Syntax errors are quite common while coding.
But, things go for a toss when it results in website errors.
PostgreSQL error 42601 also occurs due to syntax errors in the database queries.
At Bobcares, we often get requests from PostgreSQL users to fix errors as part of our Server Management Services.
Today, let’s check PostgreSQL error in detail and see how our Support Engineers fix it for the customers.
What causes error 42601 in PostgreSQL?
PostgreSQL is an advanced database engine. It is popular for its extensive features and ability to handle complex database situations.
Applications like Instagram, Facebook, Apple, etc rely on the PostgreSQL database.
But what causes error 42601?
PostgreSQL error codes consist of five characters. The first two characters denote the class of errors. And the remaining three characters indicate a specific condition within that class.
Here, 42 in 42601 represent the class “Syntax Error or Access Rule Violation“.
In short, this error mainly occurs due to the syntax errors in the queries executed. A typical error shows up as:

Here, the syntax error has occurred in position 119 near the value “parents” in the query.
How we fix the error?
Now let’s see how our PostgreSQL engineers resolve this error efficiently.
Recently, one of our customers contacted us with this error. He tried to execute the following code,
CREATE OR REPLACE FUNCTION prc_tst_bulk(sql text)
RETURNS TABLE (name text, rowcount integer) AS
$$
BEGIN
WITH m_ty_person AS (return query execute sql)
select name, count(*) from m_ty_person where name like '%a%' group by name
union
select name, count(*) from m_ty_person where gender = 1 group by name;
END
$$ LANGUAGE plpgsql;But, this ended up in PostgreSQL error 42601. And he got the following error message,
ERROR: syntax error at or near "return"
LINE 5: WITH m_ty_person AS (return query execute sql)Our PostgreSQL Engineers checked the issue and found out the syntax error. The statement in Line 5 was a mix of plain and dynamic SQL. In general, the PostgreSQL query should be either fully dynamic or plain. Therefore, we changed the code as,
RETURN QUERY EXECUTE '
WITH m_ty_person AS (' || sql || $x$)
SELECT name, count(*)::int FROM m_ty_person WHERE name LIKE '%a%' GROUP BY name
UNION
SELECT name, count(*)::int FROM m_ty_person WHERE gender = 1 GROUP BY name$x$;This resolved the error 42601, and the code worked fine.
[Need more assistance to solve PostgreSQL error 42601?- We’ll help you.]
Conclusion
In short, PostgreSQL error 42601 occurs due to the syntax errors in the code. Today, in this write-up, we have discussed how our Support Engineers fixed this error for our customers.
PREVENT YOUR SERVER FROM CRASHING!
Never again lose customers to poor server speed! Let us help you.
Our server experts will monitor & maintain your server 24/7 so that it remains lightning fast and secure.
GET STARTED
var google_conversion_label = «owonCMyG5nEQ0aD71QM»;
Syntax errors are quite common while coding.
But, things go for a toss when it results in website errors.
PostgreSQL error 42601 also occurs due to syntax errors in the database queries.
At Bobcares, we often get requests from PostgreSQL users to fix errors as part of our Server Management Services.
Today, let’s check PostgreSQL error in detail and see how our Support Engineers fix it for the customers.
What causes error 42601 in PostgreSQL?
PostgreSQL is an advanced database engine. It is popular for its extensive features and ability to handle complex database situations.
Applications like Instagram, Facebook, Apple, etc rely on the PostgreSQL database.
But what causes error 42601?
PostgreSQL error codes consist of five characters. The first two characters denote the class of errors. And the remaining three characters indicate a specific condition within that class.
Here, 42 in 42601 represent the class “Syntax Error or Access Rule Violation“.
In short, this error mainly occurs due to the syntax errors in the queries executed. A typical error shows up as:
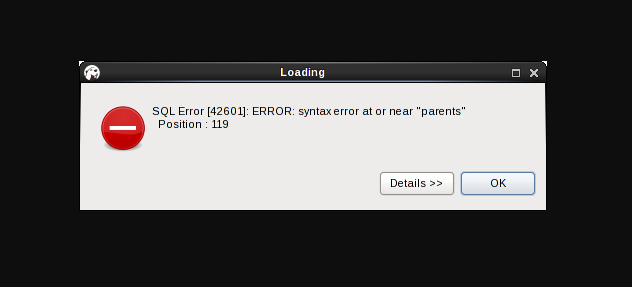
Here, the syntax error has occurred in position 119 near the value “parents” in the query.
How we fix the error?
Now let’s see how our PostgreSQL engineers resolve this error efficiently.
Recently, one of our customers contacted us with this error. He tried to execute the following code,
CREATE OR REPLACE FUNCTION prc_tst_bulk(sql text)
RETURNS TABLE (name text, rowcount integer) AS
$$
BEGIN
WITH m_ty_person AS (return query execute sql)
select name, count(*) from m_ty_person where name like '%a%' group by name
union
select name, count(*) from m_ty_person where gender = 1 group by name;
END
$$ LANGUAGE plpgsql;But, this ended up in PostgreSQL error 42601. And he got the following error message,
ERROR: syntax error at or near "return"
LINE 5: WITH m_ty_person AS (return query execute sql)Our PostgreSQL Engineers checked the issue and found out the syntax error. The statement in Line 5 was a mix of plain and dynamic SQL. In general, the PostgreSQL query should be either fully dynamic or plain. Therefore, we changed the code as,
RETURN QUERY EXECUTE '
WITH m_ty_person AS (' || sql || $x$)
SELECT name, count(*)::int FROM m_ty_person WHERE name LIKE '%a%' GROUP BY name
UNION
SELECT name, count(*)::int FROM m_ty_person WHERE gender = 1 GROUP BY name$x$;This resolved the error 42601, and the code worked fine.
[Need more assistance to solve PostgreSQL error 42601?- We’ll help you.]
Conclusion
In short, PostgreSQL error 42601 occurs due to the syntax errors in the code. Today, in this write-up, we have discussed how our Support Engineers fixed this error for our customers.
PREVENT YOUR SERVER FROM CRASHING!
Never again lose customers to poor server speed! Let us help you.
Our server experts will monitor & maintain your server 24/7 so that it remains lightning fast and secure.
GET STARTED
var google_conversion_label = «owonCMyG5nEQ0aD71QM»;
I’m trying to add a column named order to my table. I realize that order is a reserved word in SQL. So, how do I do it?
My command:
alter table mytable add column order integer;
I’ve also tried:
alter table mytable add column 'order' integer;
PostgreSQL 9.1.
![]()
asked Apr 15, 2014 at 19:08
3
Use this:
alter table mytable add column "order" integer;
But, you might want to consider using a non-reserved name instead, like sort_order or something similar that reflects what the column is used for (and isn’t a reserved word).
answered Apr 15, 2014 at 19:12
![]()
jpwjpw
44k6 gold badges67 silver badges85 bronze badges
3
I think you don’t need «column». Plus «order» is a keyword in SQL, so you should use a different name for your column. Follow this syntax:
ALTER TABLE table_name ADD column_name datatype
Source: W3Schools
answered Apr 15, 2014 at 19:14
![]()
DerStrom8DerStrom8
1,3212 gold badges23 silver badges45 bronze badges
ALTER TABLE table_name
ADD COLUMN "order" integer
answered Apr 15, 2014 at 19:13
0
You are using order which is a reserved keyword you should consider renaming that to something like orders. And the problem should go away.
answered Sep 10, 2021 at 7:06
![]()
- Печать
Страницы: [1] Вниз
Тема: Postgres (db error) (Прочитано 18485 раз)
0 Пользователей и 1 Гость просматривают эту тему.
ПРивет!
Решил вот попробовать вашу софтину! Но никак не получается ее завести
Установил POstgresql сервер и ОДБЦ драйвер!
Создал базу данных!
Настроил в подключении парамеры — нажал Тест! Получил Ответ ОК!
Далее залил в базу дамп
Пробую войти и получаю ошибку
BKO.NET 1.7.5.1
Версия базы данных не является эталонной
Вносим изменения в базу …
Жму ОК
Внесение изменений закончилось неудачей, воспользуйтесь конвертором или скриптами
ОК — и программазакрывается!
ЧТо делать ?
Спасибо

Записан
select access from configure
дальше будем смотреть…

Записан

«1.7.3.5»
Я пробовал поменять на 1.7.5.1 — но результат тот же
« Последнее редактирование: 28 Февраль 2014, 10:38:35 от Digitec »

Записан
ALTER TABLE Remont ADD COLUMN GARANT Date;
ALTER TABLE kompy ADD COLUMN MB_NAME varchar(255) Mb;
UPDATE TABLE kompy SET MB_NAME=Mb;
ALTER TABLE kompy DROP COLUMN Mb, nomerPC, TEXT_RED, EXCELL_RED, ACCESS_RED, VG, IG;
ALTER TABLE kompy ADD COLUMN data_sp Date,ADD COLUMN data_nb Date;
Update CONFIGURE SET access='1.7.3.9' WHERE access<>'1.7.3.9';

Записан

ОШИБКА: ошибка синтаксиса (примерное положение: «Mb»)
LINE 2: ALTER TABLE kompy ADD COLUMN MB_NAME varchar(255) Mb;
^
********** Ошибка **********
ОШИБКА: ошибка синтаксиса (примерное положение: «Mb»)
SQL-состояние: 42601
Символ: 94
И кстати при внесении дампа в постгрес имеем две ошибки
ОШИБКА: ошибка синтаксиса (примерное положение: «EXTENSION»)
СТРОКА 1: CREATE EXTENSION IF NOT EXISTS plpgsql WITH SCHEMA pg_catalo…
^
ОШИБКА: ошибка синтаксиса (примерное положение: «EXTENSION»)
СТРОКА 1: COMMENT ON EXTENSION plpgsql IS ‘PL/pgSQL procedural languag…
^
« Последнее редактирование: 28 Февраль 2014, 11:02:03 от Digitec »

Записан
ALTER TABLE kompy ADD COLUMN MB_NAME varchar(255);

Записан

пробуем так
ALTER TABLE Remont ADD COLUMN GARANT Date;
ALTER TABLE kompy ADD COLUMN MB_NAME varchar(255);
UPDATE kompy SET MB_NAME=Mb;
ALTER TABLE kompy DROP COLUMN Mb, nomerPC, TEXT_RED, EXCELL_RED, ACCESS_RED, VG, IG;
ALTER TABLE kompy ADD COLUMN data_sp Date,ADD COLUMN data_nb Date;
Update CONFIGURE SET access=’1.7.3.9′ WHERE access<>’1.7.3.9′;
Получаем
ОШИБКА: ошибка синтаксиса (примерное положение: «nomerPC»)
LINE 4: ALTER TABLE kompy DROP COLUMN Mb, nomerPC, TEXT_RED, EXCELL_…
^
********** Ошибка **********

Записан
Так
Немного поиграв в кашпировского
выполняем такой запрос
ALTER TABLE Remont ADD COLUMN GARANT Date;
ALTER TABLE kompy ADD COLUMN MB_NAME varchar(255);
UPDATE kompy SET MB_NAME=Mb;
ALTER TABLE kompy DROP COLUMN Mb;
ALTER TABLE kompy DROP COLUMN nomerPC;
ALTER TABLE kompy DROP COLUMN TEXT_RED;
ALTER TABLE kompy DROP COLUMN EXCELL_RED;
ALTER TABLE kompy DROP COLUMN ACCESS_RED;
ALTER TABLE kompy DROP COLUMN VG;
ALTER TABLE kompy DROP COLUMN IG;
ALTER TABLE kompy ADD COLUMN data_sp Date,ADD COLUMN data_nb Date;
Update CONFIGURE SET access='1.7.3.9' WHERE access<>'1.7.3.9';
После чего пробуем войти и получаем уже совершенно другую ошибку (на дату ругается)
«Неверный синтаксис для типа date: «»09:33:10»

Записан
так получается что за место даты время…

Записан

Так как бы я это и сам вижу — вопрос в том — что и где поправить и почему оно так?
щас паралельно попробую базу под фрей развернуть

Записан
ну тут вопрос сложный, я дома пробовал все работало… сейчас проверить не могу…

Записан

ка кто можно определить какая это талица вбазе ругается? Я бы попробовал поиграть с параметрами?

Записан
думаю что это таблица kompy

Записан

Итак
есть успехи!
Взял версию 1.7.5.0
И наконецто запустиллось!
Но при входе уже пишет ошибку
колонка name_prog не существует
мои действия?

Записан
В итоге !
Скачал 1.7.3.3 — все завелось!
Мистика!
Вобщем приступаю к изучению — что правда мысль о возможно обновлении версии в будущем немного пугает

Записан
создать колонку name_prog в таблице configure

Записан

- Печать
Страницы: [1] Вверх
Пытаюсь создать табличку, вот такую
CREATE TABLE screens_items ( screenitemid bigint NOT NULL, screenid bigint NOT NULL, resourcetype integer DEFAULT '0' NOT NULL, resourceid bigint DEFAULT '0' NOT NULL, width integer DEFAULT '320' NOT NULL, height integer DEFAULT '200' NOT NULL, x integer DEFAULT '0' NOT NULL, y integer DEFAULT '0' NOT NULL, colspan integer DEFAULT '0' NOT NULL, rowspan integer DEFAULT '0' NOT NULL, elements integer DEFAULT '25' NOT NULL, valign integer DEFAULT '0' NOT NULL, halign integer DEFAULT '0' NOT NULL, style integer DEFAULT '0' NOT NULL, url varchar(255) DEFAULT '' NOT NULL, dynamic integer DEFAULT '0' NOT NULL, sort_triggers integer DEFAULT '0' NOT NULL, application varchar(255) DEFAULT '' NOT NULL, PRIMARY KEY (screenitemid) );
Получаю
Error: ОШИБКА: ошибка синтаксиса (примерное положение: "application")
psql --version psql (PostgreSQL) 9.4.9
Вроде слово «application» не зарезервировано?
Удаление колонок таблицы атрибутов для нескольких слоёв
-
HasT
- Активный участник
- Сообщения: 142
- Зарегистрирован: 16 окт 2009, 22:08
- Проекты: 1
- Репутация: 55
- Откуда: Харьков
Удаление колонок таблицы атрибутов для нескольких слоёв
Приветствую! Есть шейп-слой со следующей структурой таблицы атрибутов:
- layer.jpg (59.68 КБ) 12457 просмотров
— название объекта, уникальный номер для каждого объекта слоя
Необходимо разбить шейп-слой по «названию объекта», но в результирующих слоях в таблице атрибутов должна остаться только колонка с «порядковым номером»:
- result.jpg (50.97 КБ) 12457 просмотров
Разбитие слоя по «названию объекта» сделал в QGIS (Вектор — Управление данными — Разбить векторный слой), удаление «лишнего текста» в названии файлов удалил через коммандер. Как удалить в наборе шейп-слоев из таблицы атрибутов определённую колонку (перебор каждого слоя не предлагать, очень много их…)? Софт: ArcGIS, QGIS, PostGIS, OGR… Спасибо!
-
Petruxin
- Гуру
- Сообщения: 1695
- Зарегистрирован: 14 июн 2011, 16:47
- Статьи: 2
- Проекты: 2
- Репутация: 132
- Ваше звание: Завсегдатай
- Откуда: Череповец
Re: Удаление колонок таблицы атрибутов для нескольких слоёв
Сообщение
Petruxin » 14 дек 2012, 05:51
Доп модуль Table Manager пробовали?
-

rhot
- Гуру
- Сообщения: 1727
- Зарегистрирован: 25 янв 2011, 17:50
- Статьи: 1
- Репутация: 194
- Ваше звание: доктор
- Откуда: Архангельск
Re: Удаление колонок таблицы атрибутов для нескольких слоёв
Сообщение
rhot » 14 дек 2012, 07:28
В PostGIS:
Код: Выделить всё
CREATE TABLE new AS
SELECT number, ST_Multi(ST_Collect(the_geom))
FROM
(SELECT name, number, (ST_Dump(geom)).geom AS the_geom
FROM region) AS r
GROUP BY name;
SELECT Populate_Geometry_Columns('new'::regclass);
Вместо ST_Collect можно использовать ST_Union, если хотите, чтобы удалились общие границы между полигонами с одинаковым полем NAME.
___________(¯`·.¸(¯`·.¸ Scientia potentia est _/ {SILVA}:::{FOSS}:::{GIS} _ Знание сила ¸.·´¯)¸.·´¯)___________
-
HasT
- Активный участник
- Сообщения: 142
- Зарегистрирован: 16 окт 2009, 22:08
- Проекты: 1
- Репутация: 55
- Откуда: Харьков
Re: Удаление колонок таблицы атрибутов для нескольких слоёв
Сообщение
HasT » 14 дек 2012, 10:56
Petruxin писал(а):Доп модуль Table Manager пробовали?
Table Manager не подходит. С ним нужно каждый слой (слоёв будет не менее 700) просматривать и удалять ненужное поле.
-
HasT
- Активный участник
- Сообщения: 142
- Зарегистрирован: 16 окт 2009, 22:08
- Проекты: 1
- Репутация: 55
- Откуда: Харьков
Re: Удаление колонок таблицы атрибутов для нескольких слоёв
Сообщение
HasT » 14 дек 2012, 11:05
rhot писал(а):В PostGIS:
Код: Выделить всё
CREATE TABLE new AS SELECT number, ST_Multi(ST_Collect(the_geom)) FROM (SELECT name, number, (ST_Dump(geom)).geom AS the_geom FROM region) AS r GROUP BY name; SELECT Populate_Geometry_Columns('new'::regclass);Вместо ST_Collect можно использовать ST_Union, если хотите, чтобы удалились общие границы между полигонами с одинаковым полем NAME.
Запустил данный запрос в pgAdmin, но в строке
получил ошибку «колонка «geom» не существует», — заменил «geom» на «the_geom». Далее в строке
получаю ошибку «колонка «r.number» должна фигурировать в предложении GROUP BY или использоваться в агрегатной функции». Как быть дальше?
-

rhot
- Гуру
- Сообщения: 1727
- Зарегистрирован: 25 янв 2011, 17:50
- Статьи: 1
- Репутация: 194
- Ваше звание: доктор
- Откуда: Архангельск
Re: Удаление колонок таблицы атрибутов для нескольких слоёв
Сообщение
rhot » 14 дек 2012, 11:15
HasT писал(а):Как быть дальше?
Я вас, наверное, не правильно понял. Вы хотите из одного слоя получить несколько, разбитых по полю NAME?
___________(¯`·.¸(¯`·.¸ Scientia potentia est _/ {SILVA}:::{FOSS}:::{GIS} _ Знание сила ¸.·´¯)¸.·´¯)___________
-
HasT
- Активный участник
- Сообщения: 142
- Зарегистрирован: 16 окт 2009, 22:08
- Проекты: 1
- Репутация: 55
- Откуда: Харьков
Re: Удаление колонок таблицы атрибутов для нескольких слоёв
Сообщение
HasT » 14 дек 2012, 11:18
rhot писал(а):
HasT писал(а):Как быть дальше?
Я вас, наверное, не правильно понял. Вы хотите из одного слоя получить несколько, разбитых по полю NAME?
Да. Нужно из одного слоя сделать несколько, разбитых по полю Name, при этом в новых слоях не должно остаться поля Name.
-
HasT
- Активный участник
- Сообщения: 142
- Зарегистрирован: 16 окт 2009, 22:08
- Проекты: 1
- Репутация: 55
- Откуда: Харьков
Re: Удаление колонок таблицы атрибутов для нескольких слоёв
Сообщение
HasT » 14 дек 2012, 11:33
В базу данных PostGIS залил все разбитые слои по полю Name. Может как-то используя запрос
Код: Выделить всё
ALTER TABLE [u]"все таблицы"[/u] DROP COLUMN "NAME";можно удалить ненужное поле? только как задать все таблицы в базе для этого запроса?…
-

rhot
- Гуру
- Сообщения: 1727
- Зарегистрирован: 25 янв 2011, 17:50
- Статьи: 1
- Репутация: 194
- Ваше звание: доктор
- Откуда: Архангельск
Re: Удаление колонок таблицы атрибутов для нескольких слоёв
Сообщение
rhot » 14 дек 2012, 11:35
Тогда у меня ещё вопрос: а зачем это надо? Ведь можно при добавлении слоя сделать выборку по атрибутам, а само поле name скрыть через меню «свойства слоя».
___________(¯`·.¸(¯`·.¸ Scientia potentia est _/ {SILVA}:::{FOSS}:::{GIS} _ Знание сила ¸.·´¯)¸.·´¯)___________
-

rhot
- Гуру
- Сообщения: 1727
- Зарегистрирован: 25 янв 2011, 17:50
- Статьи: 1
- Репутация: 194
- Ваше звание: доктор
- Откуда: Архангельск
Re: Удаление колонок таблицы атрибутов для нескольких слоёв
Сообщение
rhot » 14 дек 2012, 11:43
HasT писал(а):В базу данных PostGIS залил все разбитые слои по полю Name. Может как-то используя запрос
Код: Выделить всё
ALTER TABLE [u]"все таблицы"[/u] DROP COLUMN "NAME";можно удалить ненужное поле? только как задать все таблицы в базе для этого запроса?…
Вам следует создать функцию, а потом вызвать её.
Код: Выделить всё
CREATE OR REPLACE FUNCTION test()
RETURNS VOID
AS $$
DECLARE
my_row RECORD;
BEGIN
FOR my_row IN
SELECT table_name
FROM information_schema.tables
WHERE table_schema = 'information_schema'
LOOP
ALTER TABLE my_row.table_name DROP COLUMN "NAME";
END LOOP;
END;
$$ LANGUAGE plpgsql;
SELECT test();___________(¯`·.¸(¯`·.¸ Scientia potentia est _/ {SILVA}:::{FOSS}:::{GIS} _ Знание сила ¸.·´¯)¸.·´¯)___________
-
HasT
- Активный участник
- Сообщения: 142
- Зарегистрирован: 16 окт 2009, 22:08
- Проекты: 1
- Репутация: 55
- Откуда: Харьков
Re: Удаление колонок таблицы атрибутов для нескольких слоёв
Сообщение
HasT » 14 дек 2012, 11:52
rhot писал(а):Тогда у меня ещё вопрос: а зачем это надо? Ведь можно при добавлении слоя сделать выборку по атрибутам, а само поле name скрыть через меню «свойства слоя».
слой создается в БД несколькими пользователями, затем будет производится дальнейшая его «обработка» несколькими операторами в проприетарном ПО, которое загружает слои только с определенной таблицей атрибутов
-
HasT
- Активный участник
- Сообщения: 142
- Зарегистрирован: 16 окт 2009, 22:08
- Проекты: 1
- Репутация: 55
- Откуда: Харьков
Re: Удаление колонок таблицы атрибутов для нескольких слоёв
Сообщение
HasT » 14 дек 2012, 12:40
rhot писал(а):Вам следует создать функцию, а потом вызвать её.
Код: Выделить всё
CREATE OR REPLACE FUNCTION test() RETURNS VOID AS $$ DECLARE my_row RECORD; BEGIN FOR my_row IN SELECT table_name FROM information_schema.tables WHERE table_schema = 'information_schema' LOOP ALTER TABLE my_row.table_name DROP COLUMN "NAME"; END LOOP; END; $$ LANGUAGE plpgsql; SELECT test();
Сделал функцию test(), только из-за ошибки «схема «my_row» не существует» поменял «my_row» на «public». При запуске запроса
получаю ошибку «отношение «public.table_name» не существует». Что я делаю неправильно?
-

rhot
- Гуру
- Сообщения: 1727
- Зарегистрирован: 25 янв 2011, 17:50
- Статьи: 1
- Репутация: 194
- Ваше звание: доктор
- Откуда: Архангельск
Re: Удаление колонок таблицы атрибутов для нескольких слоёв
Сообщение
rhot » 14 дек 2012, 13:04
Код: Выделить всё
CREATE OR REPLACE FUNCTION test()
RETURNS VOID
AS $$
DECLARE
my_row RECORD;
BEGIN
FOR my_row IN
SELECT table_name
FROM information_schema.tables
WHERE table_schema = 'information_schema'
LOOP
EXECUTE 'ALTER TABLE' || my_row.table_name || 'DROP COLUMN "NAME"';
END LOOP;
END;
$$ LANGUAGE plpgsql;___________(¯`·.¸(¯`·.¸ Scientia potentia est _/ {SILVA}:::{FOSS}:::{GIS} _ Знание сила ¸.·´¯)¸.·´¯)___________
-
HasT
- Активный участник
- Сообщения: 142
- Зарегистрирован: 16 окт 2009, 22:08
- Проекты: 1
- Репутация: 55
- Откуда: Харьков
Re: Удаление колонок таблицы атрибутов для нескольких слоёв
Сообщение
HasT » 14 дек 2012, 13:20
rhot писал(а):
Код: Выделить всё
CREATE OR REPLACE FUNCTION test() RETURNS VOID AS $$ DECLARE my_row RECORD; BEGIN FOR my_row IN SELECT table_name FROM information_schema.tables WHERE table_schema = 'information_schema' LOOP EXECUTE 'ALTER TABLE' || my_row.table_name || 'DROP COLUMN "NAME"'; END LOOP; END; $$ LANGUAGE plpgsql;
Пробую этот запрос… my_row — это же название схемы (у меня схема public)?
Для запроса получаю ошибку
Код: Выделить всё
ОШИБКА: ошибка синтаксиса (примерное положение: "TABLEinformation_schema_catalog_nameDROP")
LINE 1: ALTER TABLEinformation_schema_catalog_nameDROP COLUMN "Polyg...
^
QUERY: ALTER TABLEinformation_schema_catalog_nameDROP COLUMN "PolygonID"
CONTEXT: PL/pgSQL function test() line 10 at оператор EXECUTEИ в базе сейчас загружены слои разбитые по полю Name, правильно?
-

rhot
- Гуру
- Сообщения: 1727
- Зарегистрирован: 25 янв 2011, 17:50
- Статьи: 1
- Репутация: 194
- Ваше звание: доктор
- Откуда: Архангельск
Re: Удаление колонок таблицы атрибутов для нескольких слоёв
Сообщение
rhot » 14 дек 2012, 13:35
my_row здесь — это любая запись из списка ваших таблиц.
А вообще, почитайте это.
___________(¯`·.¸(¯`·.¸ Scientia potentia est _/ {SILVA}:::{FOSS}:::{GIS} _ Знание сила ¸.·´¯)¸.·´¯)___________
|
|
|
|

информация о разделе
 |
Данный раздел предназначается исключительно для обсуждения вопросов использования языка запросов SQL. Обсуждение общих вопросов, связанных с тематикой баз данных — обсуждаем в разделе «Базы данных: общие вопросы». Убедительная просьба — соблюдать «Правила форума» и не пренебрегать «Правильным оформлением своих тем». Прежде, чем создавать тему, имеет смысл заглянуть в раздел «Базы данных: FAQ», возможно там уже есть ответ. |

UPDATE SELECT
, PostgreSQL 9.4
- Подписаться на тему
- Сообщить другу
- Скачать/распечатать тему
|
|
|
|
Senior Member
Рейтинг (т): 13 |
create table t1 (id integer, f1 integer, f2 integer); create table t2 (f1 integer, f2 integer); update t1 set (f1, f2) = (select t2.f1, t2.f2 from t1 right join t2 on t1.id = t2.f1);
[Err] ОШИБКА: ошибка синтаксиса (примерное положение: «SELECT») |
|
grgdvo |
|
|
Member
Рейтинг (т): 21 |
какая версия PG у вас?? Такой синтаксис только начиная с 9.5 |
|
HighMan |
|
|
Senior Member
Рейтинг (т): 13 |
Цитата grgdvo @ 22.03.16, 20:20
Я в топе указал, что PostgreSQL 9.4. |
MIF |
|
|
Попробуй такой запрос:
update t1 set t1.f1= t2.f1, t1.f2 = t2.f2 from t1 right join t2 on t1.id = t2.f1 |
|
grgdvo |
|
|
Member
Рейтинг (т): 21 |
MIF, t1 нельзя указывать и под UPDATE и под FROM. HighMan, попробуйте вот так, вроде эквивалентно
update t1 set (f1, f2) = (t2.f1, t2.f2) from t2 where t1.id = t2.f1; |
|
HighMan |
|
|
Senior Member
Рейтинг (т): 13 |
update t1 set (f1, f2) = (t2.f1, t2.f2) from t2 where t1.id = t2.f1; Такой способ работает, но я не представляю как подобным запросом обрабатывать связи таблиц источников. |
|
grgdvo |
|
|
Member
Рейтинг (т): 21 |
Вы можете делать JOIN практически также как в SELECT. Например
update t1 set (f1, f2) = (t2.f1, t2.f2) from t2, t3 where t1.id = t2.f1 and t2.f2 = t3.id;
update t1 set (f1, f2) = (t2.f1, t2.f2) from t2 left join t3 on t2.f2 = t3.id where t1.id = t2.f1; |
0 пользователей читают эту тему (0 гостей и 0 скрытых пользователей)
0 пользователей:
- Предыдущая тема
- Базы данных: SQL
- Следующая тема
[ Script execution time: 0,0571 ] [ 15 queries used ] [ Generated: 30.01.23, 16:30 GMT ]
Syntax errors are quite common while coding.
But, things go for a toss when it results in website errors.
PostgreSQL error 42601 also occurs due to syntax errors in the database queries.
At Bobcares, we often get requests from PostgreSQL users to fix errors as part of our Server Management Services.
Today, let’s check PostgreSQL error in detail and see how our Support Engineers fix it for the customers.
What causes error 42601 in PostgreSQL?
PostgreSQL is an advanced database engine. It is popular for its extensive features and ability to handle complex database situations.
Applications like Instagram, Facebook, Apple, etc rely on the PostgreSQL database.
But what causes error 42601?
PostgreSQL error codes consist of five characters. The first two characters denote the class of errors. And the remaining three characters indicate a specific condition within that class.
Here, 42 in 42601 represent the class “Syntax Error or Access Rule Violation“.
In short, this error mainly occurs due to the syntax errors in the queries executed. A typical error shows up as:

Here, the syntax error has occurred in position 119 near the value “parents” in the query.
How we fix the error?
Now let’s see how our PostgreSQL engineers resolve this error efficiently.
Recently, one of our customers contacted us with this error. He tried to execute the following code,
CREATE OR REPLACE FUNCTION prc_tst_bulk(sql text)
RETURNS TABLE (name text, rowcount integer) AS
$$
BEGIN
WITH m_ty_person AS (return query execute sql)
select name, count(*) from m_ty_person where name like '%a%' group by name
union
select name, count(*) from m_ty_person where gender = 1 group by name;
END
$$ LANGUAGE plpgsql;But, this ended up in PostgreSQL error 42601. And he got the following error message,
ERROR: syntax error at or near "return"
LINE 5: WITH m_ty_person AS (return query execute sql)Our PostgreSQL Engineers checked the issue and found out the syntax error. The statement in Line 5 was a mix of plain and dynamic SQL. In general, the PostgreSQL query should be either fully dynamic or plain. Therefore, we changed the code as,
RETURN QUERY EXECUTE '
WITH m_ty_person AS (' || sql || $x$)
SELECT name, count(*)::int FROM m_ty_person WHERE name LIKE '%a%' GROUP BY name
UNION
SELECT name, count(*)::int FROM m_ty_person WHERE gender = 1 GROUP BY name$x$;This resolved the error 42601, and the code worked fine.
[Need more assistance to solve PostgreSQL error 42601?- We’ll help you.]
Conclusion
In short, PostgreSQL error 42601 occurs due to the syntax errors in the code. Today, in this write-up, we have discussed how our Support Engineers fixed this error for our customers.
PREVENT YOUR SERVER FROM CRASHING!
Never again lose customers to poor server speed! Let us help you.
Our server experts will monitor & maintain your server 24/7 so that it remains lightning fast and secure.
GET STARTED
var google_conversion_label = «owonCMyG5nEQ0aD71QM»;
Содержание
- PostgreSQL error 42601- How we fix it
- What causes error 42601 in PostgreSQL?
- How we fix the error?
- Conclusion
- PREVENT YOUR SERVER FROM CRASHING!
- 10 Comments
PostgreSQL error 42601- How we fix it
by Sijin George | Sep 12, 2019
Syntax errors are quite common while coding.
But, things go for a toss when it results in website errors.
PostgreSQL error 42601 also occurs due to syntax errors in the database queries.
At Bobcares, we often get requests from PostgreSQL users to fix errors as part of our Server Management Services.
Today, let’s check PostgreSQL error in detail and see how our Support Engineers fix it for the customers.
What causes error 42601 in PostgreSQL?
PostgreSQL is an advanced database engine. It is popular for its extensive features and ability to handle complex database situations.
Applications like Instagram, Facebook, Apple, etc rely on the PostgreSQL database.
But what causes error 42601?
PostgreSQL error codes consist of five characters. The first two characters denote the class of errors. And the remaining three characters indicate a specific condition within that class.
Here, 42 in 42601 represent the class “Syntax Error or Access Rule Violation“.
In short, this error mainly occurs due to the syntax errors in the queries executed. A typical error shows up as:

Here, the syntax error has occurred in position 119 near the value “parents” in the query.
How we fix the error?
Now let’s see how our PostgreSQL engineers resolve this error efficiently.
Recently, one of our customers contacted us with this error. He tried to execute the following code,
But, this ended up in PostgreSQL error 42601. And he got the following error message,
Our PostgreSQL Engineers checked the issue and found out the syntax error. The statement in Line 5 was a mix of plain and dynamic SQL. In general, the PostgreSQL query should be either fully dynamic or plain. Therefore, we changed the code as,
This resolved the error 42601, and the code worked fine.
[Need more assistance to solve PostgreSQL error 42601?- We’ll help you.]
Conclusion
In short, PostgreSQL error 42601 occurs due to the syntax errors in the code. Today, in this write-up, we have discussed how our Support Engineers fixed this error for our customers.
PREVENT YOUR SERVER FROM CRASHING!
Never again lose customers to poor server speed! Let us help you.
Our server experts will monitor & maintain your server 24/7 so that it remains lightning fast and secure.
SELECT * FROM long_term_prediction_anomaly WHERE + “‘Timestamp’” + ‘”BETWEEN ‘” +
2019-12-05 09:10:00+ ‘”AND’” + 2019-12-06 09:10:00 + “‘;”)
Hello Joe,
Do you still get PostgreSQL errors? If you need help, we’ll be happy to talk to you on chat (click on the icon at right-bottom).
У меня ошибка drop table exists “companiya”;
CREATE TABLE “companiya” (
“compania_id” int4 NOT NULL,
“fio vladelca” text NOT NULL,
“name” text NOT NULL,
“id_operator” int4 NOT NULL,
“id_uslugi” int4 NOT NULL,
“id_reklama” int4 NOT NULL,
“id_tex-specialist” int4 NOT NULL,
“id_filial” int4 NOT NULL,
CONSTRAINT “_copy_8” PRIMARY KEY (“compania_id”)
);
CREATE TABLE “filial” (
“id_filial” int4 NOT NULL,
“street” text NOT NULL,
“house” int4 NOT NULL,
“city” text NOT NULL,
CONSTRAINT “_copy_5” PRIMARY KEY (“id_filial”)
);
CREATE TABLE “login” (
“id_name” int4 NOT NULL,
“name” char(20) NOT NULL,
“pass” char(20) NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (“id_name”)
);
CREATE TABLE “operator” (
“id_operator” int4 NOT NULL,
“obrabotka obrasheniya” int4 NOT NULL,
“konsultirovanie” text NOT NULL,
“grafick work” date NOT NULL,
CONSTRAINT “_copy_2” PRIMARY KEY (“id_operator”)
);
CREATE TABLE “polsovateli” (
“id_user” int4 NOT NULL,
“id_companiya” int4 NOT NULL,
“id_obrasheniya” int4 NOT NULL,
“id_oshibka” int4 NOT NULL,
CONSTRAINT “_copy_6” PRIMARY KEY (“id_user”)
);
CREATE TABLE “reklama” (
“id_reklama” int4 NOT NULL,
“tele-marketing” text NOT NULL,
“soc-seti” text NOT NULL,
“mobile” int4 NOT NULL,
CONSTRAINT “_copy_3” PRIMARY KEY (“id_reklama”)
);
CREATE TABLE “tex-specialist” (
“id_tex-specialist” int4 NOT NULL,
“grafik” date NOT NULL,
“zarplata” int4 NOT NULL,
“ispravlenie oshibok” int4 NOT NULL,
CONSTRAINT “_copy_7” PRIMARY KEY (“id_tex-specialist”)
);
CREATE TABLE “uslugi” (
“id_uslugi” int4 NOT NULL,
“vostanavlenia parola” int4 NOT NULL,
“poterya acaunta” int4 NOT NULL,
CONSTRAINT “_copy_4” PRIMARY KEY (“id_uslugi”)
);
ALTER TABLE “companiya” ADD CONSTRAINT “fk_companiya_operator_1” FOREIGN KEY (“id_operator”) REFERENCES “operator” (“id_operator”);
ALTER TABLE “companiya” ADD CONSTRAINT “fk_companiya_uslugi_1” FOREIGN KEY (“id_uslugi”) REFERENCES “uslugi” (“id_uslugi”);
ALTER TABLE “companiya” ADD CONSTRAINT “fk_companiya_filial_1” FOREIGN KEY (“id_filial”) REFERENCES “filial” (“id_filial”);
ALTER TABLE “companiya” ADD CONSTRAINT “fk_companiya_reklama_1” FOREIGN KEY (“id_reklama”) REFERENCES “reklama” (“id_reklama”);
ALTER TABLE “companiya” ADD CONSTRAINT “fk_companiya_tex-specialist_1” FOREIGN KEY (“id_tex-specialist”) REFERENCES “tex-specialist” (“id_tex-specialist”);
ALTER TABLE “polsovateli” ADD CONSTRAINT “fk_polsovateli_companiya_1” FOREIGN KEY (“id_companiya”) REFERENCES “companiya” (“compania_id”);
ERROR: ОШИБКА: ошибка синтаксиса (примерное положение: “”companiya””)
LINE 1: drop table exists “companiya”;
^
Источник
@YohDeadfall — I understand that part about it, but this is not script that I am creating or even code that I am creating. This is all created under the hood by Npsql/EntityFramework. My quick guess is that I am extending my DbContext from IdentityDbContext<IdentityUser> which wants to create all of the tables for roles, users, claims, etc. If I change this to just extend from DbContext, then everything works as advertised.
Below is the script that EF is trying to use created from dotnet ef migrations script — please be aware that I have removed my custom part of the script for brevity.
You can see there are two specific calls that are being made where [NormalizedName] and [NormalizedUserName] are being used.
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS "__EFMigrationsHistory" ( "MigrationId" varchar(150) NOT NULL, "ProductVersion" varchar(32) NOT NULL, CONSTRAINT "PK___EFMigrationsHistory" PRIMARY KEY ("MigrationId") ); CREATE TABLE "AspNetRoles" ( "Id" text NOT NULL, "ConcurrencyStamp" text NULL, "Name" varchar(256) NULL, "NormalizedName" varchar(256) NULL, CONSTRAINT "PK_AspNetRoles" PRIMARY KEY ("Id") ); CREATE TABLE "AspNetUsers" ( "Id" text NOT NULL, "AccessFailedCount" int4 NOT NULL, "ConcurrencyStamp" text NULL, "Email" varchar(256) NULL, "EmailConfirmed" bool NOT NULL, "LockoutEnabled" bool NOT NULL, "LockoutEnd" timestamptz NULL, "NormalizedEmail" varchar(256) NULL, "NormalizedUserName" varchar(256) NULL, "PasswordHash" text NULL, "PhoneNumber" text NULL, "PhoneNumberConfirmed" bool NOT NULL, "SecurityStamp" text NULL, "TwoFactorEnabled" bool NOT NULL, "UserName" varchar(256) NULL, CONSTRAINT "PK_AspNetUsers" PRIMARY KEY ("Id") ); CREATE TABLE "AspNetRoleClaims" ( "Id" int4 NOT NULL, "ClaimType" text NULL, "ClaimValue" text NULL, "RoleId" text NOT NULL, CONSTRAINT "PK_AspNetRoleClaims" PRIMARY KEY ("Id"), CONSTRAINT "FK_AspNetRoleClaims_AspNetRoles_RoleId" FOREIGN KEY ("RoleId") REFERENCES "AspNetRoles" ("Id") ON DELETE CASCADE ); CREATE TABLE "AspNetUserClaims" ( "Id" int4 NOT NULL, "ClaimType" text NULL, "ClaimValue" text NULL, "UserId" text NOT NULL, CONSTRAINT "PK_AspNetUserClaims" PRIMARY KEY ("Id"), CONSTRAINT "FK_AspNetUserClaims_AspNetUsers_UserId" FOREIGN KEY ("UserId") REFERENCES "AspNetUsers" ("Id") ON DELETE CASCADE ); CREATE TABLE "AspNetUserLogins" ( "LoginProvider" text NOT NULL, "ProviderKey" text NOT NULL, "ProviderDisplayName" text NULL, "UserId" text NOT NULL, CONSTRAINT "PK_AspNetUserLogins" PRIMARY KEY ("LoginProvider", "ProviderKey"), CONSTRAINT "FK_AspNetUserLogins_AspNetUsers_UserId" FOREIGN KEY ("UserId") REFERENCES "AspNetUsers" ("Id") ON DELETE CASCADE ); CREATE TABLE "AspNetUserRoles" ( "UserId" text NOT NULL, "RoleId" text NOT NULL, CONSTRAINT "PK_AspNetUserRoles" PRIMARY KEY ("UserId", "RoleId"), CONSTRAINT "FK_AspNetUserRoles_AspNetRoles_RoleId" FOREIGN KEY ("RoleId") REFERENCES "AspNetRoles" ("Id") ON DELETE CASCADE, CONSTRAINT "FK_AspNetUserRoles_AspNetUsers_UserId" FOREIGN KEY ("UserId") REFERENCES "AspNetUsers" ("Id") ON DELETE CASCADE ); CREATE TABLE "AspNetUserTokens" ( "UserId" text NOT NULL, "LoginProvider" text NOT NULL, "Name" text NOT NULL, "Value" text NULL, CONSTRAINT "PK_AspNetUserTokens" PRIMARY KEY ("UserId", "LoginProvider", "Name"), CONSTRAINT "FK_AspNetUserTokens_AspNetUsers_UserId" FOREIGN KEY ("UserId") REFERENCES "AspNetUsers" ("Id") ON DELETE CASCADE ); CREATE INDEX "IX_AspNetRoleClaims_RoleId" ON "AspNetRoleClaims" ("RoleId"); CREATE UNIQUE INDEX "RoleNameIndex" ON "AspNetRoles" ("NormalizedName") WHERE [NormalizedName] IS NOT NULL; CREATE INDEX "IX_AspNetUserClaims_UserId" ON "AspNetUserClaims" ("UserId"); CREATE INDEX "IX_AspNetUserLogins_UserId" ON "AspNetUserLogins" ("UserId"); CREATE INDEX "IX_AspNetUserRoles_RoleId" ON "AspNetUserRoles" ("RoleId"); CREATE INDEX "EmailIndex" ON "AspNetUsers" ("NormalizedEmail"); CREATE UNIQUE INDEX "UserNameIndex" ON "AspNetUsers" ("NormalizedUserName") WHERE [NormalizedUserName] IS NOT NULL; INSERT INTO "__EFMigrationsHistory" ("MigrationId", "ProductVersion") VALUES ('20180514204732_initial', '2.0.3-rtm-10026');
Помогаю со студенческими работами здесь
Динамическая ссылка на таблицу
Здраствуйте.
Необходимо сделать так, чтобы при протягивании диапазона в ячейку подставлялись…
Ссылка на внешнюю таблицу стилей
Мне непонятен синтаксис. Если указываем в атрибуте type что это ссылка на CSS, то зачем указывать…
Ссылка на таблицу стилей в блоках php
Если я делаю блочную систему файлов. То есть присоединяю какой либо блок к главному файлу index…
Ссылка таблицу на фору редактирования mysql
может кто поможет.выдаются страницы из базы mysql. нужно что бы в таблице был 4 столбец, с…
Ссылка из одного столбца на другую таблицу
Всем привет от начинающего изучение PHP и MySQL программешника. И вот такой вопрос. Есть задача -…
Двухкратная ссылка на одну и ту же таблицу, но к разным записям
есть главная таблица и в ней есть поле — исполнитель(isp) в котором записан id пользователя.
и в…
Искать еще темы с ответами
Или воспользуйтесь поиском по форуму:
Syntax errors are quite common while coding.
But, things go for a toss when it results in website errors.
PostgreSQL error 42601 also occurs due to syntax errors in the database queries.
At Bobcares, we often get requests from PostgreSQL users to fix errors as part of our Server Management Services.
Today, let’s check PostgreSQL error in detail and see how our Support Engineers fix it for the customers.
What causes error 42601 in PostgreSQL?
PostgreSQL is an advanced database engine. It is popular for its extensive features and ability to handle complex database situations.
Applications like Instagram, Facebook, Apple, etc rely on the PostgreSQL database.
But what causes error 42601?
PostgreSQL error codes consist of five characters. The first two characters denote the class of errors. And the remaining three characters indicate a specific condition within that class.
Here, 42 in 42601 represent the class “Syntax Error or Access Rule Violation“.
In short, this error mainly occurs due to the syntax errors in the queries executed. A typical error shows up as:

Here, the syntax error has occurred in position 119 near the value “parents” in the query.
How we fix the error?
Now let’s see how our PostgreSQL engineers resolve this error efficiently.
Recently, one of our customers contacted us with this error. He tried to execute the following code,
CREATE OR REPLACE FUNCTION prc_tst_bulk(sql text)
RETURNS TABLE (name text, rowcount integer) AS
$$
BEGIN
WITH m_ty_person AS (return query execute sql)
select name, count(*) from m_ty_person where name like '%a%' group by name
union
select name, count(*) from m_ty_person where gender = 1 group by name;
END
$$ LANGUAGE plpgsql;But, this ended up in PostgreSQL error 42601. And he got the following error message,
ERROR: syntax error at or near "return"
LINE 5: WITH m_ty_person AS (return query execute sql)Our PostgreSQL Engineers checked the issue and found out the syntax error. The statement in Line 5 was a mix of plain and dynamic SQL. In general, the PostgreSQL query should be either fully dynamic or plain. Therefore, we changed the code as,
RETURN QUERY EXECUTE '
WITH m_ty_person AS (' || sql || $x$)
SELECT name, count(*)::int FROM m_ty_person WHERE name LIKE '%a%' GROUP BY name
UNION
SELECT name, count(*)::int FROM m_ty_person WHERE gender = 1 GROUP BY name$x$;This resolved the error 42601, and the code worked fine.
[Need more assistance to solve PostgreSQL error 42601?- We’ll help you.]
Conclusion
In short, PostgreSQL error 42601 occurs due to the syntax errors in the code. Today, in this write-up, we have discussed how our Support Engineers fixed this error for our customers.
PREVENT YOUR SERVER FROM CRASHING!
Never again lose customers to poor server speed! Let us help you.
Our server experts will monitor & maintain your server 24/7 so that it remains lightning fast and secure.
GET STARTED
var google_conversion_label = «owonCMyG5nEQ0aD71QM»;
Содержание
- PostgreSQL error 42601- How we fix it
- What causes error 42601 in PostgreSQL?
- How we fix the error?
- Conclusion
- PREVENT YOUR SERVER FROM CRASHING!
- 10 Comments
- Приложение A. Коды ошибок PostgreSQL
- SQLSTATE=42601 ,SQLCODE=-104 while running HCAT_SYNC_OBJECTS procedure in IBM Db2 BigSQL
- Troubleshooting
- Problem
- Symptom
- Cause
- Environment
- Resolving The Problem
- Sql error 42601 error multiple decimal points
- Submit correction
PostgreSQL error 42601- How we fix it
by Sijin George | Sep 12, 2019
Syntax errors are quite common while coding.
But, things go for a toss when it results in website errors.
PostgreSQL error 42601 also occurs due to syntax errors in the database queries.
At Bobcares, we often get requests from PostgreSQL users to fix errors as part of our Server Management Services.
Today, let’s check PostgreSQL error in detail and see how our Support Engineers fix it for the customers.
What causes error 42601 in PostgreSQL?
PostgreSQL is an advanced database engine. It is popular for its extensive features and ability to handle complex database situations.
Applications like Instagram, Facebook, Apple, etc rely on the PostgreSQL database.
But what causes error 42601?
PostgreSQL error codes consist of five characters. The first two characters denote the class of errors. And the remaining three characters indicate a specific condition within that class.
Here, 42 in 42601 represent the class “Syntax Error or Access Rule Violation“.
In short, this error mainly occurs due to the syntax errors in the queries executed. A typical error shows up as:

Here, the syntax error has occurred in position 119 near the value “parents” in the query.
How we fix the error?
Now let’s see how our PostgreSQL engineers resolve this error efficiently.
Recently, one of our customers contacted us with this error. He tried to execute the following code,
But, this ended up in PostgreSQL error 42601. And he got the following error message,
Our PostgreSQL Engineers checked the issue and found out the syntax error. The statement in Line 5 was a mix of plain and dynamic SQL. In general, the PostgreSQL query should be either fully dynamic or plain. Therefore, we changed the code as,
This resolved the error 42601, and the code worked fine.
[Need more assistance to solve PostgreSQL error 42601?- We’ll help you.]
Conclusion
In short, PostgreSQL error 42601 occurs due to the syntax errors in the code. Today, in this write-up, we have discussed how our Support Engineers fixed this error for our customers.
PREVENT YOUR SERVER FROM CRASHING!
Never again lose customers to poor server speed! Let us help you.
Our server experts will monitor & maintain your server 24/7 so that it remains lightning fast and secure.
SELECT * FROM long_term_prediction_anomaly WHERE + “‘Timestamp’” + ‘”BETWEEN ‘” +
2019-12-05 09:10:00+ ‘”AND’” + 2019-12-06 09:10:00 + “‘;”)
Hello Joe,
Do you still get PostgreSQL errors? If you need help, we’ll be happy to talk to you on chat (click on the icon at right-bottom).
У меня ошибка drop table exists “companiya”;
CREATE TABLE “companiya” (
“compania_id” int4 NOT NULL,
“fio vladelca” text NOT NULL,
“name” text NOT NULL,
“id_operator” int4 NOT NULL,
“id_uslugi” int4 NOT NULL,
“id_reklama” int4 NOT NULL,
“id_tex-specialist” int4 NOT NULL,
“id_filial” int4 NOT NULL,
CONSTRAINT “_copy_8” PRIMARY KEY (“compania_id”)
);
CREATE TABLE “filial” (
“id_filial” int4 NOT NULL,
“street” text NOT NULL,
“house” int4 NOT NULL,
“city” text NOT NULL,
CONSTRAINT “_copy_5” PRIMARY KEY (“id_filial”)
);
CREATE TABLE “login” (
“id_name” int4 NOT NULL,
“name” char(20) NOT NULL,
“pass” char(20) NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (“id_name”)
);
CREATE TABLE “operator” (
“id_operator” int4 NOT NULL,
“obrabotka obrasheniya” int4 NOT NULL,
“konsultirovanie” text NOT NULL,
“grafick work” date NOT NULL,
CONSTRAINT “_copy_2” PRIMARY KEY (“id_operator”)
);
CREATE TABLE “polsovateli” (
“id_user” int4 NOT NULL,
“id_companiya” int4 NOT NULL,
“id_obrasheniya” int4 NOT NULL,
“id_oshibka” int4 NOT NULL,
CONSTRAINT “_copy_6” PRIMARY KEY (“id_user”)
);
CREATE TABLE “reklama” (
“id_reklama” int4 NOT NULL,
“tele-marketing” text NOT NULL,
“soc-seti” text NOT NULL,
“mobile” int4 NOT NULL,
CONSTRAINT “_copy_3” PRIMARY KEY (“id_reklama”)
);
CREATE TABLE “tex-specialist” (
“id_tex-specialist” int4 NOT NULL,
“grafik” date NOT NULL,
“zarplata” int4 NOT NULL,
“ispravlenie oshibok” int4 NOT NULL,
CONSTRAINT “_copy_7” PRIMARY KEY (“id_tex-specialist”)
);
CREATE TABLE “uslugi” (
“id_uslugi” int4 NOT NULL,
“vostanavlenia parola” int4 NOT NULL,
“poterya acaunta” int4 NOT NULL,
CONSTRAINT “_copy_4” PRIMARY KEY (“id_uslugi”)
);
ALTER TABLE “companiya” ADD CONSTRAINT “fk_companiya_operator_1” FOREIGN KEY (“id_operator”) REFERENCES “operator” (“id_operator”);
ALTER TABLE “companiya” ADD CONSTRAINT “fk_companiya_uslugi_1” FOREIGN KEY (“id_uslugi”) REFERENCES “uslugi” (“id_uslugi”);
ALTER TABLE “companiya” ADD CONSTRAINT “fk_companiya_filial_1” FOREIGN KEY (“id_filial”) REFERENCES “filial” (“id_filial”);
ALTER TABLE “companiya” ADD CONSTRAINT “fk_companiya_reklama_1” FOREIGN KEY (“id_reklama”) REFERENCES “reklama” (“id_reklama”);
ALTER TABLE “companiya” ADD CONSTRAINT “fk_companiya_tex-specialist_1” FOREIGN KEY (“id_tex-specialist”) REFERENCES “tex-specialist” (“id_tex-specialist”);
ALTER TABLE “polsovateli” ADD CONSTRAINT “fk_polsovateli_companiya_1” FOREIGN KEY (“id_companiya”) REFERENCES “companiya” (“compania_id”);
ERROR: ОШИБКА: ошибка синтаксиса (примерное положение: “”companiya””)
LINE 1: drop table exists “companiya”;
^
Источник
Приложение A. Коды ошибок PostgreSQL
Всем сообщениям, которые выдаёт сервер PostgreSQL , назначены пятисимвольные коды ошибок, соответствующие кодам «SQLSTATE» , описанным в стандарте SQL. Приложения, которые должны знать, какое условие ошибки имело место, обычно проверяют код ошибки и только потом обращаются к текстовому сообщению об ошибке. Коды ошибок, скорее всего, не изменятся от выпуска к выпуску PostgreSQL , и они не меняются при локализации как сообщения об ошибках. Заметьте, что отдельные, но не все коды ошибок, которые выдаёт PostgreSQL , определены стандартом SQL; некоторые дополнительные коды ошибок для условий, не описанных стандартом, были добавлены независимо или позаимствованы из других баз данных.
Согласно стандарту, первые два символа кода ошибки обозначают класс ошибок, а последние три символа обозначают определённое условие в этом классе. Таким образом, приложение, не знающее значение определённого кода ошибки, всё же может понять, что делать, по классу ошибки.
В Таблице A-1 перечислены все коды ошибок, определённые в PostgreSQL 9.4.1. (Некоторые коды в настоящее время не используются, хотя они определены в стандарте SQL.) Также показаны классы ошибок. Для каждого класса ошибок имеется «стандартный» код ошибки с последними тремя символами 000. Этот код выдаётся только для таких условий ошибок, которые относятся к определённому классу, но не имеют более определённого кода.
Символ, указанный в колонке «Имя условия» , определяет условие в PL/pgSQL . Имена условий могут записываться в верхнем или нижнем регистре. (Заметьте, что PL/pgSQL , в отличие от ошибок, не распознаёт предупреждения; то есть классы 00, 01 и 02.)
Для некоторых типов ошибок сервер сообщает имя объекта базы данных (таблица, колонка таблицы, тип данных или ограничение), связанного с ошибкой; например, имя уникального ограничения, вызвавшего ошибку unique_violation. Такие имена передаются в отдельных полях сообщения об ошибке, чтобы приложениям не пришлось извлекать его из возможно локализованного текста ошибки для человека. На момент выхода PostgreSQL 9.3 полностью охватывались только ошибки класса SQLSTATE 23 (нарушения ограничений целостности), но в будущем должны быть охвачены и другие классы.
Источник
SQLSTATE=42601 ,SQLCODE=-104 while running HCAT_SYNC_OBJECTS procedure in IBM Db2 BigSQL
Troubleshooting
Problem
While running HCAT_SYNC_OBJECTS procedure in BigSQL it fails with following ERROR code
Symptom
The following stack trace and ERROR message is observed in bigsql.log file
com.ibm.db2.jcc.am.SqlSyntaxErrorException: An unexpected token «name» was found following «emp.name as Employee». Expected tokens may include: » «.. SQLCODE=-104, SQLSTATE=42601, DRIVER=4.22.29
at com.ibm.db2.jcc.am.ld.a(ld.java:810)
at com.ibm.db2.jcc.am.ld.a(ld.java:66)
at com.ibm.db2.jcc.am.ld.a(ld.java:140)
at com.ibm.db2.jcc.am.up.c(up.java:2796)
at com.ibm.db2.jcc.am.up.d(up.java:2784)
at com.ibm.db2.jcc.am.up.b(up.java:2146)
at com.ibm.db2.jcc.t4.bb.j(bb.java:233)
at com.ibm.db2.jcc.t4.bb.c(bb.java:48)
at com.ibm.db2.jcc.t4.p.b(p.java:38)
at com.ibm.db2.jcc.t4.vb.h(vb.java:124)
at com.ibm.db2.jcc.am.up.kb(up.java:2141)
at com.ibm.db2.jcc.am.up.a(up.java:3336)
at com.ibm.db2.jcc.am.up.c(up.java:768)
at com.ibm.db2.jcc.am.up.executeUpdate(up.java:747)
at com.ibm.biginsights.biga.udf.HCAT_SYNC_OBJECTS.synchronizeObject(HCAT_SYNC_OBJECTS.java:1782)
at com.ibm.biginsights.biga.udf.HCAT_SYNC_OBJECTS.synchronizeTable(HCAT_SYNC_OBJECTS.java:648)
at com.ibm.biginsights.biga.udf.HCAT_SYNC_OBJECTS.syncTables(HCAT_SYNC_OBJECTS.java:564)
at com.ibm.biginsights.biga.udf.HCAT_SYNC_OBJECTS.exec(HCAT_SYNC_OBJECTS.java:314)
Cause
The hive view object has a column name with whitespace characters.
Hive supports column name with space
Environment
Resolving The Problem
BigSQL currently does not support column name with spaces, hence rename the hive columns and use non-whitespace characters
Источник
Sql error 42601 error multiple decimal points
All messages emitted by the PostgreSQL server are assigned five-character error codes that follow the SQL standard’s conventions for “ SQLSTATE ” codes. Applications that need to know which error condition has occurred should usually test the error code, rather than looking at the textual error message. The error codes are less likely to change across PostgreSQL releases, and also are not subject to change due to localization of error messages. Note that some, but not all, of the error codes produced by PostgreSQL are defined by the SQL standard; some additional error codes for conditions not defined by the standard have been invented or borrowed from other databases.
According to the standard, the first two characters of an error code denote a class of errors, while the last three characters indicate a specific condition within that class. Thus, an application that does not recognize the specific error code might still be able to infer what to do from the error class.
Table A.1 lists all the error codes defined in PostgreSQL 15.1. (Some are not actually used at present, but are defined by the SQL standard.) The error classes are also shown. For each error class there is a “ standard ” error code having the last three characters 000 . This code is used only for error conditions that fall within the class but do not have any more-specific code assigned.
The symbol shown in the column “ Condition Name ” is the condition name to use in PL/pgSQL . Condition names can be written in either upper or lower case. (Note that PL/pgSQL does not recognize warning, as opposed to error, condition names; those are classes 00, 01, and 02.)
For some types of errors, the server reports the name of a database object (a table, table column, data type, or constraint) associated with the error; for example, the name of the unique constraint that caused a unique_violation error. Such names are supplied in separate fields of the error report message so that applications need not try to extract them from the possibly-localized human-readable text of the message. As of PostgreSQL 9.3, complete coverage for this feature exists only for errors in SQLSTATE class 23 (integrity constraint violation), but this is likely to be expanded in future.
Table A.1. PostgreSQL Error Codes
| Error Code | Condition Name |
|---|---|
| Class 00 — Successful Completion | |
| 00000 | successful_completion |
| Class 01 — Warning | |
| 01000 | warning |
| 0100C | dynamic_result_sets_returned |
| 01008 | implicit_zero_bit_padding |
| 01003 | null_value_eliminated_in_set_function |
| 01007 | privilege_not_granted |
| 01006 | privilege_not_revoked |
| 01004 | string_data_right_truncation |
| 01P01 | deprecated_feature |
| Class 02 — No Data (this is also a warning class per the SQL standard) | |
| 02000 | no_data |
| 02001 | no_additional_dynamic_result_sets_returned |
| Class 03 — SQL Statement Not Yet Complete | |
| 03000 | sql_statement_not_yet_complete |
| Class 08 — Connection Exception | |
| 08000 | connection_exception |
| 08003 | connection_does_not_exist |
| 08006 | connection_failure |
| 08001 | sqlclient_unable_to_establish_sqlconnection |
| 08004 | sqlserver_rejected_establishment_of_sqlconnection |
| 08007 | transaction_resolution_unknown |
| 08P01 | protocol_violation |
| Class 09 — Triggered Action Exception | |
| 09000 | triggered_action_exception |
| Class 0A — Feature Not Supported | |
| 0A000 | feature_not_supported |
| Class 0B — Invalid Transaction Initiation | |
| 0B000 | invalid_transaction_initiation |
| Class 0F — Locator Exception | |
| 0F000 | locator_exception |
| 0F001 | invalid_locator_specification |
| Class 0L — Invalid Grantor | |
| 0L000 | invalid_grantor |
| 0LP01 | invalid_grant_operation |
| Class 0P — Invalid Role Specification | |
| 0P000 | invalid_role_specification |
| Class 0Z — Diagnostics Exception | |
| 0Z000 | diagnostics_exception |
| 0Z002 | stacked_diagnostics_accessed_without_active_handler |
| Class 20 — Case Not Found | |
| 20000 | case_not_found |
| Class 21 — Cardinality Violation | |
| 21000 | cardinality_violation |
| Class 22 — Data Exception | |
| 22000 | data_exception |
| 2202E | array_subscript_error |
| 22021 | character_not_in_repertoire |
| 22008 | datetime_field_overflow |
| 22012 | division_by_zero |
| 22005 | error_in_assignment |
| 2200B | escape_character_conflict |
| 22022 | indicator_overflow |
| 22015 | interval_field_overflow |
| 2201E | invalid_argument_for_logarithm |
| 22014 | invalid_argument_for_ntile_function |
| 22016 | invalid_argument_for_nth_value_function |
| 2201F | invalid_argument_for_power_function |
| 2201G | invalid_argument_for_width_bucket_function |
| 22018 | invalid_character_value_for_cast |
| 22007 | invalid_datetime_format |
| 22019 | invalid_escape_character |
| 2200D | invalid_escape_octet |
| 22025 | invalid_escape_sequence |
| 22P06 | nonstandard_use_of_escape_character |
| 22010 | invalid_indicator_parameter_value |
| 22023 | invalid_parameter_value |
| 22013 | invalid_preceding_or_following_size |
| 2201B | invalid_regular_expression |
| 2201W | invalid_row_count_in_limit_clause |
| 2201X | invalid_row_count_in_result_offset_clause |
| 2202H | invalid_tablesample_argument |
| 2202G | invalid_tablesample_repeat |
| 22009 | invalid_time_zone_displacement_value |
| 2200C | invalid_use_of_escape_character |
| 2200G | most_specific_type_mismatch |
| 22004 | null_value_not_allowed |
| 22002 | null_value_no_indicator_parameter |
| 22003 | numeric_value_out_of_range |
| 2200H | sequence_generator_limit_exceeded |
| 22026 | string_data_length_mismatch |
| 22001 | string_data_right_truncation |
| 22011 | substring_error |
| 22027 | trim_error |
| 22024 | unterminated_c_string |
| 2200F | zero_length_character_string |
| 22P01 | floating_point_exception |
| 22P02 | invalid_text_representation |
| 22P03 | invalid_binary_representation |
| 22P04 | bad_copy_file_format |
| 22P05 | untranslatable_character |
| 2200L | not_an_xml_document |
| 2200M | invalid_xml_document |
| 2200N | invalid_xml_content |
| 2200S | invalid_xml_comment |
| 2200T | invalid_xml_processing_instruction |
| 22030 | duplicate_json_object_key_value |
| 22031 | invalid_argument_for_sql_json_datetime_function |
| 22032 | invalid_json_text |
| 22033 | invalid_sql_json_subscript |
| 22034 | more_than_one_sql_json_item |
| 22035 | no_sql_json_item |
| 22036 | non_numeric_sql_json_item |
| 22037 | non_unique_keys_in_a_json_object |
| 22038 | singleton_sql_json_item_required |
| 22039 | sql_json_array_not_found |
| 2203A | sql_json_member_not_found |
| 2203B | sql_json_number_not_found |
| 2203C | sql_json_object_not_found |
| 2203D | too_many_json_array_elements |
| 2203E | too_many_json_object_members |
| 2203F | sql_json_scalar_required |
| 2203G | sql_json_item_cannot_be_cast_to_target_type |
| Class 23 — Integrity Constraint Violation | |
| 23000 | integrity_constraint_violation |
| 23001 | restrict_violation |
| 23502 | not_null_violation |
| 23503 | foreign_key_violation |
| 23505 | unique_violation |
| 23514 | check_violation |
| 23P01 | exclusion_violation |
| Class 24 — Invalid Cursor State | |
| 24000 | invalid_cursor_state |
| Class 25 — Invalid Transaction State | |
| 25000 | invalid_transaction_state |
| 25001 | active_sql_transaction |
| 25002 | branch_transaction_already_active |
| 25008 | held_cursor_requires_same_isolation_level |
| 25003 | inappropriate_access_mode_for_branch_transaction |
| 25004 | inappropriate_isolation_level_for_branch_transaction |
| 25005 | no_active_sql_transaction_for_branch_transaction |
| 25006 | read_only_sql_transaction |
| 25007 | schema_and_data_statement_mixing_not_supported |
| 25P01 | no_active_sql_transaction |
| 25P02 | in_failed_sql_transaction |
| 25P03 | idle_in_transaction_session_timeout |
| Class 26 — Invalid SQL Statement Name | |
| 26000 | invalid_sql_statement_name |
| Class 27 — Triggered Data Change Violation | |
| 27000 | triggered_data_change_violation |
| Class 28 — Invalid Authorization Specification | |
| 28000 | invalid_authorization_specification |
| 28P01 | invalid_password |
| Class 2B — Dependent Privilege Descriptors Still Exist | |
| 2B000 | dependent_privilege_descriptors_still_exist |
| 2BP01 | dependent_objects_still_exist |
| Class 2D — Invalid Transaction Termination | |
| 2D000 | invalid_transaction_termination |
| Class 2F — SQL Routine Exception | |
| 2F000 | sql_routine_exception |
| 2F005 | function_executed_no_return_statement |
| 2F002 | modifying_sql_data_not_permitted |
| 2F003 | prohibited_sql_statement_attempted |
| 2F004 | reading_sql_data_not_permitted |
| Class 34 — Invalid Cursor Name | |
| 34000 | invalid_cursor_name |
| Class 38 — External Routine Exception | |
| 38000 | external_routine_exception |
| 38001 | containing_sql_not_permitted |
| 38002 | modifying_sql_data_not_permitted |
| 38003 | prohibited_sql_statement_attempted |
| 38004 | reading_sql_data_not_permitted |
| Class 39 — External Routine Invocation Exception | |
| 39000 | external_routine_invocation_exception |
| 39001 | invalid_sqlstate_returned |
| 39004 | null_value_not_allowed |
| 39P01 | trigger_protocol_violated |
| 39P02 | srf_protocol_violated |
| 39P03 | event_trigger_protocol_violated |
| Class 3B — Savepoint Exception | |
| 3B000 | savepoint_exception |
| 3B001 | invalid_savepoint_specification |
| Class 3D — Invalid Catalog Name | |
| 3D000 | invalid_catalog_name |
| Class 3F — Invalid Schema Name | |
| 3F000 | invalid_schema_name |
| Class 40 — Transaction Rollback | |
| 40000 | transaction_rollback |
| 40002 | transaction_integrity_constraint_violation |
| 40001 | serialization_failure |
| 40003 | statement_completion_unknown |
| 40P01 | deadlock_detected |
| Class 42 — Syntax Error or Access Rule Violation | |
| 42000 | syntax_error_or_access_rule_violation |
| 42601 | syntax_error |
| 42501 | insufficient_privilege |
| 42846 | cannot_coerce |
| 42803 | grouping_error |
| 42P20 | windowing_error |
| 42P19 | invalid_recursion |
| 42830 | invalid_foreign_key |
| 42602 | invalid_name |
| 42622 | name_too_long |
| 42939 | reserved_name |
| 42804 | datatype_mismatch |
| 42P18 | indeterminate_datatype |
| 42P21 | collation_mismatch |
| 42P22 | indeterminate_collation |
| 42809 | wrong_object_type |
| 428C9 | generated_always |
| 42703 | undefined_column |
| 42883 | undefined_function |
| 42P01 | undefined_table |
| 42P02 | undefined_parameter |
| 42704 | undefined_object |
| 42701 | duplicate_column |
| 42P03 | duplicate_cursor |
| 42P04 | duplicate_database |
| 42723 | duplicate_function |
| 42P05 | duplicate_prepared_statement |
| 42P06 | duplicate_schema |
| 42P07 | duplicate_table |
| 42712 | duplicate_alias |
| 42710 | duplicate_object |
| 42702 | ambiguous_column |
| 42725 | ambiguous_function |
| 42P08 | ambiguous_parameter |
| 42P09 | ambiguous_alias |
| 42P10 | invalid_column_reference |
| 42611 | invalid_column_definition |
| 42P11 | invalid_cursor_definition |
| 42P12 | invalid_database_definition |
| 42P13 | invalid_function_definition |
| 42P14 | invalid_prepared_statement_definition |
| 42P15 | invalid_schema_definition |
| 42P16 | invalid_table_definition |
| 42P17 | invalid_object_definition |
| Class 44 — WITH CHECK OPTION Violation | |
| 44000 | with_check_option_violation |
| Class 53 — Insufficient Resources | |
| 53000 | insufficient_resources |
| 53100 | disk_full |
| 53200 | out_of_memory |
| 53300 | too_many_connections |
| 53400 | configuration_limit_exceeded |
| Class 54 — Program Limit Exceeded | |
| 54000 | program_limit_exceeded |
| 54001 | statement_too_complex |
| 54011 | too_many_columns |
| 54023 | too_many_arguments |
| Class 55 — Object Not In Prerequisite State | |
| 55000 | object_not_in_prerequisite_state |
| 55006 | object_in_use |
| 55P02 | cant_change_runtime_param |
| 55P03 | lock_not_available |
| 55P04 | unsafe_new_enum_value_usage |
| Class 57 — Operator Intervention | |
| 57000 | operator_intervention |
| 57014 | query_canceled |
| 57P01 | admin_shutdown |
| 57P02 | crash_shutdown |
| 57P03 | cannot_connect_now |
| 57P04 | database_dropped |
| 57P05 | idle_session_timeout |
| Class 58 — System Error (errors external to PostgreSQL itself) | |
| 58000 | system_error |
| 58030 | io_error |
| 58P01 | undefined_file |
| 58P02 | duplicate_file |
| Class 72 — Snapshot Failure | |
| 72000 | snapshot_too_old |
| Class F0 — Configuration File Error | |
| F0000 | config_file_error |
| F0001 | lock_file_exists |
| Class HV — Foreign Data Wrapper Error (SQL/MED) | |
| HV000 | fdw_error |
| HV005 | fdw_column_name_not_found |
| HV002 | fdw_dynamic_parameter_value_needed |
| HV010 | fdw_function_sequence_error |
| HV021 | fdw_inconsistent_descriptor_information |
| HV024 | fdw_invalid_attribute_value |
| HV007 | fdw_invalid_column_name |
| HV008 | fdw_invalid_column_number |
| HV004 | fdw_invalid_data_type |
| HV006 | fdw_invalid_data_type_descriptors |
| HV091 | fdw_invalid_descriptor_field_identifier |
| HV00B | fdw_invalid_handle |
| HV00C | fdw_invalid_option_index |
| HV00D | fdw_invalid_option_name |
| HV090 | fdw_invalid_string_length_or_buffer_length |
| HV00A | fdw_invalid_string_format |
| HV009 | fdw_invalid_use_of_null_pointer |
| HV014 | fdw_too_many_handles |
| HV001 | fdw_out_of_memory |
| HV00P | fdw_no_schemas |
| HV00J | fdw_option_name_not_found |
| HV00K | fdw_reply_handle |
| HV00Q | fdw_schema_not_found |
| HV00R | fdw_table_not_found |
| HV00L | fdw_unable_to_create_execution |
| HV00M | fdw_unable_to_create_reply |
| HV00N | fdw_unable_to_establish_connection |
| Class P0 — PL/pgSQL Error | |
| P0000 | plpgsql_error |
| P0001 | raise_exception |
| P0002 | no_data_found |
| P0003 | too_many_rows |
| P0004 | assert_failure |
| Class XX — Internal Error | |
| XX000 | internal_error |
| XX001 | data_corrupted |
| XX002 | index_corrupted |
| Prev | Up | Next |
| Part VIII. Appendixes | Home | Appendix B. Date/Time Support |
Submit correction
If you see anything in the documentation that is not correct, does not match your experience with the particular feature or requires further clarification, please use this form to report a documentation issue.
Источник