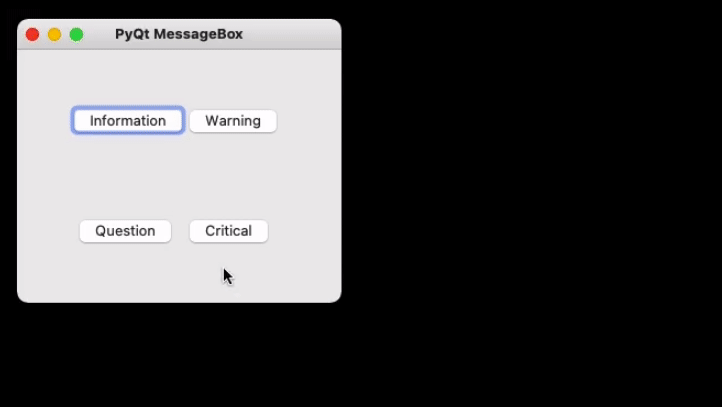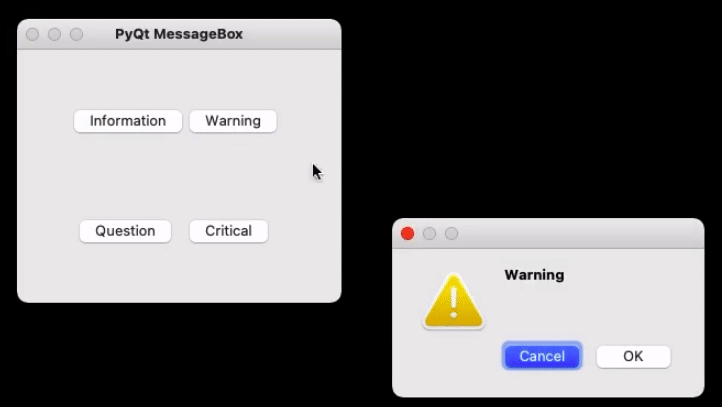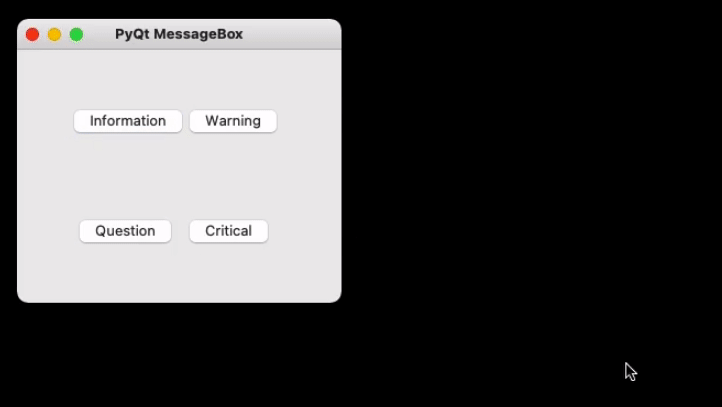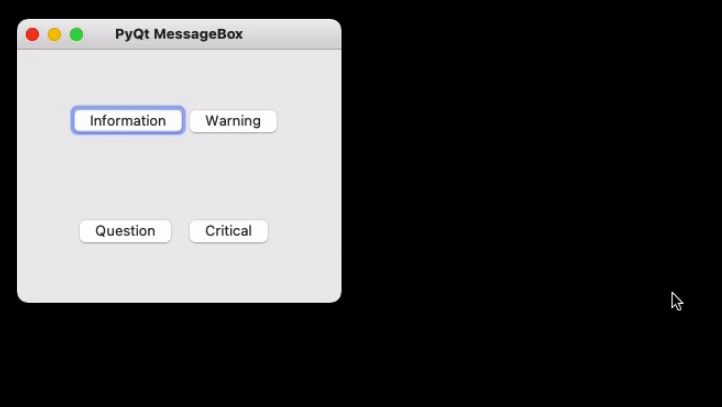
Last Updated :
23 Sep, 2021
Like Article
Save Article
Assuming you are in a QWidget from which you want to display an error message, you can simply use QMessageBox.critical(self, "Title", "Message"), replace self by another (main widget for example) if you are not is a QWidget class.
Edit: even if you are not in a QWidget (or don’t want to inherit from it), you can just use None as parent with for instance QMessageBox.critical(None, "Title", "Message").
Edit, here is an example of how to use it:
# -*-coding:utf-8 -*
from PyQt5.QtWidgets import QApplication, QMessageBox
import sys
# In this example, success is False by default, and
# - If you press Cancel, it will ends with False,
# - If you press Retry until i = 3, it will end with True
expectedVal = 3
def MyFunction(val: int) -> bool:
return val == expectedVal
app = QApplication(sys.argv)
i = 1
success = MyFunction(i)
while not success:
# Popup with several buttons, manage below depending on choice
choice = QMessageBox.critical(None,
"Error",
"i ({}) is not expected val ({})".format(i, expectedVal),
QMessageBox.Retry | QMessageBox.Cancel)
if choice == QMessageBox.Retry:
i += 1
print("Retry with i = {}".format(i))
success = MyFunction(i)
else:
print("Cancel")
break
if success:
# Standard popup with only OK button
QMessageBox.information(None, "Result", "Success is {}".format(success))
else:
# Standard popup with only OK button
QMessageBox.critical(None, "Result", "Success is {}".format(success))
In this article, we will discuss the Message Box Widget of the PyQT5 module. It is used to display the message boxes. PyQt5 is a library used to create GUI using the Qt GUI framework. Qt is originally written in C++ but can be used in Python. The latest version of PyQt5 can be installed using the command:
pip install PyQt5
What is a Message Box?
Message Boxes are usually used for declaring a small piece of information to the user. It gives users a pop-up box, that cannot be missed, to avoid important errors and information being missed by the users and in some cases, the user cannot continue without acknowledging the message box.

Based on the applications there are four types of message boxes. The following is the syntax for creating a message box. For any of the boxes, instantiation needs to be done.
Syntax:
msg_box_name = QMessageBox()
Now according to the requirement an appropriate message box is created.
Types of Message Box
Information Message Box
This type of message box is used when related information needs to be passed to the user.
Syntax:
msg_box_name.setIcon(QMessageBox.Information)

Question Message Box
This message box is used to get an answer from a user regarding some activity or action to be performed.
Syntax:
msg_box_name.setIcon(QMessageBox.Question)

Warning Message Box
This triggers a warning regarding the action the user is about to perform.
Syntax:
msg_box_name.setIcon(QMessageBox.Warning)

Critical Message Box
This is often used for getting the user’s opinion for a critical action.
Syntax:
msg_box_name.setIcon(QMessageBox.Critical)

Creating a simple Message Box using PyQt5
Now to create a program that produces a message box first import all the required modules, and create a widget with four buttons, on clicking any of these a message box will be generated.
Now for each button associate a message box that pops when the respective button is clicked. For this first, instantiate a message box and add a required icon. Now set appropriate attributes for the pop that will be generated. Also, add buttons to deal with standard mechanisms.
Given below is the complete implementation.
Program:
Python
import sys
from PyQt5.QtWidgets import *
def window():
app = QApplication(sys.argv)
w = QWidget()
b1 = QPushButton(w)
b1.setText("Information")
b1.move(45, 50)
b2 = QPushButton(w)
b2.setText("Warning")
b2.move(150, 50)
b3 = QPushButton(w)
b3.setText("Question")
b3.move(50, 150)
b4 = QPushButton(w)
b4.setText("Critical")
b4.move(150, 150)
b1.clicked.connect(show_info_messagebox)
b2.clicked.connect(show_warning_messagebox)
b3.clicked.connect(show_question_messagebox)
b4.clicked.connect(show_critical_messagebox)
w.setWindowTitle("PyQt MessageBox")
w.show()
sys.exit(app.exec_())
def show_info_messagebox():
msg = QMessageBox()
msg.setIcon(QMessageBox.Information)
msg.setText("Information ")
msg.setWindowTitle("Information MessageBox")
msg.setStandardButtons(QMessageBox.Ok | QMessageBox.Cancel)
retval = msg.exec_()
def show_warning_messagebox():
msg = QMessageBox()
msg.setIcon(QMessageBox.Warning)
msg.setText("Warning")
msg.setWindowTitle("Warning MessageBox")
msg.setStandardButtons(QMessageBox.Ok | QMessageBox.Cancel)
retval = msg.exec_()
def show_question_messagebox():
msg = QMessageBox()
msg.setIcon(QMessageBox.Question)
msg.setText("Question")
msg.setWindowTitle("Question MessageBox")
msg.setStandardButtons(QMessageBox.Ok | QMessageBox.Cancel)
retval = msg.exec_()
def show_critical_messagebox():
msg = QMessageBox()
msg.setIcon(QMessageBox.Critical)
msg.setText("Critical")
msg.setWindowTitle("Critical MessageBox")
msg.setStandardButtons(QMessageBox.Ok | QMessageBox.Cancel)
retval = msg.exec_()
if __name__ == '__main__':
window()
Output

In this article, we will discuss the Message Box Widget of the PyQT5 module. It is used to display the message boxes. PyQt5 is a library used to create GUI using the Qt GUI framework. Qt is originally written in C++ but can be used in Python. The latest version of PyQt5 can be installed using the command:
pip install PyQt5
What is a Message Box?
Message Boxes are usually used for declaring a small piece of information to the user. It gives users a pop-up box, that cannot be missed, to avoid important errors and information being missed by the users and in some cases, the user cannot continue without acknowledging the message box.

Based on the applications there are four types of message boxes. The following is the syntax for creating a message box. For any of the boxes, instantiation needs to be done.
Syntax:
msg_box_name = QMessageBox()
Now according to the requirement an appropriate message box is created.
Types of Message Box
Information Message Box
This type of message box is used when related information needs to be passed to the user.
Syntax:
msg_box_name.setIcon(QMessageBox.Information)

Question Message Box
This message box is used to get an answer from a user regarding some activity or action to be performed.
Syntax:
msg_box_name.setIcon(QMessageBox.Question)

Warning Message Box
This triggers a warning regarding the action the user is about to perform.
Syntax:
msg_box_name.setIcon(QMessageBox.Warning)

Critical Message Box
This is often used for getting the user’s opinion for a critical action.
Syntax:
msg_box_name.setIcon(QMessageBox.Critical)

Creating a simple Message Box using PyQt5
Now to create a program that produces a message box first import all the required modules, and create a widget with four buttons, on clicking any of these a message box will be generated.
Now for each button associate a message box that pops when the respective button is clicked. For this first, instantiate a message box and add a required icon. Now set appropriate attributes for the pop that will be generated. Also, add buttons to deal with standard mechanisms.
Given below is the complete implementation.
Program:
Python
import sys
from PyQt5.QtWidgets import *
def window():
app = QApplication(sys.argv)
w = QWidget()
b1 = QPushButton(w)
b1.setText("Information")
b1.move(45, 50)
b2 = QPushButton(w)
b2.setText("Warning")
b2.move(150, 50)
b3 = QPushButton(w)
b3.setText("Question")
b3.move(50, 150)
b4 = QPushButton(w)
b4.setText("Critical")
b4.move(150, 150)
b1.clicked.connect(show_info_messagebox)
b2.clicked.connect(show_warning_messagebox)
b3.clicked.connect(show_question_messagebox)
b4.clicked.connect(show_critical_messagebox)
w.setWindowTitle("PyQt MessageBox")
w.show()
sys.exit(app.exec_())
def show_info_messagebox():
msg = QMessageBox()
msg.setIcon(QMessageBox.Information)
msg.setText("Information ")
msg.setWindowTitle("Information MessageBox")
msg.setStandardButtons(QMessageBox.Ok | QMessageBox.Cancel)
retval = msg.exec_()
def show_warning_messagebox():
msg = QMessageBox()
msg.setIcon(QMessageBox.Warning)
msg.setText("Warning")
msg.setWindowTitle("Warning MessageBox")
msg.setStandardButtons(QMessageBox.Ok | QMessageBox.Cancel)
retval = msg.exec_()
def show_question_messagebox():
msg = QMessageBox()
msg.setIcon(QMessageBox.Question)
msg.setText("Question")
msg.setWindowTitle("Question MessageBox")
msg.setStandardButtons(QMessageBox.Ok | QMessageBox.Cancel)
retval = msg.exec_()
def show_critical_messagebox():
msg = QMessageBox()
msg.setIcon(QMessageBox.Critical)
msg.setText("Critical")
msg.setWindowTitle("Critical MessageBox")
msg.setStandardButtons(QMessageBox.Ok | QMessageBox.Cancel)
retval = msg.exec_()
if __name__ == '__main__':
window()
Output

When creating a Python GUI, you may want to show the message box QMessageBox at some point. The QMessageBox is a dialog that shows an informational message. It can optionally ask the user to click any of the buttons that show inside it.
Pyqt comes with messagebox support in both PyQt4 and PyQt5. The class to be used is QMessageBox.
In this tutorial you’ll learn how to show a message box on buton click.
Related course: Create PyQt Desktop Appications with Python (GUI)
QMessageBox example
The first thing to do, if you haven’t done so, is to install the PyQt GUI module.
Import QMessageBox from the PyQt5 widgets
from PyQt5.QtWidgets import QMessageBox
A messagebox can easily be added to the window using the code:
QMessageBox.about(self, "Title", "Message")

The code below create a window with a button. If you click on the button it shows a messagebox.
The messagebox is created with QMessageBox.about(self,title,message). This sets the window title and message too.
import sys
from PyQt5 import QtCore, QtWidgets
from PyQt5.QtWidgets import QMainWindow, QLabel, QGridLayout, QWidget
from PyQt5.QtWidgets import QPushButton
from PyQt5.QtWidgets import QMessageBox
from PyQt5.QtCore import QSize
class MainWindow(QMainWindow):
def __init__(self):
QMainWindow.__init__(self)
self.setMinimumSize(QSize(300, 200))
self.setWindowTitle("PyQt messagebox example - pythonprogramminglanguage.com")
pybutton = QPushButton('Show messagebox', self)
pybutton.clicked.connect(self.clickMethod)
pybutton.resize(200,64)
pybutton.move(50, 50)
def clickMethod(self):
QMessageBox.about(self, "Title", "Message")
if __name__ == "__main__":
app = QtWidgets.QApplication(sys.argv)
mainWin = MainWindow()
mainWin.show()
sys.exit( app.exec_() )
Related course: Create PyQt Desktop Appications with Python (GUI)
QMessageBox types
There are several types of icons that can be set in PyQt messagebox, they are: information, question, warning and critical.
Depending on the type of message box you want to show, you can change it to the one you need for your application.
msg.setIcon(QMessageBox.Information)
msg.setIcon(QMessageBox.Question)
msg.setIcon(QMessageBox.Warning)
msg.setIcon(QMessageBox.Critical)
QMessageBox buttons
You can set the default buttons shown in a message box. You can do that with the method setStandrdButtons(), then add the buttons you need.
msg.setStandardButtons(QMessageBox.Ok | QMessageBox.Cancel)
It comes with a whole range of buttons:
- QMessageBox.Ok
- QMessageBox.Open
- QMessageBox.Save
- QMessageBox.Cancel
- QMessageBox.Close
- QMessageBox.Yes
- QMessageBox.No
- QMessageBox.Abort
- QMessageBox.Retry
- QMessageBox.Ignore
You can test which button is clicked by capturing its return value:
ret = QMessageBox.question(self, 'MessageBox', "Click a button", QMessageBox.Yes | QMessageBox.No | QMessageBox.Cancel, QMessageBox.Cancel)
if ret == QMessageBox.Yes:
print('Button QMessageBox.Yes clicked.')
If you are new to Python PyQt, then I highly recommend this book.
Download PyQt Examples
Код файла Python:
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
import sys
from PyQt5 import QtWidgets
class MessageBox(QtWidgets.QWidget):# Унаследовано от родительского класса QtWidgets.QWidget
def __init__(self,parent = None):#parent = None означает, что этот QWidget принадлежит самому верхнему окну, то есть MainWindows.
QtWidgets.QWidget.__init__(self)# Из-за отношения наследования для инициализации родительского класса
# Инициализировать родительский класс через super, функция __init __ () не имеет self, если это непосредственно QtWidgets.QWidget .__ init __ (self), в скобках указано self
self.setGeometry(300, 300, 1000,1000) Метод # setGeometry () выполняет две функции: устанавливает положение окна на экране и устанавливает размер самого окна. Его первые два параметра - это координаты x и y окна на экране. Последние два параметра - это ширина и высота самого окна.
self.setWindowTitle(u'окно') # Задайте заголовок формы, эта строка не обязательна.
self.button = QtWidgets.QPushButton(u'контрольная работа', self) # Создайте кнопку для отображения слова "тест"
self.button.move(300,300)
self.button.clicked.connect(self.show_message) # Сигнальный слот
def show_message(self):
QtWidgets.QMessageBox.critical(self, "ошибка", «Системная ошибка, выключите и перезапустите»)
# Содержание должно быть длинным, слишком короткое приведет к неполному отображению заголовка!
app=QtWidgets.QApplication(sys.argv)
window=MessageBox()
window.show()
sys.exit(app.exec_())
Результаты приведены ниже:

This article covers the PyQt5 widget, QMessageBox.
QMessageBox is a useful PyQt5 widget used to create dialogs. These dialogs can be used for a variety of purposes and customized in many ways to display different messages and buttons.
In this PyQt5 tutorial you’ll also find a complete list of all methods, buttons types and options for the QMessageBox widget.
Creating a QMessageBox
Below we are just going to create a simple QMessageBox widget. It’s going to be a bare-bone messagebox with no added features or customization.
msg = QMessageBox(win)
msg.setWindowTitle("Message Box")
msg.setText("This is some random text")
x = msg.exec_()
And below is the output. If you want to display a simple message on screen, this is the way to do so.

Now compare this simple messagebox to the advanced and feature-rich message-boxes we are going to create below.
QMessageBox Icons
QMessageBox has 4 different types of icons that can be used by calling the setIcon() function. Decide which one to use depending on type of message you wish to display.
- QMessageBox.Question
- QMessageBox.Information
- QMessageBox.Warning
- QMessageBox.Critical
All you have to do is pass one of the above to the setIcon() function as shown below.
msg.setIcon(QMessageBox.Question)
Below are all four different messages that can be displayed.

QMessageBox Buttons
Uptil now we’ve been using the default “OK” button that QMessageBox offers. However, there are actually over a dozen different buttons that QMessageBox offers for our use. Below is an example of us utilizing some of the buttons.
Using the setStandardButtons() function, we can pass whichever button-type we want. (See the list of complete button types below)
def show_popup():
msg = QMessageBox(win)
msg.setWindowTitle("Message Box")
msg.setText("This is some random text")
msg.setIcon(QMessageBox.Question)
msg.setStandardButtons(QMessageBox.Cancel|QMessageBox.Ok
|QMessageBox.Retry)
msg.setInformativeText("This is some extra informative text")
x = msg.exec_()

You may have noticed this already, but the order the buttons has no impact on how they appear on the message box.
Default Button
Look at the above image again. You’l have noticed that there is a blue outline around the “OK” button. This is the symbol of the default button.
Using the setDefaultButton() function we can change the default button. Adding the following line to our code will cause the blue highlight to be around the “Cancel” button.
msg.setDefaultButton(QMessageBox.Cancel)

Here’s a complete list of different buttons types you can use with Messages.
- QMessageBox.Ok
- QMessageBox.No
- QMessageBox.Yes
- QMessageBox.Cancel
- QMessageBox.Close
- QMessageBox.Abort
- QMessageBox.open
- QMessageBox.Retry
- QMessageBox.Ignore
- QMessageBox.Save
- QMessageBox.Retry
- QMessageBox.Apply
- QMessageBox.Help
- QMessageBox.Reset
- QMessageBox.SaveAll
- QMessageBox.YesToAll
- QMessageBox.NoToAll
Detailed and Informative Text
By default you only have one area in the QMessageBox where you display Text. However, there are two more additional areas that we can unlock to add more text.
The first is an additional text section on the messagebox window itself. It’s like an additional line of text you can add called informative text. You only need to call the setInformativeText() function to add this new area of text.
The second is displayed on an area that expands from the QMessageBox. This is called “Detailed Text”. Setting up this section will automatically create a button that is used to show this area. You only need the setDetailedText() function to create this area.
def show_popup():
msg = QMessageBox(win)
msg.setWindowTitle("Message Box")
msg.setText("This is some random text")
msg.setIcon(QMessageBox.Question)
msg.setStandardButtons(QMessageBox.Cancel|QMessageBox.Ok)
msg.setDefaultButton(QMessageBox.Ok)
msg.setDetailedText("Extra details.....")
msg.setInformativeText("This is some extra informative text")
x = msg.exec_()
app = QApplication(sys.argv)
win = QMainWindow()
win.setGeometry(400,400,300,300)
win.setWindowTitle("CodersLegacy")
button = QtWidgets.QPushButton(win)
button.setText("A Button")
button.clicked.connect(show_popup)
button.move(100,100)
win.show()
sys.exit(app.exec_())
In case it didn’t make sense before, look the code and compare to how the output below has changed.

Clicking the Hide/Show Details button will hide/show the extra area below the messagebox respectively.
Retrieving QMessageBox Values
We’ve discussed alot of different customizations and features above, but we haven’t actually linked any of these different features and buttons to our code.
For example, if we have 3 different buttons on our messagebox, how will we know which one was pressed? This is what we’ll be exploring in this section. The code for this is shown below. Make sure to read it before moving forward.
from PyQt5 import QtWidgets
from PyQt5.QtWidgets import QApplication, QMainWindow, QMessageBox
import sys
def show_popup():
msg = QMessageBox()
msg.setWindowTitle("Message Box")
msg.setText("This is some random text")
msg.setIcon(QMessageBox.Question)
msg.setStandardButtons(QMessageBox.Cancel|QMessageBox.Ok)
msg.buttonClicked.connect(popup)
x = msg.exec_()
def popup(i):
print(i.text())
app = QApplication(sys.argv)
win = QMainWindow()
win.setGeometry(400,400,300,300)
win.setWindowTitle("CodersLegacy")
button = QtWidgets.QPushButton(win)
button.setText("A Button")
button.clicked.connect(show_popup)
button.move(100,100)
win.show()
sys.exit(app.exec_())
Using the buttonClicked.connect() method, we can cause a function to be triggered whenever a button on the message box is clicked. In this case, we’ve linked our messagebox to a function called popup. Notice that popup() takes a parameter i.
When the messagebox button is clicked it automatically passes the button that was clicked to the function declared in buttonClicked.connect(). Calling the text() function on this button will return it’s text value.
Head over to our main PyQt5 section to learn more about the other great widgets!
This marks the end of the PyQt5 QMessageBox article. Any suggestions or contributions for CodersLegacy are more than welcome. Questions regarding the article content can be asked in the comments section below.
5 ответов
Qt включает в себя класс диалога для сообщений об ошибках QErrorMessage который вы должны использовать, чтобы ваш диалог соответствовал системным стандартам. Чтобы показать диалог, просто создайте объект диалога, затем вызовите .showMessage(). Например:
error_dialog = QtWidgets.QErrorMessage()
error_dialog.showMessage('Oh no!')
Вот минимальный рабочий пример скрипта:
import PyQt5
from PyQt5 import QtWidgets
app = QtWidgets.QApplication([])
error_dialog = QtWidgets.QErrorMessage()
error_dialog.showMessage('Oh no!')
app.exec_()
mfitzp
24 окт. 2016, в 19:04
Поделиться
Все вышеперечисленные варианты не работали для меня, используя Komodo Edit 11.0. Просто вернул «1» или, если не был реализован «-1073741819».
Полезным для меня было: решение Ванлока.
def my_exception_hook(exctype, value, traceback):
# Print the error and traceback
print(exctype, value, traceback)
# Call the normal Exception hook after
sys._excepthook(exctype, value, traceback)
sys.exit(1)
# Back up the reference to the exceptionhook
sys._excepthook = sys.excepthook
# Set the exception hook to our wrapping function
sys.excepthook = my_exception_hook
ZF007
13 нояб. 2017, в 20:15
Поделиться
Следующее должно работать:
msg = QMessageBox()
msg.setIcon(QMessageBox.Critical)
msg.setText("Error")
msg.setInformativeText(e)
msg.setWindowTitle("Error")
Это не тот же тип сообщения (разные GUI), но довольно близко. e — выражение для ошибки в python3
Надеюсь, что это помогло,
Narusan
24 окт. 2016, в 18:21
Поделиться
Не забудьте вызвать .exec() _ для отображения ошибки:
msg = QMessageBox()
msg.setIcon(QMessageBox.Critical)
msg.setText("Error")
msg.setInformativeText('More information')
msg.setWindowTitle("Error")
msg.exec_()
NShiell
08 янв. 2019, в 12:47
Поделиться
Чтобы показать окно сообщения, вы можете вызвать это определение:
from PyQt5.QtWidgets import QMessageBox
def clickMethod(self):
QMessageBox.about(self, "Title", "Message")
Karam Qusai
17 апр. 2019, в 10:06
Поделиться
Ещё вопросы
- 1Keras / Tensorflow: комбинированная функция потерь для одного выхода
- 1Не могу установить размер JPanel внутри JDialog
- 1Как я могу обновить свойство скрипта MonoBehaviour?
- 0angular CacheFactory не устанавливает никакого значения
- 0Как показать / скрыть элементы управления при загрузке страницы на основе выбора с универсальным классом?
- 0Безопасно ли вставлять веб-страницы на мою веб-страницу?
- 0Показать только выпадающий список Выбранные строки опций в таблице
- 0результат ввода поля раз 2 появляется в окне не div
- 1Angular 2 — компонент не может правильно отображать теги таблицы
- 0AngularJS в Mongoose params по запросам
- 1Как я могу добиться этого базового макета в Android с надлежащим z-упорядочением представлений
- 0Угловая неосведомленная ошибка провайдера в пользовательском сервисе
- 0Как скрыть класс в условии
- 0Угловая переменная доступа / изменения ng-контроллера?
- 0Как использовать аутентифицированные функции мыла в PHP, приведите любой рабочий пример.
- 0Показывать только подменю после нажатия на родительское меню
- 1индекс в списке панд серии
- 0Как предотвратить $ event for fire дважды
- 0_CRT_SECURE_NO_DEPRECATE глобально?
- 0Подменю Jquery должно иметь выбранный класс при нажатии
- 1Android я могу избежать вызова onCreate ()?
- 1Полностью шкала цветов в обратном направлении
- 0остановить размытие событие от срабатывания в результате нажатия клавиши
- 1использование Sesame для обработки потока SPARQL / XML (вывод из Vitruoso)
- 0Использование нескольких файлов в C ++ для функций и классов
- 1Зашифруйте простой текстовый пароль для связи GAE <> Android
- 0Не удается перенаправить на ту же страницу после использования входа в Google в Joomla
- 0установить фоновое изображение из выпадающего меню — JavaScript
- 1Массив сортировки Javascript по возрастным группам и полу
- 0Доступ к данным массива в объекте
- 0MySQL Проверка, находится ли временной диапазон за пределами заданных временных интервалов для дня
- 0jQuery и PHP получают определенную таблицу из MYSQL для определенного переданного идентификатора через jquery
- 1Как разместить изображение и сообщение на Facebook без использования браузера в Windows Phone7
- 0Проверка формы jQuery: факторизация проверки писем
- 0MySQL вложенный запрос не работает с условием AND
- 1JavaScript-код для отображения предупреждающего сообщения после 15 нажатий клавиш
- 1C # — правильно запустить элемент управления или формы в отдельном потоке
- 0AngularJS — Запуск функции один раз при загрузке
- 1Как решить NoClassDefFoundError в сервлете Java?
- 1FileNotFoundException при попытке прочитать файл, который я написал
- 0VB.Net Удалить выбранную строку в DataGridView MySql
- 0Вставка одной строки MySQL со значениями из нескольких вложенных операторов SELECT
- 1Эффективный SQL-запрос один-ко-многим
- 02 вопроса на Backbone.js MVC
- 0Можно ли ждать ForForMultipleObjects для события и IOCompletionPort с вводом?
- 1Очень простой вопрос меню для Android
- 1Зачем использовать infer_datetime_format при импорте файла CSV?
- 1Как использовать служебное свойство в маршруте?
- 1Значение типа «Стиль» нельзя добавить в коллекцию или словарь типа «UIElementCollection».
- 0Меню jquery имеет белую рамку / фон. Как это покрасить?
Subscribe to Tech With Tim!
This PyQt5 Tutorial will show you how to create message boxes/popup windows using pyqt. We will use the QMessageBox class to accomplish this.
Creating a Basic GUI
I’ve started this tutorial by creating a very minimal GUI that contains one button. This way we can use the button press to trigger a popup/mesagebox.
This is what my GUI looks like:

Importing QMessageBox
To make our lives a little easier we will start by importing the QMessageBox class. This way each time we want to reference it we can use it directly.
from PyQt5.QtWidgets import QMessageBox
Creating a MessageBox
Note: I’m placing the code seen below inside the method that is linked to my button press. This way when the button is clicked a messagebox will appear on the screen.
Everytime we create a new popup window we need to create a new instance of QMessageBox.
Then we can start changing some properties of the messagebox like the title and the text.
msg.setWindowTitle("Tutorial on PyQt5")
msg.setText("This is the main text!")
The method names are pretty intuitive so I’ll pass on explaining them.
We will add some more to our messagebox later but for now lets test it out. To actually see the messagebox when we run the code we need to add one last line to the end of our method:
x = msg.exec_() # this will show our messagebox
And this is what we get when we click the button!

Adding an Icon
A nice feature that our message boxes have it the ability to add an icon!
msg.setIcon(QMessageBox.Critical)
List of Icons
— QMessageBox.Critical
— QMessageBox.Warning
— QMessageBox.Information
— QMessageBox.Question
Here’s what our messagebox looks like with the Critical icon.
![]()
Adding/Changing Buttons
Now it’s time to change the buttons that show up in our QMessageBox. To do this we need to first select from a list of buttons that we’d like.
List of Buttons
— QMessageBox.Ok
— QMessageBox.Open
— QMessageBox.Save
— QMessageBox.Cancel
— QMessageBox.Close
— QMessageBox.Yes
— QMessageBox.No
— QMessageBox.Abort
— QMessageBox.Retry
— QMessageBox.Ignore
We can add any combinations of these buttons to our message box by using the following:
msg.setStandardButtons(QMessageBox.Retry | QMessageBox.Ignore | QMessageBox.Cancel) # seperate buttons with "|"
We can also set the button that will be highlighted by default by using:
msg.setDefaultButton(QMessageBox.Ignore) # setting default button to Cancel
Now our messagebox looks like this!

Getting Button Pressed
Now that we’ve learned how to add more than one button is probably important to determine which button the user is clicking.
To do this we need to create a new method/function that takes one argument. This argument will be the button widget that was clicked.
def popup_clicked(self, i): print(i.text()) # will print out the text on the button clicked
No we can link our messagebox to trigger that method when any button is pressed.
msg.buttonClicked.connect(self.popup_clicked)
Now when we click a button on the messagebox it’s text will be printed out to the console.
Other Properties
A few other things we can add are listed below:
Informative Text
This is the text that shows below the main text.
msg.setInformativeText("informative text, ya!")

Detail Text
This will generate a new button that will allow us to expand the message box and view more details.
msg.setDetailedText("details")

Full Code
from PyQt5 import QtCore, QtGui, QtWidgets from PyQt5.QtWidgets import QMessageBox class Ui_MainWindow(object): ... def show_popup(self): msg = QMessageBox() msg.setWindowTitle("Tutorial on PyQt5") msg.setText("This is the main text!") msg.setIcon(QMessageBox.Question) msg.setStandardButtons(QMessageBox.Cancel|QMessageBox.Retry|QMessageBox.Ignore|) msg.setDefaultButton(QMessageBox.Retry) msg.setInformativeText("informative text, ya!") msg.setDetailedText("details") msg.buttonClicked.connect(self.popup_button) def popup_button(self, i): print(i.text())
