Пересказ статьи Rajendra Gupta. How to manage SQL Server logs effectively
В статье дается обзор журналов SQL Server для управления и устранения неполадок на сервере.
Введение
Журналы являются лучшим средством администратора баз данных при решении любых проблем. Эти проблемы могут быть связаны с конфигурацией сервера, запуском, восстановлением, производительностью, флагами трассировки, тупиковыми ситуациями, вводом-выводом или задержками. Предположим, например, что ваш экземпляр SQL Server перезапускается по непонятным причинам, и после перезапуска службы SQL работают, однако ваше приложение не имеет доступа к базе данных. Таким образом, для исследования проблемы вам нужно заглянуть в последний журнал SQL Server, чтобы проконтролировать процесс восстановления базы данных и узнать оценку времени его завершения.
Администратор базы данных может также сконфигурировать SQL Server для выполнения дополнительных записей в журналы ошибок. Например, мы можем включить флаг трассировки для захвата информации о тупиковых ситуациях. DBA должен регулярно просматривать эти журналы в поисках потенциальных проблем. Вы можете обнаружить в журналах такую информацию, как сбой резервного копирования, ошибки входа, ошибки ввода-вывода. Эти журналы ошибок являются отличным средством для обнаружения существующих и потенциальных проблем в экземплярах SQL Server.
Журналы SQL Server известны как SQL Server Error logs. Журналы ошибок содержат информационные сообщения, предупреждения и сообщения о критичных ошибках. Вы можете просматривать некоторые из этих журналов также в просмотрщике событий Windows. Однако рекомендуется использовать журналы SQL Server для получения подробной информации.
Журналы SQL Server и их местонахождение
Если вы подключены к экземпляру SQL Server в SSMS, перейдите к Management -> SQL Server Logs. Как показано ниже, имеется текущий журнал и шесть архивных журналов (Archive#1 — Archive #6).
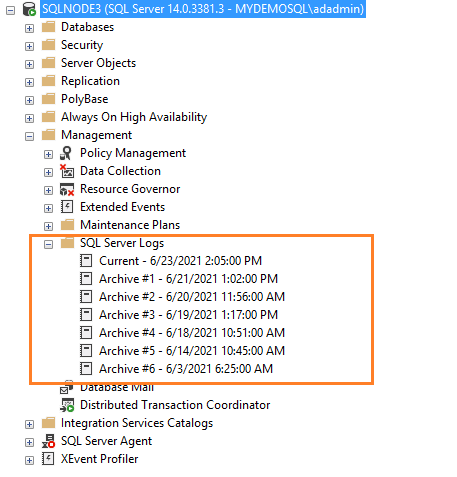
Метод 1: Использование расширенной процедуры xp_readerrorlog
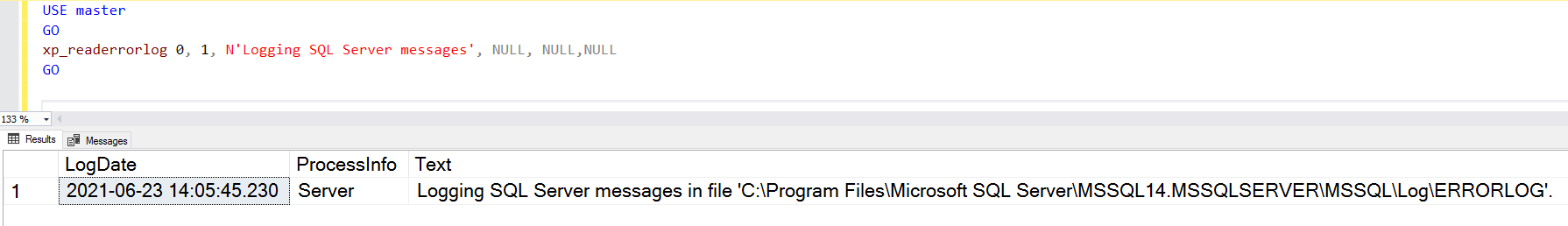
Текущие журналы являются самыми последними файлами журнала ошибок, и вы можете использовать их для просмотра недавней деятельности с момента запуска SQL Server или ручного перезапуска файла журнала. Журнал ошибок SQL Server является текстовым файлом, хранящимся в каталоге журналов экземпляра SQL Server. Вы можете использовать расширенную процедуру xp_readerrorlog для нахождения текущего местоположения журнала ошибок.
USE master
GO
xp_readerrorlog 0, 1, N'Logging SQL Server messages', NULL, NULL,NULL
GO
Этот запрос имеет следующие параметры:
- Файл журнала ошибок: значение 0 для текущего, 1 для Archive#1, 2 для Archive #2.
- Тип файла журнала: значение 0 для журнала ошибок SQL Server, 1 для агента SQL Server.
- Строка поиска 1
- Строка поиска 2
- Время от
- Время до
- Сортировка результатов — по возрастанию (N’ASC) или по убыванию (N’Desc)
Для моего демонстрационного экземпляра файл журнала ошибок находится в папке C:Program FilesMicrosoft SQL ServerMSSQL14.MSSQLSERVERMSSQLLogERRORLOG.
Метод 2: Использование функции SERVERPROPERTY()
Мы можем использовать в запросе функцию SERVERPROPERTY, и также определить местонахождение SQL Server ERRORLOG.
SELECT SERVERPROPERTY('ErrorLogFileName') AS 'Error log location'

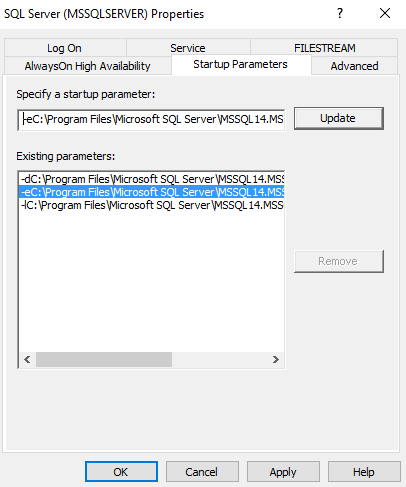
Метод 3: использование менеджера конфигурации SQL Server
Откройте SQL Server Configuration Manager и посмотрите параметры запуска. Местоположение файлов журнала указывается с помощью переключателя -e.
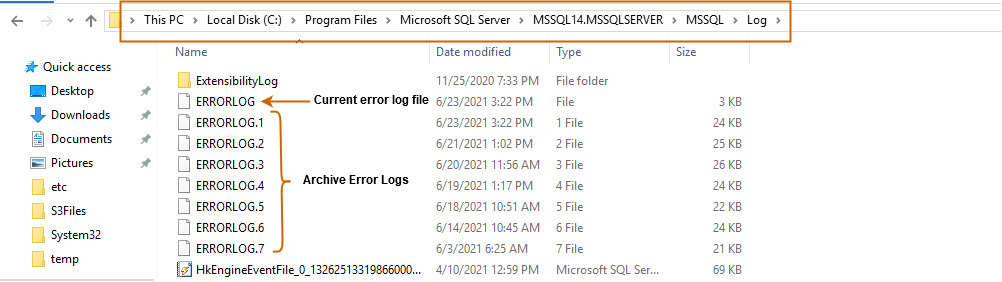
Вы можете развернуть каталог журналов и просмотреть текущий или архивные файлы журнала. Эти журналы ошибок можно открыть в текстовом редакторе, таком как Notepad или Visual Studio Code.
Конфигурирование числа файлов журнала SQL Server и их размеров
По умолчанию SQL Server поддерживает текущий и 6 архивных файлов журнала. Чтобы уточнить значение, выполните щелчок правой кнопкой на папке SQL Server Logs в SSMS и выберите Configure.
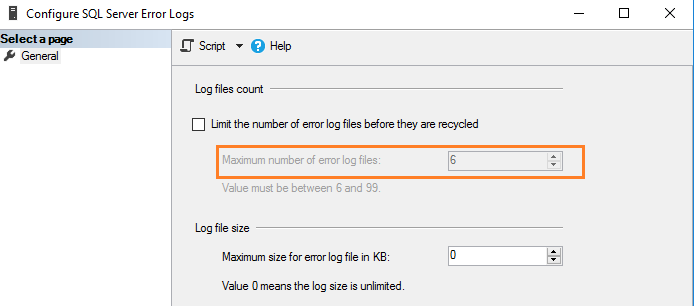
SQL Server записывает всю информацию в текущий файл журнала, независимо от размера файла журнала. В загруженной системе или в экземпляре с большим количеством ошибок вам может быть сложно просмотреть файл журнала в SSMS. SQL Server создает новый файл журнала и архивирует текущий файл в следующих случях.
- При перезапуске службы SQL.
- При перезагрузке журнала ошибок вручную.
Однако если вы часто перезапускаете серверы по неизвестным причинам, то можете потерять все исторические данные в архивных журналах, поскольку их поддерживается только шесть. Поскольку ошибки содержат ценную информацию, которая может помочь в решении проблем, вы можете не захотеть потерять эти важные данные. Тогда, возможно, вы захотите сохранять файлы журнала производственной системы в течение недели или даже месяца.
SQL Server позволяет сконфигурировать от 6 до 99 файлов журнала ошибок. Вы не можете указать значение меньше шести, поскольку в любом случае будет поддерживаться шесть архивных журналов ошибок.
Для изменения значения по умолчанию числа файлов журнала ошибок поставьте галочку в поле с названием “Limit the number of error log files before they are recycled”. Например, следующий скриншот показывает максимальное число файлов журнала ошибок, равное 30.
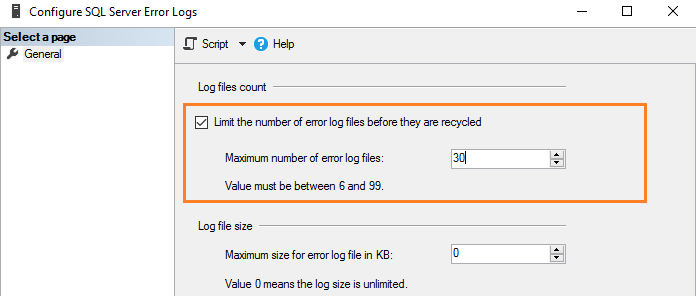
Это эквивалентно выполнению скрипта T-SQL, который использует расширенную хранимую процедуру и обновляет значение регистра.
USE [master]
GO
EXEC xp_instance_regwrite N'HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE', N'SoftwareMicrosoftMSSQLServerMSSQLServer', N'NumErrorLogs', REG_DWORD, 30
GO
Замечание. Следует перезапустить службу SQL, чтобы изменения вступили в силу.
Как утверждалось ранее, по умолчанию размер журнала ошибок не ограничен. Например, если вы не запускаете SQL Server в течение длительного периода и вручную не перегружаете файлы журнала, этот файл вырастет до громадных размеров. Поэтому в конфигурации журнала ошибок показано значение 0, соответствующее неограниченному размеру журнала.
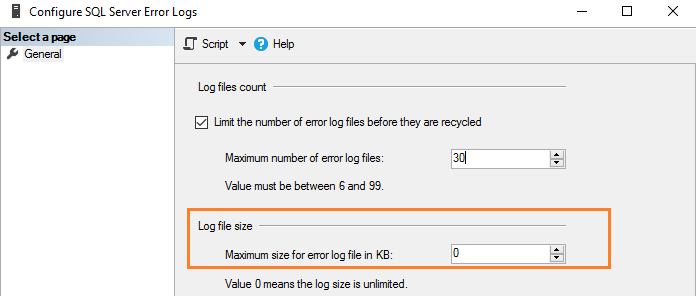
Вы можете задать размер в Кб для ограничения размера журнала ошибок в соответствии с вашими требованиями. Например, здесь мы ограничиваем размер файла журнала в 1Гб.
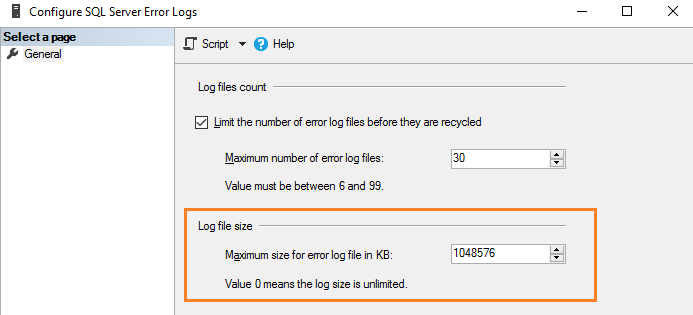
Эквивалентный скрипт T-SQL обновляет ErrorLogSizeInKb в регистре SQL Server.
USE [master]
GO
EXEC xp_instance_regwrite N'HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE', N'SoftwareMicrosoftMSSQLServerMSSQLServer', N'ErrorLogSizeInKb', REG_DWORD, 1048576
GO
Перезагрузка журналов ошибок вручную
SQL Server позволяет вручную перегружать журналы ошибок для эффективного управления ими. Например, предположим, что вы увеличили число файлов журнала ошибок до 30. Тогда мы можем создать задание для агента SQL Server, который перегружает журналы ошибок в полночь. Тем самым мы имеем файл журнала ошибок на каждый день, если SQL Server не будет перезапущен в этом промежутке. Для перезагрузки вручную выполните системную хранимую процедуру sp_cycle_errorlog. Эту процедуру может выполнить пользователь с фиксированной серверной ролью sysadmin.
EXEC sp_cycle_errorlog
GO
Файл журнала SQL Server Agent
Агент SQL Server также имеет отдельный журнал ошибок, подобный журналам SQL Server. Вы можете обнаружить его в папке SQL Server Agent – > Error logs.
Щелкните правой кнопкой на папке Error log и выберите команду Configure. Это даст местоположение журнала ошибок агента и уровень журнала агента.
Файл журнала агента имеет расширение *.OUT и хранится в папке log при конфигурации по умолчанию. Например, в моей системе файл журнала находится здесь: C:Program FilesMicrosoft SQL ServerMSSQL14.MSSQLSERVERMSSQLLogSQLAGENT.OUT.
По умолчанию в файл журнала записываются ошибки и предупреждения; однако мы можем включить информационные сообщения:
- Предупреждения: Эти сообщения предоставляют информацию о потенциальных проблемах. Например, “Job X was deleted while it was running” (задание Х было удалено во время выполнения).
- Сообщение об ошибках: оно дает информацию, которая требует немедленного вмешательства администратора баз данных, например, невозможность почтового сеанса.
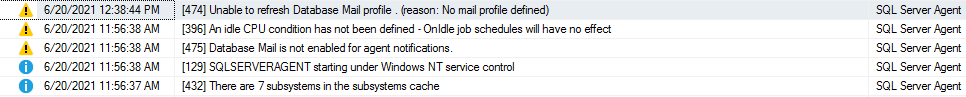
Чтобы добавить информационное сообщение, поставьте галочку в поле Information.
SQL Server использует до 9 файлов журнала агента SQL Server. Имя текущего файла SQLAGENT.OUT. Файл с расширением .1 указывает на первый архивный журнал ошибок агента. Аналогично расширение .9 указывает на 9-й (самый старый) архив журнала ошибок.
Файлы журнала агента SQL Server перегружаются всякий раз, когда перезапускается SQL Server Agent. Для того, чтобы сделать это вручную, выполните щелчок правой кнопкой на папке Error Logs folder и выберите Recycle.
Или используйте хранимую процедуру sp_cycle_agent_errorlog для перезагрузки файлов журнала агента SQL Server вручную.
USE msdb ;
GO
EXEC dbo.sp_cycle_agent_errorlog ;
GO
Хранимая процедура архивирует текущий журнал ошибок агента, используя следующий процесс:
- Создается новый текущий журнал ошибок агента.
- Текущий журнал ошибок SQLAgent.out преобразуется в SQLAgent.1.
- SQLAgent.1 преобразуется в SQLAgent.2
Заключение
Файл журнала ошибок SQL Server содержит информацию, предупреждения и критические сообщения экземпляра. Это полезно для решения проблем, аудита входа (успешно, отказ). Администратор базы данных может сконфигурировать требуемое число архивных журналов ошибок и каталогов для хранения этих файлов.
Вы должны регулярно просматривать записи в журнале в качестве подготовки ежедневных или еженедельных отчетов о состоянии сервера.
The SQL Server error log is a great source of information for DBAs for monitoring errors and the operation of the server. Greg Larsen explains the details and how to configure the SQL Server error log.
Most applications have a log of some sort that tracks activity. SQL Server is no different. It has a log file known as the error log for tracking what’s happening on an instance of SQL Server. Server. Each instance of SQL Server has its own set of error log files. In this article, I will discuss what the error log is, how SQL Server manages it, and where you can find it. I’ll also show you how to configure the SQL Server error log.
What is the error log?
The error log is a file that tracks what kind of activity is happening on an instance. The log is just a journal of events that have occurred on a SQL Server instance, in chronological order. The log doesn’t track everything, but it does track significant events and errors that occur while SQL Server is running. These errors could be informational only, warnings, as well as actual instance and application errors. You can find things like start up and shut down information, backup and restore commands, as well as custom application messages in the error log file. A DBA can also configure SQL Server to write additional logging, for example, logins and logouts. The error log is a great place to look for problems or potential problems associated with an instance of SQL Server.
The error log is not a single file but a series of files. Each time SQL Server starts up, a new error log file is created. A running instance of SQL Server writes to current log (the one created at startup) and by default has six archived error log files. If you need to keep more than six archived files, you can override the default to keep as many as you need (more on this later).
If an instance of SQL Server crashes or will not start for some reason, the error log is the place to go for troubleshooting these problems. As a DBA, you should periodically review the error log to look for potential problems. By reviewing the log, you might find some unusual things going on that might otherwise go unnoticed, like a backup job has failed or someone trying to hack the SA password.
Where can the error log files be found?
By default, the error log files are stored in the following location: Program FilesMicrosoft SQL ServerMSSQL<n>.<instance name>MSSQLLOGERRORLOG, where <n> is an archived version number, and <instance name> is the name of the instance. This is only the default location. Some instances might be set up to write their error log files to a different location. If the error log files are not in the default location, then there are a number of different ways to find them. I will show you two of those methods.
The first method is to use SQL Server Configuration Manager. To find the location of the log using this method, first, open up SQL Server Configuration Manager. Next double click on the instance of SQL Server that you want to locate the error log file location. Then click on the Advanced tab. The location of the error log file directory is identified in the Dump Directory item. To see the full name of the error log file directory, click on the little down error to the right of the Dump Directory item, as shown below in Figure 1.

Figure 1: Location of error log file directory in Configuration Manager
A second method to find the location of the error log files is to use SSMS to browse one of the error log files. To do this, you must connect to the instance of SQL Server in which you want to find the error log location with SSMS. Expand the Management item and the SQL Server Logs item. Then double-click on the Current error log file. When you do this, the Log File Viewer will be displayed. To find the error log file location you can either browse thru the log file until you find it or use the Search… option to find it. When using the search option, use the string Logging SQL Server messages in file as the search criteria. The image in Figure 2 shows these steps. The log location can be found in the line that is highlighted in the log.

Figure 2: Using SSMS to find the location of error log files
Types of error log files and their naming conventions
Each SQL Server instance has two different types of error log files. There is an error log file for the currently running instance and then a number of archived error log files.
All error log files names start with ERRORLOG. The error log for the running instance is called just ERRORLOG, whereas all other error log files names start with ERRORLOG but have a number for the file extension. The archived error log files are ERRORLOG.1, ERRORLOG.2, ERROLOG.3, … up to the number to the configured number of archived error log files. Where ERRORLOG.1 is most recently archived error log file, ERRORLOG.2 is the second most recently archived error log file, ERRORLOG.3 is the third most recently archived error log file, etc. If an instance is configured with the default number of error log files, then the last archived error log file is named ERRORLOG.6.
When an instance is restarted, the oldest archived error log file (ERRORLOG.6 if the default number is used) is deleted, then each of the remaining error log files is renamed. ERRORLOG.5 is renamed to ERRORLOG.6, ERROLOG.4 is renamed to ERRORLOG.5, etc. until ERRORLOG.1 is renamed to ERRORLOG.2. The last current error log file (ERRORLOG) is renamed to ERRORLOG.1, and the error log file for the newly started instance is created with the name ERRORLOG.
Changing the number and size of the error log
By default, an instance of SQL Server retains six archived error log files, and the size of each log file is unlimited. An unlimited size means it will grow as big as it needs to be, or until it runs out of disk space. You may find that these default setting are fine, but they can also be overridden.
How many archived error log files do you need and what is an appropriate maximum size? Like most SQL Server questions, the answer is “it depends.” Here, I will demonstrate how the number and size of the error logs might help or hinder your use of the error log files and share my personal opinion of how many log files I like to have.
First, let me explore the number of archived log files. I like to retain at least two months’ worth of error log files. By having multiple months of error log information, I can track trends from one month to the next. Keep in mind that depending on what is logged and the activity of an instance, two months’ worth of error log files might take up a lot of disk space.
There is no easy way to keep exactly two months’ worth of error log files since a new error log is created and the oldest archived one is deleted every time an instance is restarted. The number of months of error log files depends on how often SQL Server is restarted and the number of archived error log files that are kept. Suppose an instance is recycled frequently over a short period of time due to some maintenance activity. Error log information will be cycled off based on the configured value for the number of archived error log files that should be retained.
There a few different methods to change the error log file configuration, I’ll mention two of them. The first method is to use SSMS. To use this method, first connect to the instance, expand the Management folder, right click on the SQL Server Log folder and then select the Configure item from the menu displayed, as shown in Figure 3.

Figure 3: Bringing up the error log configuration screen
When clicking on Configure, the window shown in Figure 4 is displayed.

Figure 4; Configuration Options for the Error Log
By reviewing Figure 4, you can see that my instance is currently configured to retain 6 archived error log files and the maximum size of the error log file is set to be 0, which means unlimited.
To change the number of archived error log files to retrain, first click on the checkbox labeled Limit the number of error log files before they are recycled. Doing this will enable the Maximum number of error log files option, so the number of error logs to retain can be changed. Note the number of error log files to retrain needs to be between 6 and 99.
To set a maximum limit of each error log file, enter the desired size into the Maximum size of the error log file in KB. When the error log configuration is set to limit the size of the error log file, a new error log file will be created automatically after the current log file reaches the maximum size. I personally don’t like to limit the size of the log file, but keep in mind, having an unlimited size setting means each log file will be different sizes, whereas limiting the size would make every error log file the same size.
Issues with multiple restarts
When SQL Server is restarted, the oldest archived error log file is deleted, and a new one is created. This cycling of the error log every time SQL Server restarts normally isn’t a problem, unless it deletes an archived error log file automatically that contains information that is needed for troubleshooting or trend reporting.
Since the log file contains messages and errors related to an instance, it is crucial not to lose this information until you no longer need it. The problem with having the default number of archived error log files is you might lose valuable troubleshooting information if an instance is restarted more than six times over a short period of time. This can happen for a number of different reasons. I have seen nighttime operations staff and DBAs restart an instance multiple times in an attempt to get an instance that has crashed back up and running. Suppose an instance of SQL Server is restarted multiple times without review of the error log files. The restarts might inadvertently cycle off the one critical error log file containing the error messages related to the crash. For this reason, it is important to configure SQL Server to retain enough archived error log files so they are not automatically deleted until they are no longer needed.
Keep in mind that cycling off a critical error log file is a rare situation. However, if an error log file that has valuable information about a crash is cycled off, it does hamper your troubleshooting options. Therefore, it is wise to have someone review the error log, or at least copy the error log file to a backup location after a crash to make sure you have all the log files to help with troubleshooting. At least by copying off the error log file after a crash, you can guarantee it will not be cycled off if lots of restarts are performed.
Cycling the ERRORLOG
A new error log is created every time SQL Server is restarted. Sometimes SQL Server stays up for weeks or even months before an instance is restarted. When an instance has been running for a long time, the error log will be quite large. It’s hard to review and find errors in large log files, especially when they contain error messages that could cover long periods of time.
To help keep the error log files from spanning months’ worth of messages without recycling, you can cycle the error log with a command. Cycling the error log will close the current log and create a new one. The code in Listing 1 uses the system stored procedure sp_cycle_errorlog to cycle the error log file.
Listing 1: Cycling the errorlog.
To execute the sp_cycle_errorlog system stored procedure, you need to be a member of the sysadmin fixed server role. Stored procedure sp_cycle_errorlog takes no parameters and returns a 0 if the error log is successfully recycled and a 1 if the cycling of the log has failed.
Error log file
The error log file contains messages and errors associated with a SQL Server instance. It is a valuable tool for troubleshooting problems with SQL Server as well as auditing what goes on within an instance of SQL Server. A DBA can configure SQL Server to store the error logs wherever they’d like and adjust the configuration to keep as many archived error log files as needed. As a DBA you should review this log every time SQL Server crashes and as part of your daily and weekly system checks. This review will ensure that SQL Server is functioning normally, with no unexpected errors showing up in the log.
How to Open, Read & Check MS SQL Error Log File – Ultimate Tutorial

This blog gives you a big picture of the SQL Server Error Log file, where it is located in the system & the bets way to open & view it. So, let’s have a deeper look at it.
The SQL Server Error Log sounds like SQL Transaction Log, which keeps a record of database transactions and ensures database integrity. Right? Unfortunately, Error Log file is not like that.
Topics To Be Covered
- What is Inside SQL Server Error Log ?
- Where is SQL Server Error Log Located ?
- How to Change Error Log File Location in SQL Server?
- How to Read SQL Error Log?
SQL Error Log files are very much different from SQL Server LDF. It majorly comprises User-defined events and is used to troubleshoot system problems. In this technical guide, we are going to provide complete information about Microsoft SQL Server Error Log File.
Let’s get started!
SQL Server Logs & What’s Inside Them?
SQL Server logs are the files storing complete data for the transactions of the SQL Server, whereas error log files are different. It comprises information regarding the Audit Collection, Database Mail, Windows Events, SQL Server Agent, SQL Server, Job History, and Data Collection. Moreover, it shows a summary report that use to analyze which activities took place in SSMS. So, it can easily be troubleshoot by the user.
Where is MS SQL Server Error Log Stored?
You can easily find the SQL Error Log location for your dedicated SQL Server version. All you need to use the following path to access it.
Drive: Program Files Microsoft SQL Server MSSQLV.SQLEXPRESS MSSQL Log ERRORLOG
It is a general path that provides you SQL Server 2017 / 2016 / 2014 / 2012 / 2008 / 2008 R2 / 2005 error log file location. For example, it is the SQL Server 2016 Error Log file location in Windows 10.
C: Program Files Microsoft SQL Server MSSQL13.SQLEXPRESS MSSQL Log

How to Change Error Log File Location in MS SQL Server 2017/ 2016/ 2014/ 2012
Sometime SQL users need to update the path of an SQL Error log file. The overall procedure is classified into two stages.
Stage 1: Start the SQL Server Configuration Manager
One can open the Configuration Manager with different techniques. All of them are mentioned below.
Method #1 – To open Configuration Manager, you can type the SQL Server Configuration Manager in the search box of Start and open it as shown in the screenshot.

Method #2 – Else, you can use the following path to open SQL Server Configuration Manager.
| SQL Server Version | SQL Server Configuration Manager Exe Location |
|---|---|
| SQL Server 2017 | C: Windows System32 SQLServerManager14.msc |
| SQL Server 2016 | C: Windows System32 SQLServerManager13.msc |
| SQL Server 2014 | C: Windows System32 SQLServerManager12.msc |
| SQL Server 2012 | C: Windows System32 SQLServerManager11.msc |
| SQL Server 2008 | C: Windows System32 SQLServerManager10.msc |
Here, we opened the SQL Server Configuration Configuration Manager with the above–mentioned location in SQL Server 2017.

Method #3 – You can also open the Run dialog box and type ‘compmgmt.msc’ in the box.

From the following screen, expand the Services and Applications section and get the SQL Server Configuration Manager.

Stage 2: Change the SQL Server Error Log Path
Step-1. Under the SQL Server Configuration Manager, go to the SQL Server Services option.

Step-2. Perform right-click on SQL Server(SQLEXPRESS) as shown in the screenshot and choose the Properties option.

Step-3. From the SQL Server(SQLEXPRESS) Properties, click on the Startup Parameters tab. Afterward, under the Existing parameters section, choose the log file whose location you want to change.

Step-4. The starting prefix (like e,d) and the current Error Log file Name will not change. Rest of the folder can be changed. Mention the new path under the Specify a startup parameter box and update it.
Step-5. The changes to SQL error logs location are saved but they are not active. For this. You need to start the SQL Server Services.
Quick Steps to Open SQL Server Error Logs
- Launch Log Analyzer & Add SQL Server Error Log.
- Set offline or Online Mode & Enter Server Details.
- Preview the Concerned Files and then Proceed.
- Set the Filters and the Destination Location.
- Click on Export to Get the Desired Results.
Methods to Open SQL Server Error Log Files
There are two ways through which one can view the Error Log. Now, whenever, the SQL Server could not open Error Log file, then use any of the below-mentioned techniques.
Approach #1: Use T-SQL to Read SQL Error Log
Connect with the SSMS and type ‘sp_readererrorlog’ in the panel. It is a SQL Server query to read Error Log.

Approach #2: Use Object Explorer Option
Without the help of T-SQL, you can also view the error log. Let’s check out how to read SQL Server Error Log.
Step-1. Open Microsoft SQL Server Management Studio on your system.
Step-2. Time to connect with Object Explorer. Open Connect to Server Window and select the Server name. Afterward, choose the Authentication Type and click on Connect.

Step-3. Go to the Management section from the Object Explorer in order to read SQL Error Log.

Step-4. Expand the Management Section and go to the SQL Server Logs.

Step-5. Right-click on SQL Server Logs option. Go to the View option and select SQL Server Log from the menu.

Step-6. The Log File Summary will appear on the screen. From the same window, you can opt for different Log – SQL Server Agent, Database Mail.

That’s all about Microsoft SQL Server Error Log.
Automated Solution to Read & Examine Error Log
Well, the manual method works but not all the time. The success ratio here is quite low. Evidently. experts recommend users opt for an advanced automated solution. And this is exactly why experts recomd the automated solution. Moreover, if you want to examine the SQL Transaction Log file, then you can try SysTools LDF File Reader Software. Download this tool & then simply follow the below instructions to read & examine your SQL error log files.
Step-1. Launch the Software & then Click on the Open button to add LDF log files.

Step-2. Select the Online or Offline mode & Enter SQL Server Details in the dialog box.

Step-3. Preview the Files that you are concerned with by selecting them from the left panel.

Step-4. Enter Filters if you want to Export the records for further examination.

Step-5. Click on the Export button to get the records on your preferred location.

Automated Tool Features for SQL Server Logs
The automated tool is way better than the manual one because of several factors. Let’s have a look at these features in detail that makes this utility special.
- Execute complete analysis of SQL transaction log files without hassles.
- Recover & repair corrupt SQL LDF files as well to restore the database files.
- Analyze all transactions like Insert, Update, and Delete with advanced features.
- Easily examine the error log files without any need for the SQL Server application.
- Supports data types: Datetime2, datetimeoffset, sql_variant, hierarchyid, geometry & geography.
- Microsoft SQL Server 2019, 2017, 2016, 2014, 2012, 2008 & SQL Server 2005 LDF are supported here.
Conclusion
Finally, after understanding all the core concepts of SQL Server logs carefully, it’s time for us to conclude this article. Now, we know the best ways as well to open, read & check SQL Server error logs in a smart manner. The above-mentioned manual & automated solutions are good enough for users to get the desired results they want.
However, when we dig deep, it’s very easy for us to say that manual solutions are a bit complex. Therefore, as per experts’ opinion, the automated tool is the only reliable option left which makes the task hassle-free.
Frequently Asked Questions –
Q-1. How to find log path where the files are kept?
Ans: The location of Error Log – C: Program Files Microsoft SQL Server MSSQLn.SQLEXPRESS MSSQL Log, where n is equivalent to the number basis on the Server version.
Q-2. How to perform SQL Server error log monitoring?
Ans: Open ErrorLog using Log File Viewer in Management Studio and analyze all the events happened in the system.
Q-3. What is the difference between SQL Log & SQL ErrorLog File?
Ans: The SQL Log or Transaction Log file keeps record of every transaction performed on the database. Whereas, the Error Log used to keep track of events happened in SSMS related to ports, network and much more.
Q-4. What’s the best way to find error logs but not their path?
Ans: Firstly, check for the error message. Now, examine errlog.log primarily. Also, check the optional log files for errors. Identify the respective errors easily.
Q-5. How to create an error log in SQL Server?
Ans: Follow the instruction as mentioned carefully:
- Go to Object Explorer & Expand Database.
- Navigate to Expand Management.
- Right Click SQL Server Logs here.
- Now Click on Configure to create errors.
 Автор: Alexey Knyazev
Автор: Alexey Knyazev
Сегодня я расскажу про недокументированные расширенные хранимые процедуры (Extended Stored Procedures) для работы с журналом ошибок SQL Server и SQL Server Agent.
На самом деле при просмотре журнала SQL Server Logs через SSMS (SQL Server Management Studio) идёт обращение именно к этим двум основным процедурам (xp_readerrorlog и xp_enumerrorlogs), хоть и не на прямую, а через системные интерфейсные процедуры.
Особое внимание я уделю описанию входных параметрам этих недокументированных процедур.
И так, что же происходит, когда мы просматриваем журнал ошибок через SSMS?

Во первых мы определяем путь к нашей папке с журналами
|
select ServerProperty(‘ErrorLogFileName’) |

Затем выводим информацию о текущем журнале и о шести предыдущих
|
exec master.dbo.sp_enumerrorlogs |

в качестве входного параметра можно указать
- 1 — Список журналов SQL Server (значение по умолчанию)
- 2 — Список журналов SQL Server Agent
Если обратиться к тексту этой процедуры, то можно увидеть, что это не более, чем «обёртка» для вызова другой процедуры
|
create proc sys.sp_enumerrorlogs( @p1 int = 1) as begin IF (not is_srvrolemember(N‘securityadmin’) = 1) begin raiserror(15003,—1,—1, N‘securityadmin’) return (1) end exec sys.xp_enumerrorlogs @p1 end |
По коду процедуры видно, прежде чем обратиться к расширенной хранимой процедуре xp_enumerrorlogs, идёт проверка, что пользователь входит в серверную роль securityadmin.
Теперь если мы нажмём View SQL Server Log

то мы сможем просмотреть все события выбранного журнала:

В этот момент идёт обращение к ещё одной процедуре-обёртке master..sp_readerrorlog.
Ниже текст этой процедуры:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 |
create proc sys.sp_readerrorlog( @p1 int = 0, @p2 int = NULL, @p3 nvarchar(4000) = NULL, @p4 nvarchar(4000) = NULL) as begin if (not is_srvrolemember(N‘securityadmin’) = 1) begin raiserror(15003,—1,—1, N‘securityadmin’) return (1) end if (@p2 is NULL) exec sys.xp_readerrorlog @p1 else exec sys.xp_readerrorlog @p1,@p2,@p3,@p4 end |
Как вы видите у неё четыре входных параметра:
- @p1 — номер журнала (0-6); 0 — текущий
- @p2 — чей журнал; 1 — SQL Server, 2 — SQL Server Agent
- @p3 — фильтр для поиска
- @p4 — второе условие для поиска
Пример:
|
exec master.dbo.sp_readerrorlog 0, 1, N‘error’ |

|
exec master.dbo.sp_readerrorlog 0, 1, N‘error’, N‘34050’ |

Но это ещё не всё. Если обратиться к самой расширенной процедуре xp_readerrorlog, то у неё есть ещё несколько параметров:
- @p5 — условие с какой даты выводить результат
- @p6 — условие до какой даты выводить результат из журнала
- @p7 — тип сортировки (asc/desc)
- @p8 — экземпляр SQL Server (@InstanceName), параметр появился в SQL Server 2012
Пример:
|
exec master.dbo.xp_readerrorlog 0, 1, null, null, ‘20130418’, ‘20130419’ |

|
exec master.dbo.xp_readerrorlog 0, 1, null, null, ‘20130418’, ‘20130419’, N‘desc’ |

Если необходимо работать с журналом пользователю с минимальными привилегиями, то достаточно дать явные права на эти расширенные процедуры, но обращаться к ним придётся через запросы, т.к. SSMS использует интерфейсные процедуры, которые проверяют входимость пользователя в группу securityadmin.
|
use master go grant execute on xp_readerrorlog to [Ваш юзер] go |
Запись опубликована в рубрике В помощь администратору с метками error log. Добавьте в закладки постоянную ссылку.
SQL server maintains its own informational and Error events in Error log. The SQL Server error log is a great place to find the information what is happening in your database. SQL Server error log maintain information about failures/ Success and Errors that
occurred in the database since SQL Server was last restarted or since the last time you have recycled the error logs. SQL Server error log contains user define events and certain system events.
By default there are 6 Archived error logs and 1 Current error log available in SQL Server instance.

By default error Log available in the location C:Program FilesMicrosoft SQL ServerMSSQL10.MSSQLSERVERMSSQLLog
In the above path the filename called ERRORLOG is the currently using error log and 6 archived error logs are like ErrorLog.1, ErrorLog.2 to ErrorLog.6.
How to configure number of Error log to be maintained by SQL Server.
SQL Server management studio -> Management -> SQL Server Logs


Here can increase SQL Server error log up to 99 files.
How to start new SQL Server error log file.
Every time SQL server restart will start with new SQL server error log with name ERRORLOG and old file are renamed to ErrorLog.1, ErrorLog.1 and soon.
Here method to create new error log without server restart.
Exec sp_cycle_errorlog
Go
Before Sp_cycle_errorlog

After Sp_cycle_errorlog

Get Size of 6 default log files
EXEC master..sp_enumerrorlogs
Go
Log file data in Table
xp_readerrorlog
Have a nice day!!
