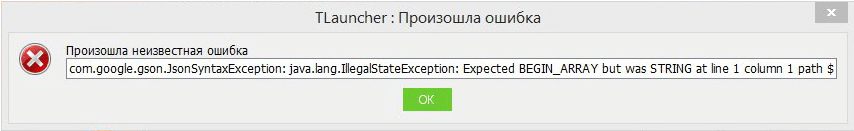
При запуске игры, может появится ошибка com.google.gson.JsonSyntaxException: java.lang.IllegalStateException: Expected BEGIN_ARRAY but was STRING at line 1 column 1 path $ и запуск не произойдёт.
1 решение
Скачать последнюю версию лаунчера: Скачать TLauncher
2 решение
Удалить из папки .minecraft (Чтобы зайти в неё, нажмите на иконку «Папки» в лаунчере) следующий файл: TempOptifineStore-1.0.json (Плюс удалить файлы из папки mods)
3 решение
Если не помог первый способ, полностью попробуйте удалить папку .minecraft (Сохранив нужные вам папки: saves и mods, например) и переустановить версию игры.
Читайте также:
— Как установить HD скин в TLauncher
— Как установить плащ в TLauncher
Если Ваша проблема остаётся актуальной, запросите поддержку у TLauncher:
Написать разработчикам с помощью VK.com
In this article I have told how you can fix this error of Minecraft – (Failed to connect to the server internal exception: java.lang.IllegalStateException: Invalid Characters in Username)
Before fixing this Invalid Username Error, we will know why this Invalid Characters in Username Error comes, after that we will fix this error.
Why does (Invalid characters in Username) error occur in Minecraft?
When you open any world by running minecraft java edition by Tlauncher, then you will get to see this (Failed to connect to the server Internal Exception: java.lang.illegalStateException: Invalid Characters in Username) problem.
The reason for this error to come is Username because if you have left space in Username in Tlauncher, then you get to see this problem due to not writing the name in Username correctly, so let us now know that this (Invalid Characters in Username ) How to fix the problem.
Fix Minecraft java.lang.illegalStateException: Invalid Characters in Username
So now we know how to fix this Minecraft Java Edition (Invalid Characters in Username) Error. There is a very easy way to solve this Minecraft Java Edition Errors, you have to first open your Tlauncher, after that whenever you write the name in username, you do not have to give space at all, you have to write name in the username simultaneously and As soon as you write name at once without leaving a space.

Then after that in Tlauncher you will see a box unchecked at the bottom, then you have to tick it there, so now this minecraft problem is fixed, now if you open any world in Minecraft Java Edition, there you will find this (Invalid Character in) username) problems will not be found, you can fix it like this (java.lang.illegalStateException: Invalid character in username) problem.
Note :- Please ignore
JRE for Android
PojavLauncher (old) Download
PojavLauncher New Custom Control Download :-
Download Now
Пожалуйста, расскажите про вашу проблему и не забывайте указать ссылку на проблемную сборку.
Небольшое объявление №2

Автор
are244,
16 февраля, 2022 в Технические проблемы
Рекомендуемые сообщения
В теме 3 сообщения

are244
Опубликовано 16 февраля, 2022
-
- Поделиться
Опубликовано 16 февраля, 2022
Ощибка java.lang.IllegalStateException: Expected BEGIN_OBJECT but was STRING at line 1 column 1 path $ : Expected BEGIN_OBJECT but was STRING at line 1 column 1 path $
Что делать?
Ссылка на комментарий
Поделиться на другие сайты

Shomen
Опубликовано 16 февраля, 2022
-
- Поделиться
Опубликовано 16 февраля, 2022
3 минуты назад, are244 сказал:
Ощибка java.lang.IllegalStateException: Expected BEGIN_OBJECT but was STRING at line 1 column 1 path $ : Expected BEGIN_OBJECT but was STRING at line 1 column 1 path $
Что делать?
удалить это г0вно с пк и установить tlauncher legacy
-
are244
-

1
Ссылка на комментарий
Поделиться на другие сайты

Code123123
Опубликовано 16 февраля, 2022
-
- Поделиться
Опубликовано 16 февраля, 2022
Решение ошибки: Expected BEGIN_ARRAY but was STRING at line 1 column 1 path $ в TLauncher
Ссылка на комментарий
Поделиться на другие сайты
Для публикации сообщений создайте учётную запись или авторизуйтесь
Вы должны быть пользователем, чтобы оставить комментарий
Создать учетную запись
Зарегистрируйте новую учётную запись в нашем сообществе. Это очень просто!
Регистрация нового пользователя
Войти
Уже есть аккаунт? Войти в систему.
Войти
Перейти к списку тем
-
Последние посетители
0 пользователей онлайн
- Ни одного зарегистрированного пользователя не просматривает данную страницу
For the past two days my sister has tried to start Minecraft but only to get this error after she presses play. —- Minecraft Crash Report —-
// Uh… Did I do that?
Time: 7/26/13 3:51 PM
Description: Unexpected error
java.lang.IllegalStateException: Cannot determine close requested state of uncreated window
at org.lwjgl.opengl.Display.isCloseRequested(Display.java:549)
at ats.S(SourceFile:647)
at ats.d(SourceFile:619)
at net.minecraft.client.main.Main.main(SourceFile:101)
A detailed walkthrough of the error, its code path and all known details is as follows:
—————————————————————————————
— System Details —
Details:
Minecraft Version: 1.6.2
Operating System: Windows 8 (x86) version 6.2
Java Version: 1.7.0_25, Oracle Corporation
Java VM Version: Java HotSpot™ Client VM (mixed mode, sharing), Oracle Corporation
Memory: 31330528 bytes (29 MB) / 69771264 bytes (66 MB) up to 518979584 bytes (494 MB)
JVM Flags: 1 total; -Xmx512M
AABB Pool Size: 0 (0 bytes; 0 MB) allocated, 0 (0 bytes; 0 MB) used
Suspicious classes: No suspicious classes found.
IntCache: cache: 0, tcache: 0, allocated: 0, tallocated: 0
Launched Version: 1.6.2
LWJGL: 2.9.0
OpenGL: ~~ERROR~~ RuntimeException: No OpenGL context found in the current thread.
Is Modded: Probably not. Jar signature remains and client brand is untouched.
Type: Client (map_client.txt)
Resource Pack: Default
Current Language: English (US)
Profiler Position: N/A (disabled)
Vec3 Pool Size: ~~ERROR~~ NullPointerException: null
I have no clue what it could be, we have the latest version of Java and Minecraft and we tried re installing Minecraft as well.
An unexpected, unwanted event that disturbed the normal flow of a program is called Exception.
Most of the time exception is caused by our program and these are recoverable. Example: If our program requirement is to read data from the remote file locating in U.S.A. At runtime, if a remote file is not available then we will get RuntimeException saying fileNotFoundException. If fileNotFoundException occurs we can provide the local file to the program to read and continue the rest of the program normally.
There are mainly two types of exception in java as follows:
1. Checked Exception:
The exception which is checked by the compiler for the smooth execution of the program at runtime is called a checked exception. In our program, if there is a chance of rising checked exception then compulsory we should handle that checked exception (either by try-catch or throws keyword) otherwise we will get compile-time error.
Examples of checked exceptions are ClassNotFoundException, IOException, SQLException, etc.
2. Unchecked Exception:
The exceptions which are not checked by the compiler, whether programmer handling or not such type of exception are called an unchecked exception.
Examples of unchecked Exceptions are ArithmeticException, ArrayStoreException etc.
Whether the exception is checked or unchecked every exception occurs at run time only if there is no chance of occurring any exception at compile time.
IllegalStateException is the child class of RuntimeException and hence it is an unchecked exception. This exception is rise explicitly by programmer or by the API developer to indicate that a method has been invoked at the wrong time. Generally, this method is used to indicate a method is called at an illegal or inappropriate time.
Example: After starting a thread we are not allowed to restart the same thread once again otherwise we will get Runtime Exception saying IllegalStateException.
Example 1: We call start() method when it’s already executing the run() method.
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
class myThread extends Thread {
public void run()
{
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
System.out.println("GeeksForGeeks");
}
}
}
class Thread1 {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
myThread t = new myThread();
t.start();
System.out.println("Main Thread");
t.start();
}
}

Example 2: We call start() method on a thread when it has finished executing run() method.
Java
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
class myThread extends Thread {
public void run()
{
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
System.out.println("GeeksForGeeks");
}
}
}
class Thread1 {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
myThread t = new myThread();
t.start();
try {
System.out.println("Main Thread is going to sleep");
t.sleep(2000);
System.out.println("Main Thread awaken");
}
catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println(e);
}
System.out.println("Main Thread");
t.start();
}
}

How to solve this error?
In order to avoid java.lang.IllegalStateException in Java main Thread we must ensure that any method in our code cannot be called at an illegal or an inappropriate time.
In the above example if we call start() method only once on thread t then we will not get any java.lang.IllegalStateException because we are not calling the start() method after the starting of thread (i.e we are not calling the start() method at an illegal or an inappropriate time.)
Java
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
class myThread extends Thread {
public void run()
{
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
System.out.println("GeeksForGeeks");
}
}
}
class Thread1 {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
myThread t = new myThread();
t.start();
try {
System.out.println("Main Thread is going to sleep");
t.sleep(2000);
System.out.println("Main Thread awaken");
}
catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println(e);
}
System.out.println("Main Thread");
}
}

An unexpected, unwanted event that disturbed the normal flow of a program is called Exception.
Most of the time exception is caused by our program and these are recoverable. Example: If our program requirement is to read data from the remote file locating in U.S.A. At runtime, if a remote file is not available then we will get RuntimeException saying fileNotFoundException. If fileNotFoundException occurs we can provide the local file to the program to read and continue the rest of the program normally.
There are mainly two types of exception in java as follows:
1. Checked Exception:
The exception which is checked by the compiler for the smooth execution of the program at runtime is called a checked exception. In our program, if there is a chance of rising checked exception then compulsory we should handle that checked exception (either by try-catch or throws keyword) otherwise we will get compile-time error.
Examples of checked exceptions are ClassNotFoundException, IOException, SQLException, etc.
2. Unchecked Exception:
The exceptions which are not checked by the compiler, whether programmer handling or not such type of exception are called an unchecked exception.
Examples of unchecked Exceptions are ArithmeticException, ArrayStoreException etc.
Whether the exception is checked or unchecked every exception occurs at run time only if there is no chance of occurring any exception at compile time.
IllegalStateException is the child class of RuntimeException and hence it is an unchecked exception. This exception is rise explicitly by programmer or by the API developer to indicate that a method has been invoked at the wrong time. Generally, this method is used to indicate a method is called at an illegal or inappropriate time.
Example: After starting a thread we are not allowed to restart the same thread once again otherwise we will get Runtime Exception saying IllegalStateException.
Example 1: We call start() method when it’s already executing the run() method.
Java
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
class myThread extends Thread {
public void run()
{
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
System.out.println("GeeksForGeeks");
}
}
}
class Thread1 {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
myThread t = new myThread();
t.start();
System.out.println("Main Thread");
t.start();
}
}

Example 2: We call start() method on a thread when it has finished executing run() method.
Java
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
class myThread extends Thread {
public void run()
{
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
System.out.println("GeeksForGeeks");
}
}
}
class Thread1 {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
myThread t = new myThread();
t.start();
try {
System.out.println("Main Thread is going to sleep");
t.sleep(2000);
System.out.println("Main Thread awaken");
}
catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println(e);
}
System.out.println("Main Thread");
t.start();
}
}

How to solve this error?
In order to avoid java.lang.IllegalStateException in Java main Thread we must ensure that any method in our code cannot be called at an illegal or an inappropriate time.
In the above example if we call start() method only once on thread t then we will not get any java.lang.IllegalStateException because we are not calling the start() method after the starting of thread (i.e we are not calling the start() method at an illegal or an inappropriate time.)
Java
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
class myThread extends Thread {
public void run()
{
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
System.out.println("GeeksForGeeks");
}
}
}
class Thread1 {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
myThread t = new myThread();
t.start();
try {
System.out.println("Main Thread is going to sleep");
t.sleep(2000);
System.out.println("Main Thread awaken");
}
catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println(e);
}
System.out.println("Main Thread");
}
}

When trying to invoke the Firebase Auth UI, using the below code the compiler throws java.lang.IllegalStateException: Launcher has not been initialized. Not sure, why the launcher is not initialized
@Composable
internal fun ProfileUI(profileViewModel: ProfileViewModel) {
val loginLauncher = rememberLauncherForActivityResult(
ActivityResultContracts.StartActivityForResult()
) { result ->
if (result != null) {
//do something
}
}
if (profileViewModel.isAnonymousUser) {
loginLauncher.launch(profileViewModel.buildLoginIntent())
} else {
}
}
override fun buildLoginIntent(): Intent {
val authUILayout = AuthMethodPickerLayout.Builder(R.layout.auth_ui)
.setGoogleButtonId(R.id.btn_gmail)
.setEmailButtonId(R.id.btn_email)
.build()
return AuthUI.getInstance().createSignInIntentBuilder()
.setIsSmartLockEnabled(!BuildConfig.DEBUG)
.setAvailableProviders(
listOf(
AuthUI.IdpConfig.EmailBuilder().build(),
AuthUI.IdpConfig.GoogleBuilder().build()
)
)
.enableAnonymousUsersAutoUpgrade()
.setLogo(R.mipmap.ic_launcher)
.setAuthMethodPickerLayout(authUILayout)
.build()
}
java.lang.IllegalStateException: Launcher has not been initialized
at androidx.activity.compose.ActivityResultLauncherHolder.launch(ActivityResultRegistry.kt:153)
at androidx.activity.compose.ManagedActivityResultLauncher.launch(ActivityResultRegistry.kt:142)
at androidx.activity.result.ActivityResultLauncher.launch(ActivityResultLauncher.java:47)
at com.madhu.locationbuddy.profile.ProfileUIKt.ProfileUI(ProfileUI.kt:37)
at com.madhu.locationbuddy.profile.ProfileUIKt.ProfileUI(ProfileUI.kt:15)
Any ideas on how to resolve this issue?
asked Jul 10, 2021 at 21:03
As per the Side-effects in Compose documentation:
Composables should be side-effect free.
Key Term: A side-effect is a change to the state of the app that happens outside the scope of a composable function.
Launching another activity, such as calling launch, is absolutely a side effect and therefore should never be done as part of the composition itself.
Instead, you should put your call to launch within one of the Effect APIs, such as SideEffect (if you want it to run on every composition) or LaunchedEffect (which only runs when the input changes — that would be appropriate if profileViewModel.isAnonymousUser was being driven by a mutableStateOf()).
Therefore your code could be changed to:
internal fun ProfileUI(profileViewModel: ProfileViewModel) {
val loginLauncher = rememberLauncherForActivityResult(
ActivityResultContracts.StartActivityForResult()
) { result ->
if (result != null) {
//do something
}
}
if (profileViewModel.isAnonymousUser) {
SideEffect {
loginLauncher.launch(profileViewModel.buildLoginIntent())
}
} else {
// Output your UI, etc.
}
}
answered Jul 10, 2021 at 21:17
ianhanniballakeianhanniballake
185k30 gold badges454 silver badges429 bronze badges
1
Скопируй сюда под спойлер содержимое файла:
C:Usersuserdownloadscrash-03-01-2017_22-55-40
RedServer V3 Crash Report
========================================
launcher.path = C:UsersUserDesktopRedServerV3 (1).exe
user.home = C:UsersUser
java.home = C:Program FilesJavajre1.8.0_144
java.lang.RuntimeException: Exception in Application init method
at com.sun.javafx.application.LauncherImpl.launchApplication1(LauncherImpl.java:912)
at com.sun.javafx.application.LauncherImpl.lambda$launchApplication$155(LauncherImpl.java:182)
at java.lang.Thread.run(Unknown Source)
Caused by: java.lang.RuntimeException: Failed to load launcher settings
at redserver3.ah.init(ah.java:101)
at com.sun.javafx.application.LauncherImpl.launchApplication1(LauncherImpl.java:841)
… 2 more
Caused by: java.io.IOException: JSON parse error
at redserver3.r.b(r.java:49)
at redserver3.ah.init(ah.java:99)
… 3 more
Caused by: com.google.gson.JsonSyntaxException: java.lang.IllegalStateException: Expected BEGIN_OBJECT but was STRING at line 1 column 1 path $
at com.google.gson.internal.bind.ReflectiveTypeAdapterFactory$Adapter.a(ReflectiveTypeAdapterFactory.java:224)
at com.google.gson.Gson.a(Gson.java:887)
at com.google.gson.Gson.a(Gson.java:825)
at redserver3.r.b(r.java:47)
… 4 more
Caused by: java.lang.IllegalStateException: Expected BEGIN_OBJECT but was STRING at line 1 column 1 path $
at com.google.gson.stream.JsonReader.y(JsonReader.java:385)
at com.google.gson.internal.bind.ReflectiveTypeAdapterFactory$Adapter.a(ReflectiveTypeAdapterFactory.java:213)
… 7 more
An IllegalStateException is a runtime exception in Java that is thrown to indicate that a method has been invoked at the wrong time. This exception is used to signal that a method is called at an illegal or inappropriate time.
For example, once a thread has been started, it is not allowed to restart the same thread again. If such an operation is performed, the IllegalStateException is thrown.
Since the IllegalStateException is an unchecked exception, it does not need to be declared in the throws clause of a method or constructor.
What Causes IllegalStateException
The IllegalStateException is thrown when the Java environment or application is not in an appropriate state for the requested operation. This can occur when dealing with threads or the Collections framework of the java.util package under specific conditions. Here are examples of some situations where this exception can occur:
- When the
Thread.start()method is called on a thread that has already been started. - When the
remove()method of theIteratorinterface is called on aListwithout calling thenext()method. This leaves theListcollection in an unstable state, causing anIllegalStateException. - If an element is attempted to be added to a
Queuethat is full. Adding elements beyond the size of the queue will cause anIllegalStateException.
IllegalStateException Example
Here’s an example of an IllegalMonitorStateException thrown when the Iterator.remove() method is called to remove an element from an ArrayList before calling the next() method:
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Iterator;
public class IllegalStateExceptionExample {
public static void main(String args[]) {
ArrayList<String> list = new ArrayList<String>();
list.add("a");
list.add("b");
list.add("c");
Iterator<String> it = list.iterator();
it.remove();
}
}Since the remove() method is used to remove the previous element being referred to by the Iterator, the next() method should be called before an element is attempted to be removed. In this case, the next() method was never called, so the Iterator attempts to remove the element before the first element.
Since this action is illegal, running the above code throws an IllegalStateException:
Exception in thread "main" java.lang.IllegalStateException
at java.base/java.util.ArrayList$Itr.remove(ArrayList.java:980)
at IllegalStateExceptionExample.main(IllegalStateExceptionExample.java:12)How to Fix IllegalStateException
To avoid the IllegalStateException in Java, it should be ensured that any method in code is not called at an illegal or inappropriate time.
In the above example, calling the Iterator.next() method on the ArrayList before using the remove() method to remove an element from it will help fix the issue:
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Iterator;
public class IllegalStateExceptionExample {
public static void main(String args[]) {
ArrayList<String> list = new ArrayList<String>();
list.add("a");
list.add("b");
list.add("c");
Iterator<String> it = list.iterator();
it.next();
it.remove();
System.out.println(list);
}
}Calling the next() method moves the Iterator position to the next element. Calling the remove() method afterwards will remove the first element in the ArrayList, which is a legal operation and helps fix the exception.
Running the above code produces the correct output as expected:
[b, c]Track, Analyze and Manage Errors With Rollbar
Managing Java errors and exceptions in your code is challenging. It can make deploying production code an unnerving experience. Being able to track, analyze, and manage errors in real-time can help you to proceed with more confidence. Rollbar automates error monitoring and triaging, making fixing Java errors easier than ever. Sign Up Today!
An IllegalStateException is a runtime exception in Java that is thrown to indicate that a method has been invoked at the wrong time. This exception is used to signal that a method is called at an illegal or inappropriate time.
For example, once a thread has been started, it is not allowed to restart the same thread again. If such an operation is performed, the IllegalStateException is thrown.
Since the IllegalStateException is an unchecked exception, it does not need to be declared in the throws clause of a method or constructor.
What Causes IllegalStateException
The IllegalStateException is thrown when the Java environment or application is not in an appropriate state for the requested operation. This can occur when dealing with threads or the Collections framework of the java.util package under specific conditions. Here are examples of some situations where this exception can occur:
- When the
Thread.start()method is called on a thread that has already been started. - When the
remove()method of theIteratorinterface is called on aListwithout calling thenext()method. This leaves theListcollection in an unstable state, causing anIllegalStateException. - If an element is attempted to be added to a
Queuethat is full. Adding elements beyond the size of the queue will cause anIllegalStateException.
Here’s an example of an IllegalMonitorStateException thrown when the Iterator.remove() method is called to remove an element from an ArrayList before calling the next() method:
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Iterator;
public class IllegalStateExceptionExample {
public static void main(String args[]) {
ArrayList<String> list = new ArrayList<String>();
list.add("a");
list.add("b");
list.add("c");
Iterator<String> it = list.iterator();
it.remove();
}
}Since the remove() method is used to remove the previous element being referred to by the Iterator, the next() method should be called before an element is attempted to be removed. In this case, the next() method was never called, so the Iterator attempts to remove the element before the first element.
Since this action is illegal, running the above code throws an IllegalStateException:
Exception in thread "main" java.lang.IllegalStateException
at java.base/java.util.ArrayList$Itr.remove(ArrayList.java:980)
at IllegalStateExceptionExample.main(IllegalStateExceptionExample.java:12)How to Fix IllegalStateException
To avoid the IllegalStateException in Java, it should be ensured that any method in code is not called at an illegal or inappropriate time.
In the above example, calling the Iterator.next() method on the ArrayList before using the remove() method to remove an element from it will help fix the issue:
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Iterator;
public class IllegalStateExceptionExample {
public static void main(String args[]) {
ArrayList<String> list = new ArrayList<String>();
list.add("a");
list.add("b");
list.add("c");
Iterator<String> it = list.iterator();
it.next();
it.remove();
System.out.println(list);
}
}Calling the next() method moves the Iterator position to the next element. Calling the remove() method afterwards will remove the first element in the ArrayList, which is a legal operation and helps fix the exception.
Running the above code produces the correct output as expected:
[b, c]Track, Analyze and Manage Errors With Rollbar
Managing Java errors and exceptions in your code is challenging. It can make deploying production code an unnerving experience. Being able to track, analyze, and manage errors in real-time can help you to proceed with more confidence. Rollbar automates error monitoring and triaging, making fixing Java errors easier than ever. Sign Up Today!
An unexpected, unwanted event that disturbed the normal flow of a program is called Exception.
Most of the time exception is caused by our program and these are recoverable. Example: If our program requirement is to read data from the remote file locating in U.S.A. At runtime, if a remote file is not available then we will get RuntimeException saying fileNotFoundException. If fileNotFoundException occurs we can provide the local file to the program to read and continue the rest of the program normally.
There are mainly two types of exception in java as follows:
1. Checked Exception:
The exception which is checked by the compiler for the smooth execution of the program at runtime is called a checked exception. In our program, if there is a chance of rising checked exception then compulsory we should handle that checked exception (either by try-catch or throws keyword) otherwise we will get compile-time error.
Examples of checked exceptions are ClassNotFoundException, IOException, SQLException, etc.
2. Unchecked Exception:
The exceptions which are not checked by the compiler, whether programmer handling or not such type of exception are called an unchecked exception.
Examples of unchecked Exceptions are ArithmeticException, ArrayStoreException etc.
Whether the exception is checked or unchecked every exception occurs at run time only if there is no chance of occurring any exception at compile time.
IllegalStateException is the child class of RuntimeException and hence it is an unchecked exception. This exception is rise explicitly by programmer or by the API developer to indicate that a method has been invoked at the wrong time. Generally, this method is used to indicate a method is called at an illegal or inappropriate time.
Example: After starting a thread we are not allowed to restart the same thread once again otherwise we will get Runtime Exception saying IllegalStateException.
Example 1: We call start() method when it’s already executing the run() method.
Java
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
class myThread extends Thread {
public void run()
{
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
System.out.println("GeeksForGeeks");
}
}
}
class Thread1 {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
myThread t = new myThread();
t.start();
System.out.println("Main Thread");
t.start();
}
}

Example 2: We call start() method on a thread when it has finished executing run() method.
Java
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
class myThread extends Thread {
public void run()
{
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
System.out.println("GeeksForGeeks");
}
}
}
class Thread1 {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
myThread t = new myThread();
t.start();
try {
System.out.println("Main Thread is going to sleep");
t.sleep(2000);
System.out.println("Main Thread awaken");
}
catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println(e);
}
System.out.println("Main Thread");
t.start();
}
}

How to solve this error?
In order to avoid java.lang.IllegalStateException in Java main Thread we must ensure that any method in our code cannot be called at an illegal or an inappropriate time.
In the above example if we call start() method only once on thread t then we will not get any java.lang.IllegalStateException because we are not calling the start() method after the starting of thread (i.e we are not calling the start() method at an illegal or an inappropriate time.)
Java
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
class myThread extends Thread {
public void run()
{
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
System.out.println("GeeksForGeeks");
}
}
}
class Thread1 {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
myThread t = new myThread();
t.start();
try {
System.out.println("Main Thread is going to sleep");
t.sleep(2000);
System.out.println("Main Thread awaken");
}
catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println(e);
}
System.out.println("Main Thread");
}
}

Last Updated :
03 Mar, 2022
Like Article
Save Article
I am very new to android and just starting to understand how to develop simple apps (AndroidStudio, Ubuntu 14.04, LG G3). From a main activity I want to start another activity (i.e. to show a different screen where the user can make some input) following this solution. In the file MainActivity.java I have the following method:
@Override
public boolean onOptionsItemSelected(MenuItem item) {
switch (item.getItemId()) {
case R.id.menu_add:
Intent myIntent = new Intent(MainActivity.this, NewEntryActivity.class);
MainActivity.this.startActivity(myIntent);
return true;
default:
return super.onOptionsItemSelected(item);
}
}
And the file NewEntryActivity.java is defined as follows:
package com.example.alexander.myapplication;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.support.v7.app.AppCompatActivity;
import android.widget.Button;
import android.widget.EditText;
public class NewEntryActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.content_newentry);
final EditText editNewIsin = (EditText) findViewById(R.id.new_isin);
final EditText editNewPrice = (EditText) findViewById(R.id.new_price);
final EditText editNewNumber = (EditText) findViewById(R.id.new_number);
Button buttonNewOk = (Button) findViewById(R.id.new_ok);
Button buttonNewCancel = (Button) findViewById(R.id.new_cancel);
}
}
No error is indicated for this file (everything seems to be defined properly). When I start the app on my phone, the main activity starts without problem, but when I choose the menu item to start the other activity the app closes immediately and I see an error:
Caused by: java.lang.IllegalStateException: You need to use a Theme.AppCompat theme (or descendant) with this activity
However, both activities are derived from AppCompatActivity. Maybe it refers to something else (Manifest, layout.xml, …?), but this is not clear from the error message. Any help is appreciated here…
Here is also the manifest file:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<manifest
xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
package="com.example.alexander.myapplication" >
<application>
android:allowBackup="true"
android:icon="@mipmap/stoxx"
android:label="@string/app_name"
android:supportsRtl="true"
android:theme="@style/Theme.AppCompat.Light.DarkActionBar" />
<activity
android:name=".MainActivity"
android:label="@string/app_name"
android:theme="@style/AppTheme.NoActionBar" >
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="android.intent.action.MAIN" />
<category android:name="android.intent.category.LAUNCHER" />
</intent-filter>
</activity>
<activity
android:name=".NewEntryActivity"
android:label="@string/menu_add"
/>
</application>
</manifest>
Сбои — головная боль для всех вовлеченных. Команды разработки ненавидят разбираться с ними, а пользователи не желают мириться — 62% пользователей удаляют приложение в случае сбоев, говорит исследование DCI. Нестабильность приложения может быстро привести к провалу всего проекта или, по крайней мере, дорого обойтись. Чтобы свести к минимуму сбои приложения и время, необходимое для их устранения, мы собрали наиболее распространенные ошибки Android-приложений и способы их устранения.
5 самых распространенных ошибок в Android-приложениях и способы их устранения
java.lang.NullPointerException
Определенно, самый частый креш в Android. Скорее всего, если вы когда-либо разрабатывали приложение для Android, то сталкивались с этой ошибкой. Наиболее частой причиной NullPointerException является ссылка на данные после выхода за пределы области видимости или сборки мусора.
Обычно это происходит, когда приложение переходит в фоновый режим, и избавляется от ненужной памяти. Это приводит к потере некоторых ссылок, и когда метод Android onResume () вызывается снова, это может привести к ошибке NullPointException.
Чтобы точно определить, где произошла ошибка, используйте трассировку стека. И, чтобы избежать ошибки и потери данных, вы должны стремиться сохранить свои данные в более надежном месте, когда вызывается метод onPause(). Просто вытащите их обратно при вызове onResume(). И, в общем, старайтесь обрабатывать любые потенциальные нулевые указатели, которые могут вызвать ошибку.
java.lang.IllegalStateException
Одна из наиболее распространенных ошибок Android-приложений, имеющих дело с Фрагментами. Ошибка IllegalStateException может происходить по множеству причин, но в основе ее лежит неправильное управление состояниями Activity.
Она возникает, когда в фоновом потоке выполняется трудоемкая операция, но тем временем создается новый Фрагмент, который отсоединяется от Activity до завершения фонового потока. Это приводит к вызову отсоединенного фрагмента и появлению такого исключения.
Чтобы решить эту проблему, вы должны отменить фоновый поток при приостановке или остановке Фрагмента. Кроме того, вы можете использовать метод isAdded(), чтобы проверить, прикреплен ли Фрагмент, а затем использовать getResources() из Activity.
java.lang.IndexOutOfBoundsException
IndexOutOfBoundsException — одно из самых распространенных исключений RunTimeExceptions, с которыми вы можете столкнуться. Эта ошибка указывает на то, что какой-либо индекс (обычно в массиве, но может быть и в строке или векторе) находится вне допустимого диапазона.
Есть несколько распространенных причин возникновения этого сбоя — использование отрицательного индекса с массивами, charAt или функцией substring. Также, если beginIndex меньше 0 или endIndex больше длины входной строки, или beginIndex больше endIndex. Другая причина — когда endIndex — beginIndex меньше 0. Но, вероятно, наиболее распространенная причина — когда входной массив (строка/вектор) пуст.
Исправить эту проблему относительно просто, всегда лучше проверять трассировку стека всякий раз, когда возникает ошибка. Первым ключевым шагом является понимание того, что вызвало сбой. После этого нужно убедиться, что этот массив, строка или вектор соответствуют требуемому индексу.
java.lang.IllegalArgumentException
Вероятно, наиболее общая причина сбоя в списке — исключение IllegalArgumentException. Самое простое его определение заключается в том, что ваш аргумент неправильный. Этому может быть много причин. Однако есть несколько общих правил.
Одна из наиболее частых причин — попытка получить доступ к элементам пользовательского интерфейса непосредственно из фонового потока. Также, если вы пытаетесь использовать переработанное растровое изображение. Другая распространенная причина — вы забыли добавить Activity в Manifest. Это не будет показано компилятором, так как это RuntimeException.
Чтобы предотвратить этот сбой, сосредоточьтесь на том, чтобы кастинг всегда был правильный. Компилятор не отлавливает множество ошибок, поэтому вам нужно проявлять понимание при обращении к ресурсам, поскольку, например, многие методы пользовательского интерфейса принимают как строки, так и целые числа.
java.lang.OutOfMemoryError
И последний, но не менее важный в нашем списке — один из самых неприятных крешей. Устройства Android бывают всех форм и с разным объемом памяти. Часто бывает, что вы имеете дело с ограниченными ресурсами. OutOfMemoryError возникает, когда ОС необходимо освободить память для высокоприоритетных операций, и она берется из выделенной вашему приложению кучи. Управление памятью становится проще, поскольку новые устройства имеют гораздо больше памяти. Однако не все пользователи вашего приложения будут работать с ними.
Что касается самой ошибки, то одна из основных причин утечки памяти, приводящей к OutOfMemoryError, — это слишком долгое сохранение ссылки на объект. Это может привести к тому, что ваше приложение будет использовать намного больше памяти, чем необходимо. Одна из наиболее распространенных причин — растровые изображения, которые в настоящее время могут быть большого размера. Поэтому не забудьте утилизировать любой объект, который возможно, когда он больше не нужен.
Вы можете запросить у ОС больше памяти для кучи, добавив в свой файл манифеста атрибут
android:largeHeap="true"
Однако это не рекомендуется, кроме случаев крайней необходимости, поскольку это всего лишь запрос и он может быть отклонен.
Источник
Если вы нашли опечатку — выделите ее и нажмите Ctrl + Enter! Для связи с нами вы можете использовать info@apptractor.ru.
java.lang.illegalStateException — это ошибка, которая возникает при несоответствии состояния объекта и операции, которую вы пытаетесь выполнить. Эта ошибка может возникать при работе с Кристаликс, если вы пытаетесь запустить приложение на устройстве с недостаточными ресурсами или если вы не правильно настроили параметры приложения.
Советы для избавления от ошибки
1. Проверьте параметры приложения
Первым делом, проверьте, что вы правильно настроили параметры приложения. Проверьте, что вы настроили Кристаликс на использование соответствующей версии Java и что у вас достаточно памяти для запуска приложения.
2. Очистите папку с кэшем
Если проблема не устранилась после проверки параметров, попробуйте очистить папку с кэшем. Для этого выполните следующие действия:
- Остановите приложение Кристаликс, если оно запущено.
- Откройте папку, в которой хранятся файлы кеша. Для большинства операционных систем это будет
C:Users<ваше_имя>AppDataLocalCrystalixcache. - Удалите все файлы в этой папке, кроме папки
data. - Попробуйте запустить приложение Кристаликс.
3. Обновите Java
Если проблема не устранилась после проверки параметров и очистки кеша, обновите свою версию Java до последней доступной версии. Это может помочь устранить несоответствие состояния объекта и операции.
Заключение
java.lang.illegalStateException — это ошибка, которая может возникнуть при работе с Кристаликс. Если вы столкнулись с этой ошибкой, следуйте приведенным выше советам, чтобы избавиться от нее и продолжить работу с приложением.
New issue
Have a question about this project? Sign up for a free GitHub account to open an issue and contact its maintainers and the community.
By clicking “Sign up for GitHub”, you agree to our terms of service and
privacy statement. We’ll occasionally send you account related emails.
Already on GitHub?
Sign in
to your account
Labels
1.19
Bug
This request reports or fixes a new or existing bug.
Confirmed
This request has been verified to be factually correct by at least one member of the team.
