I am using SQL Server 2008 developer edition. I was trying to attach the AdventureWorks2008 database.
When I tried to attach, I received an «access is denied» error. According to the event log, it came from the O/S:
Open failed: Could not open file D:ProjectDataAdventureWorksAdventureWorksLT2008_Data.mdf for file number 0. OS error: 5(Access is denied.).
I thought «NTFS problem», but System (and I) have modify access to both files.
I found that I can successfully attach the database if I log in as sa, but my user account won’t work.
I am a member of the local administrators group on my machine, and I am in the sysadmins role in SQL Server instance.
Any idea why I had to be logged in as sa?
Rob
45.2k24 gold badges122 silver badges150 bronze badges
asked Feb 24, 2010 at 23:19
4
Run SQL Server Management Studio as an Administrator. (right click-> run as administrator) that took care of all the weirdness in my case.
SQL SRV EXPRESS 2008 R2. Windows 7
answered May 22, 2012 at 18:18
![]()
MandoMandoMandoMando
5,1954 gold badges28 silver badges35 bronze badges
10
Thank you for all of the comments. Some of you helped to lead me to the answer. Here’s what I found:
It was an NTFS permission problem, and not a SQL problem. Further, it looks kind of bug-like (and it’s repeatable).
The problem:
The account that I was using had full control NTFS permissions to the mdf and ldf files. However, it had those permissions through group membership (the Local Administrators group had permissions, and my account is a member of local admins). (I verified the permissions)
If I try to do the attach, connect to SQL Server as me (where I am in the admins group), it fails with the NTFS problem.
However, if I grant the same file permissions that the local admin group has directly to my Domain Account, then I can attach with no problems.
(oh, and yes, I checked the local groups on this machine, and I verified that my domain account is indeed a member of the local admins group).
So, it looks as though the error occurs because some code (either in SQL Server or Management Studio) checks for the permissions that the user account holds, but it doesn’t go so far as to check group permissions that the user account inherits.
That sounds weird to me, but I can reproduce it over and over again, so I have concluded that it is the answer.
Update: I reported this as a bug: https://connect.microsoft.com/SQLServer/feedback/details/539703/access-denied-attaching-a-database-when-permissions-are-inherited
![]()
answered Mar 5, 2010 at 18:04
JMarschJMarsch
21.4k15 gold badges77 silver badges124 bronze badges
13
I’d like to add additional info to the answers that were posted.
Be careful when detaching the database because the windows user you are logged in as becomes the only user with permissions to the .mdf file! The original permissions the .mdf file had which included the user SQLServerMSSQLUser$<computer_name>$<instance_name> and the Administrators account get overwritten by whichever windows user you are logged in as (not sql server user). Boom, all permissions gone just like that. So do as others have said and right click your .mdf file and double check the permissions.
I ran into this problem because I used SSMS to connect to the database (doesn’t matter which sql server account) and detached the database. After doing that my windows user was the only one that had any permissions to the .mdf file. So later on when I tried to attach the db using the sa account, it threw the «access denied» error.
To keep the original permissions in tact you should take the database offline, then detach, then attach in that order like so:
USE [master]
GO
-- kick all users out of the db
ALTER DATABASE mydb
SET SINGLE_USER WITH ROLLBACK IMMEDIATE
GO
-- Take the Database Offline
ALTER DATABASE mydb SET OFFLINE WITH
ROLLBACK IMMEDIATE
GO
-- detach the db
EXEC master.dbo.sp_detach_db @dbname = N'mydb'
GO
answered Oct 26, 2011 at 15:48
goku_da_mastergoku_da_master
4,2371 gold badge40 silver badges42 bronze badges
3
Add permission to the folder where your .mdf file is.
Check this name: NT ServiceMSSQLSERVER
And change the Location to your server name.
gvlasov
18.5k20 gold badges73 silver badges109 bronze badges
answered Feb 4, 2015 at 16:17
LeonardoLeonardo
2112 silver badges2 bronze badges
1
Run SQL Server Management Studio as an Administrator. (right click-> run as administrator) worked for me with Windows 7 — SQL server 2008 R2
answered Aug 27, 2014 at 9:50
![]()
Rolwin CrastaRolwin Crasta
4,2093 gold badges35 silver badges45 bronze badges
2
This problem is caused by UAC (User Account Control), isn’t it? Although your user account is a member of Administrators group, the UAC in Windows 7 doesn’t allow you do do administrator things unless you run programs «as administrator». It is not a real bug in SQL Server or Management Studio or whatever. (Although it could possibly know the problem and ask you for elevated permissions instead of just complaining «error 5».)
answered Jun 16, 2012 at 1:52
Al KeppAl Kepp
5,8112 gold badges27 silver badges48 bronze badges
A SQL2005 database can be attached in this way in Windows 7:
start menu >
all program >
Microsoft sql server 2005 >
sql server management studio >
right click >
run as administrator >
click ok
And then attached database successfully completed.
Artjom B.
61.1k24 gold badges124 silver badges222 bronze badges
answered Dec 11, 2015 at 14:50
1
When you login as sa (or any Sql Server account), you’re functioning as the SQL Server service account, when you’re logged in as you, you have the permissions of your account. For some reason you don’t have the appropriate file access but the service account does.
answered Feb 24, 2010 at 23:27
![]()
Nick CraverNick Craver
622k136 gold badges1295 silver badges1155 bronze badges
4
I found this solution: Right click on folder where you store your .mdf file —> click Properties —> choose Security tab, click Edit… and give it full control.
Hope this helps!
answered Oct 1, 2016 at 7:40
dnguyendnguyen
1491 gold badge2 silver badges12 bronze badges
it can be fixed easly but radicaly, just go to the folder where you have stored mdf file. select file-> Right click ->click on properties and give full permissions to file for logged in user Security.
answered Sep 19, 2014 at 9:12
![]()
Ema.HEma.H
2,8623 gold badges27 silver badges41 bronze badges
The sa user uses NTFS accounts SQLServerMSSQLUser$<computer_name>$<instance_name> and SQLServerSQLAgentUser$<computer_name>$<instance_name> to access the database files. You may want to try adding permissions for one or both these users.
I don’t know if solves your problem since you say you have no problems with the sa user, but I hope it helps.
answered Mar 5, 2010 at 13:08
djeidotdjeidot
4,5344 gold badges42 silver badges45 bronze badges
0
With me
— Running on window 8
— RIght click SQL Server Manager Studio -> Run with admin. -> attach no problems
answered Feb 27, 2014 at 14:02
![]()
WolfWolf
6,3222 gold badges28 silver badges25 bronze badges
Every time I have run into this issue was when attempting to attach a database that is in a different directory from the default database directory that is setup in SQL server.
I would highly recommend that instead of jacking with permissions on various directories and accounts that you simply move your data file into the directory that sql server expects to find it.
answered Apr 8, 2011 at 0:17
NotMeNotMe
87.2k27 gold badges170 silver badges244 bronze badges
4
I just wanted to add this information as well.
http://www.mssqltips.com/sqlservertip/2528/database-attach-failure-in-sql-server-2008-r2/
Solution
You get this error because two different logins did the detach and attach operations. So the files, when detached, were owned by the first login, but the attach failed because the login that was used was not the owner of the mdf and ldf files.
When we detach database files, the owner becomes the person who did the detach command, so to resolve the issue we need to change or add the other login as the owner of the mdf and ldf files.
Right click on the «filename.mdf» file and select properties to check the permissions of the mdf file. Here we can see that only one account has permission to the «filename.mdf» file because that was the account that was used to detach the database.
To resolve this issue, click on the Add… button to add the other login or any other login needed and give the login Full Control. You should do this for the «ldf» file as well. Once you have completed this task click the OK button. (Note for other OS versions you may have an Edit option , click this first and then you will see the Add… option.)
1
For what it’s worth to anyone having the particular variation of this problem that I had:
- SQL Express 2008
- Visual Studio 2010 Premium
Through the context menu of the App_data folder I had created a SQL Express database for debugging purposes. The connection string (used by NHibernate) was as follows:
Server=.SQLExpress;
AttachDbFilename=|DataDirectory|DebugDatabase.mdf;
Database=DebugDatabase;
Trusted_Connection=Yes;
This gave me the same «Access denied» error on the database file. I tried giving various users Full Control to the folder and files, at one point even to «Everyone». Nothing helped, so I removed the added permissions again.
What finally solved it was to open the Server Explorer in Visual Studio, then connect to the MDF, and detach it again. After I’d done that my web app could access the database just fine.
PS. Credits go to this blog post I found while googling this particular problem, triggering the idea to attach/detach the database to solve the issue.
answered Mar 6, 2012 at 21:48
JeroenJeroen
60.2k40 gold badges203 silver badges338 bronze badges
I moved a database mdf from the default Data folder to my asp.net app_data folder and ran into this problem trying to set the database back online.
I compared the security settings of the other file databases in the original location to the moved files and noticed that MSSQL$SQLEXPRESS was not assigned permissions to the files in their new location. I added Full control for «NT SERVICEMSSQL$SQLEXPRESS» (must include that NT SERVICE) and it attached just fine.
It appears that the original Data folder has these permissions and the files inherit it. Move the files and the inheritance breaks of course.
I checked another project’s mdf file which I created directly into its app_data folder. it does not have MSSQL$SQLEXPRESS permissions. Hmmm. I wonder why SQL Express likes one but not the other?
answered Feb 18, 2016 at 5:36
![]()
Brad MathewsBrad Mathews
1,5452 gold badges22 silver badges45 bronze badges
1
I got this error as sa.
In my case, database security didn’t matter.
I added everyone full control to the mdf and ldf files,
and attach went fine.
answered Nov 14, 2011 at 15:34
toddmotoddmo
20.3k14 gold badges94 silver badges104 bronze badges
This sounds like NTFS permissions. It usually means your SQL Server service account has read only access to the file (note that SQL Server uses the same service account to access database files regardless of how you log in). Are you sure you didn’t change the folder permissions in between logging in as yourself and logging in as sa? If you detach and try again, does it still have the same problem?
answered Mar 5, 2010 at 12:25
2
I had the same issue when attaching a database. It wasn’t a SQL issue it was an account issue. Go to the panel control/User Account Control Settings/Set to «never notify». Finally,restart the computer and it worked for me.
answered Sep 1, 2011 at 16:42
PaolaPaola
111 bronze badge
I attached the mdf file by right clicking the database and removing the log file
AdventureWorks2012_Data_log.ldf in the wizard . The mdf file was placed in the following location
C:Program FilesMicrosoft SQL ServerMSSQL10.SQLEXPRESSMSSQLDATA
The above method helped me to resolve the issue .
answered Apr 26, 2012 at 15:03
praveenpraveen
12k1 gold badge41 silver badges49 bronze badges
Copy Database to an other folder and attach or Log in SQLServer with «Windows Authentication»

answered May 16, 2015 at 8:23
![]()
Chưa biếtChưa biết
9198 silver badges6 bronze badges
I was reading this page and they have an interesting sentence in there:
Caution: Be very selective when adding
users to these roles. For example,
sysadmin maps out to dbo in every
database and is the equivalent of
logging in using the sa account.
Of course, they also have this:
Permissions that are granted to users
and roles and are database specific.
All permissions are cumulative with
the exception of a DENY. A denied
permission at either a user level or
at a role level overrides the same
permission granted via other role
memberships with the exception of the
sysadmin fixed server role. (A
sysadmin retains all permissions, even
if a role they are a member of has a
DENY permission.)
So if you’re a domain admin and in SQL ‘sysadmin’ group, the world should be your crustacean.
Of course, according to Microsoft, you should be taking a quick look at these two pages:
Link to Database Prerequisites
Link to Installing Databases
You’re being naughty and trying to attach them manually  Seriously though, do you have all the prerequisites for the AdventureWorks2008 database?
Seriously though, do you have all the prerequisites for the AdventureWorks2008 database?
I suspect this is just another Microsoft oddity/edge case, but I could be wrong.
![]()
sudhansu63
5,9854 gold badges39 silver badges51 bronze badges
answered Mar 2, 2010 at 13:57
TrevokeTrevoke
4,1051 gold badge27 silver badges48 bronze badges
1

USE [master]
GO
CREATE DATABASE [DataBasename] ON
( FILENAME = N'C:dataDataBasename.mdf' )
FOR ATTACH
GO
change to
FOR ATTACH — > FOR ATTACH_FORCE_REBUILD_LOG
USE [master]
GO
CREATE DATABASE [DataBasename] ON
( FILENAME = N'C:dataDataBasename.mdf' )
FOR ATTACH_FORCE_REBUILD_LOG
GO
answered Sep 3, 2017 at 2:57
0
I was facing same issue in VS 2019. if anyone still facing same issue then please make sure you have/do following things:
- You should have SQL Express installed on your m/c
- Should have SSDT installed in VS (in VS 2019- make sure to check
this component while installing) for previous versions — you
have to add this component externally - Add ‘User Instance = True’ to your connectionstring
- I think its optional — open VS and SQL Express in administrative mode and login as admin to SQL Express
answered Feb 10, 2020 at 17:42
Ashu_90Ashu_90
9047 silver badges8 bronze badges
It is in fact NTFS permissions, and a strange bug in SQL Server. I’m not sure the above bug report is accurate, or may refer to an additional bug.
To resolve this on Windows 7, I ran SQL Server Management Studio normally (not as Administrator). I then attempted to Attach the MDF file. In the process, I used the UI rather than pasting in the path. I noticed that the path was cut off from me. This is because the MS SQL Server (SQLServerMSSQLUser$machinename$SQLEXPRESS) user that the software adds for you does not have permissions to access the folder (in this case a folder deep in my own user folders).
Pasting the path and proceeding results in the above error. So — I gave the MS SQL Server user permissions to read starting from the first directory it was denied from (my user folder). I then immediately cancelled the propagation operation because it can take an eternity, and again applied read permissions to the next subfolder necessary, and let that propagate fully.
Finally, I gave the MS SQL Server user Modify permissions to the .mdf and .ldf files for the db.
I can now Attach to the database files.
answered Apr 8, 2011 at 0:12
Chris MoschiniChris Moschini
36.5k19 gold badges160 silver badges188 bronze badges
If you run sql server 2012 you can get this error by trying to attach an older version of an mdf-file. ex an mdf file from sql server 2008.
answered Oct 18, 2012 at 9:23
1
I have solved the problem by just move the .mdf file that you want to attach to the public folder, in my case I moved it to the users/public folder. Then I attach it from there without any problem. Hope this helps.
answered Aug 26, 2013 at 0:44
For those who could not fix the problem with the other solutions here, the following fix worked for me:
Go to your «DATA» folder in your SQL Server installation, right click, properties, security tab, and add full control permissions for the «NETWORK SERVICE» user.
(The above link is for SQL 2005, but this fixed a SQL 2008 R2 installation for me).
Some additional info: This problem showed up for me after replacing a secondary hard drive (which the SQL installation was on). I copied all the files, and restored the original drive letter to the new hard disk. However, the security permissions were not copied over. I think next time I will use a better method of copying data.
answered Dec 10, 2013 at 20:15
marknuzzmarknuzz
2,8071 gold badge25 silver badges29 bronze badges
In my case what solved the problem was the folowing:
USE [master]
GO
CREATE DATABASE [AdventureWorks2008R2] ON
( FILENAME = 'C:Program FilesMicrosfot SQL ServerMSSQL10_50.SQLEXPRESSMSSQLDATAAdventureWors2008R2_Data.mdf')
FOR ATTACH_REBUILD_LOG
answered Feb 21, 2015 at 14:13
![]()
Nick_Nick_
111 silver badge4 bronze badges
I’ve had the same issue when re-attaching database after detaching it and moving ldf and mdf files from drive C to F.
In order to fix it I had to add OWNER RIGHTS principal to both files and gave it full control over them in the Security tab of the Properties dialog.
answered Nov 30, 2015 at 14:17

Добрый день, пытаюсь присоединить базу данных созданную в sql server 2008 r2 в sql server 2008 r2.
Но вылетает ошибка
ЗАГОЛОВОК: Microsoft SQL Server Management Studio
——————————
Действие Присоединить базу данных завершилось неудачно для объекта «Сервер» «DESKTOP-P4T3G98». (Microsoft.SqlServer.Smo)
Чтобы получить справку, щелкните: http://go.microsoft.com/fwlink… nkId=20476
——————————
ДОПОЛНИТЕЛЬНЫЕ СВЕДЕНИЯ:
При выполнении инструкции или пакета Transact-SQL возникло исключение. (Microsoft.SqlServer.ConnectionInfo)
——————————
Не удалось открыть физический файл «F:Cinema.mdf». Ошибка операционной системы 5: «5(Отказано в доступе.)». (Microsoft SQL Server, ошибка: 5120)
Чтобы получить справку, щелкните: http://go.microsoft.com/fwlink… nkId=20476
——————————
КНОПКИ:
ОК
——————————
в чем проблема?
При попытке присоединия базывот такое вылетает:
ЗАГОЛОВОК: Microsoft SQL Server Management Studio
——————————
Действие Присоединить базу данных завершилось неудачно для объекта «Сервер» «192.168.0.198».
(Microsoft.SqlServer.Smo)
Чтобы получить справку, щелкните: http://go.microsoft.com/fwlink?ProdName=Microsoft+SQL+Server&ProdVer=10.0.2531.0+((Katmai_PCU_Main).090329-1045+)&EvtSrc=Microsoft.SqlServer.Management.Smo.ExceptionTemplates.FailedOperationExceptionText&EvtID=Присоединить+базу+данных+Server&LinkId=20476
——————————
ДОПОЛНИТЕЛЬНЫЕ СВЕДЕНИЯ:
При выполнении инструкции или пакета Transact-SQL возникло исключение. (Microsoft.SqlServer.ConnectionInfo)
——————————
Возможно, файл «C:Program FilesMicrosoft SQL ServerMSSQL10.MSSQLSERVERMSSQLDATAInetOlds.ndf» был усечен операционной системой. Ожидаемый размер составляет 119808000 КБ, однако реальный размер — 115712000 КБ.
Невозможно открыть новую базу данных «InetStat». Операция CREATE DATABASE прервана. (Microsoft SQL Server, ошибка: 5125)
как видно, ошибка не с mdf, а с ndf файлом — который уже и увеличивал и обнулял — база подключаться не хочет никак — даже с потерей данных. Подскажите, как насильно ее подключить? чтоб dbcc делать начать?
(логов и баков увы…  нет)
нет)
При попытке присоединения базы данных на школьном пк, появляется ошибка. Возможно ли это исправить? Можно ли изменить версию базы данных на 612? Так как обноление версии на школьном пк невозможно.

задан 22 мар 2018 в 8:12
![]()
Версия 706 — это файл базы данных с Sql Server 2012
Версия 663 — это файл базы данных из Sql Server 2008R2 (> SP1)
С учетом совместимости версий, нет способов работать с версией файла 2012 года на инстансе с версией 2008R2.
Варианты решения проблемы:
- Апдейт инстанса
- Экспорт схемы и данных стандартными инструментами экспорта
ответ дан 22 мар 2018 в 8:59
![]()
Nick ProskuryakovNick Proskuryakov
3,7222 золотых знака14 серебряных знаков39 бронзовых знаков
1
Сделать даунгрейд базы невозможно.
Вам необходимо присоединить базу к актуальной версии SQL Server.
Судя по сообщению ошибки, Вам подойдет SQL Server 2012 и выше.
Можно воспользоваться бесплатной версией Express.
ответ дан 22 мар 2018 в 8:59
![]()
The solutions on this page can be applied to resolve 5123 error with access denied or database attach failure in MS SQL Server 2014/2012/2008 R2/2005.
When you try to attach a database in SQL Server, but get an error message, reporting that «Microsoft SQL Server, Error: 5123» as the image shown below:
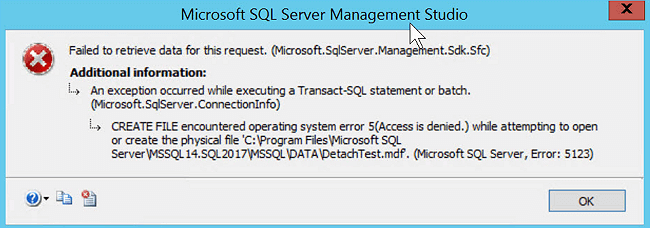
You will not be able to access the SQL Server database. Check the list of reasons that cause SQL error 5123, and if you find that your problem matches the listed reasons, read on to find the solution and fix this error:
- Database Attach Failure: Attaching and detaching database data file with several different logins.
- Access Denied: Attach a database which is placed on a different location and doesn’t have sufficient privileges to the folder directory or no proper permission to run the program folder.
Although, many experienced administrators know how to resolve the 5123 error in SQL Server. It’s still necessary to know better and more effective methods to fix and repair more SQL Server database problems. Read on, and learn how to fix SQL Server 5123 error on your own.
Manual workaround to fix MS SQL Server 5123 error
By following the below manual steps, you’ll be able to resolve the Microsoft SQL Server error 5123 quickly:
- Step 1: Run SQL Server and right-click on the MDF or NDF file that you wish to attack.
- Step 2: Select «Properties» to check the permission of .mdf or .ndf file.
- Step 3: Click the «Add» button to grant the login permission and gain full control during the login process.
Also, you can attempt «Run as Administrator» to gain permission instead of granting permission to a new user.
Recommended tools to resolve SQL Server 5123 error
If you are using MS SQL Server Management Studio (SSMS) or Transaction SQL Server (T-SQL) to configure and manage the SQL Server, you can use these two tools to resolve the 5123 error.
Also, you can turn to a third party MS SQL Recovery tool for help.
Use SSMS to fix SQL 5123 error
- Step 1: Log in to SSMS: use valid domain credentials and Windows Authentication to log in.
- Step 2: Click on «Object Explorer», select «Database».
- Step 3: Right-click on the database that you are trying to attach, and select «Attach».
- Step 4: Click «Add» when a new attach database dialog box appears.
- Step 5: Select the database, confirm the MDF and LDF files are running alright. And click «OK» to finish.
Then, you can view all attached database files in MS SQL Server again.
If the program reminds you that the MDF file is corrupted, relax, follow the link here and apply EaseUS MS SQL recovery tool to repair corrupted MDF file immediately.
Use T-SQL to resolve MS SQL 5123 error
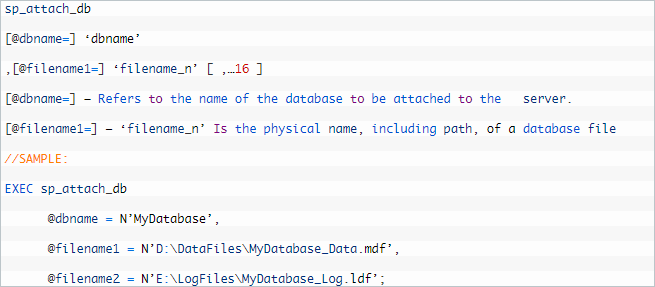
Transaction SQL Server with its sp_attach_db stored procedure can help you easily attach all desired databases in SQL.
Here are the detail process of attaching SQL Server databse:
- sp_attach_db
- [@dbname=] ‘dbname’
- ,[@filename1=] ‘filename_n’ [ ,…16 ]
- [@dbname=] – Refers to the name of the database to be attached to the server.
- [@filename1=] – ‘filename_n’ Is the physical name, including path, of a database file
Use SQL Server recovery tool to solve MS SQL error 5123
If the above-provided methods don’t work efficiently to resolve the 5123 attach database error in SQL, you can go for a reliable SQL Server recovery tool for help. It helps you to repair corrupted MFD and NDF file in SQL Server and some other complex database corruption issues. This software enables any user to operate SQL Server repair with its clear and self-explanatory interface.
Note: Mostly, EaseUS SQL Server Recovery can always work to fix this issue. But if it fails in a rare case, you can turn to Microsoft customer support team for help.
Step 1. Run EaseUS MS SQL Recovery.
Step 2. Select the MDF/NDF file: Click «Browse» or «Search” to navigate the location of your MDF or NDF file > Click «Repair».
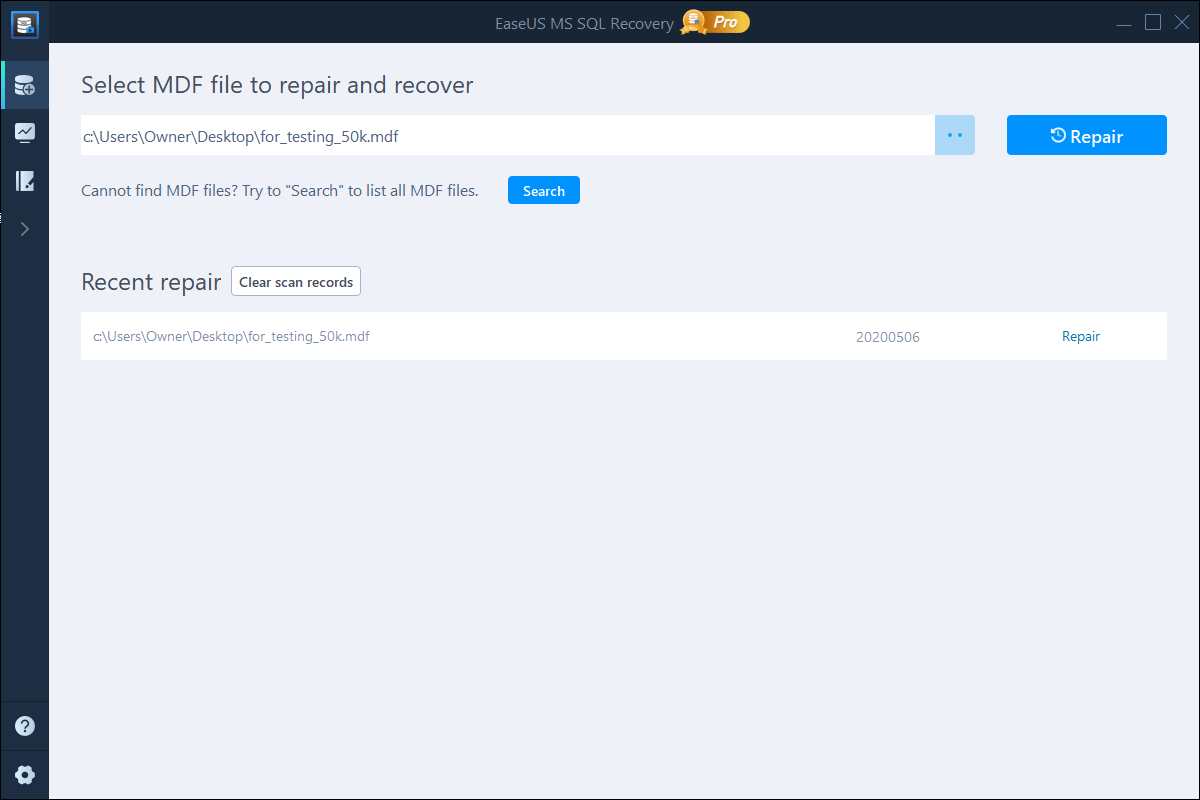
Step 3. Select the database objects you want to recover: When the process has completed, select the database objects you want to recover and click «Export».
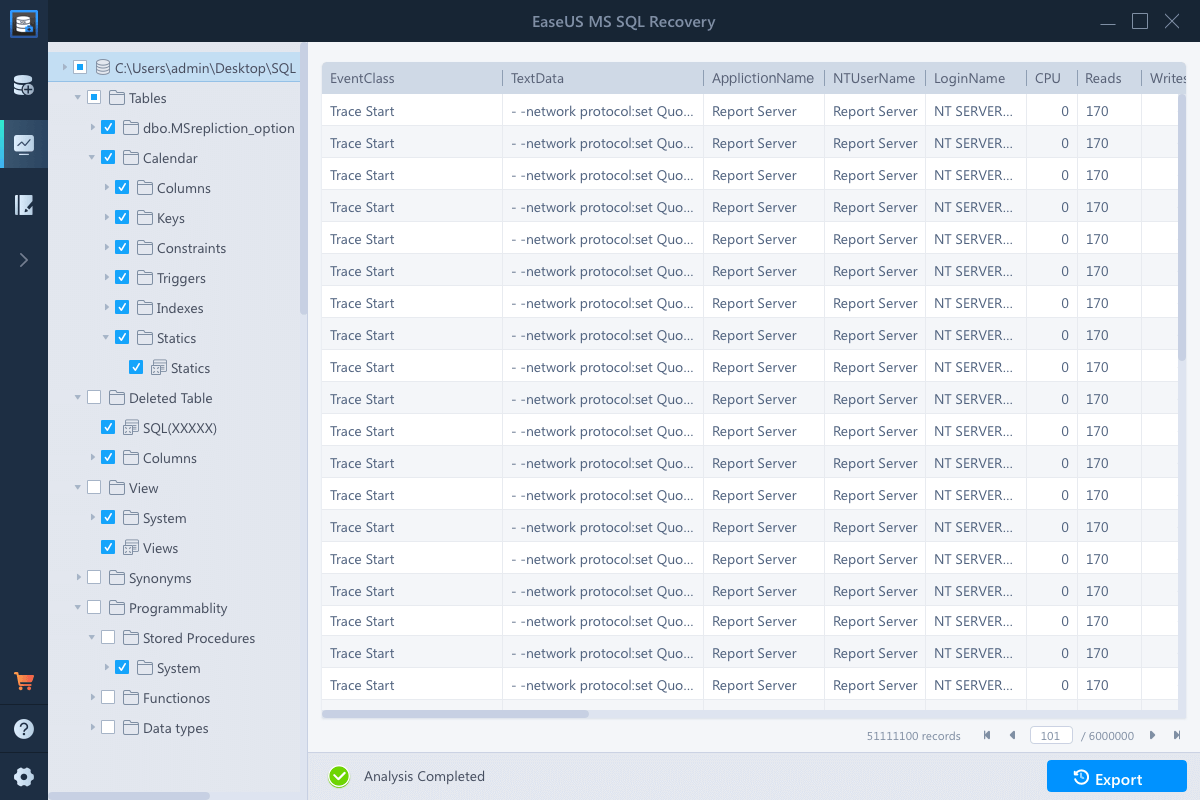
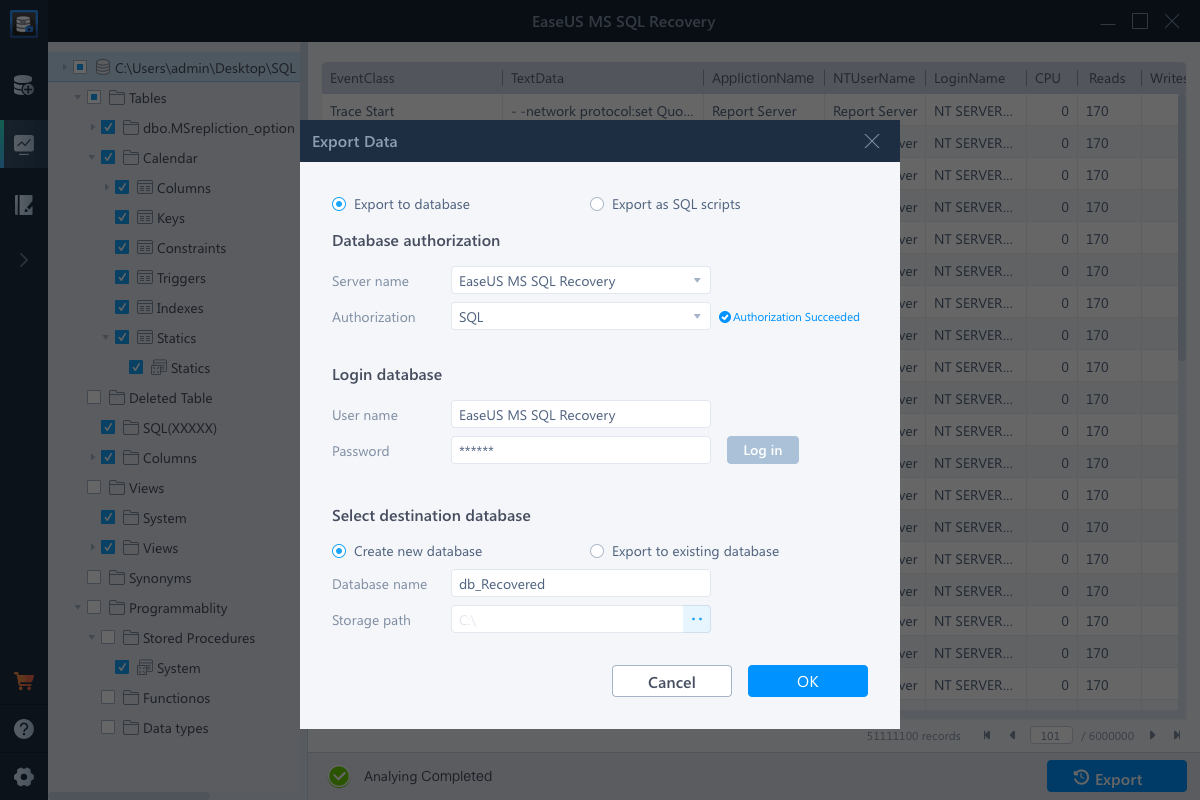
Step 4. Export the database to the database or export the selected items as SQL scripts. If you choose «Export to database», you will need to enter the required information and select the destination database, either a new one or an existing one.
Hence, we would like to recommend you always to keep this software handy. In addition to solving this error, EaseUS SQL Server Recovery can be used to rectify other SQL database problems too:
- Resolve SQL Database corruption with 823/824/825 error
- Recover deleted SQL records
- Repair MDF/NDF file
- Recover ROW and PAGE compressed data
- Free to preview the repaired database before activation
- Save the repaired file in MS SQL (MDF), HTML, XLS & CSV formats
- Support transferring the license to another system (one key for three systems)
The solutions on this page can be applied to resolve 5123 error with access denied or database attach failure in MS SQL Server 2014/2012/2008 R2/2005.
When you try to attach a database in SQL Server, but get an error message, reporting that «Microsoft SQL Server, Error: 5123» as the image shown below:

You will not be able to access the SQL Server database. Check the list of reasons that cause SQL error 5123, and if you find that your problem matches the listed reasons, read on to find the solution and fix this error:
- Database Attach Failure: Attaching and detaching database data file with several different logins.
- Access Denied: Attach a database which is placed on a different location and doesn’t have sufficient privileges to the folder directory or no proper permission to run the program folder.
Although, many experienced administrators know how to resolve the 5123 error in SQL Server. It’s still necessary to know better and more effective methods to fix and repair more SQL Server database problems. Read on, and learn how to fix SQL Server 5123 error on your own.
Manual workaround to fix MS SQL Server 5123 error
By following the below manual steps, you’ll be able to resolve the Microsoft SQL Server error 5123 quickly:
- Step 1: Run SQL Server and right-click on the MDF or NDF file that you wish to attack.
- Step 2: Select «Properties» to check the permission of .mdf or .ndf file.
- Step 3: Click the «Add» button to grant the login permission and gain full control during the login process.
Also, you can attempt «Run as Administrator» to gain permission instead of granting permission to a new user.
Recommended tools to resolve SQL Server 5123 error
If you are using MS SQL Server Management Studio (SSMS) or Transaction SQL Server (T-SQL) to configure and manage the SQL Server, you can use these two tools to resolve the 5123 error.
Also, you can turn to a third party MS SQL Recovery tool for help.
Use SSMS to fix SQL 5123 error
- Step 1: Log in to SSMS: use valid domain credentials and Windows Authentication to log in.
- Step 2: Click on «Object Explorer», select «Database».
- Step 3: Right-click on the database that you are trying to attach, and select «Attach».
- Step 4: Click «Add» when a new attach database dialog box appears.
- Step 5: Select the database, confirm the MDF and LDF files are running alright. And click «OK» to finish.
Then, you can view all attached database files in MS SQL Server again.
If the program reminds you that the MDF file is corrupted, relax, follow the link here and apply EaseUS MS SQL recovery tool to repair corrupted MDF file immediately.
Use T-SQL to resolve MS SQL 5123 error
Transaction SQL Server with its sp_attach_db stored procedure can help you easily attach all desired databases in SQL.
Here are the detail process of attaching SQL Server databse:
- sp_attach_db
- [@dbname=] ‘dbname’
- ,[@filename1=] ‘filename_n’ [ ,…16 ]
- [@dbname=] – Refers to the name of the database to be attached to the server.
- [@filename1=] – ‘filename_n’ Is the physical name, including path, of a database file

Use SQL Server recovery tool to solve MS SQL error 5123
If the above-provided methods don’t work efficiently to resolve the 5123 attach database error in SQL, you can go for a reliable SQL Server recovery tool for help. It helps you to repair corrupted MFD and NDF file in SQL Server and some other complex database corruption issues. This software enables any user to operate SQL Server repair with its clear and self-explanatory interface.
Note: Mostly, EaseUS SQL Server Recovery can always work to fix this issue. But if it fails in a rare case, you can turn to Microsoft customer support team for help.
Step 1. Run EaseUS MS SQL Recovery.
Step 2. Select the MDF/NDF file: Click «Browse» or «Search” to navigate the location of your MDF or NDF file > Click «Repair».

Step 3. Select the database objects you want to recover: When the process has completed, select the database objects you want to recover and click «Export».

Step 4. Export the database to the database or export the selected items as SQL scripts. If you choose «Export to database», you will need to enter the required information and select the destination database, either a new one or an existing one.

Hence, we would like to recommend you always to keep this software handy. In addition to solving this error, EaseUS SQL Server Recovery can be used to rectify other SQL database problems too:
- Resolve SQL Database corruption with 823/824/825 error
- Recover deleted SQL records
- Repair MDF/NDF file
- Recover ROW and PAGE compressed data
- Free to preview the repaired database before activation
- Save the repaired file in MS SQL (MDF), HTML, XLS & CSV formats
- Support transferring the license to another system (one key for three systems)
Поврежденная база данных — это, наверное, один из худших ночных кошмаров большинства администраторов баз данных. Результатом повреждения являются простои, вопли менеджеров и всякие другие неприятные штуки.
В этой статье я объясню что нельзя делать с поврежденной базой данных и опишу кое-что из того, что должно быть сделано, некоторые виды повреждений и как их можно исправить.
Как обнаружить, что база данных повреждена
Обычно повреждения превосходно обнаруживаются при попытке доступа к поврежденной странице. Запросы, бэкапы или процедуры реиндексации завершаются ошибками с высокими уровнями серьезности.
Вот пара примеров системных сообщений при обнаружении повреждения БД:
SQL Server detected a logical consistency-based I/O error: incorrect checksum (expected: 0xfdff74c9; actual: 0xfdff74cb). It occurred during a read of page (1:69965) in database ID 13 at offset 0x0000002229a000 in file ‘D:DevelopDatabasesBroken1.mdf’.
Attempt to fetch logical page 1:69965 in database 13 failed. It belongs to allocation unit 72057594049069056 not to 281474980642816.
Основная проблема заключается в том, что если проверки целостности базы данных не производятся на постоянной основе, то повреждение может быть обнаружено спустя часы, дни и даже месяцы, после того, как оно образовалось, в тот момент, когда уже сложно будет что-то исправить.
Я не буду описывать ситуацию когда база данных перешла в состояние «suspect» («подозрительная» в русской редакции SQL Server — прим. переводчика). Описание всевозможных причин почему база данных может перейти в «suspect» и множества вариантов исправления этого — тема отдельной статьи, если не книги.
Что делать если база данных все-таки повреждена
- Не паниковать
- Не отсоединять (detach) ее
- Не перезапускать SQL Server
- Не начинать восстановление сразу
- Запустить проверку целостности
- Найти причину
Не паниковать
Самое важное, при обнаружении повреждения БД — это не паниковать. Любые принимаемые решения должны быть тщательно взвешаны, во внимание должны быть приняты все возможные факторы. Чертовски просто ухудшить ситуацию приняв не до конца обдуманное решение.
Не отсоединять базу данных
В большинстве случаев, когда SQL Server обнарживает повреждение базы данных, это означает, что в БД на самом деле есть поврежденные страницы. Попытка убедить SQL Server что это не так, путем отсоединения (detach) и повторного присоединения (attach) БД, бэкапа и последующего восстановления, перезапуска службы SQL Server, либо перезагрузки сервера, не приведет к тому, что ошибка исчезнет.
Если база данных повреждена и SQL Server обнаружит это при присоединении, он не сможет присоединить ее. Есть несколько способов заставить его увидеть эту БД, но намного лучше просто не отсоединять ее.
Не перезапускать SQL Server
Точно так же, как при отсоединении-присоединении, перезапуск службы SQL Server не сможет исправить обнаруженные ошибки (если они есть).
Перезапуск службы может сделать ситуацию хуже. Если SQL Server обнаружит ошибки во время выполнения фазы восстановления (recovery) БД после перезапуска, он пометит ее как «suspect», что сильно усложнит процесс восстановления БД.
Не начинать восстановление сразу
У вас может возникнуть соблазн просто запустить DBCC CHECKDB с одним из «восстановительных» параметров (обычно допускающими потерю данных) и надеяться, что все станет лучше (по моему опыту — первое что рекомендуют на «непрофильных» форумах по SQL Server — запустить DBCC CHECKDB REPAIR_ALLOW_DATA_LOSS — прим. переводчика). Во многих случаях запуск такого восстановления не рекомендуется. Он не гарантирует исправления всех ошибок и может привести к недопустимой потере данных.
Такое восстановление — это последний шаг при исправлении ошибок. Оно должно быть запущено только если у вас уже нет другого выбора, но никак не в первую очередь.
Запустить проверку целостности
Для того чтобы решить как исправить базу данных, мы точно должны знать что именно повреждено. Единственный способ, которым мы можем это выяснить — запустить DBCC CHECKDB с параметром All_ErrorMsgs (в SQL Server 2005 SP3, SQL Server 2008 SP1 и в более старших версиях, этот параметр включен по умолчанию, указывать его не обязательно). Помните, что если вы запустите DBCC CHECKDB без параметра No_InfoMsgs, в выводе этой процедуры будет информация о количестве строк и страниц в каждой таблице, что вряд ли будет вас интересовать при анализе ошибок.
DBCC CHECKDB может долго выполняться на больших БД, но необходимо дождаться пока эта процедура не закончит работу. Грамотная стратегия восстановления может быть построена только при наличии информации обо всех проблемах в БД.
Найти причину
После того как ошибки исправлены, работу нельзя считать законченной. Если причина этих ошибок не установлена, они могут возникнуть снова. Обычно, основной причиной ошибок являются проблемы с подсистемой ввода-вывода, но они также могут быть вызваны неправильной работой «низкоуровнего ПО» (вроде антивируса), действиями человека, либо багами самого SQL Server.
Что дальше
Дальнейшие действия по исправлению ошибок целиком и полностью зависят от результатов выполнения CheckDB. Чуть дальше я покажу несколько наиболее часто возникающих ошибок (учтите, что эта статья не претендует на звание полного описания всевозможных ошибок).
Описанные ошибки располагаются по возрастанию уровня серьезности — от наименее серьезных к наиболее серьезным. В общем-то, для наиболее серьезных ошибок, находимых CheckDB, есть описание доступных методов их резрешения.
Если у вас вдруг обнаружится ошибка не описанная в статье, обратите внимание на последний раздел — «Поиск помощи».
Неверная информация о свободном месте на странице
Msg 2508, Level 16, State 3, Line 1
The In-row data RSVD page count for object «Broken1», index ID 0, partition ID 76911687695381, alloc unit ID 76911687695381 (type In-row data) is incorrect. Run DBCC UPDATEUSAGE.
В SQL Server 2000, количество строк и страниц в таблице или индексе, хранящееся в метаданных, могло не соответствовать действительности (и даже быть отрицательным) и DBCC CHECKDB не видел в этом ничего плохого. В SQL Server 2005, это количество должно быть правильным и CheckDB выдаст предупреждение, если вдруг найдет несоответствие.
Это несерьезная прблема и очень легко разрешается. Как говорится в сообщении, нужно всего лишь запустить DBCC UPDATEUSAGE в контексте нужной БД и предупреждение исчезнет. Эта ошибка часто встречается в базах данных обновленных с SQL Server 2000 и не должна появляться в базах данных, созданных в SQL Server 2005/2008.
Msg 8914, Level 16, State 1, Line 1
Incorrect PFS free space information for page (1:26839) in object ID 181575685, index ID 1, partition ID 293374720802816, alloc unit ID 76911687695381 (type LOB data). Expected value 0_PCT_FULL, actual value 100_PCT_FULL.
Эта ошибка появляется, когда PFS-страница (Page Free Space), которая учитывает насколько заполнены страницы в БД, содержит некорректные значения. Эта ошибка, как и упомянутая ранее, не является серьезной. Алгоритм, по которому определялось насколько заполнены страницы, в SQL Server 2000 не всегда отрабатывал правильно. Для решения этой проблемы нужно запустить DBCC CHECKDB с параметром REPAIR_ALLOW_DATA_LOSS и, если это единственная ошибка в БД, никакие данные, на самом деле, не пострадают.
Повреждение только некластерных индексов
Если все ошибки, найденные CheckDB, относятся к индексам с ID = 2 и больше, это означет, что были повреждены только некластерные индексы. Поскольку информация, содержащаяся в некластерных индексах, является «избыточной» (те же самые данные хранятся в куче, либо в кластерном индексе — прим. переводчика), эти повреждения могут быть исправлены без потери каких-либо данных.
Если все ошибки, найденные CheckDB, относятся к некластерным индексам, рекомендуемый «уровень восстановления» для DBCC CHECKDB — REPAIR_REBUILD. Примеры таких ошибок (на самом деле ошибок такого типа намного больше):
Msg 8941, Level 16, State 1, Line 1
Table error: Object ID 181575685, index ID 4, page (3:224866). Test (sorted [i].offset >= PAGEHEADSIZE) failed. Slot 159, offset 0x1 is invalid.
Msg 8942, Level 16, State 1, Line 1
Table error: Object ID 181575685, index ID 4, page (3:224866). Test (sorted[i].offset >= max) failed. Slot 0, offset 0x9f overlaps with the prior row.
В этом случае, повреждение может быть полностью исправлено удалением поврежденных некластерных индексов и повторным их созданием. Перестроение индекса (ALTER INDEX REBUILD) в режиме on-line (и иногда в off-line) читает страницы старого индекса для создания нового и, следовательно, завершится с ошибкой. Поэтому, необходимо удалить старые индексы и создать их заново.
Именно это сделает DBCC CHECKDB с параметром REPAIR_REBUILD, но база данных при этом должна быть в однопользовательском режиме. Вот почему обычно лучше вручную выполнить эти операции, чтобы с базой данных можно было продолжать работать, пока индексы будут пересоздаваться.
Если у вас недостаточно времени на то, чтобы пересоздать нужные индексы и в наличии есть «чистый» (не содержащий в себе ошибок) полный бэкап и бэкапы журнала транзакций с неразорванной цепочкой журналов, вы можете восстановить поврежденные страницы из них.
Повреждение LOB-страниц
Msg 8964, Level 16, State 1, Line 1
Table error: Object ID 181575685, index ID 1, partition ID 72057594145669120, alloc unit ID 72057594087800832 (type LOB data). The off-row data node at page (1:2444050), slot 0, text ID 901891555328 is not referenced.
Ошибка говорит о том, что существуют LOB-страницы (Large OBject), на которые не ссылается ни одна страница с данными. Такое может произойти, если ранее был поврежден кластерный индекс (или куча) и его поврежденные страницы были удалены.
Если CheckDB говорит только о таких ошибках, то можно запускать DBCC CHECKDB с параметром REPAIR_ALLOW_DATA_LOSS — эти страницы будут уничтожены. Поскольку у вас все равно нет страниц с данными, которые ссылаются на эти страницы, бОльшей потери данных уже не будет.
Ошибки, связанные с выходом за пределы допустимого диапазона
Msg 2570, Sev 16, State 3, Line 17
Page (1:1103587), slot 24 in object ID 34, index ID 1, partition ID 281474978938880, alloc unit ID 281474978938880 (type «In-row data»). Column «modified» value is out of range for data type «datetime». Update column to a legal value.
Эти ошибки показывают, что в столбце есть значения выходящие за пределы допустимого диапазона. Это может быть значение типа datetime, предполагающее, что с полуночи прошло больше 1440 минут, строка-Unicode, в которой количество байт не делится на 2, или float/real с неверным значением точности.
Проверка на эти ошибки не выполняется по умолчанию, для баз данных обновленных с версии SQL Server 2000 или более ранних, если перед этим ни разу не выполнялась команда DBCC CHECKDB со включенным параметром DATA_PURITY.
CheckDB не сможет исправить эти ошибки, поскольку неизвестно какие значения поставить взамен неправильных. Исправление таких ошибок не требует особых усилий, но выполняется вручную. Неправильные значения должны быть заменены на что-нибудь приемлимое. Основная проблема — это поиск неверных значений. В этой статье базы знаний есть пошаговая инструкция.
Повреждение кластерного индекса или кучи
Если обнаруживается, что повреждены страницы кучи или листового уровня (leaf pages) кластерного индекса — это означает, что данные на них потеряны. Страницы листового уровня кластерного индекса содержат непосредственно страницы данных и для них избыточность никак не обеспечивается.
Если CheckDB сообщает о повреждении страниц листового уровня кластерного индекса, необходимый «уровень восстановления» для DBCC CHECKDB — REPAIR_ALLOW_DATA_LOSS.
Примеры таких ошибок:
Server: Msg 8976, Level 16, State 1, Line 2
Table error: Object ID 181575685, index ID 1, partition ID 76911687695381, alloc unit ID 76911687695381 (type In-row data). Page (1:22417) was not seen in the scan although its parent (1:479) and previous (1:715544) refer to it.
Server: Msg 8939, Level 16, State 1, Line 2
Table error: Object ID 181575685, index ID 0, page (1:168576). Test (m_freeData >= PAGEHEADSIZE && m_freeData <= (UINT)PAGESIZE — m_slotCnt * sizeof (Slot)) failed. Values are 44 and 8028.
Следует помнить, что если ошибки, возвращаемые CheckDB, относятся к index id = 0 или 1, это значит, что повреждены непосредственно данные.
Такой тип ошибок исправляется, но исправление заключается в уничтожении строк или целых страниц. Когда CheckDB удаляет данные для исправления ошибки, ограничения, налагаемые внешними ключами, не проверяются и никакие триггеры не срабатывают. Строки или страницы просто удаляются. В результате данные могут оказаться не согласованными, либо может быть нарушена логическая целостность (на LOB-страницы может больше не ссылаться ни одна строка, либо строки некластерного индекса могут указывать «в никуда»). Из-за таких последствий, подобное восстановление, не рекомендуется использовать.
Если у вас есть «чистый» бэкап, восстановление из него обычно является более предпочительным, для исправления таких ошибок. Если база данных находится в полной модели восстановления и у вас есть бэкапы журнала транзакций с неразорванной цепочкой журналов (начиная с последнего «чистого» полного бэкапа), вы можете сделать бэкап активной части лога и восстановить базу данных целиком (или только поврежденные страницы), в результате чего данные вообще не будут потеряны.
Если бэкапа с неповрежденными данными нет, у вас остается только один вариант — запуск DBCC CHECKDB с параметром REPAIR_ALLOW_DATA_LOSS. Это потребует перевода базы данных в однопользовательский режим на все время выполнения этой процедуры.
И хотя у вас нет возможности избежать потери данных, вы можете посмотреть какие данные будут удалены из кластерного индекса. Для этого, посмотрите этот пост Пола Рэнадала.
Повреждение метаданных
Msg 3853, Level 16, State 1, Line 1
Attribute (object_id=181575685) of row (object_id=181575685,column_id=1) in sys.columns does not have a matching row (object_id=181575685) in sys.objects.
Подобные ошибки, обычно, возникают в базах данных, обновленных с SQL Server 2000, когда кто-то ковырялся напрямую в системных таблицах.
В системных таблицах любой версии SQL Server внешние ключи не используются, поэтому в SQL Server 2000 была возможность удалить строку из sysobjects (например, таблицу) и оставить в таблицах syscolumns и sysindexes строки, ссылающиеся на удаленную строку.
В SQL Server 2000 CheckDB не проверял целостность системного каталога и такие проблемы зачастую висели незамеченными. В SQL Server 2005, CheckDB проверяет целостность системного каталога и такие ошибки могут проявиться.
Исправление этих ошибок дело не самое легкое. CheckDB не может их исправить, поскольку единственное что можно сделать — это удалить записи из системных таблиц, что, в свою очередь, может вызвать потерю большого количества данных. Если у вас есть бэкап этой БД, сделанный до обновления на SQL Server 2005 и обновление было совсем недавно, вы можете развернуть его на SQL Server 2000, на нем вручную подправить системные таблицы и снова перенести БД на SQL Server 2005.
Если у вас нет бэкапа БД на SQL Server 2000 или обновление прошло слишком давно и потеря данных неприемлима, есть два пути. Первый — отредактировать системные таблицы в SQL Server 2005, но следует учитывать, что это довольно сложный и рискованный процесс, поскольку системные таблицы не документированы и гораздо более сложны, чем в ранних версиях. В этом посте можно найти дополнительную информацию.
Второй путь — это заскриптовать все объекты БД и экспортировать все данные, после чего создать новую базу данных, восстановить объекты и залить данные. Этот вариант более предпочтителен.
Неисправимые повреждения
CheckDB не может исправить все. Любые ошибки вроде приведенных ниже неисправимы и единственный вариант — это восстановление базы данных из бэкапа, в котором нет этих повреждений. Если у вас есть полный бэкап и цепочка журналов не нарушена до текущего времени, вы можете забэкапить заключительный фрагмент журнала транзакций и база данных может быть восстановлена без потери каких-либо данных.
Если таких бэкапов нет, единственное что вы можете сделать — заскриптовать те объекты и выгрузить те данные, которые еще доступны. Вполне вероятно, что из-за повреждений не все данные будут доступны, и, скорее всего, не все объекты смогут быть заскриптованы без ошибок.
Повреждение системных таблиц
Msg 7985, Level 16, State 2, Line 1
System table pre-checks: Object ID 4. Could not read and latch page (1:358) with latch type SH.
Check statement terminated due to unrepairable error.
Msg 8921, Level 16, State 1, Line 1
Check terminated. A failure was detected while collecting facts. Possibly tempdb out of space or a system table is inconsistent.
CheckDB зависит от нескольких критически важных системных таблиц, для того чтобы получить представление о том, что должно быть в базе данных. Если сами эти таблицы повреждены, то CheckDB не может даже предположить что должно быть в базе данных и с чем сравнить текущее положение дел, не говоря уже о том, чтобы что-то исправить.
Повреждение «карт распределения»
Msg 8946, Level 16, State 12, Line 1
Table error: Allocation page (1:2264640) has invalid PFS_PAGE page header values. Type is 0. Check type, alloc unit ID and page ID on the page.
Msg 8998, Level 16, State 2, Line 1
Page errors on the GAM, SGAM, or PFS pages prevent allocation integrity checks in database ID 13 pages from (1:2264640) to (1:2272727)
В этом случае, одна или несколько страниц определяющих размещение данных в БД (карты распределения — прим. переводчика) повреждены. Эти страницы используются для того чтобы определять какие страницы и экстенты в БД используются, а какие свободны. CheckDB не может исправить такие ошибки, поскольку практически невозможно определить (без этих страниц) какие экстенты используются для размещения данных, а какие нет. Простое удаление такой «карты распределения» невозможно, поскольку удаление любой из них повлечет за собой удаление 4 GB данных.
Поиск помощи
Если вы не уверены в том что вам нужно сделать — обратитесь за помощью. Если вдруг вы получаете сообщение о повреждении БД, которое вам непонятно и которое не описано выше — обратитесь за помощью. Если вы не уверены в том, что выбрали наилучший метод восстановления — обратитесь за помощью.
Если у вас есть Senior DBA, обратитесь к нему. Если у вас есть «наставник» — спросите у него. Спросите совета на форумах, но помните, что не все советы полученные на форумах полезны. На самом деле, именно там время от времени публикуются абсолютно неправильные и даже опасные решения.
Обратитесь в службу поддержки Microsoft, наконец. Это будет небесплатно, но они действительно знают что можно сделать с поврежденной базой данных и вполне вероятно, что если ваша база данных критична для предприятия, то стоимость простоя во время самостоятельного поиска решения будет намного выше чем стоимость обращения в саппорт.
Заключение
В этой статье я дал несколько примеров того, что можно сделать при обнаружении поврежденной БД и, что даже важнее, того, что делать не надо. Надеюсь, что теперь вы лучше понимаете какие методы можно применять для решения описанных проблем и насколько важно иметь хорошие бэкапы (и правильно выбрать модель восстановления — прим. переводчика).
Примечание: это мой первый перевод, который, к тому же делался не за раз, а в несколько подходов, вечерами, когда появлялось свободное время, поэтому текст целиком, возможно, кому-то покажется несколько несогласованым. Если где-то я был излишне косноязычен и какая-то часть текста вдруг окажется трудной для понимания — с радостью выслушаю все замечания.
С уважением, unfilled.
P.S. Когда я уже собрался было нажать на кнопочку «Опубликовать», мне на почту свалилась рассылка от SQL Server Central с вот таким вот комиксом.