I use PostgreSQL 12
I have the following two tables:
table_a:
table_a_id | version
1 | v1
2 | v1
3 | v1
4 | v2
5 | v2
6 | v2
table_b:
table_b_id | version | table_a_id
1 | v1 | 1
2 | v1 | 2
3 | v1 | 3
4 | v2 | 4
5 | v2 | 5
6 | v2 | 6
table_b must reference same version table_a_id
i.e The below data is valid entry because table_a_id -> 1 belongs to version ‘v1’
table_b_id | version | table_a_id
1 | v1 | 1
But the below data is invalid entry because table_a_id -> 4 belongs to version ‘v2’
table_b_id | version | table_a_id
1 | v1 | 4
I am new to Postgres trigger functions
I have created the following trigger function to validate ON BEFORE INSERT OR UPDATE to table_b:
CREATE FUNCTION version_check()
RETURNS TRIGGER AS
$BODY$
BEGIN
IF NOT EXISTS (
SELECT
*
FROM
"table_a"
WHERE
"table_a"."table_a_id" = NEW."table_a_id"
AND
"table_a"."version" = NEW."version";
)
THEN
RAISE EXCEPTION 'table_a and table_b Version do not match';
END IF;
RETURN NEW;
END;
$BODY$
LANGUAGE plpgsql;
CREATE TRIGGER "version_check" BEFORE INSERT OR UPDATE ON "table_b"
FOR EACH ROW EXECUTE PROCEDURE version_check();
I am getting the following error on saving the Trigger function in pgAdmin 4
ERROR: syntax error at or near "BEGIN"
LINE 8: BEGIN
^
Am i doing any syntax error? Also will the above trigger function work fine for my requirement ?
Thanks in advance!
I’m trying to create a function, like so:
CREATE FUNCTION RETURNONE(DATE)
BEGIN
RETURN 1;
END
However, when I run this in psql 9.5 I get the following error:
ERROR: syntax error at or near "BEGIN"
LINE 2: BEGIN
^
END
I did see this other StackOverflow thread with a reminiscent problem. Per the second answer, I re-encoded my code in UTF 8, which did nothing. This is my first ever SQL function, so I’m sure I’m missing something painfully obvious. Let me know what!
asked Feb 27, 2019 at 1:00
![]()
3
You omitted some essential syntax elements:
CREATE FUNCTION returnone(date)
RETURNS integer
LANGUAGE plpgsql AS
$func$
BEGIN
RETURN 1;
END
$func$;
The manual about CREATE FUNCTION.
answered Feb 27, 2019 at 1:19
Erwin BrandstetterErwin Brandstetter
577k139 gold badges1034 silver badges1188 bronze badges
4
Syntax errors are quite common while coding.
But, things go for a toss when it results in website errors.
PostgreSQL error 42601 also occurs due to syntax errors in the database queries.
At Bobcares, we often get requests from PostgreSQL users to fix errors as part of our Server Management Services.
Today, let’s check PostgreSQL error in detail and see how our Support Engineers fix it for the customers.
What causes error 42601 in PostgreSQL?
PostgreSQL is an advanced database engine. It is popular for its extensive features and ability to handle complex database situations.
Applications like Instagram, Facebook, Apple, etc rely on the PostgreSQL database.
But what causes error 42601?
PostgreSQL error codes consist of five characters. The first two characters denote the class of errors. And the remaining three characters indicate a specific condition within that class.
Here, 42 in 42601 represent the class “Syntax Error or Access Rule Violation“.
In short, this error mainly occurs due to the syntax errors in the queries executed. A typical error shows up as:
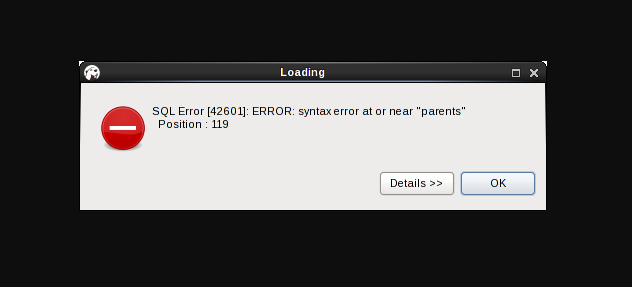
Here, the syntax error has occurred in position 119 near the value “parents” in the query.
How we fix the error?
Now let’s see how our PostgreSQL engineers resolve this error efficiently.
Recently, one of our customers contacted us with this error. He tried to execute the following code,
CREATE OR REPLACE FUNCTION prc_tst_bulk(sql text)
RETURNS TABLE (name text, rowcount integer) AS
$$
BEGIN
WITH m_ty_person AS (return query execute sql)
select name, count(*) from m_ty_person where name like '%a%' group by name
union
select name, count(*) from m_ty_person where gender = 1 group by name;
END
$$ LANGUAGE plpgsql;But, this ended up in PostgreSQL error 42601. And he got the following error message,
ERROR: syntax error at or near "return"
LINE 5: WITH m_ty_person AS (return query execute sql)Our PostgreSQL Engineers checked the issue and found out the syntax error. The statement in Line 5 was a mix of plain and dynamic SQL. In general, the PostgreSQL query should be either fully dynamic or plain. Therefore, we changed the code as,
RETURN QUERY EXECUTE '
WITH m_ty_person AS (' || sql || $x$)
SELECT name, count(*)::int FROM m_ty_person WHERE name LIKE '%a%' GROUP BY name
UNION
SELECT name, count(*)::int FROM m_ty_person WHERE gender = 1 GROUP BY name$x$;This resolved the error 42601, and the code worked fine.
[Need more assistance to solve PostgreSQL error 42601?- We’ll help you.]
Conclusion
In short, PostgreSQL error 42601 occurs due to the syntax errors in the code. Today, in this write-up, we have discussed how our Support Engineers fixed this error for our customers.
PREVENT YOUR SERVER FROM CRASHING!
Never again lose customers to poor server speed! Let us help you.
Our server experts will monitor & maintain your server 24/7 so that it remains lightning fast and secure.
GET STARTED
var google_conversion_label = «owonCMyG5nEQ0aD71QM»;
|
Ayil 0 / 0 / 0 Регистрация: 15.05.2019 Сообщений: 2 |
||||
|
1 |
||||
|
26.03.2020, 09:11. Показов 846. Ответов 1 Метки pgadmin, sql (Все метки)
Напишите процедуру на ввод записей о преподавателях ВГУ. Идентификационные номера преподавателей должны вводится в порядке возрастания.
но выдает:»ошибка синтаксиса (примерное положение: «begin»)» Вот таблица.
__________________ 0 |
|
Programming Эксперт 94731 / 64177 / 26122 Регистрация: 12.04.2006 Сообщений: 116,782 |
26.03.2020, 09:11 |
|
1 |
|
1184 / 914 / 367 Регистрация: 02.09.2012 Сообщений: 2,785 |
|
|
26.03.2020, 16:25 |
2 |
|
декларация переменной должны заканчиваться точкой с запятой 0 |
|
IT_Exp Эксперт 87844 / 49110 / 22898 Регистрация: 17.06.2006 Сообщений: 92,604 |
26.03.2020, 16:25 |
|
Помогаю со студенческими работами здесь Не заходит в pgAdmin PgAdmin настройка Распределенная БД в pgAdmin Ограничить ввод определенных записей в форме Организовать ввод, хранение и сортировку записей Изменение и ввод записей непосредственно в DBGrid Искать еще темы с ответами Или воспользуйтесь поиском по форуму: 2 |
БЛОГ НА HUSL
- Деловая переписка на английском языке: фразы и советы
- Принцип цикады и почему он важен для веб-дизайнеров
- В популярных антивирусах для ПК обнаружили лазейки в защите
Триггерная функция, которая удаляет роль
Автор вопроса: Azonos
Код триггерной функции:
begin
prepare myfun(text) as
drop role $1;
execute myfun(old.employee_login);
end;
При попытке сохранения выдает ошибку : ошибка синтаксиса (примерное положение: «drop»). В чем может быть проблема?
Источник
Ответы (1 шт):
Автор решения: Azonos
Рабочий код:
begin
execute 'DROP ROLE '|| old.employee_login;
return null;
end;
→ Ссылка
licensed under cc by-sa 3.0 with attribution.
Вопрос:
Я пытаюсь создать функцию, которая суммирует результат всех значений запроса и сравнивает ее с рядом других простых запросов.
Это то, что у меня есть, однако я получаю синтаксическую ошибку около начала (2-я строка):
CREATE FUNCTION trigf1(sbno integer, scid numeric(4,0)) RETURNS integer
BEGIN
declare sum int default 0;
declare max as SELECT totvoters FROM ballotbox WHERE cid=scid AND bno=sbno;
for r as
SELECT nofvotes FROM votes WHERE cid=scid AND bno=sbno;
do
set sum = sum + r.nofvotes;
end for
if sum > max
then return(0);
else
return(1);
END
Это приводит к:
Ошибка синтаксиса рядом с ‘BEGIN’
Я использую postgreSQL и pgadminIII (на всякий случай это актуально).
Я понятия не имею, почему я получаю эту ошибку, все, кажется, точно так же, как определяется учебник. (Это текстовая книга, которую я использую: http://digilib.usu.ac.id/buku/107859/Database-systems-concepts,-6th-ed.html)
Лучший ответ:
Я не знаю, какой “учебник” вы использовали, но если все, что вы написали, точно так же, как в этой книге, эта книга совершенно неверна:
CREATE FUNCTION trigf1(sbno integer, scid numeric(4,0))
RETURNS integer
AS -- error #1: no AS keyword
$body$ -- error #2: use dollar quoting to specify the function body as a string
DECLARE -- error #3: the declare block comes before the actual code
sum_ integer := 0; -- error #5: you can't use a reserved keyword as a variable
max_ integer; -- error #6: you can't initialize a variable with a select,
r record; -- you need to declare the record for the cursor loop
BEGIN
select totvoters
into max_
from ballotbox
WHERE cid=scid AND bno=sbno;
-- error #7: the syntax for a loop uses IN not AS
-- error #8: you need to declare R before you can use it
-- error #9: the SELECT for a cursor loop must NOT be terminated with a ;
FOR r IN SELECT nofvotes FROM votes WHERE cid=scid AND bno=sbno
loop -- error #10: you need to use LOOP, not DO
sum_ := sum_ + r.nofvotes; -- error #11: you need to use := for an assignment, not SET
end loop; -- error #12: it END LOOP
-- error #13: you need to terminate the statement with a ;
if sum_ > max_ then
return 0;
else
return 1;
end if; -- error #14: an END if is required
END;
$body$
language plpgsql; -- error #14: you need to specify the language
В руководстве указано все это:
- ошибка № 1, № 2: http://www.postgresql.org/docs/current/static/sql-createfunction.html
- ошибка № 3: http://www.postgresql.org/docs/current/static/plpgsql-structure.html
- ошибка № 6: http://www.postgresql.org/docs/current/static/plpgsql-declarations.html
- ошибка # 7, # 8, # 9, # 10, # 12: http://www.postgresql.org/docs/current/static/plpgsql-control-structures.html#PLPGSQL-RECORDS-ITERATING
- ошибка № 11: http://www.postgresql.org/docs/current/static/plpgsql-statements.html#PLPGSQL-STATEMENTS-ASSIGNMENT
- ошибка № 14: http://www.postgresql.org/docs/current/static/plpgsql-control-structures.html#PLPGSQL-CONDITIONALS
Весь цикл FOR не нужен и крайне неэффективен. Его можно заменить на:
SELECT sum(nofvotes)
into sum_
FROM votes
WHERE cid=scid AND bno=sbno;
Postgres имеет собственный булевский тип, лучше использовать это вместо целых чисел. Если вы объявите функцию как returns boolean, последняя строка может быть упрощена до
return max_ > sum_;
Эта часть:
select totvoters
into max_
from ballotbox
WHERE cid=scid AND bno=sbno;
будет работать только в том случае, если cid, bno уникален в камере голосования. В противном случае вы можете получить ошибку во время выполнения, если выбор возвращает более одной строки.
Предполагая, что выбор на ballotbox использует первичный (или уникальный) ключ, вся функция может быть упрощена до небольшого выражения SQL:
create function trigf1(sbno integer, scid numeric(4,0))
returns boolean
as
$body$
return (select totvoters from ballotbox WHERE cid=scid AND bno=sbno) >
(SELECT sum(nofvotes) FROM votes WHERE cid=scid AND bno=sbno);
$body$
language sql;
Ответ №1
Я не человек postgresSQL, но я бы подумал
declare max as SELECT totvoters FROM ballotbox WHERE cid=scid AND bno=sbno;
должно быть
declare max := SELECT totvoters FROM ballotbox WHERE cid=scid AND bno=sbno;
Ответ №2
Тело функции должно быть строкой после ключевого слова as, то есть as 'code...'. Обычно используется строка с кавычками в долларах:
CREATE FUNCTION trigf1(sbno integer, scid numeric(4,0)) RETURNS integer
AS $$
BEGIN
declare sum int default 0;
declare max as SELECT totvoters FROM ballotbox WHERE cid=scid AND bno=sbno;
for r as
SELECT nofvotes FROM votes WHERE cid=scid AND bno=sbno;
do
set sum = sum + r.nofvotes;
end for
if sum > max
then return(0);
else
return(1);
END
$$
- Remove From My Forums
-
Question
-
Hello ,
I am getting this error. Whats the issue?
begin
if
not exists(select 1 from dbo.Dashboard where Effective_Date=@cut_date)
begin
INSERT INTO dbo.dashboard (
[Effective_Date]
,[Invoice_gen]
,[unclaimed_payments]
,[Tot_Payments_received]
,[tdu_charge]
,[payments_received]
,[meter_cnt_active]
,[meter_cnt_cancelled]
,[meter_cnt_churn]
,[meter_cnt_intransit]
,[ag_tot_unstat]
,[ag_active_unstat]
,[ag_inactive_unstat]
)
select
@cut_date
,@invoice_gen
,@unclaimed_payment
,@payment_received
,@tdu_charge
,@coll_payment_received
,@meter_active
,@meter_Cancelled
,@meter_churn
,@meter_intransit
,tot_cte.tot_unstat
,tot_cte.active_unstat
,tot_cte.inactive_unstat
FROM ecp_tot_cte
CROSS JOIN tot_cte
end
Please help.
Thanks
Answers
-
Since there is no variable declarations in the code you posted, and there are variables in the batch, you did obviously not the post the full batch. I guess the error is in the part you did not post.
If you post the complete code, please also post the complete error message. The full error message includes a line number. That information is valuable.
Also, please use the squiggly button in the web UI to post code. It is not particularly amusing to read code where every second line is blank.
Erland Sommarskog, SQL Server MVP, esquel@sommarskog.se
-
Marked as answer by
Thursday, January 19, 2012 3:35 PM
-
Marked as answer by
-
-
Edited by
Naomi N
Friday, January 6, 2012 4:10 PM -
Marked as answer by
Kalman Toth
Thursday, January 19, 2012 3:35 PM
-
Edited by
-
You really like derived tables, don’t you… It make the entire thing quite unreadable.
Others have already pointed out the obvious syntax error. You are not using the CTEs immediately following their declaration, which is mandatory.
I notice you are not using recursion in your CTEs. That means that you could rewrite them as views (not in your stored procedure, but permanent). You can access views whenever you want, also in your current «if» or «else» block.
The same is true for many of your derived tables. With smart naming, turning them into views would make your code must more readable, and because of that better to maintain.
Gert-Jan
-
Proposed as answer by
Naomi N
Friday, January 6, 2012 9:55 PM -
Marked as answer by
Kalman Toth
Thursday, January 19, 2012 3:34 PM
-
Proposed as answer by
So, you’re creating a custom SQL query to perform a task in the database. After putting the code together and running it in PHPmyAdmin it responds with a 1064 error. It may look similar to this:
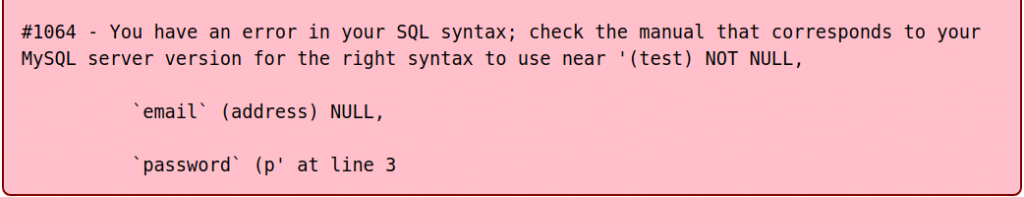
The 1064 error displays any time you have an issue with your SQL syntax, and is often due to using reserved words, missing data in the database, or mistyped/obsolete commands. So follow along and learn more about what the 1064 error is, some likely causes, and general troubleshooting steps.
Note: Since syntax errors can be hard to locate in long queries, the following online tools can often save time by checking your code and locating issues:
- PiliApp MySQL Syntax Check
- EverSQL SQL Query Syntax Check & Validator
Causes for the 1064 error
- Reserved Words
- Missing Data
- Mistyped Commands
- Obsolete Commands
This may seem cryptic since it is a general error pointing to a syntax issue in the SQL Query statement. Since the 1064 error can have multiple causes, we will go over the most common things that will result in this error and show you how to fix them. Follow along so you can get your SQL queries updated and running successfully.
Using Reserved Words
Every version of MySQL has its own list of reserved words. These are words that are used for specific purposes or to perform specific functions within the MySQL engine. If you attempt to use one of these reserved words, you will receive the 1064 error. For example, below is a short SQL query that uses a reserved word as a table name.
CREATE TABLE alter (first_day DATE, last_day DATE);
How to fix it:
Just because the word alter is reserved does not mean it cannot be used, it just has special requirements to use it as the MySQL engine is trying to call the functionality for the alter command. To fix the issue, you will want to surround the word with backticks, this is usually the button just to the left of the “1” button on the keyboard. The code block below shows how the code will need to look in order to run properly.
CREATE TABLE `alter` (first_day DATE, last_day DATE);
Missing Data
Sometimes data can be missing from the database. This causes issues when the data is required for a query to complete. For example, if a database is built requiring an ID number for every student, it is reasonable to assume a query will be built to pull a student record by that ID number. Such a query would look like this:
SELECT * from students WHERE studentID = $id
If the $id is never properly filled in the code, the query would look like this to the server:
SELECT * from students WHERE studentID =
Since there is nothing there, the MySQL engine gets confused and complains via a 1064 error.
How to fix it:
Hopefully, your application will have some sort of interface that will allow you to bring up the particular record and add the missing data. This is tricky because if the missing data is the unique identifier, it will likely need that information to bring it up, thus resulting in the same error. You can also go into the database (typically within phpMyAdmin) where you can select the particular row from the appropriate table and manually add the data.
Mistyping of Commands
One of the most common causes for the 1064 error is when a SQL statement uses a mistyped command. This is very easy to do and is easily missed when troubleshooting at first. Our example shows an UPDATE command that is accidentally misspelled.
UDPATE table1 SET id = 0;
How to fix it:
Be sure to check your commands prior to running them and ensure they are all spelled correctly.
Below is the syntax for the correct query statement.
UPDATE table1 SET id = 0;
Obsolete Commands
Some commands that were deprecated (slated for removal but still allowed for a period of time) eventually go obsolete. This means that the command is no longer valid in the SQL statement. One of the more common commands is the ‘TYPE‘ command. This has been deprecated since MySQL 4.1 but was finally removed as of version 5.1, where it now gives a syntax error. The ‘TYPE‘ command has been replaced with the ‘ENGINE‘ command. Below is an example of the old version:
CREATE TABLE t (i INT) TYPE = INNODB;
This should be replaced with the new command as below:
CREATE TABLE t (i INT) ENGINE = INNODB;
For developers or sysadmins experienced with the command line, get High-Availability and Root Access for your application, service, and websites with Cloud VPS Hosting.
Error 1064 Summary
As you can see there is more than one cause for the 1064 error within MySQL code. Now, you know how to correct the issues with your SQL Syntax, so your query can run successfully. This list will be updated as more specific instances are reported.
Пытаюсь загрузить данные в таблицу Postgres. Скрипт и данные находятся на локальном сервере Open Server, а бд на другом, удаленном серваке, к которому есть полный доступ (соединяюсь с базой через менеджер бд и все редактирую). Подключение к базе при запуске скрипта успешно происходит, но вот запрос INSERT INTO не срабатывает:
$pg = "INSERT INTO public.1253_data () VALUES " . implode(",", $temp_array);
Ошибка выдается от функции pg_query, пишет: Warning: pg_query(): Query failed: Ошибка синтаксиса (примерное положение: .1253_data).
Я запускаю функцию pg_result_query():
$result = pg_query($conn, $sql);
if ($result) {
echo "New record created successfully";
} else {
$k = pg_get_result($result);
echo 'Query failed1: ' . pg_result_error($k);
}
pg_close($conn);
В результате pg_result_error дает пустоту:

Судя по документации, pg_result_дает такое только тогда, когда ошибок никаких нет. Но тогда почему собственный дескриптор ошибки pg_query такой?
Только начинаю pg изучать, все перепробовал в поисках ошибки ( Эксперты, подскажите, в чем она может быть?
Syntax errors are quite common while coding.
But, things go for a toss when it results in website errors.
PostgreSQL error 42601 also occurs due to syntax errors in the database queries.
At Bobcares, we often get requests from PostgreSQL users to fix errors as part of our Server Management Services.
Today, let’s check PostgreSQL error in detail and see how our Support Engineers fix it for the customers.
What causes error 42601 in PostgreSQL?
PostgreSQL is an advanced database engine. It is popular for its extensive features and ability to handle complex database situations.
Applications like Instagram, Facebook, Apple, etc rely on the PostgreSQL database.
But what causes error 42601?
PostgreSQL error codes consist of five characters. The first two characters denote the class of errors. And the remaining three characters indicate a specific condition within that class.
Here, 42 in 42601 represent the class “Syntax Error or Access Rule Violation“.
In short, this error mainly occurs due to the syntax errors in the queries executed. A typical error shows up as:

Here, the syntax error has occurred in position 119 near the value “parents” in the query.
How we fix the error?
Now let’s see how our PostgreSQL engineers resolve this error efficiently.
Recently, one of our customers contacted us with this error. He tried to execute the following code,
CREATE OR REPLACE FUNCTION prc_tst_bulk(sql text)
RETURNS TABLE (name text, rowcount integer) AS
$$
BEGIN
WITH m_ty_person AS (return query execute sql)
select name, count(*) from m_ty_person where name like '%a%' group by name
union
select name, count(*) from m_ty_person where gender = 1 group by name;
END
$$ LANGUAGE plpgsql;But, this ended up in PostgreSQL error 42601. And he got the following error message,
ERROR: syntax error at or near "return"
LINE 5: WITH m_ty_person AS (return query execute sql)Our PostgreSQL Engineers checked the issue and found out the syntax error. The statement in Line 5 was a mix of plain and dynamic SQL. In general, the PostgreSQL query should be either fully dynamic or plain. Therefore, we changed the code as,
RETURN QUERY EXECUTE '
WITH m_ty_person AS (' || sql || $x$)
SELECT name, count(*)::int FROM m_ty_person WHERE name LIKE '%a%' GROUP BY name
UNION
SELECT name, count(*)::int FROM m_ty_person WHERE gender = 1 GROUP BY name$x$;This resolved the error 42601, and the code worked fine.
[Need more assistance to solve PostgreSQL error 42601?- We’ll help you.]
Conclusion
In short, PostgreSQL error 42601 occurs due to the syntax errors in the code. Today, in this write-up, we have discussed how our Support Engineers fixed this error for our customers.
PREVENT YOUR SERVER FROM CRASHING!
Never again lose customers to poor server speed! Let us help you.
Our server experts will monitor & maintain your server 24/7 so that it remains lightning fast and secure.
GET STARTED
var google_conversion_label = «owonCMyG5nEQ0aD71QM»;
Syntax errors are quite common while coding.
But, things go for a toss when it results in website errors.
PostgreSQL error 42601 also occurs due to syntax errors in the database queries.
At Bobcares, we often get requests from PostgreSQL users to fix errors as part of our Server Management Services.
Today, let’s check PostgreSQL error in detail and see how our Support Engineers fix it for the customers.
What causes error 42601 in PostgreSQL?
PostgreSQL is an advanced database engine. It is popular for its extensive features and ability to handle complex database situations.
Applications like Instagram, Facebook, Apple, etc rely on the PostgreSQL database.
But what causes error 42601?
PostgreSQL error codes consist of five characters. The first two characters denote the class of errors. And the remaining three characters indicate a specific condition within that class.
Here, 42 in 42601 represent the class “Syntax Error or Access Rule Violation“.
In short, this error mainly occurs due to the syntax errors in the queries executed. A typical error shows up as:

Here, the syntax error has occurred in position 119 near the value “parents” in the query.
How we fix the error?
Now let’s see how our PostgreSQL engineers resolve this error efficiently.
Recently, one of our customers contacted us with this error. He tried to execute the following code,
CREATE OR REPLACE FUNCTION prc_tst_bulk(sql text)
RETURNS TABLE (name text, rowcount integer) AS
$$
BEGIN
WITH m_ty_person AS (return query execute sql)
select name, count(*) from m_ty_person where name like '%a%' group by name
union
select name, count(*) from m_ty_person where gender = 1 group by name;
END
$$ LANGUAGE plpgsql;But, this ended up in PostgreSQL error 42601. And he got the following error message,
ERROR: syntax error at or near "return"
LINE 5: WITH m_ty_person AS (return query execute sql)Our PostgreSQL Engineers checked the issue and found out the syntax error. The statement in Line 5 was a mix of plain and dynamic SQL. In general, the PostgreSQL query should be either fully dynamic or plain. Therefore, we changed the code as,
RETURN QUERY EXECUTE '
WITH m_ty_person AS (' || sql || $x$)
SELECT name, count(*)::int FROM m_ty_person WHERE name LIKE '%a%' GROUP BY name
UNION
SELECT name, count(*)::int FROM m_ty_person WHERE gender = 1 GROUP BY name$x$;This resolved the error 42601, and the code worked fine.
[Need more assistance to solve PostgreSQL error 42601?- We’ll help you.]
Conclusion
In short, PostgreSQL error 42601 occurs due to the syntax errors in the code. Today, in this write-up, we have discussed how our Support Engineers fixed this error for our customers.
PREVENT YOUR SERVER FROM CRASHING!
Never again lose customers to poor server speed! Let us help you.
Our server experts will monitor & maintain your server 24/7 so that it remains lightning fast and secure.
GET STARTED
var google_conversion_label = «owonCMyG5nEQ0aD71QM»;
So, you’re creating a custom SQL query to perform a task in the database. After putting the code together and running it in PHPmyAdmin it responds with a 1064 error. It may look similar to this:

The 1064 error displays any time you have an issue with your SQL syntax, and is often due to using reserved words, missing data in the database, or mistyped/obsolete commands. So follow along and learn more about what the 1064 error is, some likely causes, and general troubleshooting steps.
Note: Since syntax errors can be hard to locate in long queries, the following online tools can often save time by checking your code and locating issues:
- PiliApp MySQL Syntax Check
- EverSQL SQL Query Syntax Check & Validator
Causes for the 1064 error
- Reserved Words
- Missing Data
- Mistyped Commands
- Obsolete Commands
This may seem cryptic since it is a general error pointing to a syntax issue in the SQL Query statement. Since the 1064 error can have multiple causes, we will go over the most common things that will result in this error and show you how to fix them. Follow along so you can get your SQL queries updated and running successfully.
Using Reserved Words
Every version of MySQL has its own list of reserved words. These are words that are used for specific purposes or to perform specific functions within the MySQL engine. If you attempt to use one of these reserved words, you will receive the 1064 error. For example, below is a short SQL query that uses a reserved word as a table name.
CREATE TABLE alter (first_day DATE, last_day DATE);
How to fix it:
Just because the word alter is reserved does not mean it cannot be used, it just has special requirements to use it as the MySQL engine is trying to call the functionality for the alter command. To fix the issue, you will want to surround the word with backticks, this is usually the button just to the left of the “1” button on the keyboard. The code block below shows how the code will need to look in order to run properly.
CREATE TABLE `alter` (first_day DATE, last_day DATE);
Missing Data
Sometimes data can be missing from the database. This causes issues when the data is required for a query to complete. For example, if a database is built requiring an ID number for every student, it is reasonable to assume a query will be built to pull a student record by that ID number. Such a query would look like this:
SELECT * from students WHERE studentID = $id
If the $id is never properly filled in the code, the query would look like this to the server:
SELECT * from students WHERE studentID =
Since there is nothing there, the MySQL engine gets confused and complains via a 1064 error.
How to fix it:
Hopefully, your application will have some sort of interface that will allow you to bring up the particular record and add the missing data. This is tricky because if the missing data is the unique identifier, it will likely need that information to bring it up, thus resulting in the same error. You can also go into the database (typically within phpMyAdmin) where you can select the particular row from the appropriate table and manually add the data.
Mistyping of Commands
One of the most common causes for the 1064 error is when a SQL statement uses a mistyped command. This is very easy to do and is easily missed when troubleshooting at first. Our example shows an UPDATE command that is accidentally misspelled.
UDPATE table1 SET id = 0;
How to fix it:
Be sure to check your commands prior to running them and ensure they are all spelled correctly.
Below is the syntax for the correct query statement.
UPDATE table1 SET id = 0;
Obsolete Commands
Some commands that were deprecated (slated for removal but still allowed for a period of time) eventually go obsolete. This means that the command is no longer valid in the SQL statement. One of the more common commands is the ‘TYPE‘ command. This has been deprecated since MySQL 4.1 but was finally removed as of version 5.1, where it now gives a syntax error. The ‘TYPE‘ command has been replaced with the ‘ENGINE‘ command. Below is an example of the old version:
CREATE TABLE t (i INT) TYPE = INNODB;
This should be replaced with the new command as below:
CREATE TABLE t (i INT) ENGINE = INNODB;
For developers or sysadmins experienced with the command line, get High-Availability and Root Access for your application, service, and websites with Cloud VPS Hosting.
Error 1064 Summary
As you can see there is more than one cause for the 1064 error within MySQL code. Now, you know how to correct the issues with your SQL Syntax, so your query can run successfully. This list will be updated as more specific instances are reported.
восстановить базу из дампа:
--
-- PostgreSQL database dump
--
-- Dumped from database version 10.19 (Ubuntu 10.19-0ubuntu0.18.04.1)
-- Dumped by pg_dump version 10.19 (Ubuntu 10.19-0ubuntu0.18.04.1)
SET statement_timeout = 0;
SET lock_timeout = 0;
SET idle_in_transaction_session_timeout = 0;
SET client_encoding = 'UTF8';
SET standard_conforming_strings = on;
SELECT pg_catalog.set_config('search_path', '', false);
SET check_function_bodies = false;
SET xmloption = content;
SET client_min_messages = warning;
SET row_security = off;
--
-- Name: plpgsql; Type: EXTENSION; Schema: -; Owner:
--
CREATE EXTENSION IF NOT EXISTS plpgsql WITH SCHEMA pg_catalog;
--
-- Name: EXTENSION plpgsql; Type: COMMENT; Schema: -; Owner:
--
COMMENT ON EXTENSION plpgsql IS 'PL/pgSQL procedural language';
--
-- Name: attribute_id_seq; Type: SEQUENCE; Schema: public; Owner: bender
--
CREATE SEQUENCE public.attribute_id_seq
START WITH 1
INCREMENT BY 1
NO MINVALUE
NO MAXVALUE
CACHE 1;
ALTER TABLE public.attribute_id_seq OWNER TO bender;
SET default_tablespace = '';
SET default_with_oids = false;
--
-- Name: attribute; Type: TABLE; Schema: public; Owner: bender
--
CREATE TABLE public.attribute (
attribute_id integer DEFAULT nextval('public.attribute_id_seq'::regclass) NOT NULL,
name character varying(30) NOT NULL,
attribute_type_id integer NOT NULL
);
ALTER TABLE public.attribute OWNER TO bender;
--
-- Name: attribute_type_id_seq; Type: SEQUENCE; Schema: public; Owner: bender
--
CREATE SEQUENCE public.attribute_type_id_seq
START WITH 1
INCREMENT BY 1
NO MINVALUE
NO MAXVALUE
CACHE 1;
ALTER TABLE public.attribute_type_id_seq OWNER TO bender;
--
-- Name: attribute_type; Type: TABLE; Schema: public; Owner: bender
--
CREATE TABLE public.attribute_type (
attribute_type_id integer DEFAULT nextval('public.attribute_type_id_seq'::regclass) NOT NULL,
name character varying(50) NOT NULL
);
ALTER TABLE public.attribute_type OWNER TO bender;
--
-- Name: film_id_seq; Type: SEQUENCE; Schema: public; Owner: bender
--
CREATE SEQUENCE public.film_id_seq
START WITH 1
INCREMENT BY 1
NO MINVALUE
NO MAXVALUE
CACHE 1;
ALTER TABLE public.film_id_seq OWNER TO bender;
--
-- Name: film; Type: TABLE; Schema: public; Owner: bender
--
CREATE TABLE public.film (
film_id integer DEFAULT nextval('public.film_id_seq'::regclass) NOT NULL,
name character varying(50) NOT NULL
);
ALTER TABLE public.film OWNER TO bender;
--
-- Name: film_attributes_id_seq; Type: SEQUENCE; Schema: public; Owner: bender
--
CREATE SEQUENCE public.film_attributes_id_seq
START WITH 1
INCREMENT BY 1
NO MINVALUE
NO MAXVALUE
CACHE 1;
ALTER TABLE public.film_attributes_id_seq OWNER TO bender;
--
-- Name: film_attributes; Type: TABLE; Schema: public; Owner: bender
--
CREATE TABLE public.film_attributes (
film_attributes_id integer DEFAULT nextval('public.film_attributes_id_seq'::regclass) NOT NULL,
attribute_id integer NOT NULL,
film_id integer NOT NULL,
value_text character varying,
value_integer integer,
value_float double precision,
value_boolean boolean,
value_timestamp timestamp with time zone
);
ALTER TABLE public.film_attributes OWNER TO bender;
--
-- Name: film_attributes_values; Type: VIEW; Schema: public; Owner: bender
--
CREATE VIEW public.film_attributes_values AS
SELECT
NULL::character varying(50) AS name,
NULL::character varying(50) AS attribute_type,
NULL::character varying(30) AS attribute_name,
NULL::character varying AS attribute_value;
ALTER TABLE public.film_attributes_values OWNER TO bender;
--
-- Name: film_tasks; Type: VIEW; Schema: public; Owner: bender
--
CREATE VIEW public.film_tasks AS
SELECT
NULL::character varying(50) AS name,
NULL::character varying[] AS today_tasks,
NULL::character varying[] AS twenty_days_tasks;
ALTER TABLE public.film_tasks OWNER TO bender;
--
-- Data for Name: attribute; Type: TABLE DATA; Schema: public; Owner: bender
--
COPY public.attribute (attribute_id, name, attribute_type_id) FROM stdin;
1 Рецензии 3
3 Премия Оскар 2
4 Премия Ника 2
5 Премия Золотой Глобус 2
10 Описание фильма 3
11 Длительность (мин.) 1
12 Длительность проката (дней) 1
2 Рейтинг 7
6 Премьера в мире 6
7 Премьера в России 6
8 Старт продажи билетов 6
9 Старт проката 6
13 Окончание проката 6
.
--
-- Data for Name: attribute_type; Type: TABLE DATA; Schema: public; Owner: bender
--
COPY public.attribute_type (attribute_type_id, name) FROM stdin;
1 integer
2 boolean
3 text
4 date
5 numeric
6 timestamp
7 float
.
--
-- Data for Name: film; Type: TABLE DATA; Schema: public; Owner: bender
--
COPY public.film (film_id, name) FROM stdin;
1 Spoiler-man: No Way
2 Matrix 4
.
--
-- Data for Name: film_attributes; Type: TABLE DATA; Schema: public; Owner: bender
--
COPY public.film_attributes (film_attributes_id, attribute_id, film_id, value_text, value_integer, value_float, value_boolean, value_timestamp) FROM stdin;
1 1 1 Годный фильм, распинаюсь про сюжет, пишу про игру актеров, все круто N N N N
2 1 2 Джон Уик уже не тот, сестры Вачовски сбрендили, полная фигня N N N N
5 3 1 f N N N N
7 6 2 N N N N 2021-12-10 00:00:00+03
9 7 2 N N N N 2021-12-30 00:00:00+03
10 8 1 N N N N 2021-12-10 00:00:00+03
11 8 2 N N N N 2021-12-07 00:00:00+03
12 12 1 N 21 N N N
13 12 2 N 14 N N N
14 9 1 N N N N 2021-12-15 00:00:00+03
15 9 2 N N N N 2021-12-15 00:00:00+03
16 13 1 N N N N 2022-01-04 00:00:00+03
17 13 2 N N N N 2022-01-04 00:00:00+03
18 3 2 t N N N N
6 6 1 N N N N 2021-12-15 00:00:00+03
8 7 1 N N N N 2022-01-04 00:00:00+03
.
--
-- Name: attribute_id_seq; Type: SEQUENCE SET; Schema: public; Owner: bender
--
SELECT pg_catalog.setval('public.attribute_id_seq', 13, true);
--
-- Name: attribute_type_id_seq; Type: SEQUENCE SET; Schema: public; Owner: bender
--
SELECT pg_catalog.setval('public.attribute_type_id_seq', 6, true);
--
-- Name: film_attributes_id_seq; Type: SEQUENCE SET; Schema: public; Owner: bender
--
SELECT pg_catalog.setval('public.film_attributes_id_seq', 18, true);
--
-- Name: film_id_seq; Type: SEQUENCE SET; Schema: public; Owner: bender
--
SELECT pg_catalog.setval('public.film_id_seq', 2, true);
--
-- Name: attribute attribute_pkey; Type: CONSTRAINT; Schema: public; Owner: bender
--
ALTER TABLE ONLY public.attribute
ADD CONSTRAINT attribute_pkey PRIMARY KEY (attribute_id);
--
-- Name: attribute_type attribute_type_name_key; Type: CONSTRAINT; Schema: public; Owner: bender
--
ALTER TABLE ONLY public.attribute_type
ADD CONSTRAINT attribute_type_name_key UNIQUE (name);
--
-- Name: attribute_type attribute_type_pkey; Type: CONSTRAINT; Schema: public; Owner: bender
--
ALTER TABLE ONLY public.attribute_type
ADD CONSTRAINT attribute_type_pkey PRIMARY KEY (attribute_type_id);
--
-- Name: attribute attribute_unq; Type: CONSTRAINT; Schema: public; Owner: bender
--
ALTER TABLE ONLY public.attribute
ADD CONSTRAINT attribute_unq UNIQUE (name);
--
-- Name: film_attributes film_attributes_pkey; Type: CONSTRAINT; Schema: public; Owner: bender
--
ALTER TABLE ONLY public.film_attributes
ADD CONSTRAINT film_attributes_pkey PRIMARY KEY (film_attributes_id);
--
-- Name: film film_pkey; Type: CONSTRAINT; Schema: public; Owner: bender
--
ALTER TABLE ONLY public.film
ADD CONSTRAINT film_pkey PRIMARY KEY (film_id);
--
-- Name: film film_unq; Type: CONSTRAINT; Schema: public; Owner: bender
--
ALTER TABLE ONLY public.film
ADD CONSTRAINT film_unq UNIQUE (name);
--
-- Name: attribute_index; Type: INDEX; Schema: public; Owner: bender
--
CREATE INDEX attribute_index ON public.attribute USING btree (name COLLATE "C.UTF-8" varchar_ops);
--
-- Name: film_index; Type: INDEX; Schema: public; Owner: bender
--
CREATE INDEX film_index ON public.film USING btree (name COLLATE "C.UTF-8");
--
-- Name: attribute attribute_type_fkey; Type: FK CONSTRAINT; Schema: public; Owner: bender
--
ALTER TABLE ONLY public.attribute
ADD CONSTRAINT attribute_type_fkey FOREIGN KEY (attribute_type_id) REFERENCES public.attribute_type(attribute_type_id) NOT VALID;
--
-- Name: film_attributes film_attribute_attribute_fkey; Type: FK CONSTRAINT; Schema: public; Owner: bender
--
ALTER TABLE ONLY public.film_attributes
ADD CONSTRAINT film_attribute_attribute_fkey FOREIGN KEY (attribute_id) REFERENCES public.attribute(attribute_id);
--
-- Name: film_attributes film_attribute_film_fkey; Type: FK CONSTRAINT; Schema: public; Owner: bender
--
ALTER TABLE ONLY public.film_attributes
ADD CONSTRAINT film_attribute_film_fkey FOREIGN KEY (film_id) REFERENCES public.film(film_id);
--
-- PostgreSQL database dump complete
--ERROR: ОШИБКА: ошибка синтаксиса (примерное положение: "1")
LINE 180: 1 Рецензии 3
^
SQL state: 42601
Character: 4115Алексей
@falcon_digit
Начинающий в AI
Делаю задачи по курсу SQL на Stepik’е, параллельно их же делаю в PostgreSQL.
Такой запрос UPDATE с вложенным SELECT’ом в PostgreSQL выдаёт ошибку синтаксиса
UPDATE fine,
(SELECT name, number_plate, violation
FROM fine
GROUP BY name, number_plate, violation
HAVING count(*) > 1
) query_in
SET sum_fine = sum_fine * 2
WHERE fine.name = query_in.name AND fine.number_plate = query_in.number_plate AND fine.violation = query_in.violation AND fine.date_payment IS NULL;
ERROR: ОШИБКА: ошибка синтаксиса (примерное положение: «,»)
LINE 1: UPDATE fine,
На Stepik’е этот код принимается без ошибки.
Т.е. в PostgreSQL так нельзя делать? Или это как то лечится?
P.S. В SQLiteStudio тоже ошибка синтаксиса.
-
Вопрос задан04 дек. 2022
-
195 просмотров
Пригласить эксперта
А чего спрашивать-то? Прочитайте документацию postgresql про update — есть там подобный синтаксис или нет? Уже понятно, что нет. Возможно, Вам подойдёт with?
А что касается Степиков и подобных, то в курсах по SQL обязательно должна быть указана версия/стандарт sql на которых курс основан, чтобы подобные казусы выявлять.
Это скорее всего неправильно.
SELECT name, number_plate, violation
FROM fine
GROUP BY name, number_plate, violation
HAVING count(*) > 1если используется GROUP BY то в выражении SELECT должна стоять функция агрегации (count в данном случае)
-
Показать ещё
Загружается…
22 июн. 2023, в 00:59
8000 руб./за проект
22 июн. 2023, в 00:56
8000 руб./за проект
22 июн. 2023, в 00:39
12000 руб./за проект
Минуточку внимания
Loading
