Вчера всё работало, а сегодня не работает / Код не работает как задумано
или
Debugging (Отладка)
В чем заключается процесс отладки? Что это такое?
Процесс отладки состоит в том, что мы останавливаем выполнения скрипта в любом месте, смотрим, что находится в переменных, в функциях, анализируем и переходим в другие места; ищем те места, где поведение отклоняется от правильного.
Важное замечание:
Есть много IDE и редакторов кода, которые позволяют производить отладку. Процесс настройки в них у всех различается. Поэтому стОит обратиться к документации по настройке отладки для непосредственно той среды разработки и той версии, в которой работаете именно ВЫ.
На текущий момент будет рассмотрен пример с PHPStorm 2017.
Подготовка
Для начала необходимо, чтобы в PHP имелась библиотека для отладки под названием xdebug. Если её еще нет, то надо установить.
ВАЖНО! Для очень новых версий PHP (например 8), требуется и новый xdebug, а он, в свою очередь, работает на порту 9003. Не пропустите указание правильного порта в IDE!! (Примерно в разделе PHP -> Debug -> Debug Port . Где точно — зависит от конкретной IDE)
Для WINDOWS:
скачать dll, например на xdebug.org.
Обычно все библиотеки лежат в папке ext внутри папки PHP. Туда и надо поместить dll.
Далее в php.ini прописываем настройки:
[Xdebug]
zend_extension="C:/server/php/ext/php_xdebug.dll" // <!-- тут свой путь до dll!!! Это для среды Windows.
; Для Linux путь должен быть что-то типа zend_extension=/usr/lib/php/20151012/xdebug.so
xdebug.default_enable = 1
xdebug.remote_enable = 1
xdebug.remote_handler = "dbgp"
xdebug.remote_host = "localhost"
xdebug.remote_port = 9000
xdebug.auto_trace = 0
Перезагружаем сервер, на всякий случай.
Для UBUNTU:
-
sudo apt updateИЛИsudo apt-get update -
sudo apt install php-xdebugили если нужнен отладчик для конкретной версии PHP, тоsudo apt install php7.0-xdebugгде7.0указывается версия PHP -
sudo nano /etc/php/7.0/mods-available/xdebug.iniвписываем строки:
zend_extension=/usr/lib/php/20151012/xdebug.so xdebug.remote_autostart = 1 xdebug.remote_enable = 1 xdebug.remote_handler = dbgp xdebug.remote_host = 127.0.0.1 xdebug.remote_log = /tmp/xdebug_remote.log xdebug.remote_mode = reqПримечание: каталог
20151012, скорее всего, будет другим.cdв/usr/lib/phpи проверьте, в каком каталоге в этом формате находится файлxdebug.so, и используйте этот путь.7.0— тоже отличается, в зависимости от того, какая версия у вас используется -
Перезагружаем сервер, на всякий случай.
Теперь если в файле .php написать phpinfo(); то можно будет увидеть в самом низу такую картину:

Открываем PHPStorm
- нажимаем
create project from existing files - выбираем
Web server is installed locally, source files are located under its document root - выбираем папку с файлами, и нажав вверху кнопку «Project Root» помечаем папку как корень проекта
- нажимаем «Next»
- нажимаем Add new local server

- вводим имя сервера любое и
Web Server root URL. В рассматриваемом примере этоhttp://localhost/testy2

- нажимаем «Next» и затем «Finish»
Запуск
Для начала в левой части панели с кодом на любой строке можно кликнуть ЛКМ, тем самым поставив точку останова (breakpoint — брейкпойнт). Это то место, где отладчик автоматически остановит выполнение PHP, как только до него дойдёт. Количество breakpoint’ов не ограничено. Можно ставить везде и много.

Если кликнуть ПКМ и во всплывающем меню выбрать Debug (или в верхнем меню — Run → Debug), то при первом запуске PHPStorm попросит настроить интерпретатор. Т.е. надо выбрать версию PHP из папки, где он лежит, чтобы шторм знал, какую версию он будет отлаживать.

Теперь можно нажать Debug!!!
В данном случае, т.к. функция вызывается сразу на той же странице, то при нажатии кнопки Debug — отладчик моментально вызовет функцию, выполнение «заморозится» на первом же брейкпойнте. В ином случае, для активации требуется исполнить действие, при котором произойдет исполнение нужного участка кода (клик на кнопку, передача POST-запроса с формы с данными и другие действия).

Цифрами обозначены:
- Стэк вызовов, все вложенные вызовы, которые привели к текущему месту кода.
- Переменные. На текущий момент строки ниже номера 3 ещё не выполнились, поэтому определена лишь
$data - Показывает текущие значения любых переменных и выражений. В любой момент здесь можно нажать на
+, вписать имя любой переменной и посмотреть её значение в реальном времени. Например:$dataили$nums[0], а можно и$nums[i]иitem['test']['data'][$name[5]][$info[$key[1]]]и т.д. На текущий момент строки ниже номера 3 ещё не выполнились, поэтому$sumи$outputобозначены красным цветом с надписью «cannot evaluate expression».
Процесс
Для самого процесса используются элементы управления (см. изображение выше, выделено зеленым прямоугольником) и немного из дополнительно (см. изображение выше, выделено оранжевым прямоугольником).

Show Execution Point (Alt+F10) — переносит в файл и текущую линию отлаживаемого скрипта. Например, если файлов много, решили посмотреть что в других вкладках, а потом забыли где у вас отладка
Step Over (F8) — делает один шаг, не заходя внутрь функции. Т.е. если на текущей линии есть какая-то функция, а не просто переменная со значением, то при клике данной кнопки, отладчик не будет заходить внутрь неё.
Step Into (F7) — делает шаг. Но в отличие от предыдущей, если есть вложенный вызов (например функция), то заходит внутрь неё.
Step Out (Shift+F8) — выполняет команды до завершения текущей функции. Удобно, если случайно вошли во вложенный вызов и нужно быстро из него выйти, не завершая при этом отладку.
Rerun (Ctrl+F5) — перезапускает отладку.
Resume Program(F9) — продолжает выполнение скрипта с текущего момента. Если больше нет других точек останова, то отладка заканчивается и скрипт продолжает работу. В ином случае работа прерывается на следующей точке останова.
Stop (Ctrl+F2) — завершает отладку.
View Breakpoints (Ctrl+Shift+F8) — просмотр всех установленных брейкпойнтов.
Mute Breakpoints — отключает брейкпойнты.
…
Итак, в текущем коде видно значение входного параметра:
$data = "23 24 11 18"— строка с данными через пробел$nums = (4) ["23", "24", "11", "18"]— массив, который получился из входной переменной.

Если нажмем F8 2 раза, то окажемся на строке 7; во вкладках Watches и Variables и в самой странице с кодом увидим, что переменная $sum была инициализирована и её значение равно 0.
Если теперь нажмем F8, то попадем внутрь цикла foreach и, нажимая теперь F8, пока не окончится цикл, можно будет наблюдать на каждой итерации, как значения $num и $sum постоянно изменяются. Тем самым мы можем проследить шаг за шагом весь процесс изменения любых переменных и значений на любом этапе, который интересует.
Дальнейшие нажатия F8 переместят линию кода на строки 11, 12 и, наконец, 15.
Дополнительно
Если нажать на View Breakpoints в левой панели, то можно не только посмотреть все брейкпойнты, но в появившемся окне можно еще более тонко настроить условие, при котором на данной отметке надо остановиться.
В функции выше, например, нужно остановиться только когда $sum превысит значение 20.

Это удобно, если останов нужен только при определённом значении, а не всегда (особенно в случае с циклами).
В этом руководстве мы расскажем о различных способах того, как в PHP включить вывод ошибок. Мы также обсудим, как записывать ошибки в журнал (лог).
Самый быстрый способ отобразить все ошибки и предупреждения php — добавить эти строки в файл PHP:
ini_set('display_errors', 1);
ini_set('display_startup_errors', 1);
error_reporting(E_ALL);
Что именно делают эти строки?
Функция ini_set попытается переопределить конфигурацию, найденную в вашем ini-файле PHP.
Display_errors и display_startup_errors — это только две из доступных директив. Директива display_errors определяет, будут ли ошибки отображаться для пользователя. Обычно директива dispay_errors не должна использоваться для “боевого” режима работы сайта, а должна использоваться только для разработки.
display_startup_errors — это отдельная директива, потому что display_errors не обрабатывает ошибки, которые будут встречаться во время запуска PHP. Список директив, которые могут быть переопределены функцией ini_set, находится в официальной документации .
К сожалению, эти две директивы не смогут отображать синтаксические ошибки, такие как пропущенные точки с запятой или отсутствующие фигурные скобки.
Отображение ошибок PHP через настройки в php.ini
Если ошибки в браузере по-прежнему не отображаются, то добавьте директиву:
display_errors = on
Директиву display_errors следует добавить в ini-файл PHP. Она отобразит все ошибки, включая синтаксические ошибки, которые невозможно отобразить, просто вызвав функцию ini_set в коде PHP.
Актуальный INI-файл можно найти в выводе функции phpinfo (). Он помечен как “загруженный файл конфигурации” (“loaded configuration file”).
Отображать ошибки PHP через настройки в .htaccess
Включить или выключить отображение ошибок можно и с помощью файла .htaccess, расположенного в каталоге сайта.
php_flag display_startup_errors on
php_flag display_errors on
.htaccess также имеет директивы для display_startup_errors и display_errors.
Вы можете настроить display_errors в .htaccess или в вашем файле PHP.ini. Однако многие хостинг-провайдеры не разрешают вам изменять ваш файл PHP.ini для включения display_errors.
В файле .htaccess также можно включить настраиваемый журнал ошибок, если папка журнала или файл журнала доступны для записи. Файл журнала может быть относительным путем к месту расположения .htaccess или абсолютным путем, например /var/www/html/website/public/logs.
php_value error_log logs/all_errors.log
Включить подробные предупреждения и уведомления
Иногда предупреждения приводят к некоторым фатальным ошибкам в определенных условиях. Скрыть ошибки, но отображать только предупреждающие (warning) сообщения можно вот так:
error_reporting(E_WARNING);
Для отображения предупреждений и уведомлений укажите «E_WARNING | E_NOTICE».
Также можно указать E_ERROR, E_WARNING, E_PARSE и E_NOTICE в качестве аргументов. Чтобы сообщить обо всех ошибках, кроме уведомлений, укажите «E_ALL & ~ E_NOTICE», где E_ALL обозначает все возможные параметры функции error_reporting.
Более подробно о функции error_reporting ()
Функция сообщения об ошибках — это встроенная функция PHP, которая позволяет разработчикам контролировать, какие ошибки будут отображаться. Помните, что в PHP ini есть директива error_reporting, которая будет задана этой функцией во время выполнения.
error_reporting(0);
Для удаления всех ошибок, предупреждений, сообщений и уведомлений передайте в функцию error_reporting ноль. Можно сразу отключить сообщения отчетов в ini-файле PHP или в .htaccess:
error_reporting(E_NOTICE);
PHP позволяет использовать переменные, даже если они не объявлены. Это не стандартная практика, поскольку необъявленные переменные будут вызывать проблемы для приложения, если они используются в циклах и условиях.
Иногда это также происходит потому, что объявленная переменная имеет другое написание, чем переменная, используемая для условий или циклов. Когда E_NOTICE передается в функцию error_reporting, эти необъявленные переменные будут отображаться.
error_reporting(E_ALL & ~E_NOTICE);
Функция сообщения об ошибках позволяет вам фильтровать, какие ошибки могут отображаться. Символ «~» означает «нет», поэтому параметр ~ E_NOTICE означает не показывать уведомления. Обратите внимание на символы «&» и «|» между возможными параметрами. Символ «&» означает «верно для всех», в то время как символ «|» представляет любой из них, если он истинен. Эти два символа имеют одинаковое значение в условиях PHP OR и AND.
error_reporting(E_ALL);
error_reporting(-1);
ini_set('error_reporting', E_ALL);
Эти три строки кода делают одно и то же, они будут отображать все ошибки PHP. Error_reporting(E_ALL) наиболее широко используется разработчиками для отображения ошибок, потому что он более читабелен и понятен.
Включить ошибки php в файл с помощью функции error_log ()
У сайта на хостинге сообщения об ошибках не должны показываться конечным пользователям, но эта информация все равно должна быть записана в журнал (лог).
Простой способ использовать файлы журналов — использовать функцию error_log, которая принимает четыре параметра. Единственный обязательный параметр — это первый параметр, который содержит подробную информацию об ошибке или о том, что нужно регистрировать. Тип, назначение и заголовок являются необязательными параметрами.
error_log("There is something wrong!", 0);
Параметр type, если он не определен, будет по умолчанию равен 0, что означает, что эта информация журнала будет добавлена к любому файлу журнала, определенному на веб-сервере.
error_log("Email this error to someone!", 1, "someone@mydomain.com");
Параметр 1 отправит журнал ошибок на почтовый ящик, указанный в третьем параметре. Чтобы эта функция работала, PHP ini должен иметь правильную конфигурацию SMTP, чтобы иметь возможность отправлять электронные письма. Эти SMTP-директивы ini включают хост, тип шифрования, имя пользователя, пароль и порт. Этот вид отчетов рекомендуется использовать для самых критичных ошибок.
error_log("Write this error down to a file!", 3, "logs/my-errors.log");
Для записи сообщений в отдельный файл необходимо использовать тип 3. Третий параметр будет служить местоположением файла журнала и должен быть доступен для записи веб-сервером. Расположение файла журнала может быть относительным путем к тому, где этот код вызывается, или абсолютным путем.
Журнал ошибок PHP через конфигурацию веб-сервера
Лучший способ регистрировать ошибки — это определить их в файле конфигурации веб-сервера.
Однако в этом случае вам нужно попросить администратора сервера добавить следующие строки в конфигурацию.
Пример для Apache:
ErrorLog "/var/log/apache2/my-website-error.log"
В nginx директива называется error_log.
error_log /var/log/nginx/my-website-error.log;
Теперь вы знаете, как в PHP включить отображение ошибок. Надеемся, что эта информация была вам полезна.
The behaviour of these functions is affected by settings in php.ini.
Errors and Logging Configuration Options
| Name | Default | Changeable | Changelog |
|---|---|---|---|
| error_reporting | NULL | PHP_INI_ALL | |
| display_errors | «1» | PHP_INI_ALL | |
| display_startup_errors | «1» | PHP_INI_ALL |
Prior to PHP 8.0.0, the default value was "0".
|
| log_errors | «0» | PHP_INI_ALL | |
| log_errors_max_len | «1024» | PHP_INI_ALL | |
| ignore_repeated_errors | «0» | PHP_INI_ALL | |
| ignore_repeated_source | «0» | PHP_INI_ALL | |
| report_memleaks | «1» | PHP_INI_ALL | |
| track_errors | «0» | PHP_INI_ALL | Deprecated as of PHP 7.2.0, removed as of PHP 8.0.0. |
| html_errors | «1» | PHP_INI_ALL | |
| xmlrpc_errors | «0» | PHP_INI_SYSTEM | |
| xmlrpc_error_number | «0» | PHP_INI_ALL | |
| docref_root | «» | PHP_INI_ALL | |
| docref_ext | «» | PHP_INI_ALL | |
| error_prepend_string | NULL | PHP_INI_ALL | |
| error_append_string | NULL | PHP_INI_ALL | |
| error_log | NULL | PHP_INI_ALL | |
| error_log_mode | 0o644 | PHP_INI_ALL | Available as of PHP 8.2.0 |
| syslog.facility | «LOG_USER» | PHP_INI_SYSTEM | Available as of PHP 7.3.0. |
| syslog.filter | «no-ctrl» | PHP_INI_ALL | Available as of PHP 7.3.0. |
| syslog.ident | «php» | PHP_INI_SYSTEM | Available as of PHP 7.3.0. |
For further details and definitions of the
PHP_INI_* modes, see the Where a configuration setting may be set.
Here’s a short explanation of
the configuration directives.
-
error_reporting
int -
Set the error reporting level. The parameter is either an integer
representing a bit field, or named constants. The error_reporting
levels and constants are described in
Predefined Constants,
and in php.ini. To set at runtime, use the
error_reporting() function. See also the
display_errors directive.The default value is
E_ALL.Prior to PHP 8.0.0, the default value was:
E_ALL&
~E_NOTICE&
~E_STRICT&
~E_DEPRECATED
This means diagnostics of levelE_NOTICE,
E_STRICTandE_DEPRECATED
were not shown.Note:
PHP Constants outside of PHPUsing PHP Constants outside of PHP, like in httpd.conf,
will have no useful meaning so in such cases the int values
are required. And since error levels will be added over time, the maximum
value (forE_ALL) will likely change. So in place of
E_ALLconsider using a larger value to cover all bit
fields from now and well into the future, a numeric value like
2147483647(includes all errors, not just
E_ALL). -
display_errors
string -
This determines whether errors should be printed to the screen
as part of the output or if they should be hidden from the user.Value
"stderr"sends the errors tostderr
instead ofstdout.Note:
This is a feature to support your development and should never be used
on production systems (e.g. systems connected to the internet).Note:
Although display_errors may be set at runtime (with ini_set()),
it won’t have any effect if the script has fatal errors.
This is because the desired runtime action does not get executed. -
display_startup_errors
bool -
Even when display_errors is on, errors that occur during PHP’s startup
sequence are not displayed. It’s strongly recommended to keep
display_startup_errors off, except for debugging. -
log_errors
bool -
Tells whether script error messages should be logged to the
server’s error log or error_log.
This option is thus server-specific.Note:
You’re strongly advised to use error logging in place of
error displaying on production web sites. -
log_errors_max_len
int -
Set the maximum length of log_errors in bytes. In
error_log information about
the source is added. The default is 1024 and 0 allows to not apply
any maximum length at all.
This length is applied to logged errors, displayed errors and also to
$php_errormsg, but not to explicitly called functions
such as error_log().When an int is used, the
value is measured in bytes. Shorthand notation, as described
in this FAQ, may also be used.
-
ignore_repeated_errors
bool -
Do not log repeated messages. Repeated errors must occur in the same
file on the same line unless
ignore_repeated_source
is set true. -
ignore_repeated_source
bool -
Ignore source of message when ignoring repeated messages. When this setting
is On you will not log errors with repeated messages from different files or
sourcelines. -
report_memleaks
bool -
If this parameter is set to On (the default), this parameter will show a
report of memory leaks detected by the Zend memory manager. This report
will be sent to stderr on Posix platforms. On Windows, it will be sent
to the debugger using OutputDebugString() and can be viewed with tools
like » DbgView.
This parameter only has effect in a debug build and if
error_reporting includesE_WARNINGin the allowed
list. -
track_errors
bool -
If enabled, the last error message will always be present in the
variable $php_errormsg. -
html_errors
bool -
If enabled, error messages will include HTML tags. The format for HTML
errors produces clickable messages that direct the user to a page
describing the error or function in causing the error. These references
are affected by
docref_root and
docref_ext.If disabled, error message will be solely plain text.
-
xmlrpc_errors
bool -
If enabled, turns off normal error reporting and formats errors as
XML-RPC error message. -
xmlrpc_error_number
int -
Used as the value of the XML-RPC faultCode element.
-
docref_root
string -
The new error format contains a reference to a page describing the error or
function causing the error. In case of manual pages you can download the
manual in your language and set this ini directive to the URL of your local
copy. If your local copy of the manual can be reached by"/manual/"
you can simply usedocref_root=/manual/. Additional you have
to set docref_ext to match the fileextensions of your copy
docref_ext=.html. It is possible to use external
references. For example you can use
docref_root=http://manual/en/or
docref_root="http://landonize.it/?how=url&theme=classic&filter=Landon
&url=http%3A%2F%2Fwww.php.net%2F"Most of the time you want the docref_root value to end with a slash
"/".
But see the second example above which does not have nor need it.Note:
This is a feature to support your development since it makes it easy to
lookup a function description. However it should never be used on
production systems (e.g. systems connected to the internet). -
docref_ext
string -
See docref_root.
Note:
The value of docref_ext must begin with a dot
".". -
error_prepend_string
string -
String to output before an error message.
Only used when the error message is displayed on screen. The main purpose
is to be able to prepend additional HTML markup to the error message. -
error_append_string
string -
String to output after an error message.
Only used when the error message is displayed on screen. The main purpose
is to be able to append additional HTML markup to the error message. -
error_log
string -
Name of the file where script errors should be logged. The file should
be writable by the web server’s user. If the
special valuesyslogis used, the errors
are sent to the system logger instead. On Unix, this means
syslog(3) and on Windows it means the event log. See also:
syslog().
If this directive is not set, errors are sent to the SAPI error logger.
For example, it is an error log in Apache orstderr
in CLI.
See also error_log(). -
error_log_mode
int -
File mode for the file described set in
error_log. -
syslog.facility
string -
Specifies what type of program is logging the message.
Only effective if error_log is set to «syslog». -
syslog.filter
string -
Specifies the filter type to filter the logged messages. Allowed
characters are passed unmodified; all others are written in their
hexadecimal representation prefixed withx.-
all– the logged string will be split
at newline characters, and all characters are passed unaltered
-
ascii– the logged string will be split
at newline characters, and any non-printable 7-bit ASCII characters will be escaped
-
no-ctrl– the logged string will be split
at newline characters, and any non-printable characters will be escaped
-
raw– all characters are passed to the system
logger unaltered, without splitting at newlines (identical to PHP before 7.3)
This setting will affect logging via error_log set to «syslog» and calls to syslog().
Note:
The
rawfilter type is available as of PHP 7.3.8 and PHP 7.4.0.
This directive is not supported on Windows.
-
-
syslog.ident
string -
Specifies the ident string which is prepended to every message.
Only effective if error_log is set to «syslog».
cjakeman at bcs dot org ¶
13 years ago
Using
<?php ini_set('display_errors', 1); ?>
at the top of your script will not catch any parse errors. A missing ")" or ";" will still lead to a blank page.
This is because the entire script is parsed before any of it is executed. If you are unable to change php.ini and set
display_errors On
then there is a possible solution suggested under error_reporting:
<?php
error_reporting
(E_ALL);ini_set("display_errors", 1);
include(
"file_with_errors.php");?>
[Modified by moderator]
You should also consider setting error_reporting = -1 in your php.ini and display_errors = On if you are in development mode to see all fatal/parse errors or set error_log to your desired file to log errors instead of display_errors in production (this requires log_errors to be turned on).
ohcc at 163 dot com ¶
6 years ago
If you set the error_log directive to a relative path, it is a path relative to the document root rather than php's containing folder.
iio7 at protonmail dot com ¶
1 year ago
It's important to note that when display_errors is "on", PHP will send a HTTP 200 OK status code even when there is an error. This is not a mistake or a wrong behavior, but is because you're asking PHP to output normal HTML, i.e. the error message, to the browser.
When display_errors is set to "off", PHP will send a HTTP 500 Internal Server Error, and let the web server handle it from there. If the web server is setup to intercept FastCGI errors (in case of NGINX), it will display the 500 error page it has setup. If the web server cannot intercept FastCGI errors, or it isn't setup to do it, an empty screen will be displayed in the browser (the famous white screen of death).
If you need a custom error page but cannot intercept PHP errors on the web server you're using, you can use PHPs custom error and exception handling mechanism. If you combine that with output buffering you can prevent any output to reach the client before the error/exception occurs. Just remember that parse errors are compile time errors that cannot be handled by a custom handler, use "php -l foo.php" from the terminal to check for parse errors before putting your files on production.
Roger ¶
3 years ago
When `error_log` is set to a file path, log messages will automatically be prefixed with timestamp [DD-MMM-YYYY HH:MM:SS UTC]. This appears to be hard-coded, with no formatting options.
php dot net at sp-in dot dk ¶
8 years ago
There does not appear to be a way to set a tag / ident / program for log entries in the ini file when using error_log=syslog. When I test locally, "apache2" is used.
However, calling openlog() with an ident parameter early in your script (or using an auto_prepend_file) will make PHP use that value for all subsequent log entries. closelog() will restore the original tag.
This can be done for setting facility as well, although the original value does not seem to be restored by closelog().
jaymore at gmail dot com ¶
6 years ago
Document says
So in place of E_ALL consider using a larger value to cover all bit fields from now and well into the future, a numeric value like 2147483647 (includes all errors, not just E_ALL).
But it is better to set "-1" as the E_ALL value.
For example, in httpd.conf or .htaccess, use
php_value error_reporting -1
to report all kind of error without be worried by the PHP version.

- PHP и MySQL
- Основы PHP
- Нарушения в работе системы PHP
Внимание! Данный курс устарел!
Переходите к новому курсу «PHP для начинающих».
В этой статье приведены сведения о некоторых из наиболее распространенных проблем возникающих при работе с PHP, классифицированные по признакам нарушений в работе, и предложены некоторые широко применяемые способы устранения этих проблем.

Обработка и отладка ошибок
В процессе функционирования интерпретатора PHP вырабатываются ошибки нескольких типов, которые классифицируются по степени серьезности. Четыре наиболее распространенных типа ошибок описаны ниже. Дополнительные сведения по этой теме приведены по адресу www.php.net/error_reporting.
- Извещение (Notice)
-
Ошибки такого типа не слишком серьезны и не создают существенных проблем. По умолчанию эти ошибки подавляются. Их появление становится возможным только после изменения степени серьезности регистрируемых в журнале ошибок в файле php.ini.
- Устаревшие функции и конструкции (Deprecated)
-
Ошибки использования устаревших конструкций. Включаются для того, чтобы получать предупреждения о коде, который не будет работать в следующих версиях PHP.

Ошибка использования устаревших функций и конструкций - Предупреждение (Warning)
-
Ошибки такого типа возникают, если в коде, выполняемом со сбоями, возникло нарушение в работе, но выполнение программы не прекратилось. Обычно сообщение о такой ошибке отображается, но сценарий продолжает работать.

Предупреждение - Неисправимая ошибка (Fatal Error)
-
Значимое условие возникновения ошибки, в силу которого продолжение работы сценария становится невозможным. После возникновения неисправимой ошибки работа сценария прекращается.

Неисправимая ошибка
Кроме того, ошибка каждого типа представлена с помощью константы, на которую можно ссылаться в коде: E_USER_NOTICE (извещение), E_USER_WARNING (предупреждение), E_USER_DEPRECATED (устаревшие функции и конструкции) и E_USER_ERROR (неисправимая ошибка). Степень серьезности регистрируемых ошибок можно задать в сценарии вручную, с помощью функции error_reporting(), как показано в следующих примерах:
Код PHP
// Формировать сообщения только о неисправимых ошибках
error_reporting(E_USER_ERROR);
// Формировать предупреждающие сообщения и сообщения о неисправимых ошибках
error_reporting(E_USER_WARNING | E_USER_ERROR);
// Формировать все сообщения, в том числе извещения и сообщения E_STRICT
error_reporting(E_ALL);
// Не показывать никакие сообщения
error_reporting(0);Непродуманное подавление вывода средств формирования сообщений об ошибках значительно затрудняет процесс отладки. Вместо этого чаще всего следует использовать обработчики ошибок.
Извещения никогда не передаются в клиентскую программу и не отражаются отрицательно на функциональных возможностях программы, поэтому разработчик почти всегда может без опасений отказаться от использования извещений в целях обработки ошибок. И наоборот, специализированный обработчик ошибок не позволяет обрабатывать неисправимые ошибки; в интерпретаторе PHP такие ошибки рассматриваются как достаточно серьезные для того, чтобы прекратить выполнение сценария, не задавая дополнительных вопросов. Поэтому область применения специализированных функций обработки ошибок главным образом сводится к предупреждениям. Основное назначение таких функций заключается в том, что они позволяют избежать необходимости показывать конечному пользователю сообщения об ошибках, предназначенные для программиста, и нарушать ход выполнения приложения.
Определение обработчика ошибок
На этом этапе необходимо найти ответ на следующий важный вопрос: «Какая информация должна отображаться на экране браузера пользователя при возникновении ошибки?» Обычно считается нецелесообразным и даже не рекомендуется демонстрировать перед конечным пользователем какие-либо детали, касающиеся внутреннего функционирования приложения, не говоря уже о том, что сообщения об ошибках портят внешний вид веб-страницы. Создав функцию, формирующую специализированное сообщение об ошибках, а затем установив ее в качестве применяемого по умолчанию обработчика ошибок, можно избежать такой ситуации, в которой перед глазами пользователя появляются некрасивые и непрофессионально выполненные сообщения об ошибках.
Вначале определим, какая информация должна быть предоставлена пользователю, а затем создадим функцию, как показано ниже. Эта функция должна принимать такие входные параметры, как тип ошибки, сообщение, имя файла и номер строки:
Код PHP
<?php
function error_msg($err_type, $err_msg, $err_file, $err_line)
{
static $count = 0;
$count++;
echo "<div style="width:32px; height:32px; background:url(error.png); float:left; margin:0 12px 12px 0;"></div>"
."<b>Ошибка №$count:</b><p>Извините, но на этой странице возникла ошибка. "
."Пожалуйста, отправьте следующее сообщение администратору сайта на странице <a href='help.html'>help</a>.</p>"
."<p>Тип ошибки: <em>$err_type</em>, сообщение: <em>$err_msg</em>, файл: <em>$err_file</em>, номер строки: <em>$err_line</em>"
."<hr color='red'>";
}
// Регистрируем нашу функцию в качестве обработчика ошибок
set_error_handler("error_msg");
// Генерируем ошибку, чтобы проверить вызывается ли функция error_msg
include 'undefined.php';
?>В данном случае было решено предоставлять информацию о конкретной ошибке и о том, где она возникла. В зависимости от ситуации может оказаться оправданным решение предоставлять пользователю минимальный объем информации, поскольку ему достаточно знать, что возникла ошибка, и как ему следует действовать в дальнейшем. После того как определен специализированный обработчик ошибок, достаточно указать эту функцию обработчика в коде с помощью функции set_error_handler().
После подготовки и выполнения такого кода все ошибки, которые разрешены в соответствии с установленной степенью серьезности регистрируемых ошибок, будут обрабатываться с помощью применяемой специализированной функции, за исключением неисправимых ошибок, которые, к сожалению, также неизбежны:

Инициирование пользовательской ошибки вручную
В PHP можно инициировать пользовательскую ошибку. Такая операция приблизительно эквивалентна операции активизации исключительной ситуации в версии PHP 5 (конструкция throw). Ошибка любого типа может быть инициирована путем передачи в функцию trigger_error() сообщения об ошибке и необязательной константы с обозначением степени серьезности ошибки, как в следующем примере:
Код PHP
trigger_error("Тестируем сообщение уровня 'Notice'", E_USER_NOTICE);Средства инициирования ошибок лучше всего использовать в сочетании со специализированным обработчиком ошибок. Сразу после инициирования такой ошибки в программе вызывается определенный в ней обработчик ошибок, который предоставляет пользователю отформатированное сообщение об ошибке. Т.е. эту функцию удобно использовать для тестирования функций обработки ошибок.
Ведение журнала и отладка
Если средства обработки исключительных ситуаций и формирования сообщений об ошибках не применяются должным образом, то задача отладки существенно усложняется. Ошибка, которую и без того трудно выявить, может стать почти неуловимой, если программист непродуманно использует способы подавления или перенаправления сообщений об ошибках. Но достаточно лишь немного более тщательно продумать применение обработчиков ошибок, и сопровождение приложения существенно упрощается.
В приведенных выше примерах процесс обработки ошибок в основном рассматривался как средство создания интерфейса, в котором пользователь не обнаруживает следов возникших нарушений в работе. По такому же принципу можно обеспечить применение этих средств для упрощения регистрации ошибок и отладки в интересах программиста. Для этого достаточно включить вызов встроенной функции, такой как error_log(), и передать в эту функцию любую релевантную информацию, которая может помочь в процессе отладки, как в следующем коде. Следует учитывать, что в ходе разработки может потребоваться прибегнуть к использованию функции getTraceAsString(), позволяющей обеспечить ведение журналов:
Код PHP
function error_msg($type, $msg, $file, $line)
{
// Записать в журнал ошибок
$log_msg = "Тип ошибки: $type, сообщение: $msg, файл: $file, номер строки: $line, время возникновения: ".time();
$log_path = "tmp/php_errors.log";
error_log($log_msg, 3, $log_path);
}
set_error_handler("error_msg");
trigger_error("Тестируем сообщение уровня 'Notice'", E_USER_NOTICE);Функция error_log() принимает в качестве второго параметра одно из четырех целых чисел, описание которых приведено ниже. Этот параметр задает тип сообщения в сочетании с третьим параметром, который указывает на местонахождение объекта — получателя сообщения об ошибке:
-
0 — сообщение, регистрируемое с использованием общесистемного механизма ведения журналов операционной системы.
-
1 — сообщение об ошибке, передаваемое по указанному адресу электронной почты (в качестве четвертого параметра можно ввести дополнительные заголовки).
-
2 — сообщение об ошибке, передаваемое через отладочное соединение PHP (должна быть разрешена дистанционная отладка).
-
3 — сообщение об ошибке, добавляемое в конец указанного файла журнала ошибок.

Ошибки, обнаруживаемые интерпретатором PHP
После того, как мы рассмотрели виды ошибок и способы их обработки, давайте рассмотрим наиболее распространенные нарушения при работе с PHP.
Проблемы, связанные с инсталляцией PHP
Я не стану читать мораль на тему, что не следует одним махом проходить все этапы инсталляции, не разобравшись в документации, а приведу описание нескольких часто встречающихся признаков нарушения в работе, которые обычно появляются после того, как инсталляция PHP выполняется впервые. Если вы устанавливали PHP не вручную, а например через WAMP-сервер, то приведенные ниже проблемы скорее всего у вас не возникнут.
Признак нарушения в работе: в окне браузера отображается текст файла
Если в окне браузера появляется текст сценария PHP вместо результирующего кода HTML, такая ситуация явно свидетельствует о том, что не происходит вызов машины PHP. Проверьте, что обращаетесь к сайту с помощью веб-сервера, а не файловой системы. Применяйте следующий вариант:
https://localhostpre>а не следующий, например:
file://home/httpd/htmlpre>Признак нарушения в работе - блоки PHP отображаются при их передаче по протоколу HTTP в виде текста или браузер выводит приглашение, согласно которому вам следует сохранить файл
Вызов машины PHP не происходит должным образом. Если запрос на получение файла передан правильно, по протоколу HTTP, как было указано в предыдущем подразделе, то наиболее распространенной причиной этой ошибки является то, что заданы не все расширения имен файлов, которые должны обслуживаться веб-сервером и распознаваться интерпретатором PHP. Вторая по степени распространенности причина состоит в том, что файл php.ini находится не в должном месте или содержит неправильную директиву настройки конфигурации.
Признак нарушения в работе - не найден сервер или хост либо страница не могут быть отображены
Если браузер не может найти используемый сервер, то, по-видимому, имеет место нарушение конфигурации DNS (Domain Name Service — служба доменных имен) или веб-сервера. Если доступ к сайту может быть получен с помощью IP-адреса (например, https://127.0.0.1p>
Если невозможно получить доступ к сайту с помощью IP-адреса после выполнения новой инсталляции, то, по всей видимости, пользователь не смог успешно выполнить привязку IP-адреса к сетевому интерфейсу или настроить конфигурацию домена httpd для обработки запросов, относящихся к конкретному домену. А если доступ к сайту не может быть получен с помощью IP-адреса, притом что применяемая инсталляция уже успешно работала, то наиболее вероятное объяснение состоит в том, что веб-сервер остановлен или недоступен по причине, не относящейся к PHP.
Проблемы формирования страницы
В данном разделе рассматриваются проблемы, при возникновении которых интерпретатор PHP, собственно говоря, не сообщает о каких-либо ошибках, но пользователь обнаруживает в окне браузера не те результаты, на получение которых он рассчитывал.
Признак нарушения в работе - полностью пустая страница
Появление пустой страницы может быть вызвано самыми разнообразными причинами. Одной из наиболее распространенных становится неисправимая ошибка в коде PHP, после обнаружения которой интерпретатор PHP не может возобновить нормальную работу. Начинайте отладку с верхней части файла PHP, который вы пытаетесь открыть в браузере, поместив вызов функции die() после открывающего дескриптора <?php:
Код PHP<?php die(print "hello"); ...Если после обновления страницы вы увидите в браузере слово hello, это означает, что проблемы с веб-сервером и самим модулем PHP исключены. Продолжайте перемещать оператор вызова функции die() в коде PHP дальше, до тех пор, пока снова не появится ошибка, выражающаяся в появлении пустой страницы. Не забывайте, что неудачное завершение сценария может также происходить в результате обработки любых файлов, включенных с помощью require, require_once, include и тому подобных конструкций. Если после ввода оператора вызова функции die() непосредственно перед включенным файлом сценарий работает, а вслед за перемещением оператора вызова функции die() непосредственно после включенного файла перестает работать, то можно сделать вывод, что нарушение в работе возникает из-за включенного файла.
Безусловно, еще одной из возможных причин такой ситуации может явиться также то, что модуль PHP вообще не работает. Проверьте это предположение, просмотрев другую страницу из того же каталога, в отношении которой вы уже убедились, что она правильно обрабатывается интерпретатором PHP.
Наконец, пустое окно браузера обнаруживается в тех ситуациях, когда интерпретатор PHP сталкивается с достаточно серьезной ошибкой, а средства формирования сообщений об ошибках отключены. По-видимому, средства вывода сообщений об ошибках следует отключать на производственных серверах по соображениям безопасности, но на серверах, применяемых для разработки, средства вывода сообщений об ошибках в браузер оказывают огромную помощь. Проверьте в файле php.ini параметр display_errors и убедитесь в том, что все необходимые параметры заданы правильно. Если же пользователь действительно отвергает возможность вывода сообщений об ошибках в окно браузера, то ему придется широко использовать в составе средств обработки исключении функцию error_log() как показано выше.
Признак нарушения в работе - в окне веб-браузера обнаруживается код PHP
Если в окне браузера обнаруживается в буквальном виде код PHP, а не развертывается код HTML, который должен быть сформирован в этом фрагменте PHP, то, по-видимому, где-то пропущен начальный дескриптор PHP. (При этом предполагается, что интерпретатор PHP функционирует успешно, а в используемой инсталляции предусмотрены правильные форматы дескрипторов PHP.)
Можно легко забыть, что интерпретатор PHP рассматривает включаемые файлы как представленные в коде HTML, а не в коде PHP, если пользователь не укажет интерпретатору иное с помощью открывающего дескриптора в начале файла.
Ошибки при загрузке страницы
Если интерпретатору PHP не удается найти файл, запрос о загрузке которого получен от пользователя, то обнаруживается целый ряд разнообразных ошибок, описанных ниже.
Признак нарушения в работе — страница не может быть найдена
Если появляется сообщение о том, что страница не может быть найдена, притом, что другие файлы PHP загружаются без каких-либо нарушений, то, по-видимому, допущена ошибка при написании имени файла или определении пути доступа. Еще один вариант состоит в том, что могла возникнуть путаница в отношении того, где находится корневой каталог документов веб-сервера.
Признак нарушения в работе - сообщение Failed opening [file] for inclusion (He удалось открыть [файл] для включения)
Если в файле PHP предусмотрено включение других файлов PHP, иногда встречаются ошибки, подобные показанной ниже:
Warning Failed opening 'C:InetPubwwwrootasdf.php' for inclusion (ihclude_path='') in [no active file] on line 0Можно считать, что это сообщение представляет собой вариант сообщения Page cannot be found (He удается найти страницу), относящийся к включаемым файлам. Появление этого сообщения свидетельствует о том, что интерпретатору PHP не удалось загрузить даже первую строку активизированного файла. Активизированный файл отсутствует, поскольку не удается найти файл с указанным именем.
Появление такого сообщения возможно также в связи с тем, что права доступа к файлу, который вы пытаетесь загрузить, заданы неправильно.
Ошибки интерпретации
Наиболее распространенная категория ошибок возникает при обработке содержащего орфографические ошибки или синтаксически неправильного кода PHP, который вызывает сбои в работе машины интерпретации PHP.
Признак нарушения в работе — сообщение об ошибке интерпретации (Parse error)
Безусловно, количество причин возникновения проблем при интерпретации велико, но признак этого нарушения в работе почти всегда остается одинаковым — сообщение об ошибке интерпретации, Parse error:
Сообщение об ошибке интерпретации (Parse error) Все наиболее распространенные причины ошибок интерпретации, подробно описанные ниже, являются довольно незначительными и допускают несложное исправление, особенно если учесть, что интерпретатор PHP сам подсказывает способ их исправления. Тем не менее при любой ошибке интерпретации возвращается идентичное сообщение (в котором изменяются только имена файлов и номера строк) независимо от причины. Любой код HTML, который может находиться в файле с ошибками, не отобразится или не обнаружится в исходном коде, даже если этот код находится перед фрагментом PHP, вызвавшем появление ошибки.
Отсутствие точки с запятой
Ошибка интерпретации возникает, если точка с запятой не стоит, как положено, после каждого оператора PHP. В следующем примере фрагмента PHP в первой строке отсутствует точка с запятой, поэтому операция присваивания значения переменной так и не выполняется:
Код PHP
$count = 2 $level = 4Отсутствие знаков доллара
Еще одна весьма распространенная проблема состоит в том, что пропущен знак доллара, предшествующий имени переменной. Если знак доллара отсутствует в операторе присваивания переменной начального значения, как в следующем примере:
Код PHP
count = 2;то возникает сообщение об ошибке интерпретации. Но если вместо этого знак доллара отсутствует в применяемом впоследствии операторе вывода значения переменной, как в следующем примере:
Код PHP
$count = 2; echo "Количество: count";то интерпретатор PHP не выводит сообщение об ошибке интерпретации. Вместо этого в окне отображается строка "Количество: count".
Это — превосходный пример, показывающий, почему не следует рассчитывать на то, что интерпретатор PHP сообщит вам обо всех ошибках на странице. Безусловно, сообщения об ошибках PHP являются более информативными по сравнению с большинством других средств динамического формирования информационного наполнения, но ошибки, подобные указанной, вполне могут остаться незамеченными, если усилия, предпринятые при проверке правильности кода, не будут соответствовать требованиям решаемой задачи.
Если вам приходится затрачивать значительную часть времени на отладку кода PHP, то для вас может оказаться буквально бесценным редактор текста, позволяющий переходить к строкам с указанными номерами и подсвечивающий все синтаксические ошибки. Я, например, использую удобную IDE Adobe Dreamweaver, которая динамически подсвечивает синтаксические ошибки, а также содержит нумерацию строк, чтобы можно было легко найти другие виды ошибок, которые отображаются в окне браузера:
Подсветка ошибки в Adobe Dreamweaver Подобные программы позволяют избежать большого количества синтаксических ошибок на этапе написания кода.
Проблемы, связанные со сменой режима
Еще одна разновидность нарушений в работе возникает в связи с неправильным переходом в режим PHP и из режима PHP. Если блок PHP не закрыт должным образом, как показано ниже, то возникает ошибка интерпретации:
Код PHP
<?php $count = 2 $level = 4; </body> </html>Данная конкретная проблема переключения режима очень часто возникает при использовании коротких блоков PHP. И наоборот, если пользователь не обозначит должным образом начало блока PHP, то весь оставшийся блок, предназначенный для обработки, будет выглядеть как код HTML.
Кавычки, не обозначенные управляющими последовательностями
При использовании такого стиля разработки, в котором для выработки кода HTML в максимальной степени применяется код PHP, часто возникает еще одна ошибка интерпретации, связанная с тем, что кавычки в строках не обозначаются управляющими последовательностями:
Код PHP
// Неправильная строка echo "Он сказал, - "Что нам делать?""; // Правильная строка echo "Он сказал, - "Что нам делать?"";Другие причины ошибок интерпретации
Проблемы, названные выше, не составляют исчерпывающий список источников ошибок интерпретации. Дело в том, что сбой в работе интерпретатора возникает под воздействием любых нарушений формата оператора PHP, включая незакрытые круглые и квадратные скобки, операции без операндов, не заключенные в круглые скобки выражения проверки в управляющих структурах и т.д. Иногда сообщение об ошибке интерпретации включает сведения о том, что ожидал встретить в коде интерпретатор PHP, но так и не смог обнаружить; такие сведения могут оказаться полезной подсказкой. Если номер строки, указанный в сообщении об ошибке интерпретации, относится к самой последней строке файла, это обычно означает, что какая-то программная конструкция, заключенная в парные символы (кавычки, круглые, фигурные скобки и т.д.), была открыта, но так и не закрыта, а интерпретатор PHP продолжал искать закрывающий символ до достижения самого конца файла.
Проблемы, связанные с использованием функций
Многие проблемы, касающиеся вызова функций, приводят к возникновению неисправимых ошибок, а это означает, что интерпретатор PHP отказывается от обработки оставшейся части сценария.
Признак нарушения в работе - сообщение Call to undefined function my_function()
В коде PHP предпринимается попытка вызвать функцию my_function(), которая еще не была определена. Такая ситуация может возникнуть просто в связи с тем, что допущена ошибка при написании имени функции (встроенной или определяемой пользователем), или лишь потому, что не дано определение функции. Если для загрузки определений пользовательских функций из файлов используется конструкция include или require, следует убедиться в том, что загружаются именно те файлы, которые требуются.
Если же рассматриваемая проблема касается весьма специализированной, встроенной функции (например, относится к средствам XML или к средствам математических вычислений произвольной точности), то причина может состоять в том, что при компиляции и сборке исполняемого файла интерпретатора PHP не было разрешено применение соответствующего семейства функций.
Признак нарушения в работе - сообщение call to undefined function ()
В данном случае интерпретатор PHP пытается вызвать некоторую функцию, но не имеет даже возможности определить ее имя. Такая ситуация возникает исключительно в тех случаях, если в коде применяется выражение в форме $my_function(), где само имя функции показано как переменная. Это означает, что разработчик, скорее всего, случайно поместил знак $ перед выражением вызова функции my_function(), имеющим смысл, или ошибся, специально используя средство задания имени функции с помощью переменной языка PHP. А поскольку $my_function представляет собой переменную с незаданным значением, то интерпретатор PHP подставляет в качестве значения этой переменной пустую строку (которая не может служить в качестве имени определенной функции), после чего выдает приведенное в названии этого подраздела маловыразительное сообщение об ошибке.
Признак нарушения в работе - сообщение Cannot redeclare my_function()
Причина этой проблемы проста — где-то в используемом коде имеется повторно заданное определение функции my_function(), а такая ситуация в языке PHP является недопустимой. Убедитесь в том, что в коде не применяется конструкция include для включения одного и того же файла с определениями функций больше одного раза. Чтобы предотвратить возникновение такой ошибки, необходимо использовать конструкцию include_once или require_once, но с учетом того предостережения, что ошибка, связанная с повторным включением, при этом не устраняется, а просто перестает обнаруживаться.
Почему указанную ситуацию следует рассматривать как потенциальную причину нарушений в работе? Дело в том, что вполне можно представить себе такую ситуацию, что разработчик определил две полностью разные функции, но непреднамеренно присвоил этим функциям одинаковые имена. Это связано с тем риском, что допущенная при этом ошибка проявится в самый неожиданный момент.
Признак нарушения в работе - сообщение Wrong parameter count
Функция, имя которой указано в сообщении об ошибке Wrong parameter count, вызвана с меньшим или большим количеством фактических параметров по сравнению с тем, на обработку которого она рассчитана. Если задано больше параметров, чем требуется, то никаких затруднений не возникает, но если используется меньше параметров по сравнению с ожидаемым, то возникает ошибка.
Обработка исключений
Отладка программ
Оценить статью:
This always works for me:
ini_set('display_errors', '1');
ini_set('display_startup_errors', '1');
error_reporting(E_ALL);
However, this doesn’t make PHP to show parse errors — the only way to show those errors is to modify your php.ini with this line:
display_errors = on
(if you don’t have access to php.ini, then putting this line in .htaccess might work too):
php_flag display_errors 1
anthonyryan1
4,6472 gold badges33 silver badges27 bronze badges
answered Jan 29, 2014 at 11:25
![]()
Fancy JohnFancy John
37.5k3 gold badges26 silver badges25 bronze badges
16
You can’t catch parse errors when enabling error output at runtime, because it parses the file before actually executing anything (and since it encounters an error during this, it won’t execute anything). You’ll need to change the actual server configuration so that display_errors is on and the approriate error_reporting level is used. If you don’t have access to php.ini, you may be able to use .htaccess or similar, depending on the server.
This question may provide additional info.
answered Jun 27, 2009 at 19:14
Michael MadsenMichael Madsen
53.8k7 gold badges72 silver badges83 bronze badges
0
Inside your php.ini:
display_errors = on
Then restart your web server.
j0k
22.4k28 gold badges80 silver badges88 bronze badges
answered Jan 8, 2013 at 9:27
user1803477user1803477
1,5951 gold badge9 silver badges4 bronze badges
5
To display all errors you need to:
1. Have these lines in the PHP script you’re calling from the browser (typically index.php):
error_reporting(E_ALL);
ini_set('display_errors', '1');
2.(a) Make sure that this script has no syntax errors
—or—
2.(b) Set display_errors = On in your php.ini
Otherwise, it can’t even run those 2 lines!
You can check for syntax errors in your script by running (at the command line):
php -l index.php
If you include the script from another PHP script then it will display syntax errors in the included script. For example:
index.php
error_reporting(E_ALL);
ini_set('display_errors', '1');
// Any syntax errors here will result in a blank screen in the browser
include 'my_script.php';
my_script.php
adjfkj // This syntax error will be displayed in the browser
answered Jan 29, 2014 at 9:52
andreandre
1,8311 gold badge16 silver badges8 bronze badges
2
Some web hosting providers allow you to change PHP parameters in the .htaccess file.
You can add the following line:
php_value display_errors 1
I had the same issue as yours and this solution fixed it.
![]()
answered May 18, 2013 at 15:01
KalhuaKalhua
5614 silver badges2 bronze badges
1
You might find all of the settings for «error reporting» or «display errors» do not appear to work in PHP 7. That is because error handling has changed. Try this instead:
try{
// Your code
}
catch(Error $e) {
$trace = $e->getTrace();
echo $e->getMessage().' in '.$e->getFile().' on line '.$e->getLine().' called from '.$trace[0]['file'].' on line '.$trace[0]['line'];
}
Or, to catch exceptions and errors in one go (this is not backward compatible with PHP 5):
try{
// Your code
}
catch(Throwable $e) {
$trace = $e->getTrace();
echo $e->getMessage().' in '.$e->getFile().' on line '.$e->getLine().' called from '.$trace[0]['file'].' on line '.$trace[0]['line'];
}
answered Mar 28, 2016 at 19:26
![]()
Frank ForteFrank Forte
1,89718 silver badges18 bronze badges
9
This will work:
<?php
error_reporting(E_ALL);
ini_set('display_errors', 1);
?>
![]()
answered May 5, 2014 at 13:23
![]()
Mahendra JellaMahendra Jella
5,2801 gold badge32 silver badges38 bronze badges
1
Use:
ini_set('display_errors', 1);
ini_set('display_startup_errors', 1);
error_reporting(E_ALL);
This is the best way to write it, but a syntax error gives blank output, so use the console to check for syntax errors. The best way to debug PHP code is to use the console; run the following:
php -l phpfilename.php
![]()
answered May 4, 2016 at 19:14
Abhijit JagtapAbhijit Jagtap
2,6852 gold badges32 silver badges43 bronze badges
0
Set this in your index.php file:
ini_set('display_errors', 1);
ini_set('display_startup_errors', 1);
error_reporting(E_ALL);
![]()
answered Sep 26, 2017 at 12:32
![]()
Sumit GuptaSumit Gupta
5694 silver badges12 bronze badges
0
Create a file called php.ini in the folder where your PHP file resides.
Inside php.ini add the following code (I am giving an simple error showing code):
display_errors = on
display_startup_errors = on
![]()
answered Mar 31, 2015 at 18:38
NavyaKumarNavyaKumar
5895 silver badges3 bronze badges
As we are now running PHP 7, answers given here are not correct any more. The only one still OK is the one from Frank Forte, as he talks about PHP 7.
On the other side, rather than trying to catch errors with a try/catch you can use a trick: use include.
Here three pieces of code:
File: tst1.php
<?php
error_reporting(E_ALL);
ini_set('display_errors', 'On');
// Missing " and ;
echo "Testing
?>
Running this in PHP 7 will show nothing.
Now, try this:
File: tst2.php
<?php
error_reporting(E_ALL);
ini_set('display_errors', 'On');
include ("tst3.php");
?>
File: tst3.php
<?php
// Missing " and ;
echo "Testing
?>
Now run tst2 which sets the error reporting, and then include tst3. You will see:
Parse error: syntax error, unexpected end of file, expecting variable (T_VARIABLE) or ${ (T_DOLLAR_OPEN_CURLY_BRACES) or {$ (T_CURLY_OPEN) in tst3.php on line 4
![]()
answered May 20, 2017 at 12:07
PeterPeter
1,23318 silver badges32 bronze badges
2
I would usually go with the following code in my plain PHP projects.
if(!defined('ENVIRONMENT')){
define('ENVIRONMENT', 'DEVELOPMENT');
}
$base_url = null;
if (defined('ENVIRONMENT'))
{
switch (ENVIRONMENT)
{
case 'DEVELOPMENT':
$base_url = 'http://localhost/product/';
ini_set('display_errors', 1);
ini_set('display_startup_errors', 1);
error_reporting(E_ALL|E_STRICT);
break;
case 'PRODUCTION':
$base_url = 'Production URL'; /* https://google.com */
error_reporting(0);
/* Mechanism to log errors */
break;
default:
exit('The application environment is not set correctly.');
}
}
answered Feb 1, 2017 at 7:16
If, despite following all of the above answers (or you can’t edit your php.ini file), you still can’t get an error message, try making a new PHP file that enables error reporting and then include the problem file. eg:
error_reporting(E_ALL);
ini_set('display_errors', 1);
require_once('problem_file.php');
Despite having everything set properly in my php.ini file, this was the only way I could catch a namespace error. My exact scenario was:
//file1.php
namespace ab;
class x {
...
}
//file2.php
namespace cd;
use cdx; //Dies because it's not sure which 'x' class to use
class x {
...
}
answered Apr 24, 2015 at 2:55
jxmallettjxmallett
4,0471 gold badge28 silver badges35 bronze badges
2
If you somehow find yourself in a situation where you can’t modifiy the setting via php.ini or .htaccess you’re out of luck for displaying errors when your PHP scripts contain parse errors. You’d then have to resolve to linting the files on the command line like this:
find . -name '*.php' -type f -print0 | xargs -0 -n1 -P8 php -l | grep -v "No syntax errors"
If your host is so locked down that it does not allow changing the value via php.ini or .htaccess, it may also disallow changing the value via ini_set. You can check that with the following PHP script:
<?php
if( !ini_set( 'display_errors', 1 ) ) {
echo "display_errors cannot be set.";
} else {
echo "changing display_errors via script is possible.";
}
answered Jan 11, 2016 at 12:11
chiborgchiborg
26.1k12 gold badges98 silver badges114 bronze badges
1
You can do something like below:
Set the below parameters in your main index file:
ini_set('display_errors', 1);
ini_set('display_startup_errors', 1);
Then based on your requirement you can choose which you want to show:
For all errors, warnings and notices:
error_reporting(E_ALL); OR error_reporting(-1);
For all errors:
error_reporting(E_ERROR);
For all warnings:
error_reporting(E_WARNING);
For all notices:
error_reporting(E_NOTICE);
For more information, check here.
![]()
answered Feb 1, 2017 at 7:33
![]()
Binit GhetiyaBinit Ghetiya
1,8612 gold badges23 silver badges31 bronze badges
1
You can add your own custom error handler, which can provide extra debug information. Furthermore, you can set it up to send you the information via email.
function ERR_HANDLER($errno, $errstr, $errfile, $errline){
$msg = "<b>Something bad happened.</b> [$errno] $errstr <br><br>
<b>File:</b> $errfile <br>
<b>Line:</b> $errline <br>
<pre>".json_encode(debug_backtrace(), JSON_PRETTY_PRINT)."</pre> <br>";
echo $msg;
return false;
}
function EXC_HANDLER($exception){
ERR_HANDLER(0, $exception->getMessage(), $exception->getFile(), $exception->getLine());
}
function shutDownFunction() {
$error = error_get_last();
if ($error["type"] == 1) {
ERR_HANDLER($error["type"], $error["message"], $error["file"], $error["line"]);
}
}
set_error_handler ("ERR_HANDLER", E_ALL & ~E_NOTICE & ~E_STRICT & ~E_DEPRECATED);
register_shutdown_function("shutdownFunction");
set_exception_handler("EXC_HANDLER");
![]()
answered Jun 4, 2017 at 14:41
lintabálintabá
7319 silver badges18 bronze badges
Accepted asnwer including extra options. In PHP files for in my DEVELOPMENT apache vhost (.htaccess if you can ensure it doesn’t get into production):
ini_set('display_errors', '1');
ini_set('display_startup_errors', '1');
error_reporting(E_ALL);
However, this doesn’t make PHP to show parse errors — the only way to show those errors is to modify your php.ini with this line:
display_errors = on
(if you don’t have access to php.ini, then putting this line in .htaccess might work too):
// I've added some extra options that set E_ALL as per https://www.php.net/manual/en/errorfunc.configuration.php.
php_flag log_errors on
php_flag display_errors on
php_flag display_startup_errors on
php_value error_reporting 2147483647
php_value error_log /var/www/mywebsite.ext/logs/php.error.log
answered Jan 8, 2022 at 22:17
![]()
This code on top should work:
error_reporting(E_ALL);
However, try to edit the code on the phone in the file:
error_reporting =on
![]()
answered May 9, 2017 at 3:28
![]()
Joel WemboJoel Wembo
8146 silver badges10 bronze badges
The best/easy/fast solution that you can use if it’s a quick debugging, is to surround your code with catching exceptions. That’s what I’m doing when I want to check something fast in production.
try {
// Page code
}
catch (Exception $e) {
echo 'Caught exception: ', $e->getMessage(), "n";
}
![]()
answered Mar 27, 2017 at 2:31
![]()
XakiruXakiru
2,4211 gold badge14 silver badges11 bronze badges
1
<?php
// Turn off error reporting
error_reporting(0);
// Report runtime errors
error_reporting(E_ERROR | E_WARNING | E_PARSE);
// Report all errors
error_reporting(E_ALL);
// Same as error_reporting(E_ALL);
ini_set("error_reporting", E_ALL);
// Report all errors except E_NOTICE
error_reporting(E_ALL & ~E_NOTICE);
?>
While your site is live, the php.ini file should have display_errors disabled for security reasons. However, for the development environment, display_errors can be enabled for troubleshooting.
![]()
answered May 24, 2018 at 8:48
pardeeppardeep
3511 gold badge5 silver badges7 bronze badges
0
Just write:
error_reporting(-1);
answered Jan 13, 2017 at 18:56
![]()
jewelhuqjewelhuq
1,19214 silver badges19 bronze badges
0
You can do this by changing the php.ini file and add the following
display_errors = on
display_startup_errors = on
OR you can also use the following code as this always works for me
ini_set('display_errors', 1);
ini_set('display_startup_errors', 1);
error_reporting(E_ALL);
answered Apr 11, 2019 at 8:43
![]()
0
If you have Xdebug installed you can override every setting by setting:
xdebug.force_display_errors = 1;
xdebug.force_error_reporting = -1;
force_display_errors
Type: int, Default value: 0, Introduced in Xdebug >= 2.3 If this
setting is set to 1 then errors will always be displayed, no matter
what the setting of PHP’s display_errors is.force_error_reporting
Type: int, Default value: 0, Introduced in Xdebug >= 2.3
This setting is a bitmask, like error_reporting. This bitmask will be logically ORed with the bitmask represented by error_reporting to dermine which errors should be displayed. This setting can only be made in php.ini and allows you to force certain errors from being shown no matter what an application does with ini_set().
![]()
answered Oct 19, 2017 at 5:45
You might want to use this code:
ini_set('display_errors', 1);
ini_set('display_startup_errors', 1);
error_reporting(E_ALL);
![]()
baduker
17.3k9 gold badges31 silver badges51 bronze badges
answered Mar 28, 2019 at 12:42
Input this on the top of your code
ini_set('display_errors', '1');
ini_set('display_startup_errors', '1');
error_reporting(E_ALL);
And in the php.ini file, insert this:
display_errors = on
This must work.
answered Aug 23, 2021 at 21:22
![]()
Report all errors except E_NOTICE
error_reporting(E_ALL & ~E_NOTICE);
Display all PHP errors
error_reporting(E_ALL); or ini_set('error_reporting', E_ALL);
Turn off all error reporting
error_reporting(0);
answered Dec 31, 2019 at 10:07
![]()
If it is on the command line, you can run php with -ddisplay_errors=1 to override the setting in php.ini:
php -ddisplay_errors=1 script.php
![]()
answered Oct 24, 2019 at 23:11
gvlasovgvlasov
17.7k19 gold badges69 silver badges106 bronze badges
error_reporting(1);
ini_set('display_errors', '1');
ini_set('display_startup_errors', '1');
error_reporting(E_ALL);
Put this at the top of your page.
answered Feb 28, 2021 at 0:51
![]()
KwedKwed
2313 silver badges4 bronze badges
You can show Php error in your display via simple ways.
Firstly, just put this below code in your php.ini file.
display_errors = on;
(if you don’t have access to php.ini, then putting this line in .htaccess might work too):
php_flag display_errors 1
OR you can also use the following code in your index.php file
ini_set('display_errors', 1);
ini_set('display_startup_errors', 1);
error_reporting(E_ALL);
answered Nov 6, 2020 at 6:41
![]()
In Unix CLI, it’s very practical to redirect only errors to a file:
./script 2> errors.log
From your script, either use var_dump() or equivalent as usual (both STDOUT and STDERR will receive the output), but to write only in the log file:
fwrite(STDERR, "Debug infosn"); // Write in errors.log^
Then from another shell, for live changes:
tail -f errors.log
or simply
watch cat errors.log
answered Nov 26, 2019 at 2:28
![]()
NVRMNVRM
10.5k1 gold badge82 silver badges85 bronze badges
2
This always works for me:
ini_set('display_errors', '1');
ini_set('display_startup_errors', '1');
error_reporting(E_ALL);
However, this doesn’t make PHP to show parse errors — the only way to show those errors is to modify your php.ini with this line:
display_errors = on
(if you don’t have access to php.ini, then putting this line in .htaccess might work too):
php_flag display_errors 1
anthonyryan1
4,6472 gold badges33 silver badges27 bronze badges
answered Jan 29, 2014 at 11:25
![]()
Fancy JohnFancy John
37.5k3 gold badges26 silver badges25 bronze badges
16
You can’t catch parse errors when enabling error output at runtime, because it parses the file before actually executing anything (and since it encounters an error during this, it won’t execute anything). You’ll need to change the actual server configuration so that display_errors is on and the approriate error_reporting level is used. If you don’t have access to php.ini, you may be able to use .htaccess or similar, depending on the server.
This question may provide additional info.
answered Jun 27, 2009 at 19:14
Michael MadsenMichael Madsen
53.8k7 gold badges72 silver badges83 bronze badges
0
Inside your php.ini:
display_errors = on
Then restart your web server.
j0k
22.4k28 gold badges80 silver badges88 bronze badges
answered Jan 8, 2013 at 9:27
user1803477user1803477
1,5951 gold badge9 silver badges4 bronze badges
5
To display all errors you need to:
1. Have these lines in the PHP script you’re calling from the browser (typically index.php):
error_reporting(E_ALL);
ini_set('display_errors', '1');
2.(a) Make sure that this script has no syntax errors
—or—
2.(b) Set display_errors = On in your php.ini
Otherwise, it can’t even run those 2 lines!
You can check for syntax errors in your script by running (at the command line):
php -l index.php
If you include the script from another PHP script then it will display syntax errors in the included script. For example:
index.php
error_reporting(E_ALL);
ini_set('display_errors', '1');
// Any syntax errors here will result in a blank screen in the browser
include 'my_script.php';
my_script.php
adjfkj // This syntax error will be displayed in the browser
answered Jan 29, 2014 at 9:52
andreandre
1,8311 gold badge16 silver badges8 bronze badges
2
Some web hosting providers allow you to change PHP parameters in the .htaccess file.
You can add the following line:
php_value display_errors 1
I had the same issue as yours and this solution fixed it.
![]()
answered May 18, 2013 at 15:01
KalhuaKalhua
5614 silver badges2 bronze badges
1
You might find all of the settings for «error reporting» or «display errors» do not appear to work in PHP 7. That is because error handling has changed. Try this instead:
try{
// Your code
}
catch(Error $e) {
$trace = $e->getTrace();
echo $e->getMessage().' in '.$e->getFile().' on line '.$e->getLine().' called from '.$trace[0]['file'].' on line '.$trace[0]['line'];
}
Or, to catch exceptions and errors in one go (this is not backward compatible with PHP 5):
try{
// Your code
}
catch(Throwable $e) {
$trace = $e->getTrace();
echo $e->getMessage().' in '.$e->getFile().' on line '.$e->getLine().' called from '.$trace[0]['file'].' on line '.$trace[0]['line'];
}
answered Mar 28, 2016 at 19:26
![]()
Frank ForteFrank Forte
1,89718 silver badges18 bronze badges
9
This will work:
<?php
error_reporting(E_ALL);
ini_set('display_errors', 1);
?>
![]()
answered May 5, 2014 at 13:23
![]()
Mahendra JellaMahendra Jella
5,2801 gold badge32 silver badges38 bronze badges
1
Use:
ini_set('display_errors', 1);
ini_set('display_startup_errors', 1);
error_reporting(E_ALL);
This is the best way to write it, but a syntax error gives blank output, so use the console to check for syntax errors. The best way to debug PHP code is to use the console; run the following:
php -l phpfilename.php
![]()
answered May 4, 2016 at 19:14
Abhijit JagtapAbhijit Jagtap
2,6852 gold badges32 silver badges43 bronze badges
0
Set this in your index.php file:
ini_set('display_errors', 1);
ini_set('display_startup_errors', 1);
error_reporting(E_ALL);
![]()
answered Sep 26, 2017 at 12:32
![]()
Sumit GuptaSumit Gupta
5694 silver badges12 bronze badges
0
Create a file called php.ini in the folder where your PHP file resides.
Inside php.ini add the following code (I am giving an simple error showing code):
display_errors = on
display_startup_errors = on
![]()
answered Mar 31, 2015 at 18:38
NavyaKumarNavyaKumar
5895 silver badges3 bronze badges
As we are now running PHP 7, answers given here are not correct any more. The only one still OK is the one from Frank Forte, as he talks about PHP 7.
On the other side, rather than trying to catch errors with a try/catch you can use a trick: use include.
Here three pieces of code:
File: tst1.php
<?php
error_reporting(E_ALL);
ini_set('display_errors', 'On');
// Missing " and ;
echo "Testing
?>
Running this in PHP 7 will show nothing.
Now, try this:
File: tst2.php
<?php
error_reporting(E_ALL);
ini_set('display_errors', 'On');
include ("tst3.php");
?>
File: tst3.php
<?php
// Missing " and ;
echo "Testing
?>
Now run tst2 which sets the error reporting, and then include tst3. You will see:
Parse error: syntax error, unexpected end of file, expecting variable (T_VARIABLE) or ${ (T_DOLLAR_OPEN_CURLY_BRACES) or {$ (T_CURLY_OPEN) in tst3.php on line 4
![]()
answered May 20, 2017 at 12:07
PeterPeter
1,23318 silver badges32 bronze badges
2
I would usually go with the following code in my plain PHP projects.
if(!defined('ENVIRONMENT')){
define('ENVIRONMENT', 'DEVELOPMENT');
}
$base_url = null;
if (defined('ENVIRONMENT'))
{
switch (ENVIRONMENT)
{
case 'DEVELOPMENT':
$base_url = 'http://localhost/product/';
ini_set('display_errors', 1);
ini_set('display_startup_errors', 1);
error_reporting(E_ALL|E_STRICT);
break;
case 'PRODUCTION':
$base_url = 'Production URL'; /* https://google.com */
error_reporting(0);
/* Mechanism to log errors */
break;
default:
exit('The application environment is not set correctly.');
}
}
answered Feb 1, 2017 at 7:16
If, despite following all of the above answers (or you can’t edit your php.ini file), you still can’t get an error message, try making a new PHP file that enables error reporting and then include the problem file. eg:
error_reporting(E_ALL);
ini_set('display_errors', 1);
require_once('problem_file.php');
Despite having everything set properly in my php.ini file, this was the only way I could catch a namespace error. My exact scenario was:
//file1.php
namespace ab;
class x {
...
}
//file2.php
namespace cd;
use cdx; //Dies because it's not sure which 'x' class to use
class x {
...
}
answered Apr 24, 2015 at 2:55
jxmallettjxmallett
4,0471 gold badge28 silver badges35 bronze badges
2
If you somehow find yourself in a situation where you can’t modifiy the setting via php.ini or .htaccess you’re out of luck for displaying errors when your PHP scripts contain parse errors. You’d then have to resolve to linting the files on the command line like this:
find . -name '*.php' -type f -print0 | xargs -0 -n1 -P8 php -l | grep -v "No syntax errors"
If your host is so locked down that it does not allow changing the value via php.ini or .htaccess, it may also disallow changing the value via ini_set. You can check that with the following PHP script:
<?php
if( !ini_set( 'display_errors', 1 ) ) {
echo "display_errors cannot be set.";
} else {
echo "changing display_errors via script is possible.";
}
answered Jan 11, 2016 at 12:11
chiborgchiborg
26.1k12 gold badges98 silver badges114 bronze badges
1
You can do something like below:
Set the below parameters in your main index file:
ini_set('display_errors', 1);
ini_set('display_startup_errors', 1);
Then based on your requirement you can choose which you want to show:
For all errors, warnings and notices:
error_reporting(E_ALL); OR error_reporting(-1);
For all errors:
error_reporting(E_ERROR);
For all warnings:
error_reporting(E_WARNING);
For all notices:
error_reporting(E_NOTICE);
For more information, check here.
![]()
answered Feb 1, 2017 at 7:33
![]()
Binit GhetiyaBinit Ghetiya
1,8612 gold badges23 silver badges31 bronze badges
1
You can add your own custom error handler, which can provide extra debug information. Furthermore, you can set it up to send you the information via email.
function ERR_HANDLER($errno, $errstr, $errfile, $errline){
$msg = "<b>Something bad happened.</b> [$errno] $errstr <br><br>
<b>File:</b> $errfile <br>
<b>Line:</b> $errline <br>
<pre>".json_encode(debug_backtrace(), JSON_PRETTY_PRINT)."</pre> <br>";
echo $msg;
return false;
}
function EXC_HANDLER($exception){
ERR_HANDLER(0, $exception->getMessage(), $exception->getFile(), $exception->getLine());
}
function shutDownFunction() {
$error = error_get_last();
if ($error["type"] == 1) {
ERR_HANDLER($error["type"], $error["message"], $error["file"], $error["line"]);
}
}
set_error_handler ("ERR_HANDLER", E_ALL & ~E_NOTICE & ~E_STRICT & ~E_DEPRECATED);
register_shutdown_function("shutdownFunction");
set_exception_handler("EXC_HANDLER");
![]()
answered Jun 4, 2017 at 14:41
lintabálintabá
7319 silver badges18 bronze badges
Accepted asnwer including extra options. In PHP files for in my DEVELOPMENT apache vhost (.htaccess if you can ensure it doesn’t get into production):
ini_set('display_errors', '1');
ini_set('display_startup_errors', '1');
error_reporting(E_ALL);
However, this doesn’t make PHP to show parse errors — the only way to show those errors is to modify your php.ini with this line:
display_errors = on
(if you don’t have access to php.ini, then putting this line in .htaccess might work too):
// I've added some extra options that set E_ALL as per https://www.php.net/manual/en/errorfunc.configuration.php.
php_flag log_errors on
php_flag display_errors on
php_flag display_startup_errors on
php_value error_reporting 2147483647
php_value error_log /var/www/mywebsite.ext/logs/php.error.log
answered Jan 8, 2022 at 22:17
![]()
This code on top should work:
error_reporting(E_ALL);
However, try to edit the code on the phone in the file:
error_reporting =on
![]()
answered May 9, 2017 at 3:28
![]()
Joel WemboJoel Wembo
8146 silver badges10 bronze badges
The best/easy/fast solution that you can use if it’s a quick debugging, is to surround your code with catching exceptions. That’s what I’m doing when I want to check something fast in production.
try {
// Page code
}
catch (Exception $e) {
echo 'Caught exception: ', $e->getMessage(), "n";
}
![]()
answered Mar 27, 2017 at 2:31
![]()
XakiruXakiru
2,4211 gold badge14 silver badges11 bronze badges
1
<?php
// Turn off error reporting
error_reporting(0);
// Report runtime errors
error_reporting(E_ERROR | E_WARNING | E_PARSE);
// Report all errors
error_reporting(E_ALL);
// Same as error_reporting(E_ALL);
ini_set("error_reporting", E_ALL);
// Report all errors except E_NOTICE
error_reporting(E_ALL & ~E_NOTICE);
?>
While your site is live, the php.ini file should have display_errors disabled for security reasons. However, for the development environment, display_errors can be enabled for troubleshooting.
![]()
answered May 24, 2018 at 8:48
pardeeppardeep
3511 gold badge5 silver badges7 bronze badges
0
Just write:
error_reporting(-1);
answered Jan 13, 2017 at 18:56
![]()
jewelhuqjewelhuq
1,19214 silver badges19 bronze badges
0
You can do this by changing the php.ini file and add the following
display_errors = on
display_startup_errors = on
OR you can also use the following code as this always works for me
ini_set('display_errors', 1);
ini_set('display_startup_errors', 1);
error_reporting(E_ALL);
answered Apr 11, 2019 at 8:43
![]()
0
If you have Xdebug installed you can override every setting by setting:
xdebug.force_display_errors = 1;
xdebug.force_error_reporting = -1;
force_display_errors
Type: int, Default value: 0, Introduced in Xdebug >= 2.3 If this
setting is set to 1 then errors will always be displayed, no matter
what the setting of PHP’s display_errors is.force_error_reporting
Type: int, Default value: 0, Introduced in Xdebug >= 2.3
This setting is a bitmask, like error_reporting. This bitmask will be logically ORed with the bitmask represented by error_reporting to dermine which errors should be displayed. This setting can only be made in php.ini and allows you to force certain errors from being shown no matter what an application does with ini_set().
![]()
answered Oct 19, 2017 at 5:45
You might want to use this code:
ini_set('display_errors', 1);
ini_set('display_startup_errors', 1);
error_reporting(E_ALL);
![]()
baduker
17.3k9 gold badges31 silver badges51 bronze badges
answered Mar 28, 2019 at 12:42
Input this on the top of your code
ini_set('display_errors', '1');
ini_set('display_startup_errors', '1');
error_reporting(E_ALL);
And in the php.ini file, insert this:
display_errors = on
This must work.
answered Aug 23, 2021 at 21:22
![]()
Report all errors except E_NOTICE
error_reporting(E_ALL & ~E_NOTICE);
Display all PHP errors
error_reporting(E_ALL); or ini_set('error_reporting', E_ALL);
Turn off all error reporting
error_reporting(0);
answered Dec 31, 2019 at 10:07
![]()
If it is on the command line, you can run php with -ddisplay_errors=1 to override the setting in php.ini:
php -ddisplay_errors=1 script.php
![]()
answered Oct 24, 2019 at 23:11
gvlasovgvlasov
17.7k19 gold badges69 silver badges106 bronze badges
error_reporting(1);
ini_set('display_errors', '1');
ini_set('display_startup_errors', '1');
error_reporting(E_ALL);
Put this at the top of your page.
answered Feb 28, 2021 at 0:51
![]()
KwedKwed
2313 silver badges4 bronze badges
You can show Php error in your display via simple ways.
Firstly, just put this below code in your php.ini file.
display_errors = on;
(if you don’t have access to php.ini, then putting this line in .htaccess might work too):
php_flag display_errors 1
OR you can also use the following code in your index.php file
ini_set('display_errors', 1);
ini_set('display_startup_errors', 1);
error_reporting(E_ALL);
answered Nov 6, 2020 at 6:41
![]()
In Unix CLI, it’s very practical to redirect only errors to a file:
./script 2> errors.log
From your script, either use var_dump() or equivalent as usual (both STDOUT and STDERR will receive the output), but to write only in the log file:
fwrite(STDERR, "Debug infosn"); // Write in errors.log^
Then from another shell, for live changes:
tail -f errors.log
or simply
watch cat errors.log
answered Nov 26, 2019 at 2:28
![]()
NVRMNVRM
10.5k1 gold badge82 silver badges85 bronze badges
2
PHP — это один из самых популярных языков программирования для создания сайтов и веб-приложений. На нем разработано множество готовых систем управления контентом для блогов, сайтов фирм или даже интернет-магазинов. Несмотря на то что у этого языка есть свои недостатки, он достаточно прост в освоении и поэтому очень часто используется для разработки новых сайтов.
Интерпретатор php может поставляться в виде модуля для Apache, выполнять скрипты из командной строки или в виде отдельного сервиса php-fpm. Эти сервисы отличаются своими возможностями, и предназначением, но для любого вида интерпретатора нужно задать базовые настройки, например, рабочая папка, включенные расширения, отображение ошибок и так далее. Все эти настройки задаются через файл php.ini. В этой инструкции мы рассмотрим как выполняется настройка файла php.ini в операционных системах Linux, хотя все информация подойдет и для Windows.
Если у вас еще не установлен интерпретатор языка программирования php, то вы можете ознакомиться со статьей установка lamp в Ubuntu 16.04.
Для каждой версии интерпретатора конфигурационный файл php.ini находится в отдельной папке. Но все конфигурационные файлы находятся в папке /etc/php, например, /etc/php5:
ls /etc/php5/
Папка conf.d содержит общие настройки для различных расширений и модулей, они не будут нас сейчас интересовать. Более интересны следующие три папки — apache, cli и fpm. В них содержатся конфигурационные файлы php.ini для каждого из этих интерпретаторов.
Если вы собираетесь использовать несколько из этих интерпретаторов, то вам придется указывать настройки для каждого из них отдельно. Вы можете убедиться, что в каждой из папок лежит файл php.ini.
Что касается синтаксиса файла, то он разделен на секции, сначала идет секция настройки php, которая разделена на подсекции в зависимости от типа настроек, дальше идут секции настройки разных модулей. Синтаксис самих настроек очень прост, он соответствует привычному синтаксису ini файлов. Строка начинается с имени настройки, затем следует знак равно, а за ним значение:
имя_настройки=значение_параметра
Символами [] обозначается имя секции, например, [PHP], а символ ; означает комментарий, он и все символы после него не читаются интерпретатором. А теперь рассмотрим как выполняется настройка php.ini и переберем самые важные параметры.
Настройка файла php.ini
Для удобства ориентирования мы разобьем все параметры по категориях в зависимости от их назначения. Вам будет достаточно найти нужный параметр и изменить его значение. А теперь откройте файл настроек php, например, для модуля apache и перейдем к настройке. Чтобы избежать ошибок не добавляйте новые строки, а ищите уже существующие и изменяйте значения на нужные:
sudo gedit /etc/php5/apache/php.ini
Сначала идет немного информации о самом файле в виде комментариев, затем интересующие нас настройки.
Вывод ошибок в php
Настройка php 7 обычно начинается с конфигурации вывода ошибок. Все настройки вывода ошибок находятся в разделе Error handling and logging. По умолчанию вывод ошибок на экран во время выполнения скрипта отключен. Это сделано для того, чтобы пользователи не смогли увидеть ничего лишнего. Вместо этого, все ошибки записываются в лог файл. Если вы используете php на домашнем компьютере, то такие меры не нужны и вы можете сразу выводить все на экран:
display_errors=off
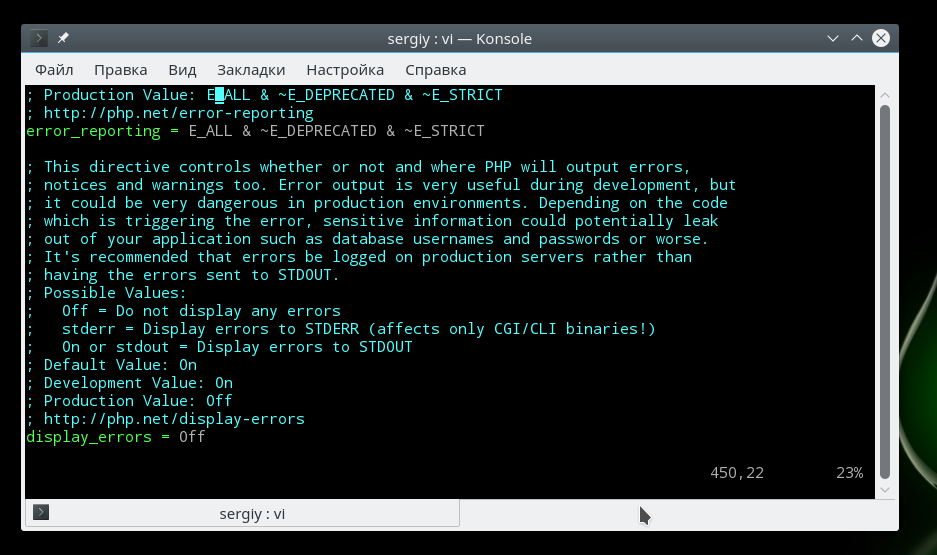
Замените off на on. В php используются различные типы ошибок, например, критические, предупреждения, ошибки синтаксиса, с помощью строки error_reporting вы можете включить вывод только определенных типов ошибок:
error_reporting = E_ALL & ~E_DEPRECATED
Если нужно объединить несколько типов ошибок, то используйте символ &, а для отключения отображения поставьте перед типом знак ~. Приведенный выше пример отображает все ошибки (E_ALL), кроме сообщений об устаревших функциях (E_DEPRECATED). Вы можете отключить все типы использовав 0:
error_reporting = 0
Включите запись ошибок php в лог файл, если не выводите их на экран:
log_errors = On
Чтобы не засорять лог однотипными сообщениями можно игнорировать повторяющиеся ошибки в пределах одного исполнения:
ignore_repeated_errors = On
Ограничения ресурсов
Если бы скрипты php никак не ограничивались в ресурсах, то они запросто могли бы перегрузить сервер и не дать ему нормально работать. Поэтому, по умолчанию php устанавливает жесткие ограничения, но, возможно, вам нужно будет их немного ослабить.
По умолчанию максимальное время выполнения скрипта — 30 секунд, сделаем минуту:
max_execution_time = 30
Если указать 0, то скрипт может выполняться бесконечно. Вы также можете ограничить время, на протяжении которого скрипт будет загружать данные, 60 секунд:
max_input_time=60
Максимальное количество переменных в GET и POST:
max_input_vars = 1000
Следующий параметр задает максимальное количество памяти, которую может использовать один скрипт во время своего выполнения, в мегабайтах:
memory_limit = 128M
Максимальный размер данных, передаваемых в POST запросе тоже ограничивается, размер по умолчанию — 8 Мегабайт:
post_max_size = 8M
Вы можете ограничить область действия php в системе с помощью опции openbase_dir, она указывает папку, выше которой скрипт не может получить доступ к файловой системе:
open_basedir = /var/www/
С помощью директив disable_functions и disable_classes вы можете отключить использование в скриптах определенных функций или классов, например, это может быть полезно для веб-хостингов. В этом примере мы отключаем использование функции ini_set, которая позволяет менять настройки php из скрипта:
disable_functions = ini_set
Директории по умолчанию
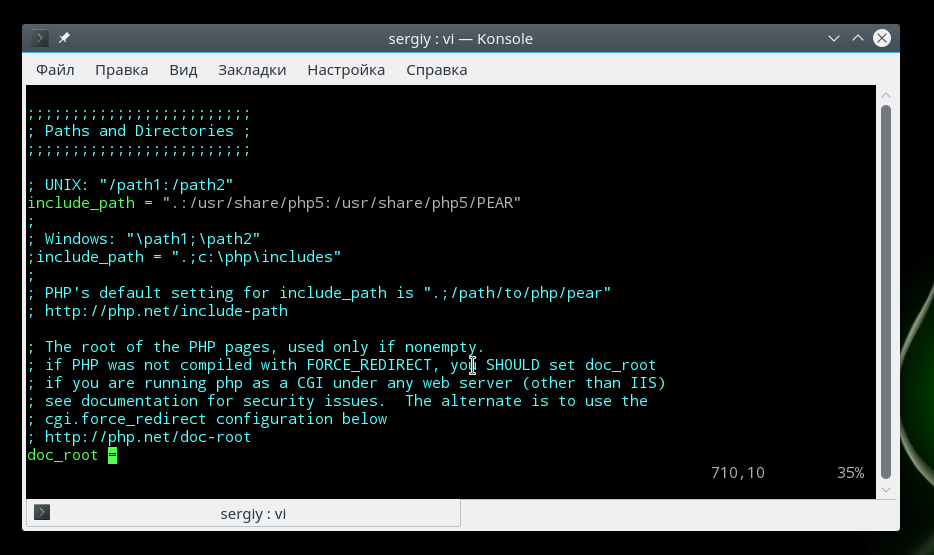
Файл настройки php.ini позволяет указать пути в файловой системе по умолчанию для различных действий. Вы можете задать папки где система будет искать скрипты, если вы попытаетесь подключить их с помощью инструкции include:
include_path = ".:/usr/share/php5:/usr/share/php5/PEAR"
Папка с модулями php:
extension_dir="./"
Папка для записи временных файлов:
sys_temp_dir = "/tmp"
Загрузка файлов
Для того чтобы пользователи могли загружать свои файлы на сервер, например, фото, нужно включить эту функцию в php:
file_uploads = On
Максимальный размер загружаемого файла:
upload_max_filesize = 2M
Максимальное количество файлов, которые может загрузить один скрипт:
max_file_uploads = 20
Настройка php.ini практически завершена, нам остались лишь расширения.
Настройка расширений
Расширения позволяют очень сильно увеличить функциональность php. Например, благодаря расширениям вы можете использовать в своих скриптах базы данных mysql, postgresql, mysqli, sqlite, графическую библиотеку gd и многое другое. Все это включается в этом разделе.
Для включения расширения достаточно убрать комментарий перед строкой с его командой, например:
extension=php_mysql.so
extension=php_mbstring.so
extension=php_pgsql.so
Обратите внимание, что для windows расширение будет иметь формат dll, но для linux нужно использовать so. В следующих секциях идет настройка каждого из расширений, но мы их рассматривать не будем потому что они обычно не требуют настройки.
Выводы
В этой статье мы рассмотрели как выполняется настройка php на сервере или обычном компьютере для разработки веб-сайтов. Файл настроек php имеет довольно простую структуру и с ним довольно не сложно справиться. После завершения всех настроек и сохранения изменений не забудьте перезагрузить веб-сервер или сервис php-fpm.
Вообще говоря, php-fpm это отдельная тема, потому что там есть много дополнительных настроек, и, возможно, мы рассмотрим его в одной из следующих статей. Если у вас остались вопросы, спрашивайте в комментариях!

Статья распространяется под лицензией Creative Commons ShareAlike 4.0 при копировании материала ссылка на источник обязательна .
DEV environment
This always works for me:
ini_set('display_errors', '1');
ini_set('display_startup_errors', '1');
error_reporting(E_ALL);
However, this doesn’t make PHP to show parse errors occurred in the same file — the only way to show those errors is to modify your php.ini with this line:
display_errors = on
(if you don’t have access to php.ini, then putting this line in .htaccess might work too):
php_flag display_errors 1
PROD environment
Note that above recommentdtion is only suitable for the dev environment. On a live site it must be
display_errors = off
log_errors = on
And then you’ll be able to see all errors in the error log. See Where to find PHP error log
AJAX calls
In case of AJAX call, on a dev server open DevTools (F12), then Network tab.
Then initiate the request which result you want to see, and it will appear in the Network tab. Click on it and then the Response tab. There you will see the exact output.
While on a live server just check the error log all the same.
![]()
answered Jan 29, 2014 at 11:25
![]()
Fancy JohnFancy John
38k3 gold badges27 silver badges27 bronze badges
16
You can’t catch parse errors in the same file where error output is enabled at runtime, because it parses the file before actually executing anything (and since it encounters an error during this, it won’t execute anything). You’ll need to change the actual server configuration so that display_errors is on and the approriate error_reporting level is used. If you don’t have access to php.ini, you may be able to use .htaccess or similar, depending on the server.
This question may provide additional info.
![]()
answered Jun 27, 2009 at 19:14
Michael MadsenMichael Madsen
54.2k8 gold badges72 silver badges83 bronze badges
0
Inside your php.ini:
display_errors = on
Then restart your web server.
j0k
22.5k28 gold badges79 silver badges89 bronze badges
answered Jan 8, 2013 at 9:27
user1803477user1803477
1,6151 gold badge10 silver badges4 bronze badges
5
To display all errors you need to:
1. Have these lines in the PHP script you’re calling from the browser (typically index.php):
error_reporting(E_ALL);
ini_set('display_errors', '1');
2.(a) Make sure that this script has no syntax errors
—or—
2.(b) Set display_errors = On in your php.ini
Otherwise, it can’t even run those 2 lines!
You can check for syntax errors in your script by running (at the command line):
php -l index.php
If you include the script from another PHP script then it will display syntax errors in the included script. For example:
index.php
error_reporting(E_ALL);
ini_set('display_errors', '1');
// Any syntax errors here will result in a blank screen in the browser
include 'my_script.php';
my_script.php
adjfkj // This syntax error will be displayed in the browser
answered Jan 29, 2014 at 9:52
andreandre
1,8311 gold badge16 silver badges8 bronze badges
2
Some web hosting providers allow you to change PHP parameters in the .htaccess file.
You can add the following line:
php_value display_errors 1
I had the same issue as yours and this solution fixed it.
![]()
answered May 18, 2013 at 15:01
KalhuaKalhua
5594 silver badges2 bronze badges
1
Warning: the below answer is factually incorrect. Nothing has been changed in error handling, uncaught exceptions are displayed just like other errors. Suggested approach must be used with caution, because it outputs errors unconditionally, despite the display_error setting and may pose a threat by revealing the sensitive information to an outsider on a live site.
You might find all of the settings for «error reporting» or «display errors» do not appear to work in PHP 7. That is because error handling has changed. Try this instead:
try{
// Your code
}
catch(Error $e) {
$trace = $e->getTrace();
echo $e->getMessage().' in '.$e->getFile().' on line '.$e->getLine().' called from '.$trace[0]['file'].' on line '.$trace[0]['line'];
}
Or, to catch exceptions and errors in one go (this is not backward compatible with PHP 5):
try{
// Your code
}
catch(Throwable $e) {
$trace = $e->getTrace();
echo $e->getMessage().' in '.$e->getFile().' on line '.$e->getLine().' called from '.$trace[0]['file'].' on line '.$trace[0]['line'];
}
![]()
answered Mar 28, 2016 at 19:26
![]()
Frank ForteFrank Forte
1,99119 silver badges19 bronze badges
9
This will work:
<?php
error_reporting(E_ALL);
ini_set('display_errors', 1);
?>
![]()
answered May 5, 2014 at 13:23
![]()
Mahendra JellaMahendra Jella
5,4101 gold badge33 silver badges38 bronze badges
1
Use:
ini_set('display_errors', 1);
ini_set('display_startup_errors', 1);
error_reporting(E_ALL);
This is the best way to write it, but a syntax error gives blank output, so use the console to check for syntax errors. The best way to debug PHP code is to use the console; run the following:
php -l phpfilename.php
![]()
answered May 4, 2016 at 19:14
Abhijit JagtapAbhijit Jagtap
2,7302 gold badges29 silver badges43 bronze badges
0
Set this in your index.php file:
ini_set('display_errors', 1);
ini_set('display_startup_errors', 1);
error_reporting(E_ALL);
![]()
answered Sep 26, 2017 at 12:32
![]()
Sumit GuptaSumit Gupta
5674 silver badges12 bronze badges
0
Create a file called php.ini in the folder where your PHP file resides.
Inside php.ini add the following code (I am giving an simple error showing code):
display_errors = on
display_startup_errors = on
![]()
answered Mar 31, 2015 at 18:38
NavyaKumarNavyaKumar
5875 silver badges3 bronze badges
In order to display a parse error, instead of setting display_errors in php.ini you can use a trick: use include.
Here are three pieces of code:
File: tst1.php
<?php
error_reporting(E_ALL);
ini_set('display_errors', 'On');
// Missing " and ;
echo "Testing
When running this file directly, it will show nothing, given display_errors is set to 0 in php.ini.
Now, try this:
File: tst2.php
<?php
error_reporting(E_ALL);
ini_set('display_errors', 'On');
include ("tst3.php");
File: tst3.php
<?php
// Missing " and ;
echo "Testing
Now run tst2.php which sets the error reporting, and then include tst3. You will see:
Parse error: syntax error, unexpected end of file, expecting variable (T_VARIABLE) or ${ (T_DOLLAR_OPEN_CURLY_BRACES) or {$ (T_CURLY_OPEN) in tst3.php on line 4
![]()
answered May 20, 2017 at 12:07
PeterPeter
1,23719 silver badges32 bronze badges
4
If, despite following all of the above answers (or you can’t edit your php.ini file), you still can’t get an error message, try making a new PHP file that enables error reporting and then include the problem file. eg:
error_reporting(E_ALL);
ini_set('display_errors', 1);
require_once('problem_file.php');
Despite having everything set properly in my php.ini file, this was the only way I could catch a namespace error. My exact scenario was:
//file1.php
namespace ab;
class x {
...
}
//file2.php
namespace cd;
use cdx; //Dies because it's not sure which 'x' class to use
class x {
...
}
answered Apr 24, 2015 at 2:55
jxmallettjxmallett
4,0771 gold badge28 silver badges35 bronze badges
2
I would usually go with the following code in my plain PHP projects.
if(!defined('ENVIRONMENT')){
define('ENVIRONMENT', 'DEVELOPMENT');
}
$base_url = null;
if (defined('ENVIRONMENT'))
{
switch (ENVIRONMENT)
{
case 'DEVELOPMENT':
$base_url = 'http://localhost/product/';
ini_set('display_errors', 1);
ini_set('display_startup_errors', 1);
error_reporting(E_ALL);
break;
case 'PRODUCTION':
$base_url = 'Production URL'; /* https://google.com */
error_reporting(E_ALL);
ini_set('display_errors', 0);
ini_set('display_startup_errors', 0);
ini_set('log_errors', 1); // Mechanism to log errors
break;
default:
exit('The application environment is not set correctly.');
}
}
![]()
answered Feb 1, 2017 at 7:16
If you somehow find yourself in a situation where you can’t modifiy the setting via php.ini or .htaccess you’re out of luck for displaying errors when your PHP scripts contain parse errors. You’d then have to resolve to linting the files on the command line like this:
find . -name '*.php' -type f -print0 | xargs -0 -n1 -P8 php -l | grep -v "No syntax errors"
If your host is so locked down that it does not allow changing the value via php.ini or .htaccess, it may also disallow changing the value via ini_set. You can check that with the following PHP script:
<?php
if( !ini_set( 'display_errors', 1 ) ) {
echo "display_errors cannot be set.";
} else {
echo "changing display_errors via script is possible.";
}
answered Jan 11, 2016 at 12:11
chiborgchiborg
26.8k14 gold badges96 silver badges115 bronze badges
1
You can do something like below:
Set the below parameters in your main index file:
ini_set('display_errors', 1);
ini_set('display_startup_errors', 1);
Then based on your requirement you can choose which you want to show:
For all errors, warnings and notices:
error_reporting(E_ALL); OR error_reporting(-1);
For all errors:
error_reporting(E_ERROR);
For all warnings:
error_reporting(E_WARNING);
For all notices:
error_reporting(E_NOTICE);
For more information, check here.
![]()
answered Feb 1, 2017 at 7:33
![]()
Binit GhetiyaBinit Ghetiya
1,9092 gold badges21 silver badges31 bronze badges
1
You can add your own custom error handler, which can provide extra debug information. Furthermore, you can set it up to send you the information via email.
function ERR_HANDLER($errno, $errstr, $errfile, $errline){
$msg = "<b>Something bad happened.</b> [$errno] $errstr <br><br>
<b>File:</b> $errfile <br>
<b>Line:</b> $errline <br>
<pre>".json_encode(debug_backtrace(), JSON_PRETTY_PRINT)."</pre> <br>";
echo $msg;
return false;
}
function EXC_HANDLER($exception){
ERR_HANDLER(0, $exception->getMessage(), $exception->getFile(), $exception->getLine());
}
function shutDownFunction() {
$error = error_get_last();
if ($error["type"] == 1) {
ERR_HANDLER($error["type"], $error["message"], $error["file"], $error["line"]);
}
}
set_error_handler ("ERR_HANDLER", E_ALL & ~E_NOTICE & ~E_STRICT & ~E_DEPRECATED);
register_shutdown_function("shutdownFunction");
set_exception_handler("EXC_HANDLER");
![]()
answered Jun 4, 2017 at 14:41
lintabálintabá
7339 silver badges18 bronze badges
Accepted asnwer including extra options. In PHP files for in my DEVELOPMENT apache vhost (.htaccess if you can ensure it doesn’t get into production):
ini_set('display_errors', '1');
ini_set('display_startup_errors', '1');
error_reporting(E_ALL);
However, this doesn’t make PHP to show parse errors — the only way to show those errors is to modify your php.ini with this line:
display_errors = on
(if you don’t have access to php.ini, then putting this line in .htaccess might work too):
// I've added some extra options that set E_ALL as per https://www.php.net/manual/en/errorfunc.configuration.php.
php_flag log_errors on
php_flag display_errors on
php_flag display_startup_errors on
php_value error_reporting 2147483647
php_value error_log /var/www/mywebsite.ext/logs/php.error.log
answered Jan 8, 2022 at 22:17
![]()
This code on top should work:
error_reporting(E_ALL);
However, try to edit the code on the phone in the file:
error_reporting =on
![]()
answered May 9, 2017 at 3:28
![]()
Joel WemboJoel Wembo
8146 silver badges10 bronze badges
The best/easy/fast solution that you can use if it’s a quick debugging, is to surround your code with catching exceptions. That’s what I’m doing when I want to check something fast in production.
try {
// Page code
}
catch (Exception $e) {
echo 'Caught exception: ', $e->getMessage(), "n";
}
![]()
answered Mar 27, 2017 at 2:31
![]()
XakiruXakiru
2,5261 gold badge15 silver badges11 bronze badges
3
<?php
// Turn off error reporting
error_reporting(0);
// Report runtime errors
error_reporting(E_ERROR | E_WARNING | E_PARSE);
// Report all errors
error_reporting(E_ALL);
// Same as error_reporting(E_ALL);
ini_set("error_reporting", E_ALL);
// Report all errors except E_NOTICE
error_reporting(E_ALL & ~E_NOTICE);
?>
While your site is live, the php.ini file should have display_errors disabled for security reasons. However, for the development environment, display_errors can be enabled for troubleshooting.
![]()
answered May 24, 2018 at 8:48
pardeeppardeep
3591 gold badge5 silver badges7 bronze badges
0
Just write:
error_reporting(-1);
answered Jan 13, 2017 at 18:56
![]()
jewelhuqjewelhuq
1,20014 silver badges19 bronze badges
0
If you have Xdebug installed you can override every setting by setting:
xdebug.force_display_errors = 1;
xdebug.force_error_reporting = -1;
force_display_errors
Type: int, Default value: 0, Introduced in Xdebug >= 2.3 If this
setting is set to 1 then errors will always be displayed, no matter
what the setting of PHP’s display_errors is.force_error_reporting
Type: int, Default value: 0, Introduced in Xdebug >= 2.3
This setting is a bitmask, like error_reporting. This bitmask will be logically ORed with the bitmask represented by error_reporting to dermine which errors should be displayed. This setting can only be made in php.ini and allows you to force certain errors from being shown no matter what an application does with ini_set().
![]()
answered Oct 19, 2017 at 5:45
If it is on the command line, you can run php with -ddisplay_errors=1 to override the setting in php.ini:
php -ddisplay_errors=1 script.php
![]()
answered Oct 24, 2019 at 23:11
gvlasovgvlasov
18.5k20 gold badges73 silver badges109 bronze badges
Report all errors except E_NOTICE
error_reporting(E_ALL & ~E_NOTICE);
Display all PHP errors
error_reporting(E_ALL); or ini_set('error_reporting', E_ALL);
Turn off all error reporting
error_reporting(0);
answered Dec 31, 2019 at 10:07
![]()
In Unix CLI, it’s very practical to redirect only errors to a file:
./script 2> errors.log
From your script, either use var_dump() or equivalent as usual (both STDOUT and STDERR will receive the output), but to write only in the log file:
fwrite(STDERR, "Debug infosn"); // Write in errors.log^
Then from another shell, for live changes:
tail -f errors.log
or simply
watch cat errors.log
answered Nov 26, 2019 at 2:28
![]()
NVRMNVRM
11.1k1 gold badge88 silver badges85 bronze badges
2
If you are on a SharedHosting plan (like on hostgator)… simply adding
php_flag display_errors 1
into a .htaccess file and uploading it to the remote folder may not yield the actual warnings/errors that were generated on the server.
What you will also need to do is edit the php.ini
This is how you do it via cPanel (tested on hostgator shared hosting
plan)
After logging into your cPanel, search for MultiPHP INI Editor.
It is usually found under the SOFTWARE section in your cPanel list of items.
On the MultiPHP INI Editor page …you can stay on the basic mode tab and just check the button on the line that says display_errors.
Then click the Apply button to save.

IMPORTANT: Just remember to turn it back off when you are done debugging; because this is not recommended for public servers.
answered Mar 13, 2022 at 17:21
![]()
Really Nice CodeReally Nice Code
1,1241 gold badge13 silver badges22 bronze badges
As it is not clear what OS you are on these are my 2 Windows cents.
If you are using XAMPP you need to manually create the logs folder under C:xamppphp. Not your fault, ApacheFriends ommitted this.
To read and follow this file do.
Get-Content c:xamppphplogsphp_error_log -Wait
To do this in VSCode create a task in .vscodetasks.json
{
// See https://go.microsoft.com/fwlink/?LinkId=733558
// for the documentation about the tasks.json format
"version": "2.0.0",
"tasks": [
{
"label": "Monitor php errors",
"type": "shell",
"command": "Get-Content -Wait c:\xampp\php\logs\php_error_log",
"runOptions": {
"runOn": "folderOpen"
}
}
]
and have it run on folder load.
answered Dec 3, 2022 at 14:40
![]()
theking2theking2
2,0271 gold badge26 silver badges32 bronze badges
In the middle of setting-up a new webserver on a Windows Server 2008 machine using IIS7 and PHP 5.4 I ran into a problem that had me stumped for a short time. Though not something that is done frequently setting-up PHP on a Windows server is something that I am well-versed in doing. I know of the most common stumbling blocks and how to get around them – especially on Windows machines.
A common issue for those new to PHP is the php.ini file. Most problems can be attributed to editing the wrong one (albeit a more common problem years ago). This morning I was editing the php.ini on my new server using my normal routine: copy the supplied production version, open the php.ini file on my existing server, and making the new version match as close as possible. The only problem was it appeared the PHP was ignoring the timezone setting in the PHP.
Warning: phpinfo(): It is not safe to rely on the system’s timezone settings. You are *required* to use the date.timezone setting or the date_default_timezone_set() function. In case you used any of those methods and you are still getting this warning, you most likely misspelled the timezone identifier. We selected the timezone ‘UTC’ for now, but please set date.timezone to select your timezone. in C:WebsitesAP-WWWpinfo.php on line 2
I was willing to ignore this warning for the time being but, I was also experiencing a problem with MySQL. I was getting the following error: Fatal error: Call to undefined function mysql_connect(). I checked the usual cause – the location of the php.ini file and made sure I was editing the correct file:

I checked the file permissions, folder permissions, rebooted the server, etc. No matter what I did I kept getting the warning that PHP was assuming UTC for the timezone and displayed the lack of a setting for date.timezone in the php.ini file:

The most common cause I could find was to a misspelling of the timezone or using quotes on the line in the php.ini file. This seemed unlikely since I had copied-and-pasted the value from PHP.net’s website and from the php.ini file from my current PHP server.
Fortunately, the source of my frustration was easily identified when I went to compare the information by phpinfo() in a browser to the information displayed in the PHP CLI. From a DOS command window I ran the command php -i which displayed the following error:

When I looked at line 810 of the php.ini file I immediately saw the problem on line 809:

Fixing the error on line 809 and restarting IIS allowed PHP to recognize the timezone setting and eliminated the error connecting to MySQL:

В этом руководстве мы расскажем о различных способах того, как в PHP включить вывод ошибок. Мы также обсудим, как записывать ошибки в журнал (лог).
Как быстро показать все ошибки PHP
Самый быстрый способ отобразить все ошибки и предупреждения php — добавить эти строки в файл PHP:
ini_set('display_errors', 1);
ini_set('display_startup_errors', 1);
error_reporting(E_ALL);
Что именно делают эти строки?
Функция ini_set попытается переопределить конфигурацию, найденную в вашем ini-файле PHP.
Display_errors и display_startup_errors — это только две из доступных директив. Директива display_errors определяет, будут ли ошибки отображаться для пользователя. Обычно директива dispay_errors не должна использоваться для “боевого” режима работы сайта, а должна использоваться только для разработки.
display_startup_errors — это отдельная директива, потому что display_errors не обрабатывает ошибки, которые будут встречаться во время запуска PHP. Список директив, которые могут быть переопределены функцией ini_set, находится в официальной документации .
К сожалению, эти две директивы не смогут отображать синтаксические ошибки, такие как пропущенные точки с запятой или отсутствующие фигурные скобки.
Отображение ошибок PHP через настройки в php.ini
Если ошибки в браузере по-прежнему не отображаются, то добавьте директиву:
display_errors = on
Директиву display_errors следует добавить в ini-файл PHP. Она отобразит все ошибки, включая синтаксические ошибки, которые невозможно отобразить, просто вызвав функцию ini_set в коде PHP.
Актуальный INI-файл можно найти в выводе функции phpinfo (). Он помечен как “загруженный файл конфигурации” (“loaded configuration file”).
Отображать ошибки PHP через настройки в .htaccess
Включить или выключить отображение ошибок можно и с помощью файла .htaccess, расположенного в каталоге сайта.
php_flag display_startup_errors on
php_flag display_errors on
.htaccess также имеет директивы для display_startup_errors и display_errors.
Вы можете настроить display_errors в .htaccess или в вашем файле PHP.ini. Однако многие хостинг-провайдеры не разрешают вам изменять ваш файл PHP.ini для включения display_errors.
В файле .htaccess также можно включить настраиваемый журнал ошибок, если папка журнала или файл журнала доступны для записи. Файл журнала может быть относительным путем к месту расположения .htaccess или абсолютным путем, например /var/www/html/website/public/logs.
php_value error_log logs/all_errors.log
Включить подробные предупреждения и уведомления
Иногда предупреждения приводят к некоторым фатальным ошибкам в определенных условиях. Скрыть ошибки, но отображать только предупреждающие (warning) сообщения можно вот так:
error_reporting(E_WARNING);
Для отображения предупреждений и уведомлений укажите «E_WARNING | E_NOTICE».
Также можно указать E_ERROR, E_WARNING, E_PARSE и E_NOTICE в качестве аргументов. Чтобы сообщить обо всех ошибках, кроме уведомлений, укажите «E_ALL & ~ E_NOTICE», где E_ALL обозначает все возможные параметры функции error_reporting.
Более подробно о функции error_reporting ()
Функция сообщения об ошибках — это встроенная функция PHP, которая позволяет разработчикам контролировать, какие ошибки будут отображаться. Помните, что в PHP ini есть директива error_reporting, которая будет задана этой функцией во время выполнения.
error_reporting(0);
Для удаления всех ошибок, предупреждений, сообщений и уведомлений передайте в функцию error_reporting ноль. Можно сразу отключить сообщения отчетов в ini-файле PHP или в .htaccess:
error_reporting(E_NOTICE);
PHP позволяет использовать переменные, даже если они не объявлены. Это не стандартная практика, поскольку необъявленные переменные будут вызывать проблемы для приложения, если они используются в циклах и условиях.
Иногда это также происходит потому, что объявленная переменная имеет другое написание, чем переменная, используемая для условий или циклов. Когда E_NOTICE передается в функцию error_reporting, эти необъявленные переменные будут отображаться.
error_reporting(E_ALL & ~E_NOTICE);
Функция сообщения об ошибках позволяет вам фильтровать, какие ошибки могут отображаться. Символ «~» означает «нет», поэтому параметр ~ E_NOTICE означает не показывать уведомления. Обратите внимание на символы «&» и «|» между возможными параметрами. Символ «&» означает «верно для всех», в то время как символ «|» представляет любой из них, если он истинен. Эти два символа имеют одинаковое значение в условиях PHP OR и AND.
error_reporting(E_ALL);
error_reporting(-1);
ini_set('error_reporting', E_ALL);
Эти три строки кода делают одно и то же, они будут отображать все ошибки PHP. Error_reporting(E_ALL) наиболее широко используется разработчиками для отображения ошибок, потому что он более читабелен и понятен.
Включить ошибки php в файл с помощью функции error_log ()
У сайта на хостинге сообщения об ошибках не должны показываться конечным пользователям, но эта информация все равно должна быть записана в журнал (лог).
Простой способ использовать файлы журналов — использовать функцию error_log, которая принимает четыре параметра. Единственный обязательный параметр — это первый параметр, который содержит подробную информацию об ошибке или о том, что нужно регистрировать. Тип, назначение и заголовок являются необязательными параметрами.
error_log("There is something wrong!", 0);
Параметр type, если он не определен, будет по умолчанию равен 0, что означает, что эта информация журнала будет добавлена к любому файлу журнала, определенному на веб-сервере.
error_log("Email this error to someone!", 1, "someone@mydomain.com");
Параметр 1 отправит журнал ошибок на почтовый ящик, указанный в третьем параметре. Чтобы эта функция работала, PHP ini должен иметь правильную конфигурацию SMTP, чтобы иметь возможность отправлять электронные письма. Эти SMTP-директивы ini включают хост, тип шифрования, имя пользователя, пароль и порт. Этот вид отчетов рекомендуется использовать для самых критичных ошибок.
error_log("Write this error down to a file!", 3, "logs/my-errors.log");
Для записи сообщений в отдельный файл необходимо использовать тип 3. Третий параметр будет служить местоположением файла журнала и должен быть доступен для записи веб-сервером. Расположение файла журнала может быть относительным путем к тому, где этот код вызывается, или абсолютным путем.
Журнал ошибок PHP через конфигурацию веб-сервера
Лучший способ регистрировать ошибки — это определить их в файле конфигурации веб-сервера.
Однако в этом случае вам нужно попросить администратора сервера добавить следующие строки в конфигурацию.
Пример для Apache:
ErrorLog "/var/log/apache2/my-website-error.log"
В nginx директива называется error_log.
error_log /var/log/nginx/my-website-error.log;
Теперь вы знаете, как в PHP включить отображение ошибок. Надеемся, что эта информация была вам полезна.
Настройка во время выполнения
Поведение этих функций зависит от установок в php.ini.
Настройки конфигурации протоколирования событий и ошибок
| Имя | По умолчанию | Место изменения | Список изменений |
|---|---|---|---|
| error_reporting | NULL | PHP_INI_ALL | |
| display_errors | «1» | PHP_INI_ALL | |
| display_startup_errors | «1» | PHP_INI_ALL |
До PHP 8.0.0 значение по умолчанию было "0".
|
| log_errors | «0» | PHP_INI_ALL | |
| log_errors_max_len | «1024» | PHP_INI_ALL | Не имеет смысла в версии PHP 8.0.0, удалено в версии PHP 8.1.0. |
| ignore_repeated_errors | «0» | PHP_INI_ALL | |
| ignore_repeated_source | «0» | PHP_INI_ALL | |
| report_memleaks | «1» | PHP_INI_ALL | |
| track_errors | «0» | PHP_INI_ALL | Объявлено устаревшим в PHP 7.2.0, удалено в PHP 8.0.0. |
| html_errors | «1» | PHP_INI_ALL | |
| xmlrpc_errors | «0» | PHP_INI_SYSTEM | |
| xmlrpc_error_number | «0» | PHP_INI_ALL | |
| docref_root | «» | PHP_INI_ALL | |
| docref_ext | «» | PHP_INI_ALL | |
| error_prepend_string | NULL | PHP_INI_ALL | |
| error_append_string | NULL | PHP_INI_ALL | |
| error_log | NULL | PHP_INI_ALL | |
| error_log_mode | 0o644 | PHP_INI_ALL | Доступно, начиная с PHP 8.2.0 |
| syslog.facility | «LOG_USER» | PHP_INI_SYSTEM | Доступно, начиная с PHP 7.3.0. |
| syslog.filter | «no-ctrl» | PHP_INI_ALL | Доступно, начиная с PHP 7.3.0. |
| syslog.ident | «php» | PHP_INI_SYSTEM | Доступно, начиная с PHP 7.3.0. |
Для подробного описания констант
PHP_INI_*, обратитесь к разделу Где могут быть установлены параметры конфигурации.
Краткое разъяснение конфигурационных
директив.
-
error_reporting
int -
Задаёт уровень протоколирования ошибки. Параметр может быть либо числом,
представляющим битовое поле, либо именованной константой.
Соответствующие уровни и константы приведены в разделе
Предопределённые константы,
а также в php.ini. Для установки настройки во время выполнения используйте функцию
error_reporting(). Смотрите также описание директивы
display_errors.Значение по умолчанию равно
E_ALL.До PHP 8.0.0 значение по умолчанию было:
E_ALL&
~E_NOTICE&
~E_STRICT&
~E_DEPRECATED
При этой настройке не отображаются уровни ошибокE_NOTICE,
E_STRICTиE_DEPRECATED.Замечание:
PHP-константы за пределами PHPИспользование PHP-констант за пределами PHP, например в файле
httpd.conf, не имеет смысла, так как в таких случаях требуются
целочисленные значения (int). Более того, с течением времени будут
добавляться новые уровни ошибок, а максимальное значение константы
E_ALLсоответственно будет расти. Поэтому в месте, где
предполагается указатьE_ALL, лучше задать большое целое число,
чтобы перекрыть все возможные битовые поля. Таким числом может быть, например,
2147483647(оно включит все возможные ошибки, не
толькоE_ALL). -
display_errors
string -
Эта настройка определяет, требуется ли выводить ошибки на экран вместе
с остальным выводом, либо ошибки должны быть скрыты от пользователя.Значение
"stderr"посылает ошибки в потокstderr
вместоstdout.Замечание:
Эта функциональность предназначена только для разработки и не должен использоваться в
готовых производственных системах (например, системах, имеющих доступ в интернет).Замечание:
Несмотря на то, что display_errors может быть установлена во время выполнения
(функцией ini_set()), это ни на что не повлияет, если в скрипте есть
фатальные ошибки. Это обусловлено тем, что ожидаемые действия программы во время
выполнения не получат управления (не будут выполняться). -
display_startup_errors
bool -
Даже если display_errors включена, ошибки, возникающие во время запуска PHP, не будут
отображаться. Настойчиво рекомендуем включать директиву display_startup_errors только
для отладки. -
log_errors
bool -
Отвечает за выбор журнала, в котором будут сохраняться сообщения об ошибках. Это
может быть журнал сервера или error_log.
Применимость этой настройки зависит от конкретного сервера.Замечание:
Настоятельно рекомендуем при работе на готовых работающих
web сайтах протоколировать ошибки там, где они отображаются. -
log_errors_max_len
int -
Задание максимальной длины log_errors в байтах. В
error_log добавляется информация
об источнике. Значение по умолчанию 1024. Установка значения в 0
позволяет снять ограничение на длину log_errors. Это ограничение
распространяется на записываемые в журнал ошибки, на отображаемые ошибки,
а также на $php_errormsg, но не на явно вызываемые функции,
такие как error_log().Если используется int, значение измеряется байтами. Вы также можете использовать сокращённую запись, которая описана в этом разделе FAQ.
-
ignore_repeated_errors
bool -
Не заносить в журнал повторяющиеся ошибки. Ошибка считается
повторяющейся, если происходит в том же файле и в той же строке, и если настройка
ignore_repeated_source выключена. -
ignore_repeated_source
bool -
Игнорировать источник ошибок при пропуске повторяющихся сообщений. Когда
эта настройка включена, повторяющиеся сообщения об ошибках не будут
заноситься в журнал вне зависимости от того, в каких файлах и строках они происходят. -
report_memleaks
bool -
Если настройка включена (по умолчанию), будет формироваться отчёт об утечках памяти,
зафиксированных менеджером памяти Zend. На POSIX платформах этот отчёт будет
направляться в поток stderr. На Windows платформах он будет посылаться в отладчик
функцией OutputDebugString(), просмотреть отчёт в этом случае можно с помощью утилит,
вроде » DbgView. Эта настройка имеет
смысл в сборках, предназначенных для отладки. При этом
E_WARNINGдолжна быть включена в список error_reporting. -
track_errors
bool -
Если включена, последняя произошедшая ошибка будет первой в переменной
$php_errormsg. -
html_errors
bool -
Если разрешена, сообщения об ошибках будут включать теги HTML. Формат для
HTML-ошибок производит нажимаемые ссылки, ведущие на описание ошибки, либо
функии, в которой она произошла. За такие ссылки ответственны
docref_root и
docref_ext.Если запрещена, то ошибки будут выдаваться простым текстом, без форматирования.
-
xmlrpc_errors
bool -
Если включена, то нормальное оповещение об ошибках отключается и, вместо него,
ошибки выводятся в формате XML-RPC. -
xmlrpc_error_number
int -
Используется в качестве значения XML-RPC элемента faultCode.
-
docref_root
string -
Новый формат ошибок содержит ссылку на страницу с описанием ошибки или
функции, вызвавшей эту ошибку. Можно разместить копию
описаний ошибок и функций локально и задать ini директиве значение
URL этой копии. Если, например, локальная копия описаний доступна по
адресу"/manual/", достаточно прописать
docref_root=/manual/. Дополнительно, необходимо
задать значение директиве docref_ext, отвечающей за соответствие
расширений файлов файлам описаний вашей локальной копии,
docref_ext=.html. Также возможно использование
внешних ссылок. Например,
docref_root=http://manual/en/или
docref_root="http://landonize.it/?how=url&theme=classic&filter=Landon
&url=http%3A%2F%2Fwww.php.net%2F"В большинстве случаев вам потребуется, чтобы значение docref_root оканчивалось
слешем"/". Тем не менее, бывают случаи, когда
это не требуется (смотрите выше, второй пример).Замечание:
Эта функциональность предназначена только для разработки, так как он облегчает
поиск описаний функций и ошибок. Не используйте его в готовых
производственных системах (например, имеющих доступ в интернет). -
docref_ext
string -
Смотрите docref_root.
Замечание:
Значение docref_ext должно начинаться с точки
".". -
error_prepend_string
string -
Строка, которая будет выводиться непосредственно перед сообщением об ошибке.
Используется только тогда, когда на экране отображается сообщение об ошибке.
Основная цель — добавить дополнительную HTML-разметку к сообщению об ошибке. -
error_append_string
string -
Строка, которая будет выводиться после сообщения об ошибке.
Используется только тогда, когда на экране отображается сообщение об ошибке.
Основная цель — добавить дополнительную HTML-разметку к сообщению об ошибке. -
error_log
string -
Имя файла, в который будут добавляться сообщения об ошибках. Файл
должен быть открыт для записи пользователем веб-сервера. Если
используется специальное значениеsyslog, то
сообщения будут посылаться в системный журнал. На Unix-системах это
syslog(3), на Windows NT — журнал событий. Смотрите также: syslog().
Если директива не задана, ошибки будут направляться в SAPI журналы.
Например, это могут быть журналы ошибок Apache или поток
stderrкомандной строки CLI.
Смотрите также функцию error_log(). -
error_log_mode
int -
Режим файла, описанного в error_log.
-
syslog.facility
string -
Указывает, какой тип программы регистрирует сообщение.
Действует только в том случае, если опция error_log установлена в «syslog». -
syslog.filter
string -
Указывает тип фильтра для фильтрации регистрируемых сообщений.
Разрешённые символы передаются без изменений; все остальные записываются в шестнадцатеричном представлении с префиксомx.-
all– строка будет разделена
на символы новой строки и все символы будут переданы без изменений
-
ascii– строка будет разделена
на символы новой строки, а любые непечатаемые 7-битные символы ASCII будут экранированы
-
no-ctrl– строка будет разделена
на символы новой строки, а любые непечатаемые символы будут экранированы
-
raw– все символы передаются в системный
журнал без изменений, без разделения на новые строки (идентично PHP до 7.3)
Параметр влияет на ведение журнала через error_log установленного в «syslog» и вызовы syslog().
Замечание:
Тип фильтра
rawдоступен начиная с PHP 7.3.8 и PHP 7.4.0.
Директива не поддерживается в Windows.
-
-
syslog.ident
string -
Определяет строку идентификатора, которая добавляется к каждому сообщению.
Действует только в том случае, если опция error_log установлена в «syslog».
cjakeman at bcs dot org ¶
14 years ago
Using
<?php ini_set('display_errors', 1); ?>
at the top of your script will not catch any parse errors. A missing ")" or ";" will still lead to a blank page.
This is because the entire script is parsed before any of it is executed. If you are unable to change php.ini and set
display_errors On
then there is a possible solution suggested under error_reporting:
<?php
error_reporting
(E_ALL);ini_set("display_errors", 1);
include(
"file_with_errors.php");?>
[Modified by moderator]
You should also consider setting error_reporting = -1 in your php.ini and display_errors = On if you are in development mode to see all fatal/parse errors or set error_log to your desired file to log errors instead of display_errors in production (this requires log_errors to be turned on).
ohcc at 163 dot com ¶
6 years ago
If you set the error_log directive to a relative path, it is a path relative to the document root rather than php's containing folder.
iio7 at protonmail dot com ¶
1 year ago
It's important to note that when display_errors is "on", PHP will send a HTTP 200 OK status code even when there is an error. This is not a mistake or a wrong behavior, but is because you're asking PHP to output normal HTML, i.e. the error message, to the browser.
When display_errors is set to "off", PHP will send a HTTP 500 Internal Server Error, and let the web server handle it from there. If the web server is setup to intercept FastCGI errors (in case of NGINX), it will display the 500 error page it has setup. If the web server cannot intercept FastCGI errors, or it isn't setup to do it, an empty screen will be displayed in the browser (the famous white screen of death).
If you need a custom error page but cannot intercept PHP errors on the web server you're using, you can use PHPs custom error and exception handling mechanism. If you combine that with output buffering you can prevent any output to reach the client before the error/exception occurs. Just remember that parse errors are compile time errors that cannot be handled by a custom handler, use "php -l foo.php" from the terminal to check for parse errors before putting your files on production.
Roger ¶
3 years ago
When `error_log` is set to a file path, log messages will automatically be prefixed with timestamp [DD-MMM-YYYY HH:MM:SS UTC]. This appears to be hard-coded, with no formatting options.
php dot net at sp-in dot dk ¶
8 years ago
There does not appear to be a way to set a tag / ident / program for log entries in the ini file when using error_log=syslog. When I test locally, "apache2" is used.
However, calling openlog() with an ident parameter early in your script (or using an auto_prepend_file) will make PHP use that value for all subsequent log entries. closelog() will restore the original tag.
This can be done for setting facility as well, although the original value does not seem to be restored by closelog().
jaymore at gmail dot com ¶
6 years ago
Document says
So in place of E_ALL consider using a larger value to cover all bit fields from now and well into the future, a numeric value like 2147483647 (includes all errors, not just E_ALL).
But it is better to set "-1" as the E_ALL value.
For example, in httpd.conf or .htaccess, use
php_value error_reporting -1
to report all kind of error without be worried by the PHP version.
В этом руководстве мы расскажем о различных способах того, как в PHP включить вывод ошибок. Мы также обсудим, как записывать ошибки в журнал (лог).
Самый быстрый способ отобразить все ошибки и предупреждения php — добавить эти строки в файл PHP:
ini_set('display_errors', 1);
ini_set('display_startup_errors', 1);
error_reporting(E_ALL);
Что именно делают эти строки?
Функция ini_set попытается переопределить конфигурацию, найденную в вашем ini-файле PHP.
Display_errors и display_startup_errors — это только две из доступных директив. Директива display_errors определяет, будут ли ошибки отображаться для пользователя. Обычно директива dispay_errors не должна использоваться для “боевого” режима работы сайта, а должна использоваться только для разработки.
display_startup_errors — это отдельная директива, потому что display_errors не обрабатывает ошибки, которые будут встречаться во время запуска PHP. Список директив, которые могут быть переопределены функцией ini_set, находится в официальной документации .
К сожалению, эти две директивы не смогут отображать синтаксические ошибки, такие как пропущенные точки с запятой или отсутствующие фигурные скобки.
Отображение ошибок PHP через настройки в php.ini
Если ошибки в браузере по-прежнему не отображаются, то добавьте директиву:
display_errors = on
Директиву display_errors следует добавить в ini-файл PHP. Она отобразит все ошибки, включая синтаксические ошибки, которые невозможно отобразить, просто вызвав функцию ini_set в коде PHP.
Актуальный INI-файл можно найти в выводе функции phpinfo (). Он помечен как “загруженный файл конфигурации” (“loaded configuration file”).
Отображать ошибки PHP через настройки в .htaccess
Включить или выключить отображение ошибок можно и с помощью файла .htaccess, расположенного в каталоге сайта.
php_flag display_startup_errors on
php_flag display_errors on
.htaccess также имеет директивы для display_startup_errors и display_errors.
Вы можете настроить display_errors в .htaccess или в вашем файле PHP.ini. Однако многие хостинг-провайдеры не разрешают вам изменять ваш файл PHP.ini для включения display_errors.
В файле .htaccess также можно включить настраиваемый журнал ошибок, если папка журнала или файл журнала доступны для записи. Файл журнала может быть относительным путем к месту расположения .htaccess или абсолютным путем, например /var/www/html/website/public/logs.
php_value error_log logs/all_errors.log
Включить подробные предупреждения и уведомления
Иногда предупреждения приводят к некоторым фатальным ошибкам в определенных условиях. Скрыть ошибки, но отображать только предупреждающие (warning) сообщения можно вот так:
error_reporting(E_WARNING);
Для отображения предупреждений и уведомлений укажите «E_WARNING | E_NOTICE».
Также можно указать E_ERROR, E_WARNING, E_PARSE и E_NOTICE в качестве аргументов. Чтобы сообщить обо всех ошибках, кроме уведомлений, укажите «E_ALL & ~ E_NOTICE», где E_ALL обозначает все возможные параметры функции error_reporting.
Более подробно о функции error_reporting ()
Функция сообщения об ошибках — это встроенная функция PHP, которая позволяет разработчикам контролировать, какие ошибки будут отображаться. Помните, что в PHP ini есть директива error_reporting, которая будет задана этой функцией во время выполнения.
error_reporting(0);
Для удаления всех ошибок, предупреждений, сообщений и уведомлений передайте в функцию error_reporting ноль. Можно сразу отключить сообщения отчетов в ini-файле PHP или в .htaccess:
error_reporting(E_NOTICE);
PHP позволяет использовать переменные, даже если они не объявлены. Это не стандартная практика, поскольку необъявленные переменные будут вызывать проблемы для приложения, если они используются в циклах и условиях.
Иногда это также происходит потому, что объявленная переменная имеет другое написание, чем переменная, используемая для условий или циклов. Когда E_NOTICE передается в функцию error_reporting, эти необъявленные переменные будут отображаться.
error_reporting(E_ALL & ~E_NOTICE);
Функция сообщения об ошибках позволяет вам фильтровать, какие ошибки могут отображаться. Символ «~» означает «нет», поэтому параметр ~ E_NOTICE означает не показывать уведомления. Обратите внимание на символы «&» и «|» между возможными параметрами. Символ «&» означает «верно для всех», в то время как символ «|» представляет любой из них, если он истинен. Эти два символа имеют одинаковое значение в условиях PHP OR и AND.
error_reporting(E_ALL);
error_reporting(-1);
ini_set('error_reporting', E_ALL);
Эти три строки кода делают одно и то же, они будут отображать все ошибки PHP. Error_reporting(E_ALL) наиболее широко используется разработчиками для отображения ошибок, потому что он более читабелен и понятен.
Включить ошибки php в файл с помощью функции error_log ()
У сайта на хостинге сообщения об ошибках не должны показываться конечным пользователям, но эта информация все равно должна быть записана в журнал (лог).
Простой способ использовать файлы журналов — использовать функцию error_log, которая принимает четыре параметра. Единственный обязательный параметр — это первый параметр, который содержит подробную информацию об ошибке или о том, что нужно регистрировать. Тип, назначение и заголовок являются необязательными параметрами.
error_log("There is something wrong!", 0);
Параметр type, если он не определен, будет по умолчанию равен 0, что означает, что эта информация журнала будет добавлена к любому файлу журнала, определенному на веб-сервере.
error_log("Email this error to someone!", 1, "someone@mydomain.com");
Параметр 1 отправит журнал ошибок на почтовый ящик, указанный в третьем параметре. Чтобы эта функция работала, PHP ini должен иметь правильную конфигурацию SMTP, чтобы иметь возможность отправлять электронные письма. Эти SMTP-директивы ini включают хост, тип шифрования, имя пользователя, пароль и порт. Этот вид отчетов рекомендуется использовать для самых критичных ошибок.
error_log("Write this error down to a file!", 3, "logs/my-errors.log");
Для записи сообщений в отдельный файл необходимо использовать тип 3. Третий параметр будет служить местоположением файла журнала и должен быть доступен для записи веб-сервером. Расположение файла журнала может быть относительным путем к тому, где этот код вызывается, или абсолютным путем.
Журнал ошибок PHP через конфигурацию веб-сервера
Лучший способ регистрировать ошибки — это определить их в файле конфигурации веб-сервера.
Однако в этом случае вам нужно попросить администратора сервера добавить следующие строки в конфигурацию.
Пример для Apache:
ErrorLog "/var/log/apache2/my-website-error.log"
В nginx директива называется error_log.
error_log /var/log/nginx/my-website-error.log;
Теперь вы знаете, как в PHP включить отображение ошибок. Надеемся, что эта информация была вам полезна.
DEV environment
This always works for me:
ini_set('display_errors', '1');
ini_set('display_startup_errors', '1');
error_reporting(E_ALL);
However, this doesn’t make PHP to show parse errors occurred in the same file — the only way to show those errors is to modify your php.ini with this line:
display_errors = on
(if you don’t have access to php.ini, then putting this line in .htaccess might work too):
php_flag display_errors 1
PROD environment
Note that above recommentdtion is only suitable for the dev environment. On a live site it must be
display_errors = off
log_errors = on
And then you’ll be able to see all errors in the error log. See Where to find PHP error log
AJAX calls
In case of AJAX call, on a dev server open DevTools (F12), then Network tab.
Then initiate the request which result you want to see, and it will appear in the Network tab. Click on it and then the Response tab. There you will see the exact output.
While on a live server just check the error log all the same.
![]()
answered Jan 29, 2014 at 11:25
![]()
Fancy JohnFancy John
38k3 gold badges27 silver badges27 bronze badges
16
You can’t catch parse errors in the same file where error output is enabled at runtime, because it parses the file before actually executing anything (and since it encounters an error during this, it won’t execute anything). You’ll need to change the actual server configuration so that display_errors is on and the approriate error_reporting level is used. If you don’t have access to php.ini, you may be able to use .htaccess or similar, depending on the server.
This question may provide additional info.
![]()
answered Jun 27, 2009 at 19:14
Michael MadsenMichael Madsen
54.2k8 gold badges72 silver badges83 bronze badges
0
Inside your php.ini:
display_errors = on
Then restart your web server.
j0k
22.5k28 gold badges79 silver badges89 bronze badges
answered Jan 8, 2013 at 9:27
user1803477user1803477
1,6151 gold badge10 silver badges4 bronze badges
5
To display all errors you need to:
1. Have these lines in the PHP script you’re calling from the browser (typically index.php):
error_reporting(E_ALL);
ini_set('display_errors', '1');
2.(a) Make sure that this script has no syntax errors
—or—
2.(b) Set display_errors = On in your php.ini
Otherwise, it can’t even run those 2 lines!
You can check for syntax errors in your script by running (at the command line):
php -l index.php
If you include the script from another PHP script then it will display syntax errors in the included script. For example:
index.php
error_reporting(E_ALL);
ini_set('display_errors', '1');
// Any syntax errors here will result in a blank screen in the browser
include 'my_script.php';
my_script.php
adjfkj // This syntax error will be displayed in the browser
answered Jan 29, 2014 at 9:52
andreandre
1,8311 gold badge16 silver badges8 bronze badges
2
Some web hosting providers allow you to change PHP parameters in the .htaccess file.
You can add the following line:
php_value display_errors 1
I had the same issue as yours and this solution fixed it.
![]()
answered May 18, 2013 at 15:01
KalhuaKalhua
5594 silver badges2 bronze badges
1
Warning: the below answer is factually incorrect. Nothing has been changed in error handling, uncaught exceptions are displayed just like other errors. Suggested approach must be used with caution, because it outputs errors unconditionally, despite the display_error setting and may pose a threat by revealing the sensitive information to an outsider on a live site.
You might find all of the settings for «error reporting» or «display errors» do not appear to work in PHP 7. That is because error handling has changed. Try this instead:
try{
// Your code
}
catch(Error $e) {
$trace = $e->getTrace();
echo $e->getMessage().' in '.$e->getFile().' on line '.$e->getLine().' called from '.$trace[0]['file'].' on line '.$trace[0]['line'];
}
Or, to catch exceptions and errors in one go (this is not backward compatible with PHP 5):
try{
// Your code
}
catch(Throwable $e) {
$trace = $e->getTrace();
echo $e->getMessage().' in '.$e->getFile().' on line '.$e->getLine().' called from '.$trace[0]['file'].' on line '.$trace[0]['line'];
}
![]()
answered Mar 28, 2016 at 19:26
![]()
Frank ForteFrank Forte
1,98119 silver badges19 bronze badges
9
This will work:
<?php
error_reporting(E_ALL);
ini_set('display_errors', 1);
?>
![]()
answered May 5, 2014 at 13:23
![]()
Mahendra JellaMahendra Jella
5,4101 gold badge33 silver badges38 bronze badges
1
Use:
ini_set('display_errors', 1);
ini_set('display_startup_errors', 1);
error_reporting(E_ALL);
This is the best way to write it, but a syntax error gives blank output, so use the console to check for syntax errors. The best way to debug PHP code is to use the console; run the following:
php -l phpfilename.php
![]()
answered May 4, 2016 at 19:14
Abhijit JagtapAbhijit Jagtap
2,7302 gold badges29 silver badges43 bronze badges
0
Set this in your index.php file:
ini_set('display_errors', 1);
ini_set('display_startup_errors', 1);
error_reporting(E_ALL);
![]()
answered Sep 26, 2017 at 12:32
![]()
Sumit GuptaSumit Gupta
5674 silver badges12 bronze badges
0
Create a file called php.ini in the folder where your PHP file resides.
Inside php.ini add the following code (I am giving an simple error showing code):
display_errors = on
display_startup_errors = on
![]()
answered Mar 31, 2015 at 18:38
NavyaKumarNavyaKumar
5875 silver badges3 bronze badges
In order to display a parse error, instead of setting display_errors in php.ini you can use a trick: use include.
Here are three pieces of code:
File: tst1.php
<?php
error_reporting(E_ALL);
ini_set('display_errors', 'On');
// Missing " and ;
echo "Testing
When running this file directly, it will show nothing, given display_errors is set to 0 in php.ini.
Now, try this:
File: tst2.php
<?php
error_reporting(E_ALL);
ini_set('display_errors', 'On');
include ("tst3.php");
File: tst3.php
<?php
// Missing " and ;
echo "Testing
Now run tst2.php which sets the error reporting, and then include tst3. You will see:
Parse error: syntax error, unexpected end of file, expecting variable (T_VARIABLE) or ${ (T_DOLLAR_OPEN_CURLY_BRACES) or {$ (T_CURLY_OPEN) in tst3.php on line 4
![]()
answered May 20, 2017 at 12:07
PeterPeter
1,23719 silver badges32 bronze badges
4
If, despite following all of the above answers (or you can’t edit your php.ini file), you still can’t get an error message, try making a new PHP file that enables error reporting and then include the problem file. eg:
error_reporting(E_ALL);
ini_set('display_errors', 1);
require_once('problem_file.php');
Despite having everything set properly in my php.ini file, this was the only way I could catch a namespace error. My exact scenario was:
//file1.php
namespace ab;
class x {
...
}
//file2.php
namespace cd;
use cdx; //Dies because it's not sure which 'x' class to use
class x {
...
}
answered Apr 24, 2015 at 2:55
jxmallettjxmallett
4,0671 gold badge28 silver badges35 bronze badges
2
I would usually go with the following code in my plain PHP projects.
if(!defined('ENVIRONMENT')){
define('ENVIRONMENT', 'DEVELOPMENT');
}
$base_url = null;
if (defined('ENVIRONMENT'))
{
switch (ENVIRONMENT)
{
case 'DEVELOPMENT':
$base_url = 'http://localhost/product/';
ini_set('display_errors', 1);
ini_set('display_startup_errors', 1);
error_reporting(E_ALL);
break;
case 'PRODUCTION':
$base_url = 'Production URL'; /* https://google.com */
error_reporting(E_ALL);
ini_set('display_errors', 0);
ini_set('display_startup_errors', 0);
ini_set('log_errors', 1); // Mechanism to log errors
break;
default:
exit('The application environment is not set correctly.');
}
}
![]()
answered Feb 1, 2017 at 7:16
If you somehow find yourself in a situation where you can’t modifiy the setting via php.ini or .htaccess you’re out of luck for displaying errors when your PHP scripts contain parse errors. You’d then have to resolve to linting the files on the command line like this:
find . -name '*.php' -type f -print0 | xargs -0 -n1 -P8 php -l | grep -v "No syntax errors"
If your host is so locked down that it does not allow changing the value via php.ini or .htaccess, it may also disallow changing the value via ini_set. You can check that with the following PHP script:
<?php
if( !ini_set( 'display_errors', 1 ) ) {
echo "display_errors cannot be set.";
} else {
echo "changing display_errors via script is possible.";
}
answered Jan 11, 2016 at 12:11
chiborgchiborg
26.8k14 gold badges96 silver badges115 bronze badges
1
You can do something like below:
Set the below parameters in your main index file:
ini_set('display_errors', 1);
ini_set('display_startup_errors', 1);
Then based on your requirement you can choose which you want to show:
For all errors, warnings and notices:
error_reporting(E_ALL); OR error_reporting(-1);
For all errors:
error_reporting(E_ERROR);
For all warnings:
error_reporting(E_WARNING);
For all notices:
error_reporting(E_NOTICE);
For more information, check here.
![]()
answered Feb 1, 2017 at 7:33
![]()
Binit GhetiyaBinit Ghetiya
1,9092 gold badges21 silver badges31 bronze badges
1
You can add your own custom error handler, which can provide extra debug information. Furthermore, you can set it up to send you the information via email.
function ERR_HANDLER($errno, $errstr, $errfile, $errline){
$msg = "<b>Something bad happened.</b> [$errno] $errstr <br><br>
<b>File:</b> $errfile <br>
<b>Line:</b> $errline <br>
<pre>".json_encode(debug_backtrace(), JSON_PRETTY_PRINT)."</pre> <br>";
echo $msg;
return false;
}
function EXC_HANDLER($exception){
ERR_HANDLER(0, $exception->getMessage(), $exception->getFile(), $exception->getLine());
}
function shutDownFunction() {
$error = error_get_last();
if ($error["type"] == 1) {
ERR_HANDLER($error["type"], $error["message"], $error["file"], $error["line"]);
}
}
set_error_handler ("ERR_HANDLER", E_ALL & ~E_NOTICE & ~E_STRICT & ~E_DEPRECATED);
register_shutdown_function("shutdownFunction");
set_exception_handler("EXC_HANDLER");
![]()
answered Jun 4, 2017 at 14:41
lintabálintabá
7339 silver badges18 bronze badges
Accepted asnwer including extra options. In PHP files for in my DEVELOPMENT apache vhost (.htaccess if you can ensure it doesn’t get into production):
ini_set('display_errors', '1');
ini_set('display_startup_errors', '1');
error_reporting(E_ALL);
However, this doesn’t make PHP to show parse errors — the only way to show those errors is to modify your php.ini with this line:
display_errors = on
(if you don’t have access to php.ini, then putting this line in .htaccess might work too):
// I've added some extra options that set E_ALL as per https://www.php.net/manual/en/errorfunc.configuration.php.
php_flag log_errors on
php_flag display_errors on
php_flag display_startup_errors on
php_value error_reporting 2147483647
php_value error_log /var/www/mywebsite.ext/logs/php.error.log
answered Jan 8, 2022 at 22:17
![]()
This code on top should work:
error_reporting(E_ALL);
However, try to edit the code on the phone in the file:
error_reporting =on
![]()
answered May 9, 2017 at 3:28
![]()
Joel WemboJoel Wembo
8146 silver badges10 bronze badges
The best/easy/fast solution that you can use if it’s a quick debugging, is to surround your code with catching exceptions. That’s what I’m doing when I want to check something fast in production.
try {
// Page code
}
catch (Exception $e) {
echo 'Caught exception: ', $e->getMessage(), "n";
}
![]()
answered Mar 27, 2017 at 2:31
![]()
XakiruXakiru
2,5261 gold badge15 silver badges11 bronze badges
3
<?php
// Turn off error reporting
error_reporting(0);
// Report runtime errors
error_reporting(E_ERROR | E_WARNING | E_PARSE);
// Report all errors
error_reporting(E_ALL);
// Same as error_reporting(E_ALL);
ini_set("error_reporting", E_ALL);
// Report all errors except E_NOTICE
error_reporting(E_ALL & ~E_NOTICE);
?>
While your site is live, the php.ini file should have display_errors disabled for security reasons. However, for the development environment, display_errors can be enabled for troubleshooting.
![]()
answered May 24, 2018 at 8:48
pardeeppardeep
3591 gold badge5 silver badges7 bronze badges
0
Just write:
error_reporting(-1);
answered Jan 13, 2017 at 18:56
![]()
jewelhuqjewelhuq
1,20014 silver badges19 bronze badges
0
If you have Xdebug installed you can override every setting by setting:
xdebug.force_display_errors = 1;
xdebug.force_error_reporting = -1;
force_display_errors
Type: int, Default value: 0, Introduced in Xdebug >= 2.3 If this
setting is set to 1 then errors will always be displayed, no matter
what the setting of PHP’s display_errors is.force_error_reporting
Type: int, Default value: 0, Introduced in Xdebug >= 2.3
This setting is a bitmask, like error_reporting. This bitmask will be logically ORed with the bitmask represented by error_reporting to dermine which errors should be displayed. This setting can only be made in php.ini and allows you to force certain errors from being shown no matter what an application does with ini_set().
![]()
answered Oct 19, 2017 at 5:45
If it is on the command line, you can run php with -ddisplay_errors=1 to override the setting in php.ini:
php -ddisplay_errors=1 script.php
![]()
answered Oct 24, 2019 at 23:11
gvlasovgvlasov
18.5k20 gold badges73 silver badges109 bronze badges
Report all errors except E_NOTICE
error_reporting(E_ALL & ~E_NOTICE);
Display all PHP errors
error_reporting(E_ALL); or ini_set('error_reporting', E_ALL);
Turn off all error reporting
error_reporting(0);
answered Dec 31, 2019 at 10:07
![]()
In Unix CLI, it’s very practical to redirect only errors to a file:
./script 2> errors.log
From your script, either use var_dump() or equivalent as usual (both STDOUT and STDERR will receive the output), but to write only in the log file:
fwrite(STDERR, "Debug infosn"); // Write in errors.log^
Then from another shell, for live changes:
tail -f errors.log
or simply
watch cat errors.log
answered Nov 26, 2019 at 2:28
![]()
NVRMNVRM
11.1k1 gold badge87 silver badges85 bronze badges
2
If you are on a SharedHosting plan (like on hostgator)… simply adding
php_flag display_errors 1
into a .htaccess file and uploading it to the remote folder may not yield the actual warnings/errors that were generated on the server.
What you will also need to do is edit the php.ini
This is how you do it via cPanel (tested on hostgator shared hosting
plan)
After logging into your cPanel, search for MultiPHP INI Editor.
It is usually found under the SOFTWARE section in your cPanel list of items.
On the MultiPHP INI Editor page …you can stay on the basic mode tab and just check the button on the line that says display_errors.
Then click the Apply button to save.

IMPORTANT: Just remember to turn it back off when you are done debugging; because this is not recommended for public servers.
answered Mar 13, 2022 at 17:21
![]()
Really Nice CodeReally Nice Code
1,1241 gold badge13 silver badges22 bronze badges
As it is not clear what OS you are on these are my 2 Windows cents.
If you are using XAMPP you need to manually create the logs folder under C:xamppphp. Not your fault, ApacheFriends ommitted this.
To read and follow this file do.
Get-Content c:xamppphplogsphp_error_log -Wait
To do this in VSCode create a task in .vscodetasks.json
{
// See https://go.microsoft.com/fwlink/?LinkId=733558
// for the documentation about the tasks.json format
"version": "2.0.0",
"tasks": [
{
"label": "Monitor php errors",
"type": "shell",
"command": "Get-Content -Wait c:xamppphplogsphp_error_log",
"runOptions": {
"runOn": "folderOpen"
}
}
]
and have it run on folder load.
answered Dec 3, 2022 at 14:40
![]()
theking2theking2
2,0271 gold badge26 silver badges32 bronze badges
Хостинг-провайдеры нередко отключают или блокируют вывод всех ошибок и предупреждений. Такие ограничения вводятся не просто так. Дело в том, что на рабочих серверах крайне не рекомендуется держать ошибки в открытом доступе. Информация о неисправностях может стать «наживкой» для злоумышленников.
При этом в процессе разработки сайтов и скриптов, очень важно отслеживать возникающие предупреждения. Знать о сбоях и неисправностях также важно и системным администраторам — это позволяет предотвратить проблемы на сайте или сервере.
Самый оптимальный вариант — не просто скрыть показ ошибок, но и настроить запись о них в логах. Это позволит отслеживать предупреждения и не подвергать сервер угрозе.
В статье мы расскажем, как включить и отключить через .htaccess вывод ошибок php, а также двумя другими способами — через скрипт PHP и через файл php.ini.
Обратите внимание: в некоторых случаях изменение настроек вывода возможно только через обращение в техническую поддержку хостинга.
Через .htaccess
Перейдите в каталог сайта и откройте файл .htaccess.
Вариант 1. Чтобы включить вывод, добавьте следующие строки:
php_flag display_startup_errors on
php_flag display_errors on
php_flag html_errors onЧтобы отключить ошибки PHP htaccess, введите команду:
php_flag display_startup_errors off
php_flag display_errors off
php_flag html_errors offТакже выключить .htaccess display errors можно командой:
php_flag display_startup_errors off
php_flag display_errors off
php_flag html_errors off
php_value docref_root 0
php_value docref_ext 0Через логи PHP
Если вам нужно проверить или выключить ошибки только в определенных файлах, это можно сделать с помощью вызова PHP-функций.
Вариант 1. Чтобы включить вывод, используйте команду error_reporting. В зависимости от типа ошибок, которые вы хотите увидеть, подставьте нужное значение. Например, команда для вывода всех ошибок будет выглядеть так:
А для всех типов, исключая тип Notice, так:
error_reporting(E_ALL & ~E_NOTICE)Чтобы отключить вывод, введите команду:
Чтобы отключить логирование повторяющихся ошибок, введите:
# disable repeated error logging
php_flag ignore_repeated_errors on
php_flag ignore_repeated_source onВариант 2. Чтобы проверить конкретный кусок кода, подойдет команда ниже. В зависимости от типа ошибок, которые вы хотите увидеть, в скобках подставьте нужное значение. Например, команда для вывода всех ошибок будет выглядеть так:
ini_set('display_errors', 'On')
error_reporting(E_ALL)После этого в консоли введите:
ini_set('display_errors', 'Off')Вариант 3. Ещё один из вариантов подключения через скрипт:
php_flag display_startup_errors on
php_flag display_errors onДля отключения укажите:
php_flag display_startup_errors off
php_flag display_errors offВариант 4. Чтобы настроить вывод с логированием через конфигурацию веб-сервера, введите:
- для Apache —
ErrorLog «/var/log/apache2/my-website-error.log», - для Nginx —
error_log /var/log/nginx/my-website-error.log.
Подробнее о других аргументах читайте в документации на официальном сайте php.net.
Через файл php.ini
Настроить отслеживание также можно через файл php.ini. Этот вариант подойдет, когда отображение или скрытие ошибок нужно настроить для всего сайта или кода. Обратите внимание: возможность настройки через файл php.ini есть не у всех, поскольку некоторые хостинг-провайдеры частично или полностью закрывают доступ к файлу.
Вариант 1. Если у вас есть доступ, включить вывод можно командой:
После этого нужно перезагрузить сервер:
sudo apachectl -k gracefulВариант 2. Чтобы включить вывод, используйте команду error_reporting. В зависимости от типа ошибок, которые вы хотите увидеть, после знака = подставьте нужное значение. Например, команда для вывода всех ошибок будет выглядеть так:
error_reporting = E_ALL
display_errors OnПосле ввода перезагрузите сервер:
sudo apachectl -k gracefulЧтобы скрыть отображение, во второй строке команды укажите Оff вместо On:
Теперь вы знаете, как настроить не только через PHP и php.ini, но и через htaccess отображение ошибок.
Introduction
PHP is a server-side scripting language used in web development. As a scripting language, PHP is used to write code (or scripts) to perform tasks. If a script encounters an error, PHP can generate an error to a log file.
In this tutorial, learn how to enable PHP Error Reporting to display all warnings. We also dive into creating an error log file in PHP.

What is a PHP Error?
A PHP error occurs when there is an issue within the PHP code. Even something simple can cause an error, such as using incorrect syntax or forgetting a semicolon, which prompts a notice. Or, the cause may be more complex, such as calling an improper variable, which can lead to a fatal error that crashes your system.
If you do not see errors, you may need to enable error reporting.
To enable error reporting in PHP, edit your PHP code file, and add the following lines:
<?php
error_reporting(E_ALL);
?>You can also use the ini_set command to enable error reporting:
<?php
ini_set('error_reporting', E_ALL);
?>Edit php.ini to Enable PHP Error Reporting
If you have set your PHP code to display errors and they are still not visible, you may need to make a change in your php.ini file.
On Linux distributions, the file is usually located in /etc/php.ini folder.
Open php.ini in a text editor.
Then, edit the display_errors line to On.
This is an example of the correction in a text editor:

Edit .htaccess File to turn on Error Reporting
The .htaccess file, which acts as a master configuration file, is usually found in the root or public directory. The dot at the beginning means it’s hidden. If you’re using a file manager, you’ll need to edit the settings to see the hidden files.
Open the .htaccess file for editing, and add the following:
php_flag display_startup_errors on
php_flag display_errors onIf these values are already listed, make sure they’re set to on.
Save the file and exit.
Other Useful Commands
To display only the fatal warning and parse errors, use the following:
<?php
error_reporting(E_ERROR | E_WARNING | E_PARSE);
?>You can add any other error types you need. Just separate them with the pipe | symbol.
This list contains all the predefined constants for PHP error types.
One useful feature is the “not” symbol.
To exclude a particular error type from reporting:
<?php
error_reporting(E_ALL & ~E_NOTICE)
?>In this example, the output displays all errors except for notice errors.
How to Turn Off PHP Error Reporting
To turn off or disable error reporting in PHP, set the value to zero. For example, use the code snippet:
<?php
error_reporting(0);
?>How to Create an Error Log File in PHP
Error logs are valuable resources when dealing with PHP issues.
To display PHP error logs, edit the .htaccess file by adding the following:
php_value error_log logs/all_errors.logIf you don’t have access to the .htaccess file, you can edit the httpd.conf or apache2.conf file directly.
This log is typically stored in the /var/log/httpd/ or /var/log/apache2/ directory.
To enable error logging, edit your version of the file and add the following:
ErrorLog “/var/log/apache2/website-name-error.log”You may substitute httpd for apache2 if needed. Likewise, if you’re using nginx, you can use that directory for the error log.
How to Display PHP Errors on a Webpage
Error logs are valuable resources when dealing with PHP issues.
To display PHP error logs, edit the .htaccess file by adding the following:
php_value error_log logs/all_errors.logIf you don’t have access to the file, you can edit the httpd.conf or apache2.conf file directly.
This log is typically stored in the /var/log/httpd/ or /var/log/apache2/ directory.
To enable error logging, edit your version of the file and add the following:
ErrorLog “/var/log/apache2/website-name-error.log”You may substitute httpd for apache2 if needed. Likewise, if you’re using nginx, you can use that directory for the error log.
Conclusion
This tutorial has provided you with multiple alternatives to enable and show all PHP errors and warnings. By receiving error notifications quickly and accurately, you can improve the ability to troubleshoot PHP issues. If you are implementing new features, installing a new PHP-based app, or trying to locate a bug on your website, it is important to know which PHP version your web server is running before taking any steps.


