Появление сообщения об ошибке 401 Unauthorized Error («отказ в доступе») при открытии страницы сайта означает неверную авторизацию или аутентификацию пользователя на стороне сервера при обращении к определенному url-адресу. Чаще всего она возникает при ошибочном вводе имени и/или пароля посетителем ресурса при входе в свой аккаунт. Другой причиной являются неправильные настройки, допущенные при администрировании web-ресурса. Данная ошибка отображается в браузере в виде отдельной страницы с соответствующим описанием. Некоторые разработчики интернет-ресурсов, в особенности крупных порталов, вводят собственную дополнительную кодировку данного сбоя:
- 401 Unauthorized;
- Authorization Required;
- HTTP Error 401 – Ошибка авторизации.
Попробуем разобраться с наиболее распространенными причинами возникновения данной ошибки кода HTTP-соединения и обсудим способы их решения.
Причины появления ошибки сервера 401 и способы ее устранения на стороне пользователя
При доступе к некоторым сайтам (или отдельным страницам этих сайтов), посетитель должен пройти определенные этапы получения прав:
- Идентификация – получение вашей учетной записи («identity») по username/login или email.
- Аутентификация («authentic») – проверка того, что вы знаете пароль от этой учетной записи.
- Авторизация – проверка вашей роли (статуса) в системе и решение о предоставлении доступа к запрошенной странице или ресурсу на определенных условиях.
Большинство пользователей сохраняют свои данные по умолчанию в истории браузеров, что позволяет быстро идентифицироваться на наиболее часто посещаемых страницах и синхронизировать настройки между устройствами. Данный способ удобен для серфинга в интернете, но может привести к проблемам с безопасностью доступа к конфиденциальной информации. При наличии большого количества авторизованных регистрационных данных к различным сайтам используйте надежный мастер-пароль, который закрывает доступ к сохраненной в браузере информации.
Наиболее распространенной причиной появления ошибки с кодом 401 для рядового пользователя является ввод неверных данных при посещении определенного ресурса. В этом и других случаях нужно попробовать сделать следующее:
- Проверьте в адресной строке правильность написания URL. Особенно это касается перехода на подстраницы сайта, требующие авторизации. Введите правильный адрес. Если переход на страницу осуществлялся после входа в аккаунт, разлогинитесь, вернитесь на главную страницу и произведите повторный вход с правильными учетными данными.
- При осуществлении входа с сохраненными данными пользователя и появлении ошибки сервера 401 проверьте их корректность в соответствующих настройках данного браузера. Возможно, авторизационные данные были вами изменены в другом браузере. Также можно очистить кэш, удалить cookies и повторить попытку входа. При удалении истории браузера или очистке кэша потребуется ручное введение логина и пароля для получения доступа. Если вы не помните пароль, пройдите процедуру восстановления, следуя инструкциям.
- Если вы считаете, что вводите правильные регистрационные данные, но не можете получить доступ к сайту, обратитесь к администратору ресурса. В этом случае лучше всего сделать скриншот проблемной страницы.
- Иногда блокировка происходит на стороне провайдера, что тоже приводит к отказу в доступе и появлению сообщения с кодировкой 401. Для проверки можно попробовать авторизоваться на том же ресурсе с альтернативного ip-адреса (например, используя VPN). При подтверждении блокировки трафика свяжитесь с провайдером и следуйте его инструкциям.
Некоторые крупные интернет-ресурсы с большим количеством подписчиков используют дополнительные настройки для обеспечения безопасности доступа. К примеру, ваш аккаунт может быть заблокирован при многократных попытках неудачной авторизации. Слишком частые попытки законнектиться могут быть восприняты как действия бота. В этом случае вы увидите соответствующее сообщение, но можете быть просто переадресованы на страницу с кодом 401. Свяжитесь с администратором сайта и решите проблему.
Иногда простая перезагрузка проблемной страницы, выход из текущей сессии или использование другого веб-браузера полностью решают проблему с 401 ошибкой авторизации.

Устранение ошибки 401 администратором веб-ресурса
Для владельцев сайтов, столкнувшихся с появлением ошибки отказа доступа 401, решить ее порою намного сложнее, чем обычному посетителю ресурса. Есть несколько рекомендаций, которые помогут в этом:
- Обращение в службу поддержки хостинга сайта. Как и в случае возникновения проблем с провайдером, лучше всего подробно описать последовательность действий, приведших к появлению ошибки 401, приложить скриншот.
- При отсутствии проблем на стороне хостинг-провайдера можно внести следующие изменения в настройки сайта с помощью строки Disallow:/адрес проблемной страницы. Запретить индексацию страницам с ошибкой в «rоbоts.txt», после чего добавить в файл «.htассеss» строку такого типа:
Redirect 301 /oldpage.html http://site.com/newpage.html.
Где в поле /oldpage.html прописывается адрес проблемной страницы, а в http://site.com/newpage.html адрес страницы авторизации.
Таким образом вы перенаправите пользователей со всех страниц, которые выдают ошибку 401, на страницу начальной авторизации.
- Если после выполнения предыдущих рекомендаций пользователи при попытках авторизации все равно видят ошибку 401, то найдите на сервере файл «php.ini» и увеличьте время жизни сессии, изменив значения следующих параметров: «session.gc_maxlifetime» и «session.cookie_lifetime» на 1440 и 0 соответственно.
- Разработчики веб-ресурсов могут использовать более сложные методы авторизации и аутентификации доступа для создания дополнительной защиты по протоколу HTTP. Если устранить сбой простыми методами администрирования не удается, следует обратиться к специалистам, создававшим сайт, для внесения соответствующих изменений в код.
Хотя ошибка 401 и является проблемой на стороне клиента, ошибка пользователя на стороне сервера может привести к ложному требованию входа в систему. К примеру, сетевой администратор разрешит аутентификацию входа в систему всем пользователям, даже если это не требуется. В таком случае сообщение о несанкционированном доступе будет отображаться для всех, кто посещает сайт. Баг устраняется внесением соответствующих изменений в настройки.
Дополнительная информация об ошибке с кодом 401
Веб-серверы под управлением Microsoft IIS могут предоставить дополнительные данные об ошибке 401 Unauthorized в виде второго ряда цифр:
- 401, 1 – войти не удалось;
- 401, 2 – ошибка входа в систему из-за конфигурации сервера;
- 401, 3 – несанкционированный доступ из-за ACL на ресурс;
- 401, 501 – доступ запрещен: слишком много запросов с одного и того же клиентского IP; ограничение динамического IP-адреса – достигнут предел одновременных запросов и т.д.
Более подробную информацию об ошибке сервера 401 при использовании обычной проверки подлинности для подключения к веб-узлу, который размещен в службе MS IIS, смотрите здесь.
Следующие сообщения также являются ошибками на стороне клиента и относятся к 401 ошибке:
- 400 Bad Request;
- 403 Forbidden;
- 404 Not Found;
- 408 Request Timeout.
Как видим, появление ошибки авторизации 401 Unauthorized не является критичным для рядового посетителя сайта и чаще всего устраняется самыми простыми способами. В более сложной ситуации оказываются администраторы и владельцы интернет-ресурсов, но и они в 100% случаев разберутся с данным багом путем изменения настроек или корректировки html-кода с привлечением разработчика сайта.
The 401 HTTP Status Code means that the request is unauthorized which indicates that the client request was not completed because the client did not provide valid authentication credentials for the requested resource. This Status Code is accompanied by an HTTP WWW-Authenticate response header that specifies how the client can re-request the resource after prompting the user for authentication credentials. It’s a bit like the 403 Forbidden Status Code, except that user authentication can allow access to the resource in some cases. The CONNECT HTTP Method is used in the 401 HTTP Status Code. The 400 HTTP Status Code indicates that the server was unable to interpret the request because of an inaccurate syntax, while the 401 HTTP Status Code indicates that the server needs to authenticate the client before it can access a resource.
What does 401 HTTP Status Code Mean?
The 401 HTTP Status Code which means unauthorized is returned when the server refuses to respond to a request because the client authentication required to access the resources is missing.
How to Use 401 HTTP Status Code for a Website?
To use the 401 HTTP Status Code, the server must authorize the client before it may access a resource.
How to Check 401 HTTP Status Code?
To check 401 HTTP Status Code Unauthorized Errors are listed below.
- Check The URL: Verifying the URL and correcting any errors will resolve the 401 error status.
- Flush the DNS: DNS errors can also result in a 401 error status. As a result, clearing the DNS will also resolve this issue. In Windows, you can flush the DNS by typing ipconfig/flushdns and pressing ENTER.
- Clear Browser Cookie: In some cases, cookies may fail to function properly, resulting in improper server authentication. Thus, the error can be corrected by clearing the cookies.
- Logging out and Logging in again: Refreshing the website and logging in with the same credentials may also resolve this error.
- Website mistake: Occasionally, even if all of the above are correct, you will receive the 401 Unauthorized Error, which is a website error. At that point, you should contact the website’s webmaster and inform them of the server’s downtime.
Which HTTP Method is used with 401 HTTP Status Code?
The HTTP methods that are used with the 401 HTTP Status Codes are given below.
- POST HTTP Method: The POST HTTP method is used in the 401 HTTP Response Status code. The POST method sends an entity to the specified resource, frequently resulting in a change in the server’s state or side effects.
- GET HTTP Method: The GET HTTP method is used in the 401 HTTP Response Status code. The GET method is used to get a representation of a resource. Requests made with the GET method should only return data.
The related HTTP Response Headers with 401 HTTP Status Code are listed below.
- HTTP Authentication: The 401 HTTP Status Code is related with the HTTP Authentication which gives a general framework for how to control and authenticate access.
- WWW-Authenticate HTTP Header: The 401 HTTP Status Code is related with the WWW-Authenticate HTTP Header which describes the HTTP authentication methods (referred to as “challenges”) that may be used to get access to a certain resource.
- Authorization HTTP Header: The 401 HTTP Status Code is related to the Authorization HTTP Header that can be used to authenticate a user agent with a server, granting access to a protected resource.
- Proxy-Authorization HTTP Header: The 401 HTTP Status Code is related with the Proxy-Authorization HTTP Header which holds the credentials required to authenticate a user agent against a proxy server, typically after the server responds with a 407 Proxy Authentication Required Status Code and the Proxy-Authenticate HTTP Header.
- Proxy-Authenticate HTTP Header: The 401 HTTP Status Code is related with the Proxy-Authenticate HTTP Header thet defines the authentication method that should be utilized to acquire access to a resource that is being accessed through a proxy server. It authenticates the request and authorizes the proxy server to relay it farther.
What are the Browsers Compatibility of 401 HTTP Status Code?
You can see the table that shows the browser’s compatibility of the 401 HTTP Status Code below.
| Browsers Name | Browser Compatibility of 401 HTTP Status Code |
| Chrome | YES |
| Edge | YES |
| Firefox | YES |
| Internet Explorer | YES |
| Opera | YES |
| Safari | YES |
| WebView Android | YES |
What are the other Similar Status Codes to 401 HTTP Status Code?
There are other similar HTTP Status Codes to the 401 HTTP Status Code. The following are listed below.
- 403 Forbidden HTTP Status Code: The 403 HTTP Status Code is similar to the 401 HTTP Status Code because they are both client error responses. The 403 HTTP Status Code indicates that the client lacks access permissions to the material; in other words, it is unauthorized, and so the server will not provide the requested resource. Unlike 401 Unauthorized, the server is aware of the client’s identity.
- 404 Not Found HTTP Status Code: The 404 HTTP Status Code is similar to the 401 HTTP Status Code because they are both client error responses. The 404 HTTP Status Code indicates that the server has been unable to locate the requested resource. This indicates that the URL is not recognized by the browser. This can also signify that the endpoint is correct but the resource does not exist in the API. Additionally, servers may use this response rather than 403 Forbidden to conceal the existence of a resource from an unauthorized client. Due to its frequent presence on the web, this response code is likely the most well-known.
- 405 Method Not Allowed HTTP Status Code: The 405 HTTP Status Code is similar to the 401 HTTP Status Code because they are both client error responses. The 405 HTTP Status Code indicates that the server is aware of the request method but the target resource does not support it. For instance, an API may not permit the use of DELETE to delete a resource.
- 407 Proxy-Authentication Required HTTP Status Code: The 407 HTTP Status Code is similar to the 401 HTTP Status Code because they are both client error responses. The 407 HTTP Status Code indicates that authentication must be performed through a proxy.
- Author
- Recent Posts
Holistic SEO & Digital has been built by Koray Tuğberk GÜBÜR. Holistic SEO is the process of developing integrated digital marketing projects with every aspect including Coding, Natural Language Processing, Data Science, Page Speed, Digital Analytics, Content Marketing, Technical SEO, and Branding. Structured, Semantic Search Engine improves its ability to detect the real-world entities, today. Having a simple website is not enough anymore. To show that your brand is authoritative, trustworthy, and expert on its own niche, you need entity-based Search Engine Optimization Projects. Holistic SEO & Digital’s main focus is on improving the brand’s organic visibility and growth potential.
The proper 401 Error meaning is an HTTP status code that indicates the request lacks valid authentication credentials for the requested resource. It means that the server knows about the client but the client doesn’t have sufficient permissions to access the resource and is not authorized to do so without proper authentication.
If you are a web developer, admin, or regular user, knowing the importance of the 401 Error is crucial because it helps you diagnose and troubleshoot issues related to authentication and access control.
For example, if you are an administrator, it will help you implement effective security measures. Meanwhile, for regular users, it will be beneficial for them to understand the reason behind denied access to certain resources.
![What is an HTTP 401 Error and How to Fix it? [7 Methods] 3 HTTP Error 401](https://www.wpoven.com/blog/wp-content/uploads/2023/05/1-3.png.webp)
401 Error variations
Here are some of the 401 error variations which indicate the same:
- HTTP Error 401
- Access denied
- 401 Unauthorized Error
- 401 Authorization Required
- 401 Unauthorized
Understanding HTTP Status codes
If you are a non-techie and don’t know exactly what are HTTP status codes, they can be understood as a set of standardized three-digit numbers used by web servers to communicate the outcome of a client’s request.
This means they provide you with the status or information about the success redirection, type of errors, and other states of the request-response cycle.
These status codes play a crucial role in web communication as they provide important feedback, indicating whether a request was successful or encountered any problems. With the assistance of these codes, one can readily take appropriate actions based on the response received from the server.
Now, when discussing the 4xx series status codes, such as 401 errors, they are typically classified as client error codes. This series indicates that the client’s request has failed or is invalid due to certain reasons. These error codes generally represent the issues or errors caused by the client’s request or a lack of proper authentication.
Some examples of 4xx Series error codes
As we have already discussed, the 4xx series is called client-side errors which includes some of the popular error codes that you might have familiar with.
- 400 (Bad Request Error)
- 403 (Forbidden)
- 404 (Not Found)
Now, let us focus on 401 Error. This error is specifically used when the client is unable to provide valid authentication credentials to access a resource. Its main purpose is to show the client that the requested resources require valid credentials to proceed further.
What causes 401 Error?
Some of the most common scenarios when you might face a 401 Error message:
- Missing or invalid credentials: If you are unable to provide authentic credentials due to any reasons or provide incurred or expired credentials, a 401 error will be triggered.
- Unauthorized access attempt: When you try to access a resource that requires authentication, but the provided credentials do not grant sufficient permission, a 401 Error will be returned.
- Revoked or Expired tokens: If you use an expired or outdated authentication token, the server may respond with a 401 error.
- Corrupt or outdated Browser cache and cookies: If you ever see a 401 error, it’s usually because your browser’s cache and cookies are outdated or corrupted. This can cause trouble with authorization. If your browser doesn’t have the correct authentication credentials (or any at all), the server won’t accept your request. Just remember to keep your browser’s cache and cookies up to date to avoid running into these kinds of errors.
- Incorrect or Outdated URL: Sometimes, in a rush, you might mistakenly enter the wrong URL or encounter a situation where the URL has been changed. This can trigger a 401 error as a result.
- Plugin conflicts: Sometimes, a 401 error can happen because of a plugin issue. For example, if you are using a firewall or security plugin that might mistakenly think your login attempt is suspicious and block access with a 401 error to keep the page safe.
How a 401 Error affects the user experience?
The 401 Error code can have various impacts on the user experience. It typically results in the user being denied access to the requested resource or receiving an error page instead. The error message associated with the 401 Error should provide guidance on how to resolve the issue or provide appropriate instructions.
Now that you have obtained a solid understanding of the 401 unauthorized error and its background, let’s delve into the methods to resolve and fix this issue.
- Ensure the URL is correct
- Check Authentic credentials
- Clear your browser cache and cookies
- Flush Your DNS cache
- Disable WordPress Plugins
- Check out your website’s .htaccess file
- Check the WWW-Authenticate header
1. Ensure the URL is correct
One of the most common mistakes that many users make is typing an incorrect URL in the browser’s address bar. Therefore, it’s important to take a moment and carefully enter the correct URL, ensuring that there are no misspelled or outdated entries.
If you happen to enter a wrong, outdated, or misspelled URL, you might encounter an “Error code 401” message. But there’s no need to worry! This error simply indicates that the URL you were trying to access doesn’t exist, resulting in a “401 unauthorized access” response from the server.
Let us understand it with an example, Suppose you have bookmarked a page or saved its address in your browsers, but things can change over time. The page’s address might have been updated or even deleted.
To investigate it further, you can try going to the website’s homepage and looking for a link to the page that is causing the “Unauthorized 401” error. If the page opens correctly through that link, make sure to compare the URL of the page with the one that initially gave you the error.
2. Ensure correct Authentication credentials
Sometimes, you might come across the frustrating 401 Error code when you’re trying to access a locked resource, such as a password-protected page. It basically means that your authentication credentials are not valid, and as a result, you’re denied access to the page you’re trying to open.
Here’s what you can do to tackle this issue. Take your time to double-check if you are logged in with the correct login credentials such as the user ID and password or not.
If you’re confident that you’ve entered the details correctly, you might want to consider changing your password. This could help ensure that you have the right credentials to access the resource without any hiccups.
However, in case you are unable to access your password-protected website, Check out our complete guide on “How To Easily Reset WordPress & Start Over?“.
3. Clear your browser cache and cookies
Without a doubt, browser cache and cookies are intended to enhance your online experience by speeding up website loading. However, there are occasions when they can also be the culprit behind triggering errors.
Specifically, corrupted or outdated cache files and cookies can result in unexpected interruptions or browsing issues. To resolve this, the best course of action is to completely clear your browser’s cache and cookies.
If you are using Chrome browser, follow the steps given below:
Read: 🚩 Browser Market Share & Usage Statistics
Step 1: Depending on your browser, Go to the settings menu.
In Google Chrome, for example, you can find the settings menu by clicking on the three vertical dots located in the upper right corner of the window.
Step 2: To proceed, select “More tools” and then click on “Clear browsing data”.
![How to fix the DNS_PROBE_STARTED Error? [8 Ways] 7 Clear browsing data in Chrome](https://www.wpoven.com/blog/wp-content/uploads/2023/03/7.png)
Step 3: A pop-up window will be displayed, and you can choose all three options located under the “Basic” section as depicted in the picture below. These options consist of “Browsing history,” “Cookies and other site data,” and “Cached images and files.
Step 4: Click on “Clear data” to initiate the process.
![How to fix the DNS_PROBE_STARTED Error? [8 Ways] 8 Clearing data in Google Chrome](https://www.wpoven.com/blog/wp-content/uploads/2023/03/8.png)
By doing so, any corrupt or invalid information stored locally in your browser will be completely erased. This ensures that if it was causing the authentication issue, it won’t occur again.
4. Flush your DNS Cache
Similar to your browser cache and cookies, the DNS cache is also stored locally on your computer. Although it is uncommon for a DNS cache to trigger a 401 error, it is worth giving it a try as a troubleshooting step.
For Windows 10 and Windows 11 users:
Step 1: Open the Run command by pressing the Windows key and R. Alternatively, you can search for it in the Start menu.
Step 2: Type “cmd” and hit Enter to open the Command Prompt.
![How to fix the DNS_PROBE_STARTED Error? [8 Ways] 13 Opening Command Prompt in Windows](https://www.wpoven.com/blog/wp-content/uploads/2023/03/6.png)
Step 3: Once the Command Prompt window is open, type “ipconfig/release” to release your current IP address.
![How to fix the DNS_PROBE_STARTED Error? [8 Ways] 14 Using Ipconfig command on CMD](https://www.wpoven.com/blog/wp-content/uploads/2023/02/ipconfig-release.png)
Step 4: Next, type “ipconfig/flushdns” to release the DNS cache.
Step 5: Type “ipconfig /renew” to obtain a new IP address.
![How to fix the DNS_PROBE_STARTED Error? [8 Ways] 15 ipconfig renew](https://www.wpoven.com/blog/wp-content/uploads/2023/02/ipconfig-renew.png)
Step 6: Type “netsh int ip set dns” and hit Enter to reset your IP settings.
Step 7: Finally, type “netsh winsock reset” to restore the Winsock Catalog.
![How to fix the DNS_PROBE_STARTED Error? [8 Ways] 16 netsh winsock reset](https://www.wpoven.com/blog/wp-content/uploads/2023/02/netsh-winsock-reset.png)
Step 8: After completing these steps, restart your computer to ensure the changes take effect.
For MacOS users:
Step 1: First of all, open the system preference options on your Mac. If you have Gas Mask installed, it can make searching for system-related tasks easier.
Step 2: Next, navigate to the Ethernet tab and click on the advanced options.
Step 3: Under the TCP/IP tab, you will find the option to release a DHCP lease. Clicking on this option will allow you to clear out the local DNS on your Mac.
![How to fix the DNS_PROBE_STARTED Error? [8 Ways] 17 Renew DHCP in MacOS](https://www.wpoven.com/blog/wp-content/uploads/2023/02/renew-DHCP-lease.png)
Step 4: Go to Utilities > Terminal and enter the command to clear the local DNS cache.
Step 5: The command for flushing the local DNS cache is “dscacheutil -flushcache”.
Step 6: Once you have entered the command, there will be no separate success or failure message that pops up. However, in most cases, the cache will be cleared without any major issues.
5. Disable WordPress Plugins
It is important to note that the cause of the 401 error may not always lie with your browser, but rather with your WordPress plugins. If you are experiencing difficulties accessing your WordPress site, it is possible that certain plugin(s) are responsible for this issue.
Especially, security plugins have a reputation for causing these types of problems. These plugins are designed to block access and return a 401 error message if they detect any suspicious activity.
Another possibility is that there may be compatibility issues with certain plugins. Some plugins can conflict with your website and trigger such issues. In such cases, the best course of action is to disable all the installed WordPress plugins and check if this resolves the issue.
Step 1: Log in to your WordPress admin dashboard
Step 2: Navigate to the “Plugins” menu option on the left-hand side of the dashboard.
Step 3: A list of installed plugins will be displayed. Take note of the currently active plugins or make a list if needed.
Step 4: Select all the plugins by ticking the checkboxes next to their names or use the “Bulk Actions” dropdown menu to select all.
Step 5: From the “Bulk Actions” dropdown menu, choose “Deactivate” and click the “Apply” button. This will deactivate all the selected plugins simultaneously.
![What is an HTTP 401 Error and How to Fix it? [7 Methods] 4 Deactivate WordPress Plugins](https://www.wpoven.com/blog/wp-content/uploads/2023/05/4-3.png.webp)
Step 6: Once the deactivation process is complete, try accessing your website and check if the 401 error is resolved.
If the error is no longer occurring, it indicates that one or more of the plugins were causing the issue. You can then proceed with identifying the conflicting or incompatible plugins by reactivating them one by one and testing the website after each activation until the error reappears. This way, you can pinpoint the specific plugin causing the conflict.
If you find the defective plugin, consider either updating it to a newer version or reaching out to the plugin developer for support. Alternatively, you may need to find an alternative plugin that serves a similar purpose but does not cause conflicts.
6. Check out your website’s .htaccess file
You might be surprised to learn, especially if you are not aware of it, that the hosting panel is not the only place where you can set a password for your website. Another method is by configuring the code in the .htaccess file.
If you have previously set a password through the .htaccess file but have either forgotten about it or it was added through a plugin, it’s essential to check or examine your website’s .htaccess file to determine if it is causing the issue.
Let us see how you can proceed.
If your web hosting provider offers you cPanel accessibility, it will become easy for you to locate WordPress .htaccess files without using an FTP client.
1. To do this, first, you need to login into your cPanel as shown below:
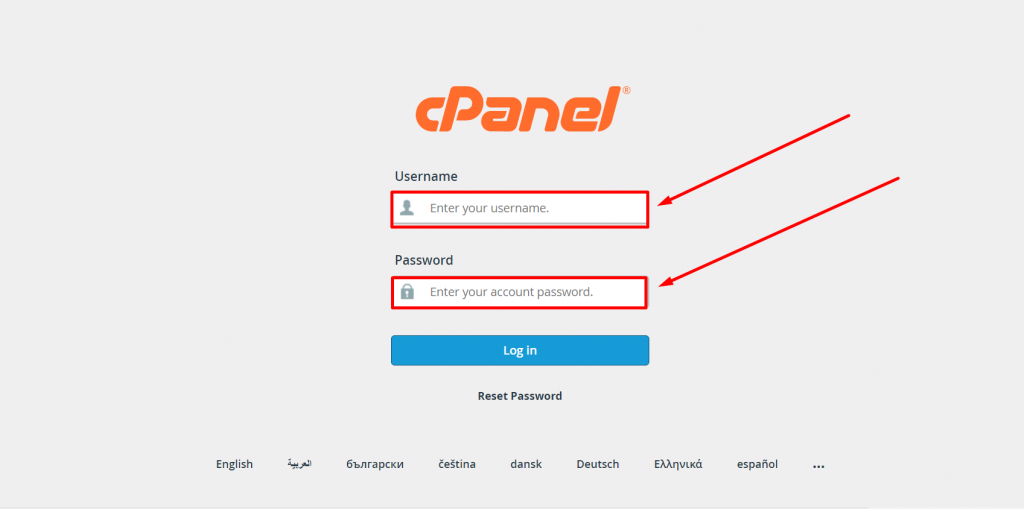
2. Lookout for the Files section and click on the File Manager option as shown.
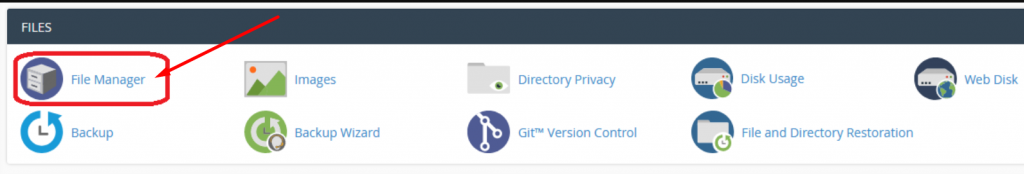
3. Now you will be able to see a list of all the core files displayed on your screen. Select and click on the public_html folder to open.
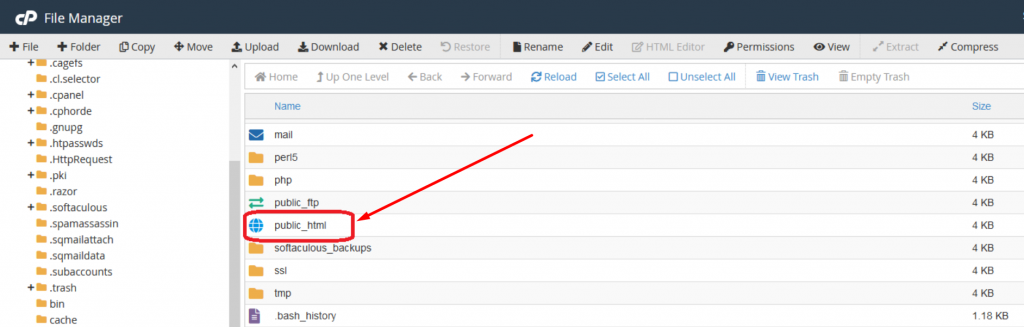
4. Now if you have an existing .htacess file available, it will reflect in the public_html or htdocs folder, if not then either it is hidden or doesn’t exist yet.
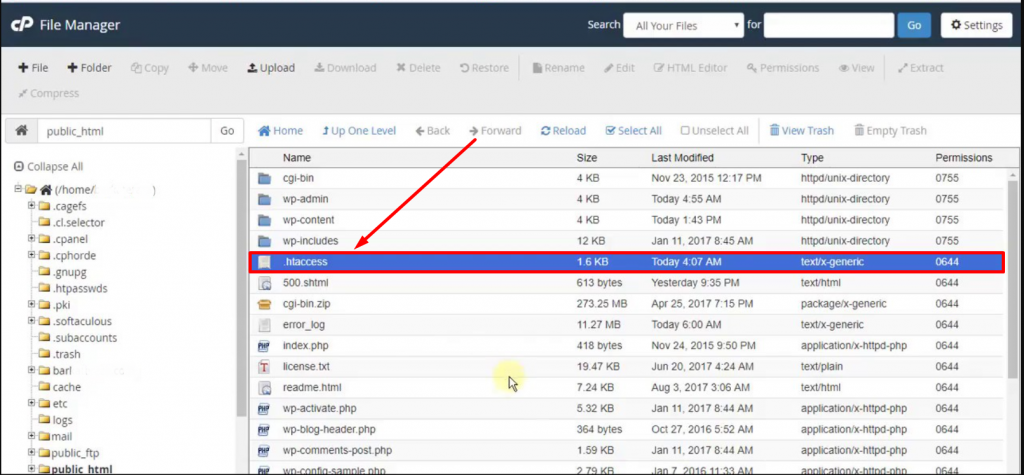
However, if your WordPress .htaccess file is hidden, you can unhide it by simply going to the Settings section located at the top right corner of the “files manager window” as shown in the image below:
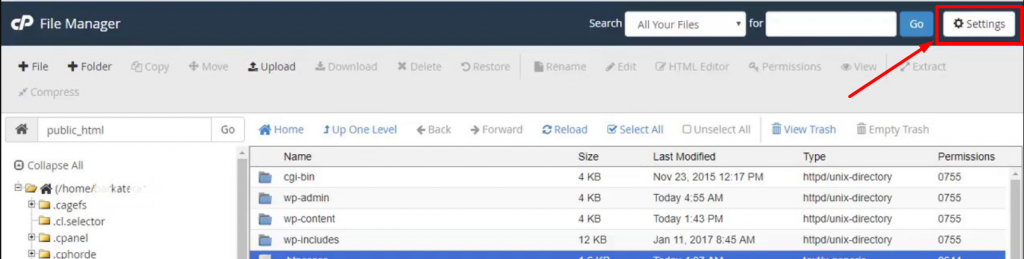
A preferences window will pop out as shown in the picture below:
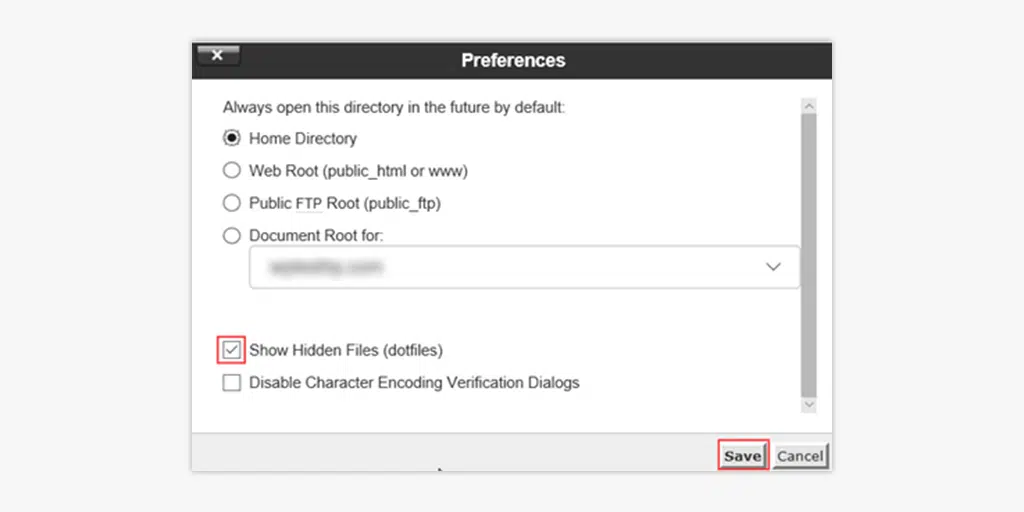
Now simply, check the ” Show Hidden Files (dotfiles)” box and click on Save. All the hidden files will start reflecting on your file manager window.
Read: 🚩 WordPress .htaccess File: How to Create And Edit it?
Now when you right-click on the .htaccess file and select the edit option, Its content should look similar to this:
AuthType Basic
AuthName "Permission required"
AuthUserFile ../../.htpasswd
require valid-user
The login credentials for the protection are stored in a file called “.htpasswd.” This file contains the encrypted password and the associated username.
If you no longer require the protection, you can remove the corresponding code from the .htaccess file and save the changes to confirm.
If the above troubleshooting methods don’t work, this means the issue is from the server side.
The “WWW-Authenticate” header is an HTTP response header that is used to indicate the type of authentication required for accessing a resource on a web server. When a server sends a “401 Unauthorized” status code, it includes the “WWW-Authenticate” header to specify the authentication scheme that the client needs to use in order to access the requested resource.
This header provides information to the client about the authentication method that should be used, such as Basic Authentication or Digest Authentication. It typically includes a challenge, which is a value that the client needs to include in subsequent requests to authenticate itself.
To check the “WWW-Authenticate” header, you can follow these steps:
Step 1: Open your web browser and navigate to the desired web page that generates a 401 error code.
Step 2: Right-click anywhere on the page and select “Inspect” or “Inspect Element” from the context menu. This will open the browser’s developer tools.
Step 3: In the developer tools, navigate to the “Network” tab.
![What is an HTTP 401 Error and How to Fix it? [7 Methods] 5 Network tab in browser's developers tools](https://www.wpoven.com/blog/wp-content/uploads/2023/05/2-2.png.webp)
Step 4: Refresh the page by pressing the “F5” key or clicking the refresh button in the browser.
Step 5: Look for the request corresponding to the resource you want to check in the list of network requests. It should have a “401 Unauthorized” status code.
Step 6: Click on the request to view its details.
Step 7: In the headers section, locate the “WWW-Authenticate” header. This header will provide information about the authentication scheme required for accessing the resource.
![What is an HTTP 401 Error and How to Fix it? [7 Methods] 6 Authentication scheme Information in header section](https://www.wpoven.com/blog/wp-content/uploads/2023/05/3-2.png.webp)
Step 8: The value of the “WWW-Authenticate” header will indicate the authentication method to be used, such as “Basic”, “Digest”, or others.
You can also refer to HTTP Authentication Scheme Registry for more information about page authentication methods.
Comparison: 401 vs 403 Error
The 401 Error differentiates itself by focusing specifically on the lack of valid authentication credentials. It indicates that the client needs to provide proper authentication to gain access to the resource, while the 400 and 403 errors highlight other issues, such as invalid requests or insufficient permissions.
Here is a comparison table between a 401 error and a 403 error:
| Error Code | Error Name | Meaning or authentication information |
|---|---|---|
| 401 | Unauthorized | Indicates the need for authentication. |
| The client lacks valid credentials |
| Error Code | Error Name | Meaning of authentication information. |
|---|---|---|
| 403 | Forbidden | Indicates that the client is authenticated, but lacks the necessary permissions to access the requested resource |
In summary, a 401 error signifies the need for authentication, while a 403 error indicates that the client is authenticated but lacks the necessary permissions to access the requested resource.
Real-world Examples of 401 Errors
Examples from popular websites or web applications
- Social media platform: If a user attempts to access a private profile or restricted content without logging in or providing valid credentials, a 401 Error may be returned.
- Cause: The user attempts to view a private post without logging in or providing valid credentials.
- Resolution: The platform returns a 401 Error and prompts the user to log in or create an account to gain access to the restricted content.
- Online banking: When a client tries to access account information or perform financial transactions without proper authentication, a 401 Error can occur.
- Cause: The user tries to access account details or perform financial transactions without providing the correct authentication credentials.
- Resolution: The banking system returns a 401 Error and directs the user to enter valid login credentials to access their account securely.
By analyzing real-world examples of 401 Errors, it becomes evident that these errors occur when accessing sensitive or restricted resources, emphasizing the importance of proper authentication and authorization.
Conclusion
A “401 Error” is triggered when the client lacks or is unable to provide valid authentication credentials to access a password-protected resource. Additionally, you may have noticed that this error is primarily caused by the client side, making it easily fixable. However, it can also be triggered from the server side, although this is rare.
So, in this post, we have compiled some of the best 7 troubleshooting methods that you can try to fix 401 errors.
- Ensure the URL is correct
- Check Authentic credentials
- Clear your browser cache and cookies
- Flush Your DNS cache
- Disable WordPress Plugins
- Check out your website’s .htaccess file
- Check the WWW-Authenticate header
We hope the methods mentioned above will help you fix the 401 error and resolve your issues. If you have any queries or would like to suggest any additional methods, please let us know in the comment section below.
Frequently Asked Questions
How do I fix a 401 error?
You can fix a 401 error by following these methods:
1. Ensure the URL is correct
2. Check Authentic credentials
3. Clear your browser cache and cookies
4. Flush Your DNS cache
5. Disable WordPress Plugins
6. Check out your website’s .htaccess file
7. Check the WWW-Authenticate header
What is the reason for 401 unauthorized error?
The reason for the 401 unauthorized error are:
1. Missing or invalid credentials
2. Unauthorized access attempt
3. Revoked or Expired tokens
4. Corrupt or outdated Browser cache and cookies
5. Incorrect or Outdated URL
6. Plugin conflicts
What is an example of a 401 error?
An example of a 401 error is If a user attempts to access a private profile or restricted content on a social media platform without logging in or providing valid credentials, a 401 Error may be returned.
Occasionally, when you try to access a web page, you may stumble across the “401 Error Unauthorized Access”. Like other HTTP errors, there could be various causes. This article will outline the most common problems and how to fix them.
The HTTP status code “401 Unauthorized Access” is a client-side error, which indicates that the website’s server sends a “WWW-Authenticate” header response back to the visitor with a challenge. Since the visitor failed to provide valid authentication credentials for the target resource, access has been denied, and the error page has been loaded.
In other words, you get this error because you are trying to access a page protected by the server. The server requires the correct login details to grant you access. The exact error message may vary depending on your browser or the website’s hosting server. Other variations of the 401 error are:
- HTTP 401 Error – Unauthorized
- Access Denied
- Error 401 Unauthorized
- 401 Unauthorized
- 401 Authorization Required
Usually, when you visit a protected page, you will first see a login prompt. It will require a username and password.

To view the page, you need to provide the correct logins. If you cancel the prompt or provide incorrect credentials, you will see the message with the error. You can see an example of the error page below.

In many cases, the website owners intentionally protect the page’s URL with a password. They prefer that the page remains inaccessible for the general visitor until fully developed, or they want this page to be available to authorized users only.
What causes the “401 Error Unauthorized Access”?
Although the URL protection may be set by design, there are cases where the restriction is set unintentionally or caused by local issues from the visitor’s side. We will examine the most common causes below.
Expired browser cache or cookies
Modern browsers keep local cache and cookies in your device to improve the loading speed. However, if your browser’s cache is corrupted or expired, it may prevent you from accessing the page correctly, and the error “401 Unauthorized Access” may occur.
Incorrect URL
Another cause of the error page is an incorrect webpage URL. It may be an outdated page address or a misspelled URL.
Protected URL from the server
Many hosting providers offer the functionality to set password protection directly on the server. The login prompt may come from such protection specified in the hosting panel.
Plugin misconfiguration
Another common cause of restricted access is plugin functionality. For example, many security plugins for WordPress provide different options to limit or restrict access. If the plugin is misconfigured, it may prevent access by mistake or detect a legitimate visit as suspicious activity.
Restrictions in the .htaccess file of the site
Password protection may come from Apache directives in the website’s .htaccess file. The website owner may have set them previously and forgotten to remove them. The directives may have been added automatically by a plugin as well.
How to Fix the 401 Unauthorized Access?
Now that we listed the most common causes of the “401 Error Code”, we can explore the solutions.
Clear your browser cache and cookies
Corrupted and outdated browser cache and cookies can lead to unexpected behavior in your internet browsing. The “HTTP Error 401” is one of the possible results. Clearing your browser cache and cookies is recommended for troubleshooting the “401 Unauthorized” error as well as for most of the errors you encounter.
Below, you can see detailed instructions on how to clear the cache for various browsers and devices.
- How to clear cache and cookies in your browser?
- How to clear the cache in your iPhone or other iOS devices?
- How to clear the cache in your Android phone?
Clear your device’s DNS cache
Corrupted or outdated local DNS settings in your device are not a very common cause of the “401 HTTP Error”. Nonetheless, it is worth considering flushing the device’s DNS cache. Depending on the operating system (OS), the process is different.
For detailed instructions, check the following guides:
- How to flush the DNS cache in Windows?
- How to flush the DNS cache in Mac?
- How to flush the DNS cache in Linux?
Inspect the website URL
Carefully check the URL of the page in your browser’s address bar. You may see the “Error code 401” if you try to access an outdated or misspelled URL. It means that the URL is non-existent, and the server may return a server error “401 Unauthorized Access”.
Maybe you saved the page address in your browser, but the page address has been changed, or it has been deleted. To test further, open the website home page and check if there is a link to the page producing the “Unauthorized 401” error. If the page opens this way, check if the URL of the page is the same as the one that triggered the error.
Revise the web hosting’s security settings
If none of the solutions so far helped and you are the website owner, you may need to look closer into the security settings of the website. If you see the login prompt on the page and you don’t recognize it, the URL may be protected by the server.
To examine this possibility, open your hosting panel and check if there is a tool for setting password protection.
SiteGround users have the feature Protected URLs in Site Tools. For more information, read this guide on how to password-protect a URL.
To check its settings, open Site Tools for the website, navigate to the Security section, and open Protected URLs.
If the URL is protected, you will see it listed in the section Manage Protected URLs.

If this protection is not needed, you can delete it. Under the Actions column, select the Delete icon (trash bin). A popup will appear to confirm the action. Select Confirm to delete the URL protection.

If the protection was intended, but the logins are not accepted in the login prompt, you may have the wrong username or password. You can see the existing user for the protected URL in Manage Protection URLs under the column Users.
To make sure you have the correct user password, select the section USERS. In the USERS section, select the kebab menu under the column Actions. Select Change Password to reset the password.

Another possibility is that the protection was set with a user that was later deleted. The protection remains active, but since there is no existing user, the login prompt can not be completed.
When you open the section URLS in Protected URLs, there will be no assigned user.

To add a user to the URL, select the Manage Access button. You will see a popup window that allows you to add one of the existing users to the URL. Select the user from the drop-down menu Users and then press Confirm. If there is no existing user yet, you will be prompted to create one.

Reload the web page after the protection is deleted or the user and password are reset. The page should load properly if the protection is deleted. If you’ve kept the protection, test the user and password. After the logins are entered, you should load the page correctly.
Inspect the website’s .htaccess file
The hosting panel is not the only source of password protection. If it is not set in the hosting panel but the website still prompts a login, it may be forced by directives in its .htaccess file.
Perhaps you set the .htaccess code earlier, and you forgot about it, or it was added by a plugin.
To check if there are such directives, open the website’s folder from FTP or File Manager and inspect the .htaccess file.
SiteGround clients can use the respective Site Tools to review the .htaccess file. Navigate to the section Site and open File Manager.
In Site Tools, the root folder for your website is the website name/public_html. In our example, the website name is sg-testing.com. Hence, the root folder is sg-testing.com/public_html.
In this directory, find the file .htaccess, select it, and then choose Edit.

It will open the file in Editor mode and you can view the code.

In this example, the website’s protection is defined by the highlighted code:
AuthType Basic
AuthName "restricted area"
AuthUserFile /home/customer/www/sg-testing.com/public_html/.htpasswd
require valid-userThe protection’s login credentials are specified in the file .htpasswd. It contains the user name and the encrypted password.
If the protection is not intended, delete the code from the .htaccess file and confirm the changes with Save.
Deactivate the website’s security plugins
Another common cause of the error “401 Not Allowed” for WordPress sites is a misconfigured plugin. A security plugin may block visitors by mistake or force restrictions on specific pages.
To troubleshoot, you may consider disabling the plugins. Open your WordPress site dashboard, go to the Plugins section, then select Installed Plugins.
Look at the plugins’ description to find out which of your plugins provide security features.

Check the box for the plugin you wish to disable, then select Deactivate from the drop-down menu and hit Apply.
Test again if the page showing the “401 Error” message will now load correctly.
Sometimes, an ongoing error may prevent access to the dashboard. In such cases, you can disable all plugins for the website from Site Tools or its database.
Read the guides below for detailed instructions.
- How to disable WordPress plugins from Site Tools?
- How to disable WordPress plugins from the database?
After the plugins are disabled, you should be able to access the dashboard and activate the plugins one by one. When you enable the culprit, the error will most likely return.
If a plugin was the cause of the “Unauthorized Error 401”, contact its support to report the error or replace it with an alternative one.
Summary
Fixing the 401 unauthorized error may require investigation, but it is important to note that it is related to the security and protection settings of the websites.
This guide examined the common causes and how to fix the error “401 Access Denied”.
Another similar error related to restricted access is the HTTP Error 403. Read more about it in the following guide on what is 403 Forbidden Error and how to fix it.
For more information on the various HTTP codes, read this article on HTTP status codes explained.
I’m using cUrl in the client side.
On my webservice (ws.php), i’ve this simple code :
<?php
header('HTTP/1.1 401 Unauthorized', true, 401);
echo 'This is an error';
exit;
?>
When i call this ws.php page, i still have http_code = 200.
Here is my cUrl code is client side :
$ch = curl_init();
curl_setopt($ch, CURLOPT_URL, "webservice_url");
curl_setopt($ch, CURLOPT_RETURNTRANSFER, true);
curl_setopt($ch, CURLOPT_HEADER, FALSE);
curl_setopt($ch, CURLOPT_REFERER, $_SERVER['HTTP_HOST'] . $_SERVER['SCRIPT_NAME']);
curl_setopt($ch, CURLOPT_POST, true);
curl_setopt($ch, CURLOPT_POSTFIELDS, $post_variables); //array()
$response = curl_exec($ch);
$code = curl_getinfo($ch,CURLINFO_HTTP_CODE);
curl_close($ch);
$code = 200 even i put the header code «401».
