Postgres 9.3.2 on heroku.
Pretty sure I’m just being an idiot, but I can’t seem to figure out why my syntax is wrong.
db=> dt
List of relations
Schema | Name | Type | Owner
--------+------------+-------+----------------
public | device | table | admin
public | post | table | admin
public | user | table | admin
(3 rows)
// why does this fail?
db=> drop table user;
ERROR: syntax error at or near "user"
LINE 1: drop table user;
// does the right thing
db=> drop table error;
ERROR: table "error" does not exist
asked Jan 10, 2014 at 18:18
User is a reserved keyword in Postgres. You’ll have to put it in quotes if you want to refer to an actual table named user:
DROP TABLE "user";
Probably best to stay away from using reserved keywords as table names if you can help it. It usually ends up creating weird problems down the road. Users might be a better name for a table.
answered Jan 10, 2014 at 18:19
Mike ChristensenMike Christensen
87.5k49 gold badges206 silver badges324 bronze badges
0
I had the same error. My database name was very unique and not a reserved keyword. Still needed to wrap the database name with quotation marks
"<database_name>"
Also for those that might forget always add a semicolon ; at the end of the statement, I always forget.
answered Nov 20, 2020 at 1:52
Syntax errors are quite common while coding.
But, things go for a toss when it results in website errors.
PostgreSQL error 42601 also occurs due to syntax errors in the database queries.
At Bobcares, we often get requests from PostgreSQL users to fix errors as part of our Server Management Services.
Today, let’s check PostgreSQL error in detail and see how our Support Engineers fix it for the customers.
What causes error 42601 in PostgreSQL?
PostgreSQL is an advanced database engine. It is popular for its extensive features and ability to handle complex database situations.
Applications like Instagram, Facebook, Apple, etc rely on the PostgreSQL database.
But what causes error 42601?
PostgreSQL error codes consist of five characters. The first two characters denote the class of errors. And the remaining three characters indicate a specific condition within that class.
Here, 42 in 42601 represent the class “Syntax Error or Access Rule Violation“.
In short, this error mainly occurs due to the syntax errors in the queries executed. A typical error shows up as:
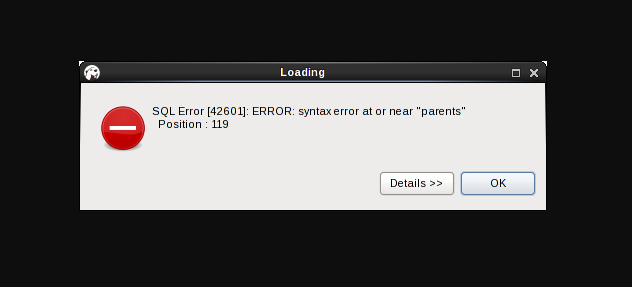
Here, the syntax error has occurred in position 119 near the value “parents” in the query.
How we fix the error?
Now let’s see how our PostgreSQL engineers resolve this error efficiently.
Recently, one of our customers contacted us with this error. He tried to execute the following code,
CREATE OR REPLACE FUNCTION prc_tst_bulk(sql text)
RETURNS TABLE (name text, rowcount integer) AS
$$
BEGIN
WITH m_ty_person AS (return query execute sql)
select name, count(*) from m_ty_person where name like '%a%' group by name
union
select name, count(*) from m_ty_person where gender = 1 group by name;
END
$$ LANGUAGE plpgsql;But, this ended up in PostgreSQL error 42601. And he got the following error message,
ERROR: syntax error at or near "return"
LINE 5: WITH m_ty_person AS (return query execute sql)Our PostgreSQL Engineers checked the issue and found out the syntax error. The statement in Line 5 was a mix of plain and dynamic SQL. In general, the PostgreSQL query should be either fully dynamic or plain. Therefore, we changed the code as,
RETURN QUERY EXECUTE '
WITH m_ty_person AS (' || sql || $x$)
SELECT name, count(*)::int FROM m_ty_person WHERE name LIKE '%a%' GROUP BY name
UNION
SELECT name, count(*)::int FROM m_ty_person WHERE gender = 1 GROUP BY name$x$;This resolved the error 42601, and the code worked fine.
[Need more assistance to solve PostgreSQL error 42601?- We’ll help you.]
Conclusion
In short, PostgreSQL error 42601 occurs due to the syntax errors in the code. Today, in this write-up, we have discussed how our Support Engineers fixed this error for our customers.
PREVENT YOUR SERVER FROM CRASHING!
Never again lose customers to poor server speed! Let us help you.
Our server experts will monitor & maintain your server 24/7 so that it remains lightning fast and secure.
GET STARTED
var google_conversion_label = «owonCMyG5nEQ0aD71QM»;
Postgres 9.3.2 on heroku.
Pretty sure I’m just being an idiot, but I can’t seem to figure out why my syntax is wrong.
db=> dt
List of relations
Schema | Name | Type | Owner
--------+------------+-------+----------------
public | device | table | admin
public | post | table | admin
public | user | table | admin
(3 rows)
// why does this fail?
db=> drop table user;
ERROR: syntax error at or near "user"
LINE 1: drop table user;
// does the right thing
db=> drop table error;
ERROR: table "error" does not exist
asked Jan 10, 2014 at 18:18
User is a reserved keyword in Postgres. You’ll have to put it in quotes if you want to refer to an actual table named user:
DROP TABLE "user";
Probably best to stay away from using reserved keywords as table names if you can help it. It usually ends up creating weird problems down the road. Users might be a better name for a table.
answered Jan 10, 2014 at 18:19
Mike ChristensenMike Christensen
86k49 gold badges207 silver badges320 bronze badges
0
I had the same error. My database name was very unique and not a reserved keyword. Still needed to wrap the database name with quotation marks
"<database_name>"
Also for those that might forget always add a semicolon ; at the end of the statement, I always forget.
answered Nov 20, 2020 at 1:52
Содержание
- PostgreSQL error 42601- How we fix it
- What causes error 42601 in PostgreSQL?
- How we fix the error?
- Conclusion
- Related posts:
- PREVENT YOUR SERVER FROM CRASHING!
- 10 Comments
- Приложение A. Коды ошибок PostgreSQL
PostgreSQL error 42601- How we fix it
by Sijin George | Sep 12, 2019
Syntax errors are quite common while coding.
But, things go for a toss when it results in website errors.
PostgreSQL error 42601 also occurs due to syntax errors in the database queries.
At Bobcares, we often get requests from PostgreSQL users to fix errors as part of our Server Management Services.
Today, let’s check PostgreSQL error in detail and see how our Support Engineers fix it for the customers.
What causes error 42601 in PostgreSQL?
PostgreSQL is an advanced database engine. It is popular for its extensive features and ability to handle complex database situations.
Applications like Instagram, Facebook, Apple, etc rely on the PostgreSQL database.
But what causes error 42601?
PostgreSQL error codes consist of five characters. The first two characters denote the class of errors. And the remaining three characters indicate a specific condition within that class.
Here, 42 in 42601 represent the class “Syntax Error or Access Rule Violation“.
In short, this error mainly occurs due to the syntax errors in the queries executed. A typical error shows up as:

Here, the syntax error has occurred in position 119 near the value “parents” in the query.
How we fix the error?
Now let’s see how our PostgreSQL engineers resolve this error efficiently.
Recently, one of our customers contacted us with this error. He tried to execute the following code,
But, this ended up in PostgreSQL error 42601. And he got the following error message,
Our PostgreSQL Engineers checked the issue and found out the syntax error. The statement in Line 5 was a mix of plain and dynamic SQL. In general, the PostgreSQL query should be either fully dynamic or plain. Therefore, we changed the code as,
This resolved the error 42601, and the code worked fine.
[Need more assistance to solve PostgreSQL error 42601?- We’ll help you.]
Conclusion
In short, PostgreSQL error 42601 occurs due to the syntax errors in the code. Today, in this write-up, we have discussed how our Support Engineers fixed this error for our customers.
PREVENT YOUR SERVER FROM CRASHING!
Never again lose customers to poor server speed! Let us help you.
Our server experts will monitor & maintain your server 24/7 so that it remains lightning fast and secure.
SELECT * FROM long_term_prediction_anomaly WHERE + “‘Timestamp’” + ‘”BETWEEN ‘” +
2019-12-05 09:10:00+ ‘”AND’” + 2019-12-06 09:10:00 + “‘;”)
Hello Joe,
Do you still get PostgreSQL errors? If you need help, we’ll be happy to talk to you on chat (click on the icon at right-bottom).
У меня ошибка drop table exists “companiya”;
CREATE TABLE “companiya” (
“compania_id” int4 NOT NULL,
“fio vladelca” text NOT NULL,
“name” text NOT NULL,
“id_operator” int4 NOT NULL,
“id_uslugi” int4 NOT NULL,
“id_reklama” int4 NOT NULL,
“id_tex-specialist” int4 NOT NULL,
“id_filial” int4 NOT NULL,
CONSTRAINT “_copy_8” PRIMARY KEY (“compania_id”)
);
CREATE TABLE “filial” (
“id_filial” int4 NOT NULL,
“street” text NOT NULL,
“house” int4 NOT NULL,
“city” text NOT NULL,
CONSTRAINT “_copy_5” PRIMARY KEY (“id_filial”)
);
CREATE TABLE “login” (
“id_name” int4 NOT NULL,
“name” char(20) NOT NULL,
“pass” char(20) NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (“id_name”)
);
CREATE TABLE “operator” (
“id_operator” int4 NOT NULL,
“obrabotka obrasheniya” int4 NOT NULL,
“konsultirovanie” text NOT NULL,
“grafick work” date NOT NULL,
CONSTRAINT “_copy_2” PRIMARY KEY (“id_operator”)
);
CREATE TABLE “polsovateli” (
“id_user” int4 NOT NULL,
“id_companiya” int4 NOT NULL,
“id_obrasheniya” int4 NOT NULL,
“id_oshibka” int4 NOT NULL,
CONSTRAINT “_copy_6” PRIMARY KEY (“id_user”)
);
CREATE TABLE “reklama” (
“id_reklama” int4 NOT NULL,
“tele-marketing” text NOT NULL,
“soc-seti” text NOT NULL,
“mobile” int4 NOT NULL,
CONSTRAINT “_copy_3” PRIMARY KEY (“id_reklama”)
);
CREATE TABLE “tex-specialist” (
“id_tex-specialist” int4 NOT NULL,
“grafik” date NOT NULL,
“zarplata” int4 NOT NULL,
“ispravlenie oshibok” int4 NOT NULL,
CONSTRAINT “_copy_7” PRIMARY KEY (“id_tex-specialist”)
);
CREATE TABLE “uslugi” (
“id_uslugi” int4 NOT NULL,
“vostanavlenia parola” int4 NOT NULL,
“poterya acaunta” int4 NOT NULL,
CONSTRAINT “_copy_4” PRIMARY KEY (“id_uslugi”)
);
ALTER TABLE “companiya” ADD CONSTRAINT “fk_companiya_operator_1” FOREIGN KEY (“id_operator”) REFERENCES “operator” (“id_operator”);
ALTER TABLE “companiya” ADD CONSTRAINT “fk_companiya_uslugi_1” FOREIGN KEY (“id_uslugi”) REFERENCES “uslugi” (“id_uslugi”);
ALTER TABLE “companiya” ADD CONSTRAINT “fk_companiya_filial_1” FOREIGN KEY (“id_filial”) REFERENCES “filial” (“id_filial”);
ALTER TABLE “companiya” ADD CONSTRAINT “fk_companiya_reklama_1” FOREIGN KEY (“id_reklama”) REFERENCES “reklama” (“id_reklama”);
ALTER TABLE “companiya” ADD CONSTRAINT “fk_companiya_tex-specialist_1” FOREIGN KEY (“id_tex-specialist”) REFERENCES “tex-specialist” (“id_tex-specialist”);
ALTER TABLE “polsovateli” ADD CONSTRAINT “fk_polsovateli_companiya_1” FOREIGN KEY (“id_companiya”) REFERENCES “companiya” (“compania_id”);
ERROR: ОШИБКА: ошибка синтаксиса (примерное положение: “”companiya””)
LINE 1: drop table exists “companiya”;
^
Источник
Приложение A. Коды ошибок PostgreSQL
Всем сообщениям, которые выдаёт сервер PostgreSQL , назначены пятисимвольные коды ошибок, соответствующие кодам «SQLSTATE» , описанным в стандарте SQL. Приложения, которые должны знать, какое условие ошибки имело место, обычно проверяют код ошибки и только потом обращаются к текстовому сообщению об ошибке. Коды ошибок, скорее всего, не изменятся от выпуска к выпуску PostgreSQL , и они не меняются при локализации как сообщения об ошибках. Заметьте, что отдельные, но не все коды ошибок, которые выдаёт PostgreSQL , определены стандартом SQL; некоторые дополнительные коды ошибок для условий, не описанных стандартом, были добавлены независимо или позаимствованы из других баз данных.
Согласно стандарту, первые два символа кода ошибки обозначают класс ошибок, а последние три символа обозначают определённое условие в этом классе. Таким образом, приложение, не знающее значение определённого кода ошибки, всё же может понять, что делать, по классу ошибки.
В Таблице A-1 перечислены все коды ошибок, определённые в PostgreSQL 9.4.1. (Некоторые коды в настоящее время не используются, хотя они определены в стандарте SQL.) Также показаны классы ошибок. Для каждого класса ошибок имеется «стандартный» код ошибки с последними тремя символами 000. Этот код выдаётся только для таких условий ошибок, которые относятся к определённому классу, но не имеют более определённого кода.
Символ, указанный в колонке «Имя условия» , определяет условие в PL/pgSQL . Имена условий могут записываться в верхнем или нижнем регистре. (Заметьте, что PL/pgSQL , в отличие от ошибок, не распознаёт предупреждения; то есть классы 00, 01 и 02.)
Для некоторых типов ошибок сервер сообщает имя объекта базы данных (таблица, колонка таблицы, тип данных или ограничение), связанного с ошибкой; например, имя уникального ограничения, вызвавшего ошибку unique_violation. Такие имена передаются в отдельных полях сообщения об ошибке, чтобы приложениям не пришлось извлекать его из возможно локализованного текста ошибки для человека. На момент выхода PostgreSQL 9.3 полностью охватывались только ошибки класса SQLSTATE 23 (нарушения ограничений целостности), но в будущем должны быть охвачены и другие классы.
Источник
Содержание
- PostgreSQL error 42601- How we fix it
- What causes error 42601 in PostgreSQL?
- How we fix the error?
- Conclusion
- PREVENT YOUR SERVER FROM CRASHING!
- 10 Comments
PostgreSQL error 42601- How we fix it
by Sijin George | Sep 12, 2019
Syntax errors are quite common while coding.
But, things go for a toss when it results in website errors.
PostgreSQL error 42601 also occurs due to syntax errors in the database queries.
At Bobcares, we often get requests from PostgreSQL users to fix errors as part of our Server Management Services.
Today, let’s check PostgreSQL error in detail and see how our Support Engineers fix it for the customers.
What causes error 42601 in PostgreSQL?
PostgreSQL is an advanced database engine. It is popular for its extensive features and ability to handle complex database situations.
Applications like Instagram, Facebook, Apple, etc rely on the PostgreSQL database.
But what causes error 42601?
PostgreSQL error codes consist of five characters. The first two characters denote the class of errors. And the remaining three characters indicate a specific condition within that class.
Here, 42 in 42601 represent the class “Syntax Error or Access Rule Violation“.
In short, this error mainly occurs due to the syntax errors in the queries executed. A typical error shows up as:

Here, the syntax error has occurred in position 119 near the value “parents” in the query.
How we fix the error?
Now let’s see how our PostgreSQL engineers resolve this error efficiently.
Recently, one of our customers contacted us with this error. He tried to execute the following code,
But, this ended up in PostgreSQL error 42601. And he got the following error message,
Our PostgreSQL Engineers checked the issue and found out the syntax error. The statement in Line 5 was a mix of plain and dynamic SQL. In general, the PostgreSQL query should be either fully dynamic or plain. Therefore, we changed the code as,
This resolved the error 42601, and the code worked fine.
[Need more assistance to solve PostgreSQL error 42601?- We’ll help you.]
Conclusion
In short, PostgreSQL error 42601 occurs due to the syntax errors in the code. Today, in this write-up, we have discussed how our Support Engineers fixed this error for our customers.
PREVENT YOUR SERVER FROM CRASHING!
Never again lose customers to poor server speed! Let us help you.
Our server experts will monitor & maintain your server 24/7 so that it remains lightning fast and secure.
SELECT * FROM long_term_prediction_anomaly WHERE + “‘Timestamp’” + ‘”BETWEEN ‘” +
2019-12-05 09:10:00+ ‘”AND’” + 2019-12-06 09:10:00 + “‘;”)
Hello Joe,
Do you still get PostgreSQL errors? If you need help, we’ll be happy to talk to you on chat (click on the icon at right-bottom).
У меня ошибка drop table exists “companiya”;
CREATE TABLE “companiya” (
“compania_id” int4 NOT NULL,
“fio vladelca” text NOT NULL,
“name” text NOT NULL,
“id_operator” int4 NOT NULL,
“id_uslugi” int4 NOT NULL,
“id_reklama” int4 NOT NULL,
“id_tex-specialist” int4 NOT NULL,
“id_filial” int4 NOT NULL,
CONSTRAINT “_copy_8” PRIMARY KEY (“compania_id”)
);
CREATE TABLE “filial” (
“id_filial” int4 NOT NULL,
“street” text NOT NULL,
“house” int4 NOT NULL,
“city” text NOT NULL,
CONSTRAINT “_copy_5” PRIMARY KEY (“id_filial”)
);
CREATE TABLE “login” (
“id_name” int4 NOT NULL,
“name” char(20) NOT NULL,
“pass” char(20) NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (“id_name”)
);
CREATE TABLE “operator” (
“id_operator” int4 NOT NULL,
“obrabotka obrasheniya” int4 NOT NULL,
“konsultirovanie” text NOT NULL,
“grafick work” date NOT NULL,
CONSTRAINT “_copy_2” PRIMARY KEY (“id_operator”)
);
CREATE TABLE “polsovateli” (
“id_user” int4 NOT NULL,
“id_companiya” int4 NOT NULL,
“id_obrasheniya” int4 NOT NULL,
“id_oshibka” int4 NOT NULL,
CONSTRAINT “_copy_6” PRIMARY KEY (“id_user”)
);
CREATE TABLE “reklama” (
“id_reklama” int4 NOT NULL,
“tele-marketing” text NOT NULL,
“soc-seti” text NOT NULL,
“mobile” int4 NOT NULL,
CONSTRAINT “_copy_3” PRIMARY KEY (“id_reklama”)
);
CREATE TABLE “tex-specialist” (
“id_tex-specialist” int4 NOT NULL,
“grafik” date NOT NULL,
“zarplata” int4 NOT NULL,
“ispravlenie oshibok” int4 NOT NULL,
CONSTRAINT “_copy_7” PRIMARY KEY (“id_tex-specialist”)
);
CREATE TABLE “uslugi” (
“id_uslugi” int4 NOT NULL,
“vostanavlenia parola” int4 NOT NULL,
“poterya acaunta” int4 NOT NULL,
CONSTRAINT “_copy_4” PRIMARY KEY (“id_uslugi”)
);
ALTER TABLE “companiya” ADD CONSTRAINT “fk_companiya_operator_1” FOREIGN KEY (“id_operator”) REFERENCES “operator” (“id_operator”);
ALTER TABLE “companiya” ADD CONSTRAINT “fk_companiya_uslugi_1” FOREIGN KEY (“id_uslugi”) REFERENCES “uslugi” (“id_uslugi”);
ALTER TABLE “companiya” ADD CONSTRAINT “fk_companiya_filial_1” FOREIGN KEY (“id_filial”) REFERENCES “filial” (“id_filial”);
ALTER TABLE “companiya” ADD CONSTRAINT “fk_companiya_reklama_1” FOREIGN KEY (“id_reklama”) REFERENCES “reklama” (“id_reklama”);
ALTER TABLE “companiya” ADD CONSTRAINT “fk_companiya_tex-specialist_1” FOREIGN KEY (“id_tex-specialist”) REFERENCES “tex-specialist” (“id_tex-specialist”);
ALTER TABLE “polsovateli” ADD CONSTRAINT “fk_polsovateli_companiya_1” FOREIGN KEY (“id_companiya”) REFERENCES “companiya” (“compania_id”);
ERROR: ОШИБКА: ошибка синтаксиса (примерное положение: “”companiya””)
LINE 1: drop table exists “companiya”;
^
Источник
БЛОГ НА HUSL
- Деловая переписка на английском языке: фразы и советы
- Принцип цикады и почему он важен для веб-дизайнеров
- В популярных антивирусах для ПК обнаружили лазейки в защите
Триггерная функция, которая удаляет роль
Код триггерной функции:
begin
prepare myfun(text) as
drop role $1;
execute myfun(old.employee_login);
end;
При попытке сохранения выдает ошибку : ошибка синтаксиса (примерное положение: «drop»). В чем может быть проблема?
Источник
Ответы (1 шт):
Автор решения: Azonos
Рабочий код:
begin
execute 'DROP ROLE '|| old.employee_login;
return null;
end;
→ Ссылка
licensed under cc by-sa 3.0 with attribution.
В этой статье представлена ошибка с номером Ошибка 3295, известная как Ошибка Microsoft Access 3295, описанная как Ошибка синтаксиса в DROP TABLE или DROP INDEX.
О программе Runtime Ошибка 3295
Время выполнения Ошибка 3295 происходит, когда Microsoft Access дает сбой или падает во время запуска, отсюда и название. Это не обязательно означает, что код был каким-то образом поврежден, просто он не сработал во время выполнения. Такая ошибка появляется на экране в виде раздражающего уведомления, если ее не устранить. Вот симптомы, причины и способы устранения проблемы.
Определения (Бета)
Здесь мы приводим некоторые определения слов, содержащихся в вашей ошибке, в попытке помочь вам понять вашу проблему. Эта работа продолжается, поэтому иногда мы можем неправильно определить слово, так что не стесняйтесь пропустить этот раздел!
- Access — НЕ ИСПОЛЬЗУЙТЕ этот тег для Microsoft Access, используйте вместо него [ms-access]
- Drop table — SQL команда для удаления всей таблицы.
- Синтаксис — Синтаксис относится к фактическим языковым элементам и самим символам.
- Синтаксическая ошибка — Синтаксическая ошибка возникает, когда программа не следует синтаксическим правилам языка программирования.
- Таблица — НЕ ИСПОЛЬЗУЙТЕ ЭТОТ ТЕГ; это неоднозначно.
- Access — Microsoft Access, также известный как Microsoft Office Access, представляет собой систему управления базами данных от Microsoft, которая обычно сочетает в себе реляционное ядро СУБД Microsoft JetACE с графическим пользовательским интерфейсом. и инструменты для разработки программного графический пользовательский интерфейс и инструменты для разработки программного обеспечения.
Симптомы Ошибка 3295 — Ошибка Microsoft Access 3295
Ошибки времени выполнения происходят без предупреждения. Сообщение об ошибке может появиться на экране при любом запуске %программы%. Фактически, сообщение об ошибке или другое диалоговое окно может появляться снова и снова, если не принять меры на ранней стадии.
Возможны случаи удаления файлов или появления новых файлов. Хотя этот симптом в основном связан с заражением вирусом, его можно отнести к симптомам ошибки времени выполнения, поскольку заражение вирусом является одной из причин ошибки времени выполнения. Пользователь также может столкнуться с внезапным падением скорости интернет-соединения, но, опять же, это не всегда так.
(Только для примера)
Причины Ошибка Microsoft Access 3295 — Ошибка 3295
При разработке программного обеспечения программисты составляют код, предвидя возникновение ошибок. Однако идеальных проектов не бывает, поскольку ошибки можно ожидать даже при самом лучшем дизайне программы. Глюки могут произойти во время выполнения программы, если определенная ошибка не была обнаружена и устранена во время проектирования и тестирования.
Ошибки во время выполнения обычно вызваны несовместимостью программ, запущенных в одно и то же время. Они также могут возникать из-за проблем с памятью, плохого графического драйвера или заражения вирусом. Каким бы ни был случай, проблему необходимо решить немедленно, чтобы избежать дальнейших проблем. Ниже приведены способы устранения ошибки.
Методы исправления
Ошибки времени выполнения могут быть раздражающими и постоянными, но это не совсем безнадежно, существует возможность ремонта. Вот способы сделать это.
Если метод ремонта вам подошел, пожалуйста, нажмите кнопку upvote слева от ответа, это позволит другим пользователям узнать, какой метод ремонта на данный момент работает лучше всего.
Обратите внимание: ни ErrorVault.com, ни его авторы не несут ответственности за результаты действий, предпринятых при использовании любого из методов ремонта, перечисленных на этой странице — вы выполняете эти шаги на свой страх и риск.
Метод 1 — Закройте конфликтующие программы
Когда вы получаете ошибку во время выполнения, имейте в виду, что это происходит из-за программ, которые конфликтуют друг с другом. Первое, что вы можете сделать, чтобы решить проблему, — это остановить эти конфликтующие программы.
- Откройте диспетчер задач, одновременно нажав Ctrl-Alt-Del. Это позволит вам увидеть список запущенных в данный момент программ.
- Перейдите на вкладку «Процессы» и остановите программы одну за другой, выделив каждую программу и нажав кнопку «Завершить процесс».
- Вам нужно будет следить за тем, будет ли сообщение об ошибке появляться каждый раз при остановке процесса.
- Как только вы определите, какая программа вызывает ошибку, вы можете перейти к следующему этапу устранения неполадок, переустановив приложение.
Метод 2 — Обновите / переустановите конфликтующие программы
Использование панели управления
- В Windows 7 нажмите кнопку «Пуск», затем нажмите «Панель управления», затем «Удалить программу».
- В Windows 8 нажмите кнопку «Пуск», затем прокрутите вниз и нажмите «Дополнительные настройки», затем нажмите «Панель управления»> «Удалить программу».
- Для Windows 10 просто введите «Панель управления» в поле поиска и щелкните результат, затем нажмите «Удалить программу».
- В разделе «Программы и компоненты» щелкните проблемную программу и нажмите «Обновить» или «Удалить».
- Если вы выбрали обновление, вам просто нужно будет следовать подсказке, чтобы завершить процесс, однако, если вы выбрали «Удалить», вы будете следовать подсказке, чтобы удалить, а затем повторно загрузить или использовать установочный диск приложения для переустановки. программа.
Использование других методов
- В Windows 7 список всех установленных программ можно найти, нажав кнопку «Пуск» и наведя указатель мыши на список, отображаемый на вкладке. Вы можете увидеть в этом списке утилиту для удаления программы. Вы можете продолжить и удалить с помощью утилит, доступных на этой вкладке.
- В Windows 10 вы можете нажать «Пуск», затем «Настройка», а затем — «Приложения».
- Прокрутите вниз, чтобы увидеть список приложений и функций, установленных на вашем компьютере.
- Щелкните программу, которая вызывает ошибку времени выполнения, затем вы можете удалить ее или щелкнуть Дополнительные параметры, чтобы сбросить приложение.
Метод 3 — Обновите программу защиты от вирусов или загрузите и установите последнюю версию Центра обновления Windows.
Заражение вирусом, вызывающее ошибку выполнения на вашем компьютере, необходимо немедленно предотвратить, поместить в карантин или удалить. Убедитесь, что вы обновили свою антивирусную программу и выполнили тщательное сканирование компьютера или запустите Центр обновления Windows, чтобы получить последние определения вирусов и исправить их.
Метод 4 — Переустановите библиотеки времени выполнения
Вы можете получить сообщение об ошибке из-за обновления, такого как пакет MS Visual C ++, который может быть установлен неправильно или полностью. Что вы можете сделать, так это удалить текущий пакет и установить новую копию.
- Удалите пакет, выбрав «Программы и компоненты», найдите и выделите распространяемый пакет Microsoft Visual C ++.
- Нажмите «Удалить» в верхней части списка и, когда это будет сделано, перезагрузите компьютер.
- Загрузите последний распространяемый пакет от Microsoft и установите его.
Метод 5 — Запустить очистку диска
Вы также можете столкнуться с ошибкой выполнения из-за очень нехватки свободного места на вашем компьютере.
- Вам следует подумать о резервном копировании файлов и освобождении места на жестком диске.
- Вы также можете очистить кеш и перезагрузить компьютер.
- Вы также можете запустить очистку диска, открыть окно проводника и щелкнуть правой кнопкой мыши по основному каталогу (обычно это C
- Щелкните «Свойства», а затем — «Очистка диска».
Метод 6 — Переустановите графический драйвер
Если ошибка связана с плохим графическим драйвером, вы можете сделать следующее:
- Откройте диспетчер устройств и найдите драйвер видеокарты.
- Щелкните правой кнопкой мыши драйвер видеокарты, затем нажмите «Удалить», затем перезагрузите компьютер.
Метод 7 — Ошибка выполнения, связанная с IE
Если полученная ошибка связана с Internet Explorer, вы можете сделать следующее:
- Сбросьте настройки браузера.
- В Windows 7 вы можете нажать «Пуск», перейти в «Панель управления» и нажать «Свойства обозревателя» слева. Затем вы можете перейти на вкладку «Дополнительно» и нажать кнопку «Сброс».
- Для Windows 8 и 10 вы можете нажать «Поиск» и ввести «Свойства обозревателя», затем перейти на вкладку «Дополнительно» и нажать «Сброс».
- Отключить отладку скриптов и уведомления об ошибках.
- В том же окне «Свойства обозревателя» можно перейти на вкладку «Дополнительно» и найти пункт «Отключить отладку сценария».
- Установите флажок в переключателе.
- Одновременно снимите флажок «Отображать уведомление о каждой ошибке сценария», затем нажмите «Применить» и «ОК», затем перезагрузите компьютер.
Если эти быстрые исправления не работают, вы всегда можете сделать резервную копию файлов и запустить восстановление на вашем компьютере. Однако вы можете сделать это позже, когда перечисленные здесь решения не сработают.
Другие языки:
How to fix Error 3295 (Microsoft Access Error 3295) — Syntax error in DROP TABLE or DROP INDEX.
Wie beheben Fehler 3295 (Microsoft Access-Fehler 3295) — Syntaxfehler in DROP TABLE oder DROP INDEX.
Come fissare Errore 3295 (Errore di Microsoft Access 3295) — Errore di sintassi in DROP TABLE o DROP INDEX.
Hoe maak je Fout 3295 (Microsoft Access-fout 3295) — Syntaxisfout in DROP TABLE of DROP INDEX.
Comment réparer Erreur 3295 (Erreur Microsoft Access 3295) — Erreur de syntaxe dans DROP TABLE ou DROP INDEX.
어떻게 고치는 지 오류 3295 (마이크로소프트 액세스 오류 3295) — DROP TABLE 또는 DROP INDEX에 구문 오류가 있습니다.
Como corrigir o Erro 3295 (Erro 3295 do Microsoft Access) — Erro de sintaxe em DROP TABLE ou DROP INDEX.
Hur man åtgärdar Fel 3295 (Microsoft Access Error 3295) — Syntaxfel i DROP TABLE eller DROP INDEX.
Jak naprawić Błąd 3295 (Błąd Microsoft Access 3295) — Błąd składni w DROP TABLE lub DROP INDEX.
Cómo arreglar Error 3295 (Error 3295 de Microsoft Access) — Error de sintaxis en DROP TABLE o DROP INDEX.
![]() Об авторе: Фил Харт является участником сообщества Microsoft с 2010 года. С текущим количеством баллов более 100 000 он внес более 3000 ответов на форумах Microsoft Support и создал почти 200 новых справочных статей в Technet Wiki.
Об авторе: Фил Харт является участником сообщества Microsoft с 2010 года. С текущим количеством баллов более 100 000 он внес более 3000 ответов на форумах Microsoft Support и создал почти 200 новых справочных статей в Technet Wiki.
Следуйте за нами: ![]()
![]()
![]()
Рекомендуемый инструмент для ремонта:
Этот инструмент восстановления может устранить такие распространенные проблемы компьютера, как синие экраны, сбои и замораживание, отсутствующие DLL-файлы, а также устранить повреждения от вредоносных программ/вирусов и многое другое путем замены поврежденных и отсутствующих системных файлов.
ШАГ 1:
Нажмите здесь, чтобы скачать и установите средство восстановления Windows.
ШАГ 2:
Нажмите на Start Scan и позвольте ему проанализировать ваше устройство.
ШАГ 3:
Нажмите на Repair All, чтобы устранить все обнаруженные проблемы.
СКАЧАТЬ СЕЙЧАС
Совместимость

Требования
1 Ghz CPU, 512 MB RAM, 40 GB HDD
Эта загрузка предлагает неограниченное бесплатное сканирование ПК с Windows. Полное восстановление системы начинается от $19,95.
ID статьи: ACX06760RU
Применяется к: Windows 10, Windows 8.1, Windows 7, Windows Vista, Windows XP, Windows 2000
- Печать
Страницы: [1] Вниз
Тема: Postgres (db error) (Прочитано 18484 раз)
0 Пользователей и 1 Гость просматривают эту тему.
ПРивет!
Решил вот попробовать вашу софтину! Но никак не получается ее завести
Установил POstgresql сервер и ОДБЦ драйвер!
Создал базу данных!
Настроил в подключении парамеры — нажал Тест! Получил Ответ ОК!
Далее залил в базу дамп
Пробую войти и получаю ошибку
BKO.NET 1.7.5.1
Версия базы данных не является эталонной
Вносим изменения в базу …
Жму ОК
Внесение изменений закончилось неудачей, воспользуйтесь конвертором или скриптами
ОК — и программазакрывается!
ЧТо делать ?
Спасибо

Записан
select access from configure
дальше будем смотреть…

Записан

«1.7.3.5»
Я пробовал поменять на 1.7.5.1 — но результат тот же
« Последнее редактирование: 28 Февраль 2014, 10:38:35 от Digitec »

Записан
ALTER TABLE Remont ADD COLUMN GARANT Date;
ALTER TABLE kompy ADD COLUMN MB_NAME varchar(255) Mb;
UPDATE TABLE kompy SET MB_NAME=Mb;
ALTER TABLE kompy DROP COLUMN Mb, nomerPC, TEXT_RED, EXCELL_RED, ACCESS_RED, VG, IG;
ALTER TABLE kompy ADD COLUMN data_sp Date,ADD COLUMN data_nb Date;
Update CONFIGURE SET access='1.7.3.9' WHERE access<>'1.7.3.9';

Записан

ОШИБКА: ошибка синтаксиса (примерное положение: «Mb»)
LINE 2: ALTER TABLE kompy ADD COLUMN MB_NAME varchar(255) Mb;
^
********** Ошибка **********
ОШИБКА: ошибка синтаксиса (примерное положение: «Mb»)
SQL-состояние: 42601
Символ: 94
И кстати при внесении дампа в постгрес имеем две ошибки
ОШИБКА: ошибка синтаксиса (примерное положение: «EXTENSION»)
СТРОКА 1: CREATE EXTENSION IF NOT EXISTS plpgsql WITH SCHEMA pg_catalo…
^
ОШИБКА: ошибка синтаксиса (примерное положение: «EXTENSION»)
СТРОКА 1: COMMENT ON EXTENSION plpgsql IS ‘PL/pgSQL procedural languag…
^
« Последнее редактирование: 28 Февраль 2014, 11:02:03 от Digitec »

Записан
ALTER TABLE kompy ADD COLUMN MB_NAME varchar(255);

Записан

пробуем так
ALTER TABLE Remont ADD COLUMN GARANT Date;
ALTER TABLE kompy ADD COLUMN MB_NAME varchar(255);
UPDATE kompy SET MB_NAME=Mb;
ALTER TABLE kompy DROP COLUMN Mb, nomerPC, TEXT_RED, EXCELL_RED, ACCESS_RED, VG, IG;
ALTER TABLE kompy ADD COLUMN data_sp Date,ADD COLUMN data_nb Date;
Update CONFIGURE SET access=’1.7.3.9′ WHERE access<>’1.7.3.9′;
Получаем
ОШИБКА: ошибка синтаксиса (примерное положение: «nomerPC»)
LINE 4: ALTER TABLE kompy DROP COLUMN Mb, nomerPC, TEXT_RED, EXCELL_…
^
********** Ошибка **********

Записан
Так
Немного поиграв в кашпировского
выполняем такой запрос
ALTER TABLE Remont ADD COLUMN GARANT Date;
ALTER TABLE kompy ADD COLUMN MB_NAME varchar(255);
UPDATE kompy SET MB_NAME=Mb;
ALTER TABLE kompy DROP COLUMN Mb;
ALTER TABLE kompy DROP COLUMN nomerPC;
ALTER TABLE kompy DROP COLUMN TEXT_RED;
ALTER TABLE kompy DROP COLUMN EXCELL_RED;
ALTER TABLE kompy DROP COLUMN ACCESS_RED;
ALTER TABLE kompy DROP COLUMN VG;
ALTER TABLE kompy DROP COLUMN IG;
ALTER TABLE kompy ADD COLUMN data_sp Date,ADD COLUMN data_nb Date;
Update CONFIGURE SET access='1.7.3.9' WHERE access<>'1.7.3.9';
После чего пробуем войти и получаем уже совершенно другую ошибку (на дату ругается)
«Неверный синтаксис для типа date: «»09:33:10»

Записан
так получается что за место даты время…

Записан

Так как бы я это и сам вижу — вопрос в том — что и где поправить и почему оно так?
щас паралельно попробую базу под фрей развернуть

Записан
ну тут вопрос сложный, я дома пробовал все работало… сейчас проверить не могу…

Записан

ка кто можно определить какая это талица вбазе ругается? Я бы попробовал поиграть с параметрами?

Записан
думаю что это таблица kompy

Записан

Итак
есть успехи!
Взял версию 1.7.5.0
И наконецто запустиллось!
Но при входе уже пишет ошибку
колонка name_prog не существует
мои действия?

Записан
В итоге !
Скачал 1.7.3.3 — все завелось!
Мистика!
Вобщем приступаю к изучению — что правда мысль о возможно обновлении версии в будущем немного пугает

Записан
создать колонку name_prog в таблице configure

Записан

- Печать
Страницы: [1] Вверх
Syntax errors are quite common while coding.
But, things go for a toss when it results in website errors.
PostgreSQL error 42601 also occurs due to syntax errors in the database queries.
At Bobcares, we often get requests from PostgreSQL users to fix errors as part of our Server Management Services.
Today, let’s check PostgreSQL error in detail and see how our Support Engineers fix it for the customers.
What causes error 42601 in PostgreSQL?
PostgreSQL is an advanced database engine. It is popular for its extensive features and ability to handle complex database situations.
Applications like Instagram, Facebook, Apple, etc rely on the PostgreSQL database.
But what causes error 42601?
PostgreSQL error codes consist of five characters. The first two characters denote the class of errors. And the remaining three characters indicate a specific condition within that class.
Here, 42 in 42601 represent the class “Syntax Error or Access Rule Violation“.
In short, this error mainly occurs due to the syntax errors in the queries executed. A typical error shows up as:

Here, the syntax error has occurred in position 119 near the value “parents” in the query.
How we fix the error?
Now let’s see how our PostgreSQL engineers resolve this error efficiently.
Recently, one of our customers contacted us with this error. He tried to execute the following code,
CREATE OR REPLACE FUNCTION prc_tst_bulk(sql text)
RETURNS TABLE (name text, rowcount integer) AS
$$
BEGIN
WITH m_ty_person AS (return query execute sql)
select name, count(*) from m_ty_person where name like '%a%' group by name
union
select name, count(*) from m_ty_person where gender = 1 group by name;
END
$$ LANGUAGE plpgsql;But, this ended up in PostgreSQL error 42601. And he got the following error message,
ERROR: syntax error at or near "return"
LINE 5: WITH m_ty_person AS (return query execute sql)Our PostgreSQL Engineers checked the issue and found out the syntax error. The statement in Line 5 was a mix of plain and dynamic SQL. In general, the PostgreSQL query should be either fully dynamic or plain. Therefore, we changed the code as,
RETURN QUERY EXECUTE '
WITH m_ty_person AS (' || sql || $x$)
SELECT name, count(*)::int FROM m_ty_person WHERE name LIKE '%a%' GROUP BY name
UNION
SELECT name, count(*)::int FROM m_ty_person WHERE gender = 1 GROUP BY name$x$;This resolved the error 42601, and the code worked fine.
[Need more assistance to solve PostgreSQL error 42601?- We’ll help you.]
Conclusion
In short, PostgreSQL error 42601 occurs due to the syntax errors in the code. Today, in this write-up, we have discussed how our Support Engineers fixed this error for our customers.
PREVENT YOUR SERVER FROM CRASHING!
Never again lose customers to poor server speed! Let us help you.
Our server experts will monitor & maintain your server 24/7 so that it remains lightning fast and secure.
GET STARTED
var google_conversion_label = «owonCMyG5nEQ0aD71QM»;
Postgres 9.3.2 on heroku.
Pretty sure I’m just being an idiot, but I can’t seem to figure out why my syntax is wrong.
db=> dt
List of relations
Schema | Name | Type | Owner
--------+------------+-------+----------------
public | device | table | admin
public | post | table | admin
public | user | table | admin
(3 rows)
// why does this fail?
db=> drop table user;
ERROR: syntax error at or near "user"
LINE 1: drop table user;
// does the right thing
db=> drop table error;
ERROR: table "error" does not exist
asked Jan 10, 2014 at 18:18
User is a reserved keyword in Postgres. You’ll have to put it in quotes if you want to refer to an actual table named user:
DROP TABLE "user";
Probably best to stay away from using reserved keywords as table names if you can help it. It usually ends up creating weird problems down the road. Users might be a better name for a table.
answered Jan 10, 2014 at 18:19
Mike ChristensenMike Christensen
87.5k49 gold badges206 silver badges324 bronze badges
0
I had the same error. My database name was very unique and not a reserved keyword. Still needed to wrap the database name with quotation marks
"<database_name>"
Also for those that might forget always add a semicolon ; at the end of the statement, I always forget.
answered Nov 20, 2020 at 1:52
Syntax errors are quite common while coding.
But, things go for a toss when it results in website errors.
PostgreSQL error 42601 also occurs due to syntax errors in the database queries.
At Bobcares, we often get requests from PostgreSQL users to fix errors as part of our Server Management Services.
Today, let’s check PostgreSQL error in detail and see how our Support Engineers fix it for the customers.
What causes error 42601 in PostgreSQL?
PostgreSQL is an advanced database engine. It is popular for its extensive features and ability to handle complex database situations.
Applications like Instagram, Facebook, Apple, etc rely on the PostgreSQL database.
But what causes error 42601?
PostgreSQL error codes consist of five characters. The first two characters denote the class of errors. And the remaining three characters indicate a specific condition within that class.
Here, 42 in 42601 represent the class “Syntax Error or Access Rule Violation“.
In short, this error mainly occurs due to the syntax errors in the queries executed. A typical error shows up as:

Here, the syntax error has occurred in position 119 near the value “parents” in the query.
How we fix the error?
Now let’s see how our PostgreSQL engineers resolve this error efficiently.
Recently, one of our customers contacted us with this error. He tried to execute the following code,
CREATE OR REPLACE FUNCTION prc_tst_bulk(sql text)
RETURNS TABLE (name text, rowcount integer) AS
$$
BEGIN
WITH m_ty_person AS (return query execute sql)
select name, count(*) from m_ty_person where name like '%a%' group by name
union
select name, count(*) from m_ty_person where gender = 1 group by name;
END
$$ LANGUAGE plpgsql;But, this ended up in PostgreSQL error 42601. And he got the following error message,
ERROR: syntax error at or near "return"
LINE 5: WITH m_ty_person AS (return query execute sql)Our PostgreSQL Engineers checked the issue and found out the syntax error. The statement in Line 5 was a mix of plain and dynamic SQL. In general, the PostgreSQL query should be either fully dynamic or plain. Therefore, we changed the code as,
RETURN QUERY EXECUTE '
WITH m_ty_person AS (' || sql || $x$)
SELECT name, count(*)::int FROM m_ty_person WHERE name LIKE '%a%' GROUP BY name
UNION
SELECT name, count(*)::int FROM m_ty_person WHERE gender = 1 GROUP BY name$x$;This resolved the error 42601, and the code worked fine.
[Need more assistance to solve PostgreSQL error 42601?- We’ll help you.]
Conclusion
In short, PostgreSQL error 42601 occurs due to the syntax errors in the code. Today, in this write-up, we have discussed how our Support Engineers fixed this error for our customers.
PREVENT YOUR SERVER FROM CRASHING!
Never again lose customers to poor server speed! Let us help you.
Our server experts will monitor & maintain your server 24/7 so that it remains lightning fast and secure.
GET STARTED
var google_conversion_label = «owonCMyG5nEQ0aD71QM»;
Содержание
- PostgreSQL error 42601- How we fix it
- What causes error 42601 in PostgreSQL?
- How we fix the error?
- Conclusion
- PREVENT YOUR SERVER FROM CRASHING!
- 10 Comments
- Приложение A. Коды ошибок PostgreSQL
- SQLSTATE=42601 ,SQLCODE=-104 while running HCAT_SYNC_OBJECTS procedure in IBM Db2 BigSQL
- Troubleshooting
- Problem
- Symptom
- Cause
- Environment
- Resolving The Problem
- Sql error 42601 error multiple decimal points
- Submit correction
PostgreSQL error 42601- How we fix it
by Sijin George | Sep 12, 2019
Syntax errors are quite common while coding.
But, things go for a toss when it results in website errors.
PostgreSQL error 42601 also occurs due to syntax errors in the database queries.
At Bobcares, we often get requests from PostgreSQL users to fix errors as part of our Server Management Services.
Today, let’s check PostgreSQL error in detail and see how our Support Engineers fix it for the customers.
What causes error 42601 in PostgreSQL?
PostgreSQL is an advanced database engine. It is popular for its extensive features and ability to handle complex database situations.
Applications like Instagram, Facebook, Apple, etc rely on the PostgreSQL database.
But what causes error 42601?
PostgreSQL error codes consist of five characters. The first two characters denote the class of errors. And the remaining three characters indicate a specific condition within that class.
Here, 42 in 42601 represent the class “Syntax Error or Access Rule Violation“.
In short, this error mainly occurs due to the syntax errors in the queries executed. A typical error shows up as:

Here, the syntax error has occurred in position 119 near the value “parents” in the query.
How we fix the error?
Now let’s see how our PostgreSQL engineers resolve this error efficiently.
Recently, one of our customers contacted us with this error. He tried to execute the following code,
But, this ended up in PostgreSQL error 42601. And he got the following error message,
Our PostgreSQL Engineers checked the issue and found out the syntax error. The statement in Line 5 was a mix of plain and dynamic SQL. In general, the PostgreSQL query should be either fully dynamic or plain. Therefore, we changed the code as,
This resolved the error 42601, and the code worked fine.
[Need more assistance to solve PostgreSQL error 42601?- We’ll help you.]
Conclusion
In short, PostgreSQL error 42601 occurs due to the syntax errors in the code. Today, in this write-up, we have discussed how our Support Engineers fixed this error for our customers.
PREVENT YOUR SERVER FROM CRASHING!
Never again lose customers to poor server speed! Let us help you.
Our server experts will monitor & maintain your server 24/7 so that it remains lightning fast and secure.
SELECT * FROM long_term_prediction_anomaly WHERE + “‘Timestamp’” + ‘”BETWEEN ‘” +
2019-12-05 09:10:00+ ‘”AND’” + 2019-12-06 09:10:00 + “‘;”)
Hello Joe,
Do you still get PostgreSQL errors? If you need help, we’ll be happy to talk to you on chat (click on the icon at right-bottom).
У меня ошибка drop table exists “companiya”;
CREATE TABLE “companiya” (
“compania_id” int4 NOT NULL,
“fio vladelca” text NOT NULL,
“name” text NOT NULL,
“id_operator” int4 NOT NULL,
“id_uslugi” int4 NOT NULL,
“id_reklama” int4 NOT NULL,
“id_tex-specialist” int4 NOT NULL,
“id_filial” int4 NOT NULL,
CONSTRAINT “_copy_8” PRIMARY KEY (“compania_id”)
);
CREATE TABLE “filial” (
“id_filial” int4 NOT NULL,
“street” text NOT NULL,
“house” int4 NOT NULL,
“city” text NOT NULL,
CONSTRAINT “_copy_5” PRIMARY KEY (“id_filial”)
);
CREATE TABLE “login” (
“id_name” int4 NOT NULL,
“name” char(20) NOT NULL,
“pass” char(20) NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (“id_name”)
);
CREATE TABLE “operator” (
“id_operator” int4 NOT NULL,
“obrabotka obrasheniya” int4 NOT NULL,
“konsultirovanie” text NOT NULL,
“grafick work” date NOT NULL,
CONSTRAINT “_copy_2” PRIMARY KEY (“id_operator”)
);
CREATE TABLE “polsovateli” (
“id_user” int4 NOT NULL,
“id_companiya” int4 NOT NULL,
“id_obrasheniya” int4 NOT NULL,
“id_oshibka” int4 NOT NULL,
CONSTRAINT “_copy_6” PRIMARY KEY (“id_user”)
);
CREATE TABLE “reklama” (
“id_reklama” int4 NOT NULL,
“tele-marketing” text NOT NULL,
“soc-seti” text NOT NULL,
“mobile” int4 NOT NULL,
CONSTRAINT “_copy_3” PRIMARY KEY (“id_reklama”)
);
CREATE TABLE “tex-specialist” (
“id_tex-specialist” int4 NOT NULL,
“grafik” date NOT NULL,
“zarplata” int4 NOT NULL,
“ispravlenie oshibok” int4 NOT NULL,
CONSTRAINT “_copy_7” PRIMARY KEY (“id_tex-specialist”)
);
CREATE TABLE “uslugi” (
“id_uslugi” int4 NOT NULL,
“vostanavlenia parola” int4 NOT NULL,
“poterya acaunta” int4 NOT NULL,
CONSTRAINT “_copy_4” PRIMARY KEY (“id_uslugi”)
);
ALTER TABLE “companiya” ADD CONSTRAINT “fk_companiya_operator_1” FOREIGN KEY (“id_operator”) REFERENCES “operator” (“id_operator”);
ALTER TABLE “companiya” ADD CONSTRAINT “fk_companiya_uslugi_1” FOREIGN KEY (“id_uslugi”) REFERENCES “uslugi” (“id_uslugi”);
ALTER TABLE “companiya” ADD CONSTRAINT “fk_companiya_filial_1” FOREIGN KEY (“id_filial”) REFERENCES “filial” (“id_filial”);
ALTER TABLE “companiya” ADD CONSTRAINT “fk_companiya_reklama_1” FOREIGN KEY (“id_reklama”) REFERENCES “reklama” (“id_reklama”);
ALTER TABLE “companiya” ADD CONSTRAINT “fk_companiya_tex-specialist_1” FOREIGN KEY (“id_tex-specialist”) REFERENCES “tex-specialist” (“id_tex-specialist”);
ALTER TABLE “polsovateli” ADD CONSTRAINT “fk_polsovateli_companiya_1” FOREIGN KEY (“id_companiya”) REFERENCES “companiya” (“compania_id”);
ERROR: ОШИБКА: ошибка синтаксиса (примерное положение: “”companiya””)
LINE 1: drop table exists “companiya”;
^
Источник
Приложение A. Коды ошибок PostgreSQL
Всем сообщениям, которые выдаёт сервер PostgreSQL , назначены пятисимвольные коды ошибок, соответствующие кодам «SQLSTATE» , описанным в стандарте SQL. Приложения, которые должны знать, какое условие ошибки имело место, обычно проверяют код ошибки и только потом обращаются к текстовому сообщению об ошибке. Коды ошибок, скорее всего, не изменятся от выпуска к выпуску PostgreSQL , и они не меняются при локализации как сообщения об ошибках. Заметьте, что отдельные, но не все коды ошибок, которые выдаёт PostgreSQL , определены стандартом SQL; некоторые дополнительные коды ошибок для условий, не описанных стандартом, были добавлены независимо или позаимствованы из других баз данных.
Согласно стандарту, первые два символа кода ошибки обозначают класс ошибок, а последние три символа обозначают определённое условие в этом классе. Таким образом, приложение, не знающее значение определённого кода ошибки, всё же может понять, что делать, по классу ошибки.
В Таблице A-1 перечислены все коды ошибок, определённые в PostgreSQL 9.4.1. (Некоторые коды в настоящее время не используются, хотя они определены в стандарте SQL.) Также показаны классы ошибок. Для каждого класса ошибок имеется «стандартный» код ошибки с последними тремя символами 000. Этот код выдаётся только для таких условий ошибок, которые относятся к определённому классу, но не имеют более определённого кода.
Символ, указанный в колонке «Имя условия» , определяет условие в PL/pgSQL . Имена условий могут записываться в верхнем или нижнем регистре. (Заметьте, что PL/pgSQL , в отличие от ошибок, не распознаёт предупреждения; то есть классы 00, 01 и 02.)
Для некоторых типов ошибок сервер сообщает имя объекта базы данных (таблица, колонка таблицы, тип данных или ограничение), связанного с ошибкой; например, имя уникального ограничения, вызвавшего ошибку unique_violation. Такие имена передаются в отдельных полях сообщения об ошибке, чтобы приложениям не пришлось извлекать его из возможно локализованного текста ошибки для человека. На момент выхода PostgreSQL 9.3 полностью охватывались только ошибки класса SQLSTATE 23 (нарушения ограничений целостности), но в будущем должны быть охвачены и другие классы.
Источник
SQLSTATE=42601 ,SQLCODE=-104 while running HCAT_SYNC_OBJECTS procedure in IBM Db2 BigSQL
Troubleshooting
Problem
While running HCAT_SYNC_OBJECTS procedure in BigSQL it fails with following ERROR code
Symptom
The following stack trace and ERROR message is observed in bigsql.log file
com.ibm.db2.jcc.am.SqlSyntaxErrorException: An unexpected token «name» was found following «emp.name as Employee». Expected tokens may include: » «.. SQLCODE=-104, SQLSTATE=42601, DRIVER=4.22.29
at com.ibm.db2.jcc.am.ld.a(ld.java:810)
at com.ibm.db2.jcc.am.ld.a(ld.java:66)
at com.ibm.db2.jcc.am.ld.a(ld.java:140)
at com.ibm.db2.jcc.am.up.c(up.java:2796)
at com.ibm.db2.jcc.am.up.d(up.java:2784)
at com.ibm.db2.jcc.am.up.b(up.java:2146)
at com.ibm.db2.jcc.t4.bb.j(bb.java:233)
at com.ibm.db2.jcc.t4.bb.c(bb.java:48)
at com.ibm.db2.jcc.t4.p.b(p.java:38)
at com.ibm.db2.jcc.t4.vb.h(vb.java:124)
at com.ibm.db2.jcc.am.up.kb(up.java:2141)
at com.ibm.db2.jcc.am.up.a(up.java:3336)
at com.ibm.db2.jcc.am.up.c(up.java:768)
at com.ibm.db2.jcc.am.up.executeUpdate(up.java:747)
at com.ibm.biginsights.biga.udf.HCAT_SYNC_OBJECTS.synchronizeObject(HCAT_SYNC_OBJECTS.java:1782)
at com.ibm.biginsights.biga.udf.HCAT_SYNC_OBJECTS.synchronizeTable(HCAT_SYNC_OBJECTS.java:648)
at com.ibm.biginsights.biga.udf.HCAT_SYNC_OBJECTS.syncTables(HCAT_SYNC_OBJECTS.java:564)
at com.ibm.biginsights.biga.udf.HCAT_SYNC_OBJECTS.exec(HCAT_SYNC_OBJECTS.java:314)
Cause
The hive view object has a column name with whitespace characters.
Hive supports column name with space
Environment
Resolving The Problem
BigSQL currently does not support column name with spaces, hence rename the hive columns and use non-whitespace characters
Источник
Sql error 42601 error multiple decimal points
All messages emitted by the PostgreSQL server are assigned five-character error codes that follow the SQL standard’s conventions for “ SQLSTATE ” codes. Applications that need to know which error condition has occurred should usually test the error code, rather than looking at the textual error message. The error codes are less likely to change across PostgreSQL releases, and also are not subject to change due to localization of error messages. Note that some, but not all, of the error codes produced by PostgreSQL are defined by the SQL standard; some additional error codes for conditions not defined by the standard have been invented or borrowed from other databases.
According to the standard, the first two characters of an error code denote a class of errors, while the last three characters indicate a specific condition within that class. Thus, an application that does not recognize the specific error code might still be able to infer what to do from the error class.
Table A.1 lists all the error codes defined in PostgreSQL 15.1. (Some are not actually used at present, but are defined by the SQL standard.) The error classes are also shown. For each error class there is a “ standard ” error code having the last three characters 000 . This code is used only for error conditions that fall within the class but do not have any more-specific code assigned.
The symbol shown in the column “ Condition Name ” is the condition name to use in PL/pgSQL . Condition names can be written in either upper or lower case. (Note that PL/pgSQL does not recognize warning, as opposed to error, condition names; those are classes 00, 01, and 02.)
For some types of errors, the server reports the name of a database object (a table, table column, data type, or constraint) associated with the error; for example, the name of the unique constraint that caused a unique_violation error. Such names are supplied in separate fields of the error report message so that applications need not try to extract them from the possibly-localized human-readable text of the message. As of PostgreSQL 9.3, complete coverage for this feature exists only for errors in SQLSTATE class 23 (integrity constraint violation), but this is likely to be expanded in future.
Table A.1. PostgreSQL Error Codes
| Error Code | Condition Name |
|---|---|
| Class 00 — Successful Completion | |
| 00000 | successful_completion |
| Class 01 — Warning | |
| 01000 | warning |
| 0100C | dynamic_result_sets_returned |
| 01008 | implicit_zero_bit_padding |
| 01003 | null_value_eliminated_in_set_function |
| 01007 | privilege_not_granted |
| 01006 | privilege_not_revoked |
| 01004 | string_data_right_truncation |
| 01P01 | deprecated_feature |
| Class 02 — No Data (this is also a warning class per the SQL standard) | |
| 02000 | no_data |
| 02001 | no_additional_dynamic_result_sets_returned |
| Class 03 — SQL Statement Not Yet Complete | |
| 03000 | sql_statement_not_yet_complete |
| Class 08 — Connection Exception | |
| 08000 | connection_exception |
| 08003 | connection_does_not_exist |
| 08006 | connection_failure |
| 08001 | sqlclient_unable_to_establish_sqlconnection |
| 08004 | sqlserver_rejected_establishment_of_sqlconnection |
| 08007 | transaction_resolution_unknown |
| 08P01 | protocol_violation |
| Class 09 — Triggered Action Exception | |
| 09000 | triggered_action_exception |
| Class 0A — Feature Not Supported | |
| 0A000 | feature_not_supported |
| Class 0B — Invalid Transaction Initiation | |
| 0B000 | invalid_transaction_initiation |
| Class 0F — Locator Exception | |
| 0F000 | locator_exception |
| 0F001 | invalid_locator_specification |
| Class 0L — Invalid Grantor | |
| 0L000 | invalid_grantor |
| 0LP01 | invalid_grant_operation |
| Class 0P — Invalid Role Specification | |
| 0P000 | invalid_role_specification |
| Class 0Z — Diagnostics Exception | |
| 0Z000 | diagnostics_exception |
| 0Z002 | stacked_diagnostics_accessed_without_active_handler |
| Class 20 — Case Not Found | |
| 20000 | case_not_found |
| Class 21 — Cardinality Violation | |
| 21000 | cardinality_violation |
| Class 22 — Data Exception | |
| 22000 | data_exception |
| 2202E | array_subscript_error |
| 22021 | character_not_in_repertoire |
| 22008 | datetime_field_overflow |
| 22012 | division_by_zero |
| 22005 | error_in_assignment |
| 2200B | escape_character_conflict |
| 22022 | indicator_overflow |
| 22015 | interval_field_overflow |
| 2201E | invalid_argument_for_logarithm |
| 22014 | invalid_argument_for_ntile_function |
| 22016 | invalid_argument_for_nth_value_function |
| 2201F | invalid_argument_for_power_function |
| 2201G | invalid_argument_for_width_bucket_function |
| 22018 | invalid_character_value_for_cast |
| 22007 | invalid_datetime_format |
| 22019 | invalid_escape_character |
| 2200D | invalid_escape_octet |
| 22025 | invalid_escape_sequence |
| 22P06 | nonstandard_use_of_escape_character |
| 22010 | invalid_indicator_parameter_value |
| 22023 | invalid_parameter_value |
| 22013 | invalid_preceding_or_following_size |
| 2201B | invalid_regular_expression |
| 2201W | invalid_row_count_in_limit_clause |
| 2201X | invalid_row_count_in_result_offset_clause |
| 2202H | invalid_tablesample_argument |
| 2202G | invalid_tablesample_repeat |
| 22009 | invalid_time_zone_displacement_value |
| 2200C | invalid_use_of_escape_character |
| 2200G | most_specific_type_mismatch |
| 22004 | null_value_not_allowed |
| 22002 | null_value_no_indicator_parameter |
| 22003 | numeric_value_out_of_range |
| 2200H | sequence_generator_limit_exceeded |
| 22026 | string_data_length_mismatch |
| 22001 | string_data_right_truncation |
| 22011 | substring_error |
| 22027 | trim_error |
| 22024 | unterminated_c_string |
| 2200F | zero_length_character_string |
| 22P01 | floating_point_exception |
| 22P02 | invalid_text_representation |
| 22P03 | invalid_binary_representation |
| 22P04 | bad_copy_file_format |
| 22P05 | untranslatable_character |
| 2200L | not_an_xml_document |
| 2200M | invalid_xml_document |
| 2200N | invalid_xml_content |
| 2200S | invalid_xml_comment |
| 2200T | invalid_xml_processing_instruction |
| 22030 | duplicate_json_object_key_value |
| 22031 | invalid_argument_for_sql_json_datetime_function |
| 22032 | invalid_json_text |
| 22033 | invalid_sql_json_subscript |
| 22034 | more_than_one_sql_json_item |
| 22035 | no_sql_json_item |
| 22036 | non_numeric_sql_json_item |
| 22037 | non_unique_keys_in_a_json_object |
| 22038 | singleton_sql_json_item_required |
| 22039 | sql_json_array_not_found |
| 2203A | sql_json_member_not_found |
| 2203B | sql_json_number_not_found |
| 2203C | sql_json_object_not_found |
| 2203D | too_many_json_array_elements |
| 2203E | too_many_json_object_members |
| 2203F | sql_json_scalar_required |
| 2203G | sql_json_item_cannot_be_cast_to_target_type |
| Class 23 — Integrity Constraint Violation | |
| 23000 | integrity_constraint_violation |
| 23001 | restrict_violation |
| 23502 | not_null_violation |
| 23503 | foreign_key_violation |
| 23505 | unique_violation |
| 23514 | check_violation |
| 23P01 | exclusion_violation |
| Class 24 — Invalid Cursor State | |
| 24000 | invalid_cursor_state |
| Class 25 — Invalid Transaction State | |
| 25000 | invalid_transaction_state |
| 25001 | active_sql_transaction |
| 25002 | branch_transaction_already_active |
| 25008 | held_cursor_requires_same_isolation_level |
| 25003 | inappropriate_access_mode_for_branch_transaction |
| 25004 | inappropriate_isolation_level_for_branch_transaction |
| 25005 | no_active_sql_transaction_for_branch_transaction |
| 25006 | read_only_sql_transaction |
| 25007 | schema_and_data_statement_mixing_not_supported |
| 25P01 | no_active_sql_transaction |
| 25P02 | in_failed_sql_transaction |
| 25P03 | idle_in_transaction_session_timeout |
| Class 26 — Invalid SQL Statement Name | |
| 26000 | invalid_sql_statement_name |
| Class 27 — Triggered Data Change Violation | |
| 27000 | triggered_data_change_violation |
| Class 28 — Invalid Authorization Specification | |
| 28000 | invalid_authorization_specification |
| 28P01 | invalid_password |
| Class 2B — Dependent Privilege Descriptors Still Exist | |
| 2B000 | dependent_privilege_descriptors_still_exist |
| 2BP01 | dependent_objects_still_exist |
| Class 2D — Invalid Transaction Termination | |
| 2D000 | invalid_transaction_termination |
| Class 2F — SQL Routine Exception | |
| 2F000 | sql_routine_exception |
| 2F005 | function_executed_no_return_statement |
| 2F002 | modifying_sql_data_not_permitted |
| 2F003 | prohibited_sql_statement_attempted |
| 2F004 | reading_sql_data_not_permitted |
| Class 34 — Invalid Cursor Name | |
| 34000 | invalid_cursor_name |
| Class 38 — External Routine Exception | |
| 38000 | external_routine_exception |
| 38001 | containing_sql_not_permitted |
| 38002 | modifying_sql_data_not_permitted |
| 38003 | prohibited_sql_statement_attempted |
| 38004 | reading_sql_data_not_permitted |
| Class 39 — External Routine Invocation Exception | |
| 39000 | external_routine_invocation_exception |
| 39001 | invalid_sqlstate_returned |
| 39004 | null_value_not_allowed |
| 39P01 | trigger_protocol_violated |
| 39P02 | srf_protocol_violated |
| 39P03 | event_trigger_protocol_violated |
| Class 3B — Savepoint Exception | |
| 3B000 | savepoint_exception |
| 3B001 | invalid_savepoint_specification |
| Class 3D — Invalid Catalog Name | |
| 3D000 | invalid_catalog_name |
| Class 3F — Invalid Schema Name | |
| 3F000 | invalid_schema_name |
| Class 40 — Transaction Rollback | |
| 40000 | transaction_rollback |
| 40002 | transaction_integrity_constraint_violation |
| 40001 | serialization_failure |
| 40003 | statement_completion_unknown |
| 40P01 | deadlock_detected |
| Class 42 — Syntax Error or Access Rule Violation | |
| 42000 | syntax_error_or_access_rule_violation |
| 42601 | syntax_error |
| 42501 | insufficient_privilege |
| 42846 | cannot_coerce |
| 42803 | grouping_error |
| 42P20 | windowing_error |
| 42P19 | invalid_recursion |
| 42830 | invalid_foreign_key |
| 42602 | invalid_name |
| 42622 | name_too_long |
| 42939 | reserved_name |
| 42804 | datatype_mismatch |
| 42P18 | indeterminate_datatype |
| 42P21 | collation_mismatch |
| 42P22 | indeterminate_collation |
| 42809 | wrong_object_type |
| 428C9 | generated_always |
| 42703 | undefined_column |
| 42883 | undefined_function |
| 42P01 | undefined_table |
| 42P02 | undefined_parameter |
| 42704 | undefined_object |
| 42701 | duplicate_column |
| 42P03 | duplicate_cursor |
| 42P04 | duplicate_database |
| 42723 | duplicate_function |
| 42P05 | duplicate_prepared_statement |
| 42P06 | duplicate_schema |
| 42P07 | duplicate_table |
| 42712 | duplicate_alias |
| 42710 | duplicate_object |
| 42702 | ambiguous_column |
| 42725 | ambiguous_function |
| 42P08 | ambiguous_parameter |
| 42P09 | ambiguous_alias |
| 42P10 | invalid_column_reference |
| 42611 | invalid_column_definition |
| 42P11 | invalid_cursor_definition |
| 42P12 | invalid_database_definition |
| 42P13 | invalid_function_definition |
| 42P14 | invalid_prepared_statement_definition |
| 42P15 | invalid_schema_definition |
| 42P16 | invalid_table_definition |
| 42P17 | invalid_object_definition |
| Class 44 — WITH CHECK OPTION Violation | |
| 44000 | with_check_option_violation |
| Class 53 — Insufficient Resources | |
| 53000 | insufficient_resources |
| 53100 | disk_full |
| 53200 | out_of_memory |
| 53300 | too_many_connections |
| 53400 | configuration_limit_exceeded |
| Class 54 — Program Limit Exceeded | |
| 54000 | program_limit_exceeded |
| 54001 | statement_too_complex |
| 54011 | too_many_columns |
| 54023 | too_many_arguments |
| Class 55 — Object Not In Prerequisite State | |
| 55000 | object_not_in_prerequisite_state |
| 55006 | object_in_use |
| 55P02 | cant_change_runtime_param |
| 55P03 | lock_not_available |
| 55P04 | unsafe_new_enum_value_usage |
| Class 57 — Operator Intervention | |
| 57000 | operator_intervention |
| 57014 | query_canceled |
| 57P01 | admin_shutdown |
| 57P02 | crash_shutdown |
| 57P03 | cannot_connect_now |
| 57P04 | database_dropped |
| 57P05 | idle_session_timeout |
| Class 58 — System Error (errors external to PostgreSQL itself) | |
| 58000 | system_error |
| 58030 | io_error |
| 58P01 | undefined_file |
| 58P02 | duplicate_file |
| Class 72 — Snapshot Failure | |
| 72000 | snapshot_too_old |
| Class F0 — Configuration File Error | |
| F0000 | config_file_error |
| F0001 | lock_file_exists |
| Class HV — Foreign Data Wrapper Error (SQL/MED) | |
| HV000 | fdw_error |
| HV005 | fdw_column_name_not_found |
| HV002 | fdw_dynamic_parameter_value_needed |
| HV010 | fdw_function_sequence_error |
| HV021 | fdw_inconsistent_descriptor_information |
| HV024 | fdw_invalid_attribute_value |
| HV007 | fdw_invalid_column_name |
| HV008 | fdw_invalid_column_number |
| HV004 | fdw_invalid_data_type |
| HV006 | fdw_invalid_data_type_descriptors |
| HV091 | fdw_invalid_descriptor_field_identifier |
| HV00B | fdw_invalid_handle |
| HV00C | fdw_invalid_option_index |
| HV00D | fdw_invalid_option_name |
| HV090 | fdw_invalid_string_length_or_buffer_length |
| HV00A | fdw_invalid_string_format |
| HV009 | fdw_invalid_use_of_null_pointer |
| HV014 | fdw_too_many_handles |
| HV001 | fdw_out_of_memory |
| HV00P | fdw_no_schemas |
| HV00J | fdw_option_name_not_found |
| HV00K | fdw_reply_handle |
| HV00Q | fdw_schema_not_found |
| HV00R | fdw_table_not_found |
| HV00L | fdw_unable_to_create_execution |
| HV00M | fdw_unable_to_create_reply |
| HV00N | fdw_unable_to_establish_connection |
| Class P0 — PL/pgSQL Error | |
| P0000 | plpgsql_error |
| P0001 | raise_exception |
| P0002 | no_data_found |
| P0003 | too_many_rows |
| P0004 | assert_failure |
| Class XX — Internal Error | |
| XX000 | internal_error |
| XX001 | data_corrupted |
| XX002 | index_corrupted |
| Prev | Up | Next |
| Part VIII. Appendixes | Home | Appendix B. Date/Time Support |
Submit correction
If you see anything in the documentation that is not correct, does not match your experience with the particular feature or requires further clarification, please use this form to report a documentation issue.
Источник

