I am using Python 3.1 on a Windows 7 machine. Russian is the default system language, and utf-8 is the default encoding.
Looking at the answer to a previous question, I have attempting using the «codecs» module to give me a little luck. Here’s a few examples:
>>> g = codecs.open("C:UsersEricDesktopbeeline.txt", "r", encoding="utf-8")
SyntaxError: (unicode error) 'unicodeescape' codec can't decode bytes in position 2-4: truncated UXXXXXXXX escape (<pyshell#39>, line 1)
>>> g = codecs.open("C:UsersEricDesktopSite.txt", "r", encoding="utf-8")
SyntaxError: (unicode error) 'unicodeescape' codec can't decode bytes in position 2-4: truncated UXXXXXXXX escape (<pyshell#40>, line 1)
>>> g = codecs.open("C:Python31Notes.txt", "r", encoding="utf-8")
SyntaxError: (unicode error) 'unicodeescape' codec can't decode bytes in position 11-12: malformed N character escape (<pyshell#41>, line 1)
>>> g = codecs.open("C:UsersEricDesktopSite.txt", "r", encoding="utf-8")
SyntaxError: (unicode error) 'unicodeescape' codec can't decode bytes in position 2-4: truncated UXXXXXXXX escape (<pyshell#44>, line 1)
My last idea was, I thought it might have been the fact that Windows «translates» a few folders, such as the «users» folder, into Russian (though typing «users» is still the correct path), so I tried it in the Python31 folder. Still, no luck. Any ideas?
Last updated on
Feb 10, 2022
In this post, you can find several solutions for:
SyntaxError: (unicode error) ‘unicodeescape’ codec can’t decode bytes in position 2-3: truncated UXXXXXXXX escape
While this error can appear in different situations the reason for the error is one and the same:
- there are special characters( escape sequence — characters starting with backslash — » ).
- From the error above you can recognize that the culprit is ‘U’ — which is considered as unicode character.
- another possible errors for SyntaxError: (unicode error) ‘unicodeescape’ will be raised for ‘x’, ‘u’
- codec can’t decode bytes in position 2-3: truncated xXX escape
- codec can’t decode bytes in position 2-3: truncated uXXXX escape
- another possible errors for SyntaxError: (unicode error) ‘unicodeescape’ will be raised for ‘x’, ‘u’
Step #1: How to solve SyntaxError: (unicode error) ‘unicodeescape’ — Double slashes for escape characters
Let’s start with one of the most frequent examples — windows paths. In this case there is a bad character sequence in the string:
import json
json_data=open("C:Userstest.txt").read()
json_obj = json.loads(json_data)
The problem is that U is considered as a special escape sequence for Python string. In order to resolved you need to add second escape character like:
import json
json_data=open("C:\Users\test.txt").read()
json_obj = json.loads(json_data)
Step #2: Use raw strings to prevent SyntaxError: (unicode error) ‘unicodeescape’
If the first option is not good enough or working then raw strings are the next option. Simply by adding r (for raw string literals) to resolve the error. This is an example of raw strings:
import json
json_data=open(r"C:Userstest.txt").read()
json_obj = json.loads(json_data)
If you like to find more information about Python strings, literals
2.4.1 String literals
In the same link we can find:
When an r' or R’ prefix is present, backslashes are still used to quote the following character, but all backslashes are left in the string. For example, the string literal r»n» consists of two characters: a backslash and a lowercase `n’.
Step #3: Slashes for file paths -SyntaxError: (unicode error) ‘unicodeescape’
Another possible solution is to replace the backslash with slash for paths of files and folders. For example:
«C:Userstest.txt»
will be changed to:
«C:/Users/test.txt»
Since python can recognize both I prefer to use only the second way in order to avoid such nasty traps. Another reason for using slashes is your code to be uniform and homogeneous.
Step #4: PyCharm — SyntaxError: (unicode error) ‘unicodeescape’ codec can’t decode bytes in position 2-3: truncated UXXXXXXXX escape
The picture below demonstrates how the error will look like in PyCharm. In order to understand what happens you will need to investigate the error log.
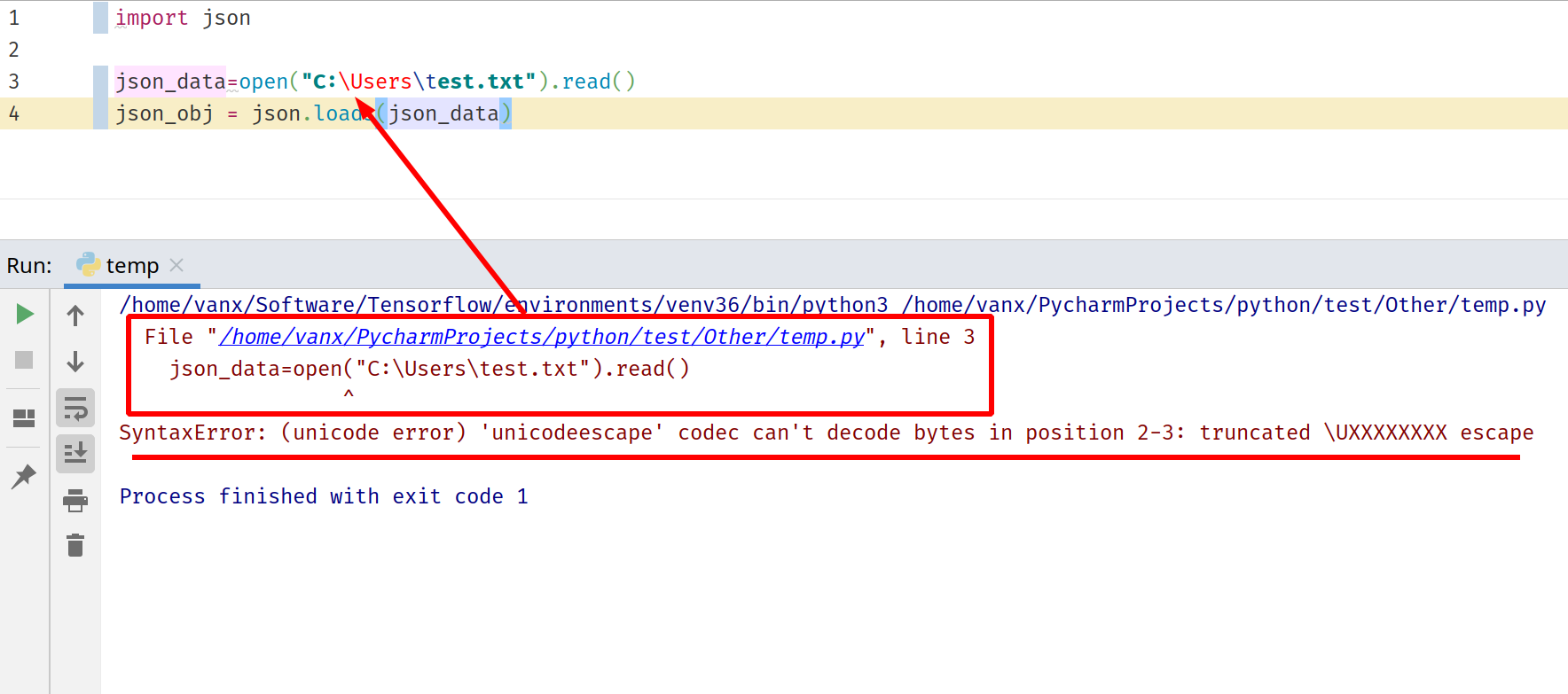
The error log will have information for the program flow as:
/home/vanx/Software/Tensorflow/environments/venv36/bin/python3 /home/vanx/PycharmProjects/python/test/Other/temp.py
File "/home/vanx/PycharmProjects/python/test/Other/temp.py", line 3
json_data=open("C:Userstest.txt").read()
^
SyntaxError: (unicode error) 'unicodeescape' codec can't decode bytes in position 2-3: truncated UXXXXXXXX escape
You can see the latest call which produces the error and click on it. Once the reason is identified then you can test what could solve the problem.
Table of Contents
Hide
- What is SyntaxError: (unicode error) ‘unicodeescape’ codec can’t decode bytes in position 2-3: truncated UXXXXXXXX escape?
- How to fix SyntaxError: (unicode error) ‘unicodeescape’ codec can’t decode bytes in position 2-3: truncated UXXXXXXXX escape?
- Solution 1 – Using Double backslash (\)
- Solution 2 – Using raw string by prefixing ‘r’
- Solution 3 – Using forward slash
- Conclusion
The SyntaxError: (unicode error) ‘unicodeescape’ codec can’t decode bytes in position 2-3: truncated UXXXXXXXX escape occurs if you are trying to access a file path with a regular string.
In this tutorial, we will take a look at what exactly (unicode error) ‘unicodeescape’ codec can’t decode bytes in position 2-3: truncated UXXXXXXXX escape means and how to fix it with examples.
The Python String literals can be enclosed in matching single quotes (‘) or double quotes (“).
String literals can also be prefixed with a letter ‘r‘ or ‘R‘; such strings are called raw strings and use different rules for backslash escape sequences.
They can also be enclosed in matching groups of three single or double quotes (these are generally referred to as triple-quoted strings).
The backslash () character is used to escape characters that otherwise have a special meaning, such as newline, backslash itself, or the quote character.
Now that we have understood the string literals. Let us take an example to demonstrate the issue.
import pandas
# read the file
pandas.read_csv("C:UsersitsmycodeDesktoptest.csv")
Output
File "c:PersonalIJSCodeprogram.py", line 4
pandas.read_csv("C:UsersitsmycodeDesktoptest.csv") ^
SyntaxError: (unicode error) 'unicodeescape' codec can't decode bytes in position 2-3: truncated UXXXXXXXX escapeWe are using the single backslash in the above code while providing the file path. Since the backslash is present in the file path, it is interpreted as a special character or escape character (any sequence starting with ‘’). In particular, “U” introduces a 32-bit Unicode character.
How to fix SyntaxError: (unicode error) ‘unicodeescape’ codec can’t decode bytes in position 2-3: truncated UXXXXXXXX escape?
Solution 1 – Using Double backslash (\)
In Python, the single backslash in the string is interpreted as a special character, and the character U(in users) will be treated as the Unicode code point.
We can fix the issue by escaping the backslash, and we can do that by adding an additional backslash, as shown below.
import pandas
# read the file
pandas.read_csv("C:\Users\itsmycode\Desktop\test.csv")Solution 2 – Using raw string by prefixing ‘r’
We can also escape the Unicode by prefixing r in front of the string. The r stands for “raw” and indicates that backslashes need to be escaped, and they should be treated as a regular backslash.
import pandas
# read the file
pandas.read_csv("C:\Users\itsmycode\Desktop\test.csv")Solution 3 – Using forward slash
Another easier way is to avoid the backslash and instead replace it with the forward-slash character(/), as shown below.
import pandas
# read the file
pandas.read_csv("C:/Users/itsmycode/Desktop/test.csv")
Conclusion
The SyntaxError: (unicode error) ‘unicodeescape’ codec can’t decode bytes in position 2-3: truncated UXXXXXXXX escape occurs if you are trying to access a file path and provide the path as a regular string.
We can solve the issue by escaping the single backslash with a double backslash or prefixing the string with ‘r,’ which converts it into a raw string. Alternatively, we can replace the backslash with a forward slash.
Srinivas Ramakrishna is a Solution Architect and has 14+ Years of Experience in the Software Industry. He has published many articles on Medium, Hackernoon, dev.to and solved many problems in StackOverflow. He has core expertise in various technologies such as Microsoft .NET Core, Python, Node.JS, JavaScript, Cloud (Azure), RDBMS (MSSQL), React, Powershell, etc.
Sign Up for Our Newsletters
Subscribe to get notified of the latest articles. We will never spam you. Be a part of our ever-growing community.
By checking this box, you confirm that you have read and are agreeing to our terms of use regarding the storage of the data submitted through this form.
Introduction
The following error message is a common Python error, the «SyntaxError» represents a Python syntax error and the «unicodeescape» means that we made a mistake in using unicode escape character.
SyntaxError: (unicode error) 'unicodeescape' codec can't decode bytes in position 0-5: truncated UXXXXXXXX escapeSimply to put, the «SyntaxError» can be occurred accidentally in Python and it is often happens because the (ESCAPE CHARACTER) is misused in a python string, it caused the unicodeescape error.
(Note: «escape character» can convert your other character to be a normal character.)
SyntaxError Example
Let’s look at an example:
print('It's a nice day.')Looks like we want to print «It’s a nice day.«, right? But the program will report an error message.
File "<stdin>", line 1
print('It's a nice day.')
^
SyntaxError: invalid syntaxThe reason is very easy-to-know. In Python, we can use print('xxx') to print out xxx. But in our code, if we had used the ' character, the Python interpreter will misinterpret the range of our characters so it will report an error.
To solve this problem, we need to add an escape character «» to convert our ‘ character to be a normal character, not a superscript of string.
print('It's a nice day.')Output:
It's a nice day.We print it successfully!
So how did the syntax error happen? Let me talk about my example:
One day, I run my program for experiment, I saved some data in a csv file. In order for this file can be viewed on the Windows OS, I add a new code uFFEF in the beginning of file.
This is «BOM» (Byte Order Mark), Explain to the system that the file format is «Big-Ending«.
I got the error message.
SyntaxError: (unicode error) 'unicodeescape' codec can't decode bytes in position 0-5: truncated UXXXXXXXX escapeAs mentioned at the beginning of this article, this is an escape character error in Python.
Solutions
There are three solutions you can try:
- Add a «r» character in the right of string
- Change
to be/ - Change
to be\
Solution 1: Add a «r» character in the beginning of string.
title = r'uFFEF'After we adding a r character at right side of python string, it means a complete string not anything else.
Solution 2: Change /.
open("C:UsersClayDesktoptest.txt")Change to:
open("C:/Users/Clay/Desktop/test.txt")This way is avoid to use escape character.
Solution 3: Change \.
open("C:UsersClayDesktoptest.txt")Change the code to:
open("C:\Users\Clay\Desktop\test.txt")It is similar to the solution 2 that it also avoids the use of escape characters.
The above are three common solutions. We can run normally on Windows.
Reference
- https://stackoverflow.com/questions/37400974/unicode-error-unicodeescape-codec-cant-decode-bytes-in-position-2-3-trunca
- https://community.alteryx.com/t5/Alteryx-Designer-Discussions/Error-unicodeescape-codec-can-t-decode-bytes/td-p/427540
Read More
- [Solved][Python] ModuleNotFoundError: No module named ‘cStringIO’
Introduction
Many times we get to see «UnicodeError: UnicodeDecodeError: ‘unicodeescape’ codec can’t decode bytes in position 2-3: truncated UXXXXXXXX escape» error in Python, and begin scratching our heads thinking about what to do next. Here, we will be seeing what this error actually means, what are its origins and how to fix it, without much effort.
What is Unicode Error in Python?
In Python, a UnicodeError is an exception that is raised when there is a problem working with Unicode strings. This can happen for a variety of reasons, such as trying to decode an invalid Unicode character or trying to encode a character that is not supported by the chosen encoding.
What is a Unicode string?
In Python, a Unicode string is a sequence of Unicode characters. Unicode is a standardized character encoding that represents most of the world’s written languages.
In Python, you can use Unicode strings by prefixing your string with the u character.
For example:
# This is a Unicode string
my_string = u'Hello World!'
Unicode strings can contain any Unicode character, including special characters and characters from non-Latin scripts such as Chinese, Japanese, and Arabic. They are stored internally as a series of 16-bit integers, with each integer representing a Unicode code point.
Operations on Unicode String
You can use Unicode strings in Python just like you would use any other string. You can manipulate them with string methods, concatenate them with other strings, and so on.
To convert a Unicode string to a regular Python string, you can use the encode method and specify an encoding such as utf-8 or latin-1. To convert a regular Python string to a Unicode string, you can use the decode method and specify an encoding.
Given below is an example of encoding and decoding of a string in Python:-
# This is a Unicode string
my_string = u'Hello World!'
# Encode the string as a bytes object using the 'utf-8' encoding
my_bytes = my_string.encode('utf-8')
# Decode the bytes object back into a Unicode string using the 'utf-8' encoding
my_string = my_bytes.decode('utf-8')
Why “Unicode Error: unicodeescape codec can’t decode bytes in position 2-3” error occurs?
The «UnicodeError: UnicodeDecodeError: ‘unicodeescape’ codec can’t decode bytes in position 2-3: truncated UXXXXXXXX escape» error in Python is raised when the interpreter is trying to decode a string that contains a Unicode escape sequence, but the sequence is invalid or incomplete.
How “Unicode Error: unicodeescape codec can’t decode bytes in position 2-3” error occurs and its fixes?
Invalid Unicode characters:
If you are trying to decode a string that contains an invalid Unicode character, you will get a UnicodeError.
For example:
# This will cause a UnicodeError because the character 'u1234' is not a valid Unicode character
my_string = b'x80x81u1234x82'.decode('utf-8')
Unsupported encoding:
If you are trying to encode a string using an encoding that does not support certain characters, you will get a UnicodeError.
For example:
# This will cause a UnicodeError because the character 'u20ac' is not supported by the 'ascii' encoding
my_string = 'u20ac'.encode('ascii')
Mismatched encoding and decoding:
If you are trying to encode a string using one encoding and then decode it using a different encoding, you may get a UnicodeError if the two encodings are incompatible.
For example:
# This will cause a UnicodeError because the 'utf-8' encoding cannot decode the 'latin-1' encoding
my_string = 'u20ac'.encode('latin-1').decode('utf-8')
Invalid escape sequence:
If you have typed an invalid Unicode escape sequence, such as U123456, the interpreter will not be able to decode it and will raise this error.
Conclusions
To fix a UnicodeError, you will need to carefully review your code and identify the cause of the error. Make sure that you are using the correct encoding and decoding functions and that your strings do not contain any invalid or unsupported characters.
