Getting the following Whitelabel Error Page while
I am running Spring Boot MVC app.
Whitelabel Error Page
This application has no explicit mapping for /error, so you are seeing this as a fallback.
Wed Apr 13 15:45:59 IST 2016
There was an unexpected error (type=Internal Server Error, status=500).
Circular view path [home]: would dispatch back to the current handler URL [/rewards/web/home] again. Check your ViewResolver setup! (Hint: This may be the result of an unspecified view, due to default view name generation.)
application.properties
server.contextPath=/rewards/web
rewardsweb-servlet.xml:
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:mvc="http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc"
xsi:schemaLocation="
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-3.2.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc
http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc/spring-mvc-3.2.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-3.2.xsd">
<context:component-scan base-package="com.rewards.web" />
<bean
class="org.springframework.web.servlet.view.InternalResourceViewResolver">
<property name="prefix">
<value>/WEB-INF/views/jsp/</value>
</property>
<property name="suffix">
<value>.jsp</value>
</property>
</bean>
<mvc:resources mapping="/resources/**" location="/resources/" />
<mvc:annotation-driven />
</beans>
web.xml
<web-app xmlns="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee
http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_2_5.xsd"
version="2.5">
<display-name>rewards-web</display-name>
<welcome-file-list>
<welcome-file>index.jsp</welcome-file>
</welcome-file-list>
<servlet>
<servlet-name>rewardsweb</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>
org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet
</servlet-class>
<load-on-startup>1</load-on-startup>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>rewardsweb</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
</web-app>
Spring Boot files
package com.rewards.web;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.context.web.SpringBootServletInitializer;
@SpringBootApplication
public class Application extends SpringBootServletInitializer {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(Application.class, args);
}
}
package com.rewards.web;
import io.undertow.Undertow.Builder;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.EnableAutoConfiguration;
import org.springframework.boot.context.embedded.undertow.UndertowBuilderCustomizer;
import org.springframework.boot.context.embedded.undertow.UndertowEmbeddedServletContainerFactory;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
@Configuration
@EnableAutoConfiguration
public class ApplicationConfiguration {
@Bean
public UndertowEmbeddedServletContainerFactory embeddedServletContainerFactory() {
UndertowEmbeddedServletContainerFactory factory = new UndertowEmbeddedServletContainerFactory();
factory.addBuilderCustomizers(new UndertowBuilderCustomizer() {
public void customize(Builder builder) {
builder.addHttpListener(9090, "0.0.0.0");
}
});
return factory;
}
}
Controller:
package com.rewards.web.controller;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.view.InternalResourceViewResolver;
@Controller
public class HomeController {
@RequestMapping("/home")
public String getHome(){
System.out.println("-------this is home----------");
return "home";
}
}
JSP
home.jsp is in this path : /src/main/webapp/WEB-INF/views/jsp/home.jsp
when i hit : http://localhost:9090/rewards/web/home
i am getting Whitelabel Error
And also i have tried following solution, added the following code in controller class. but no help.
package com.rewards.web.controller;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.ErrorController;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
@Controller
public class HomeController implements ErrorController{
private static final String PATH = "/error";
@RequestMapping(value = PATH)
public String error() {
return "Error handling";
}
public String getErrorPath() {
return PATH;
}
@RequestMapping("/home")
public String getHome(){
System.out.println("-------this is home----------");
return "home";
}
}
Can you please help me out.
Thanks.
By
Atul Rai |
Last Updated: October 2, 2019
Previous Next
In this article, we will explore how to handle Whitelabel Error Page in Spring Boot application. During the development of Spring application, sometimes we face the Whitelabel Error Page and Spring Framework suggests us ‘This application has no explicit mapping for /error, so you are seeing this as a fallback‘ as shown below:
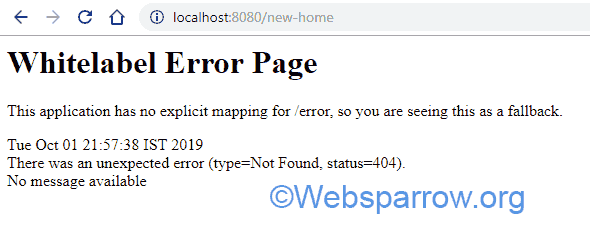
P.S Tested with Spring Boot and Thymeleaf 2.1.8.RELEASE version.
We can resolve the Whitelabel Error Page error in 3 ways:
1. Custom Error Controller
By implementing the ErrorController interface provided by the Spring Framework itself and overrides its getErrorPath() method to return a custom path to call when an error occurred:
ErrorrHandlerController.java
package org.websparrow.controller;
import org.springframework.boot.web.servlet.error.ErrorController;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController
public class ErrorrHandlerController implements ErrorController {
@GetMapping("/error")
public String customError() {
return "The link you followed may be broken, or the page may have been removed.";
}
@Override
public String getErrorPath() {
return "/error";
}
}In the customError() method, we return the custom message. If we trigger a 404, 500, etc error now, our custom message will be displayed.
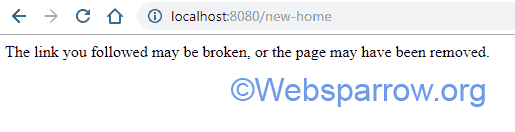
2. Displaying Custom Error Page
Create a error.html page and put it into the src/main/resources/templates directory. Spring Boot’s BasicErrorController will automatically be picked it up by default.
error.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<title>Error</title>
<body>
<h1>Something went wrong!</h1>
<p>The link you followed may be broken, or the page may have been removed.</p>
</body>
</html>Since we’re using Thymeleaf template engine to display the custom error page. Add the Thymeleaf dependency in the pom.xml:
<dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-thymeleaf</artifactId> <version>2.1.8.RELEASE</version> </dependency>
3. Disabling the Whitelabel Error Page
By setting the server.error.whitelabel.enabled property to false in the application.properties file, we can disable the white label error page.
application.properties
#Disable Whitelabel Error Page
server.error.whitelabel.enabled = falseNote: Add the right property matched with Spring Boot version:
Spring Boot Version >= 1.3 then use
server.error.whitelabel.enabled= falseSpring Boot Version <= 1.2 then use
error.whitelabel.enabled= false
We can achieve the same result by excluding the ErrorMvcAutoConfiguration class to the main class:
Main.java
@SpringBootApplication(exclude = { ErrorMvcAutoConfiguration.class })
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(WhitelabelErrorPageApplication.class, args);
}
}References
- Customize the ‘whitelabel’ Error Page
- Custom Error Pages
Let’s learn about the Whitelabel error page in Spring Boot and how to customize or disable them. White label error pages are default behavior from Spring Boot. Like any other feature, We can customize this feature to great extent.
What are Whitelabel error pages in Spring Boot?
Depending on API client request or browser request, spring boot provides an error JSON response or a full HTML error page. For example, let’s create a simple /hello endpoint that throws an exception always.
@RequestMapping("/hello")
String hello() {
throw new IntrovertException("Don't bother me please..!");
}Code language: Java (java)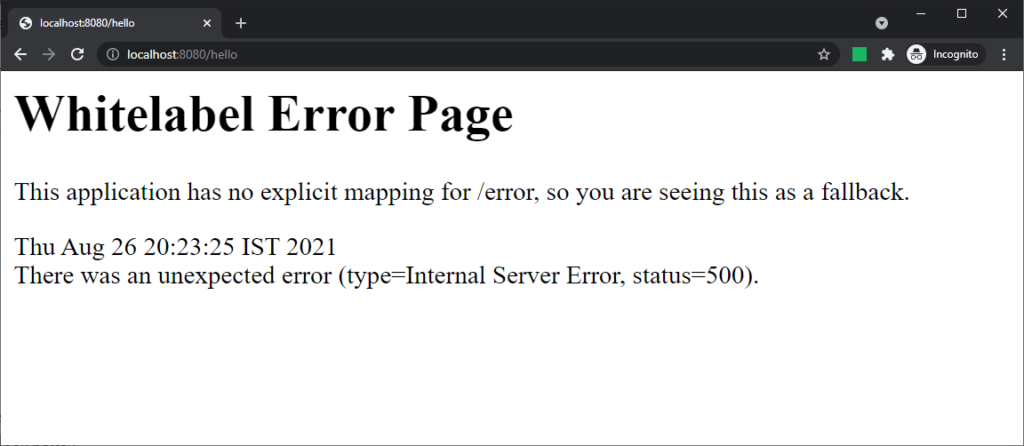
Even though this page looks simple, you can add details to it using the following configuration.
server.error.include-message=always
server.error.include-exception=true
server.error.include-stacktrace=always
server.error.include-binding-errors=alwaysCode language: Properties (properties)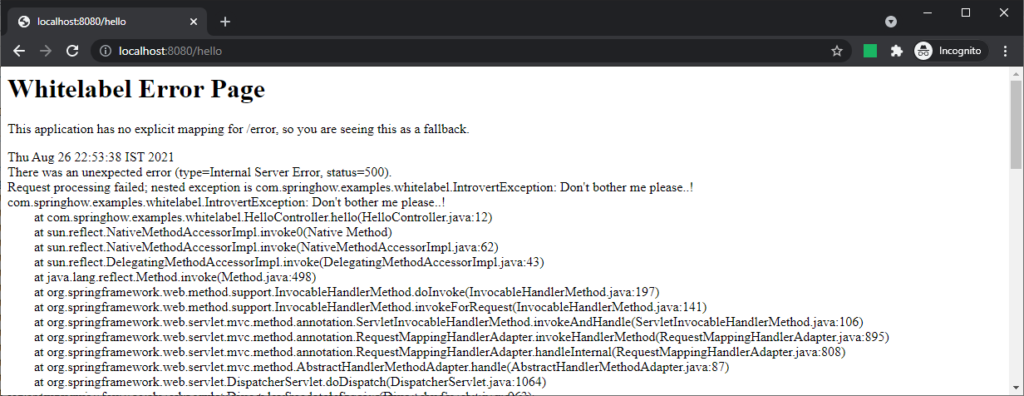
Even though the messages are helpful, this page may not fit well with your other page designs. So if you want to override this page with your own design, you are in luck.
Overriding Whitelabel Error Pages
Spring boot provides a /error mapping at a global servlet container level. This mapping handles requests and sends back JSON or HTML view as a response with error codes/messages. But the view that we saw above looks default. If you notice the first line of the error page, it says “This application has no explicit mapping for /error, so you are seeing this as a fallback.”
Here, the spring boot is trying to hint to you that you need to provide your own template to handle these error requests. So let’s see how to do that.
As we know, The handler mapped for /error expects a view to show the HTML response. If it doesn’t find a view matching “error” it will use the placeholder we have seen above. So we first need to add a template called error.html. But the template alone will not work. You also need to add one of the spring boot supported template engines. In our case, we are adding thymeleaf.
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-thymeleaf</artifactId>
</dependency>Code language: HTML, XML (xml)Next, you need to add the error.html template into your src/main/resources/templates directory.
With the above in place, the following MVC attributes will be available for you to access in the templates.
- message – Return value of exception.getMessage()
- exception – A string that contains the canonical exception name.
- trace – The complete stacktrace of the exception that caused this error.
- errors – A list of validation failures that occured during the request.
Along with these, there is also a status attribute that gives the HTTP status code for the error response. With that in place, we can rewrite our template file to show all these attributes.
<!doctype html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<title th:text="${message}"></title>
</head>
<body>
<table border="1">
<tr><td>Error Message</td><td th:text="${message}"></td></tr>
<tr><td>Status Code</td><td th:text="${status}"></td></tr>
<tr><td>Exception</td><td th:text="${exception}"></td></tr>
<tr><td>Stacktrace</td><td><pre th:text="${trace}"></pre></td></tr>
<tr><td>Binding Errors</td><td th:text="${errors}"></td></tr>
</table>
</body>
</html>Code language: HTML, XML (xml)This simple template will yield the following error page when we access /hello.
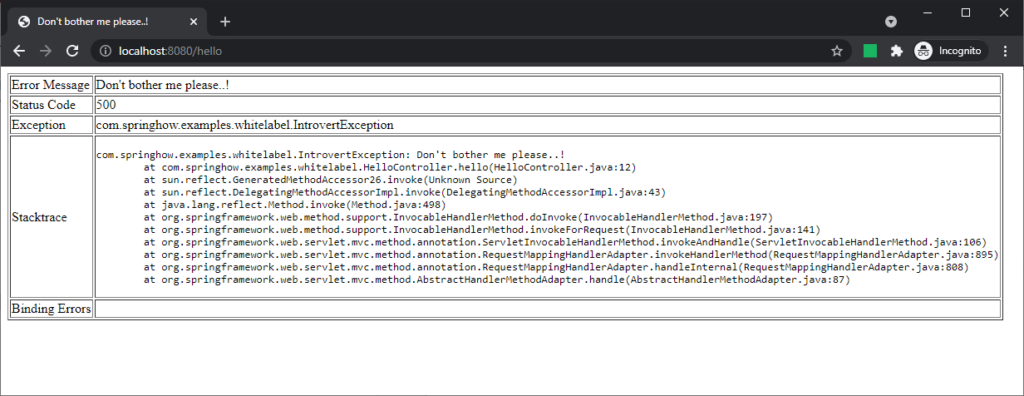
With a little bit of CSS, we can get this page to look better and more appealing.
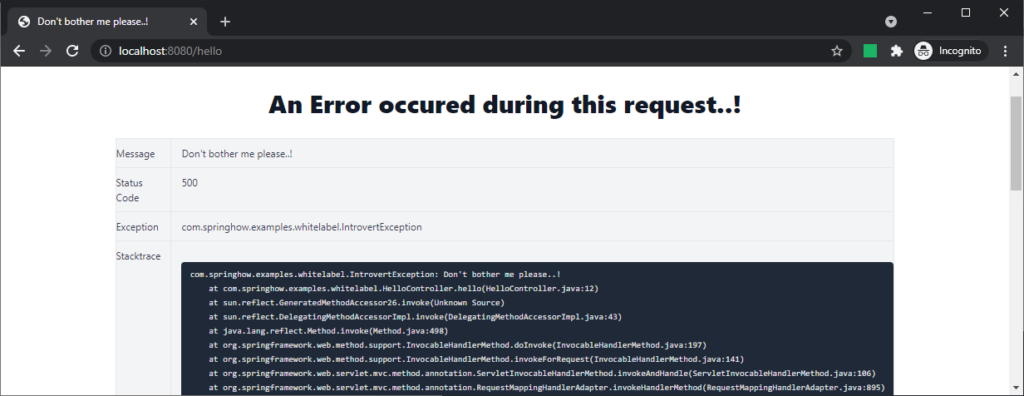
Disabling Whitelabel error page altogether /Tomcat whitelabel
Spring boot also provides a way to disable the Whitelabel error page altogether using server.error.whitelabel.enabled setting. When set to false, the server will show an error page specific to the servlet container(tomcat). For example, the below error page from tomcat will be visible if the Whitelabel is disabled and no error template is available.
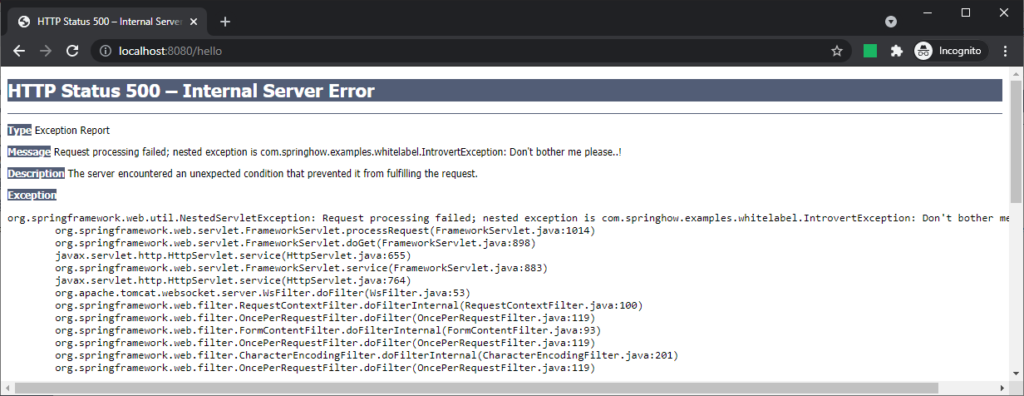
You can swap tomcat with jetty and you will still see an error page like this offered by the jetty runtime. And undertow currently doesn’t provide a view. But it does send response codes.
Important things to note
Always use a custom error.html page for the following reasons.
- Default whitelabel page lets hackers know you are using spring boot. This means they only need to try the exploits for spring boot.
- Never show exceptions in your production servers. Exceptions are great info for hackers.
- A custom error page with proper CSS will blend in to your other pages. You can even provide links and search boxes that can redirect users back to your site.
You can hide specific error attributes based on the configuration we saw earlier. Also, all these configurations are also applicable for the JSON response as well. If your request contains Accept: application/json header, then the response will be in the form of JSON. Even here, you can access all these attributes. For example, take a look at the below request.
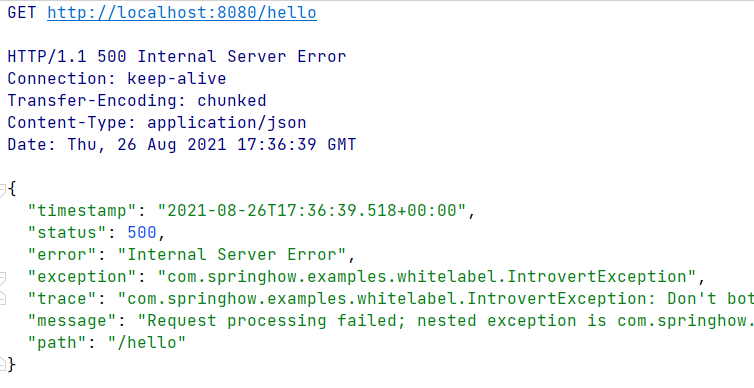
Here you can see the trace, exception, and message attributes being available as JSON.
Summary
To sum it up, we learned about white label error pages and how to customize them. We found out how to override the default Whitelabel with our own error.html. You can check out all these examples at our GitHub Repository.
Related
In this article, we will cover the famous Spring Boot Whitelabel error page. We are covering how to disable the default error page and how we can customize the Whitelabel error page in your Spring Boot application.
Introduction
Spring Boot uses a default Whitelabel error page in case server error. This is not very helpful and we may want to give more relevant information to the customer in a production environment. This article focuses on the Spring Boot whitelabel error page. We will learn how to disable this default behavior and how we can use our own custom error page to align with our UI.
1. Disabling Whitelabel Error Page
There are multiple ways to disable this behavior in your Spring Boot application. Let’s cover common options to do this.
1.1 Using Properties File
Spring Boot provides an application.properties (or YAML) file to easily configure/change your application. We can use the same property file to disable this error page globally. Set server.error.whitelabel.enabled to false to achieve this.
# Whether to enable the default error page displayed in browsers in case of a server error.
server.error.whitelabel.enabled=false Please know that using the above configuration will restore the default of the servlet container you are using. This means that if you are not using any custom error page, the default servlet container error page shown to the customer (like default tomcat server error page).
Another option is to exclude ErrorMvcAutoConfiguration from your application using application.properties file.
spring.autoconfigure.exclude=org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.servlet.error.ErrorMvcAutoConfigurationFor Spring Boot 1.x application use ErrorMvcAutoConfiguration in exclude the list.
1.2 Exclude using @EnableAutoConfiguration
In case you like to exclude using the code, you have the option to pass exclude configuration list to the @EnableAutoConfiguration annotation.
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableAutoConfiguration(exclude = {
ErrorMvcAutoConfiguration.class
})
public class SpringBootApplication { //application code
}2. Custom Error Page
As suggested, one of the first options is to Overriding the error page with your own template. For this post, we are taking Thymeleaf as our underlying templating engine. We create a custom error page with name error.html and save it under resources/templates directory. In case of error, Spring Boot system will automatically pick this custom error page. Let’s see how the page looks like before customizing error page.
Let’s create our custom error.html and place it under the <em>resources/templates</em> directory.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<title>We've got some trouble</title>
</head>
<body>
<div class="cover">
<h1>Our apologies.</h1>
<p class="lead">This page stepped out for a quick ride.</p>
<p>Please go back to our homepage to restart your browsing experience.</p>
</div>
</body>
</html>If we run our application, this is how the output shown to the customer.
Once we add the error.html in the templates directory, Spring Boot BasicErrorController automatically pick our custom template.
3. Custom ErrorController
If the above options are not suitable for your need or if we want to have a better control on the error handling mechanism, we have the option to extend Spring’s ErrorController with our own implementation. We need to implement the ErrorController interface and overrides its getErrorPath()to return a custom path.
package com.javadevjournal.controller;
import org.springframework.boot.web.servlet.error.ErrorController;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
@Controller
public class CustomErrorController implements ErrorController {
private static final String PATH = "/error";
@RequestMapping(value = PATH)
public String error() {
return "customError";
}
@Override
public String getErrorPath() {
return PATH;
}
}Let’s have a look at the above code.
- Our controller creates a mapping for the path as returned by
getErrorPath()method. - ErrorController interface shows that a
@Controlleris used to render errors. - We have the option to use
getErrorPath()to return different error pages based on the error type.
Let’s create a new error page which we will use in this new controller method.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<title>We've got some trouble</title>
</head>
<body>
<div class="cover">
<h1>Our apologies For Custom Page.</h1>
<p class="lead">This page stepped out for a quick ride.</p>
<p>Please go back to our homepage to restart your browsing experience.</p>
</div>
</body>
</html>When we run our application this time, we will have a different error page displayed to the customer.
Summary
In this post, we cover how to disable Spring Boot Whitelabel error page and how we can customize the Whitelabel error page in your Spring Boot application. We learned how to extend the error handling mechanism by implementing ErrorController in the custom error handling controller.
When you run the spring boot application in the sprint tool suite for the first time, you may encounter a Whitelabel error page error like below even if there are no coding or logic errors in the source code. You can also find there are no error messages logged out and your spring source code can not enter debug mode. This article will tell you how to resolve this issue.
Below is the Whitelabel error page error text.
Whitelabel Error Page This application has no explicit mapping for /error, so you are seeing this as a fallback Mon Nov 19 20:50:28 CST 2021 There was an unexpected error (type=Not Found. status=404). No message available
1. Resolve Whitelabel Error Page.
- If you set up the example follow the spring boot hello world example correctly, and the source code does not have any error. This is mainly because your spring boot application’s project files structure is not correct.
1.1 Correct Spring Boot Application Project Files Structure.
- As we know every spring boot application has a main application class that will be executed to initialize the spring boot application.
- And this spring boot application main class should be annotated with
@SpringBootApplicationannotation. - The
@SpringBootApplicationannotation is the combination of the annotations@Configuration, @ComponentScan and @EnableAutoConfiguration. @ComponentScancan configure the base package to scan the spring components and@EnableAutoConfigurationannotation can enable bean auto-configure in the application.- If there are more classes like the JPA class placed in a different(child) package than the spring boot main class package, so when you use the
@SpringBootApplicationannotation, you can not specify the base package value. - So if you use
@SpringBootApplicationannotation in your spring boot main class, you must place the main class in root package as bellow to avoid Whitelabel error page. - In the below spring boot example SpringBootWebMvcApplication.java is the main class. The root package is com.dev2qa.example, to avoid the Whitelabel error page, save the main class file in the root package.
C:WORKSPACEWORKDEV2QA.COM-EXAMPLE-CODESPRINGBOOTSPRINGBOOTWEBMVC │ .gitignore │ mvnw │ mvnw.cmd │ pom.xml │ ├───.mvn │ └───wrapper │ maven-wrapper.jar │ maven-wrapper.properties │ └───src ├───main │ ├───java │ │ └───com │ │ └───dev2qa │ │ └───example │ │ │ SpringBootWebMvcApplication.java │ │ │ │ │ ├───constant │ │ │ ConstantVariable.java │ │ │ │ │ ├───controller │ │ │ CustomErrorController.java │ │ │ EmployeeController.java │ │ │ │ │ ├───model │ │ │ Employee.java │ │ │ │ │ └───repository │ │ EmployeeRepository.java │ │ │ └───resources │ │ application.properties │ │ │ └───templates │ addEmployee.html │ error-500.html │ error.html │ listEmployee.html - Below is the content of the SpringBootWebMvcApplication.java file. You can see we use
@SpringBootApplicationannotation for the main class.package com.dev2qa.example; import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication; import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication; @SpringBootApplication public class SpringBootWebMvcApplication { public static void main(String[] args) { /* Responsible for launching the boot application. */ SpringApplication.run(SpringBootWebMvcApplication.class, args); } }
1.2 Use @ComponentScan Annotation And Specify Base Package.
- If you do not want to place the spring boot main class in the spring boot app root package, you can use
@Configuration, @ComponentScan and @EnableAutoConfigurationannotation to replace the@SpringBootApplicationannotation, and then specify the base package in the@ComponentScanannotation. - In the above example we place the spring boot main class SpringBootWebMvcApplication in com.dev2qa.example.mvc package and the base package is com.dev2qa.example. So to avoid the Whitelabel error page, we should use
@ComponentScanannotation and set the base packages in it.package com.dev2qa.example.mvc; import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication; import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.EnableAutoConfiguration; import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; @Configuration @ComponentScan(basePackages = {"com.dev2qa.example"}) @EnableAutoConfiguration public class SpringBootWebMvcApplication { public static void main(String[] args) { /* Responsible for launching the boot application. */ SpringApplication.run(SpringBootWebMvcApplication.class, args); } }
